OCR Chemistry Module 3
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
first ionization energy
the energy required to remove the first electron from an atom
atomic radius
the greater the distance between the nucleus and the outer shell electrons the less the nuclear attraction
nuclear charge
the more protons there are, the greater the attraction between the nucleus and outer shell electrons
electron shielding
Inner electrons repel outer electrons, reducing the nuclear attraction
large jumps in successive ionization energies for a single element are observed when passing from..
one shell to another which is closer to the nucleus
Trend in first ionisation energy down a group
atomic radius increases, more shielding electrons, nuclear attraction decreases, first ionisation energy decreases
Trend in first ionisation energy across a period
nuclear charge increases, similar shielding electrons, nuclear attraction increases, atomic radius decreases, first ionisation energy increases
sub shell trends across a period
slight fall when moving to fill a different sub shell
metallic bonding
Strong electrostatic attraction between cations and delocalised electrons
electrical conductivity of metallic bonding
they conduct as the delocalised electrons can move and carry charge
melting and boiling points of metallic bonding
most have high, due to the large amount of energy required to break the strong electrostatic attraction
solubility of metallic bonding
don't dissolve, maybe some interaction between polar solvents and the charges in the lattices, but these would lead to reactions not dissolving
Giant covalent structure
billions of atoms held together by a network of strong covalent bonds
melting and boiling points of giant covalent structure
high due to strong covalent bonds
Solubility of giant covalent structures
insoluble
electrical conductivity of giant covalent structures
non-conductors, except for graphene and graphite, where they have 3 / 4 outer shell electrons bonded to the last one is free to carry charge
Group 2 elements reactions with oxygen
metal oxide
group 2 elements reaction with water
alkaline hydroxide and hydrogen
group 2 elements reaction with dilute acid
salt and hydrogen
Group 2 reactivity down the group
ionisation energies decrease as the nuclear attraction decreases as a result of increasing atomic radius and shielding electrons
group 2 oxide compounds with water
metal hydroxide. reaction releases OH-, these hydroxides are only slightly soluble so a ppt will form
Solubility of hydroxides
Increases down the group
Group 2 compounds in agriculture
calcium hydroxide added to fields to increase their pH of acidic fields. so it neutralises forming water.
Group 2 compounds in medicine
often used as anti acids for treating acid indigestion.
halogen trend in boiling point down the group
more electrons, stronger london forces, more energy required to break these forces, boiling point increases
Halogen-halide displacement reactions
a solution of each halogen is added the the aqueous solution of another, if the halogen added is more reactive than the halogen in the aqueous solution, the solution changed colour due to a reaction that has taken place.
Halogen trend in reactivity down the group
atomic radius increases, more electron shielding, nuclear attraction decreases, reactivity decreases
chlorine and water
Cl2 + H2O -> HClO + HCl
chlorine and cold dilute aqueous NaOH
NaClO(bleach) + NaCl + H2O
Benefits of Chlorine use
purification, kills bacteria
Risks of Chlorine use
respiratory irritant in small conc. fatal in large conc., cancer causing
test for halide ions
Ag+ (aq) + X- (aq) = AgX (s)
Carbonate test
Add dilute nitric acid, effervescence of CO2 (can then bubble through lime water, turning milky)
Sulfate test
add barium nitrate (or chloride- but you cannot test for halides after) white ppt of BaSO4
Halide Test
Nitric acid and silver nitrate, then white/cream/yellow precipitate. (Chloride, bromide, iodide)
Add dilute ammonia (NH3) chloride white ppt dissolves. Add conc. ammonia bromide ppt dissolves, iodide ppt doesn't dissolve.
Ammonium test
add NaOH, when heated, ammonia gas forms, test with moist pH paper turning blue
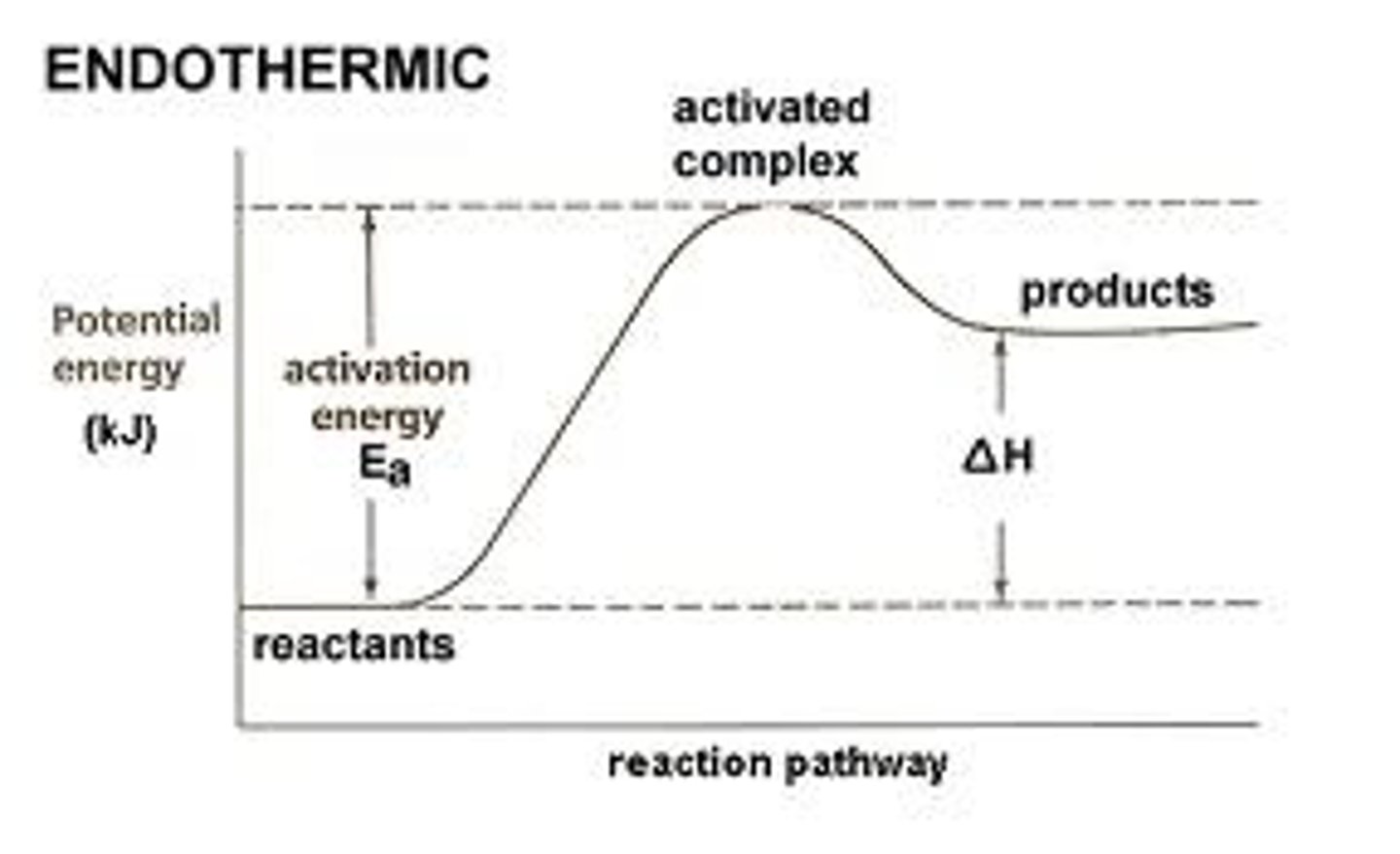
Enthalpy
energy stored within bonds, it cannot be measure, but its changes can
activation energy
the minimum amount of energy required to start a chemical reaction
exothermic
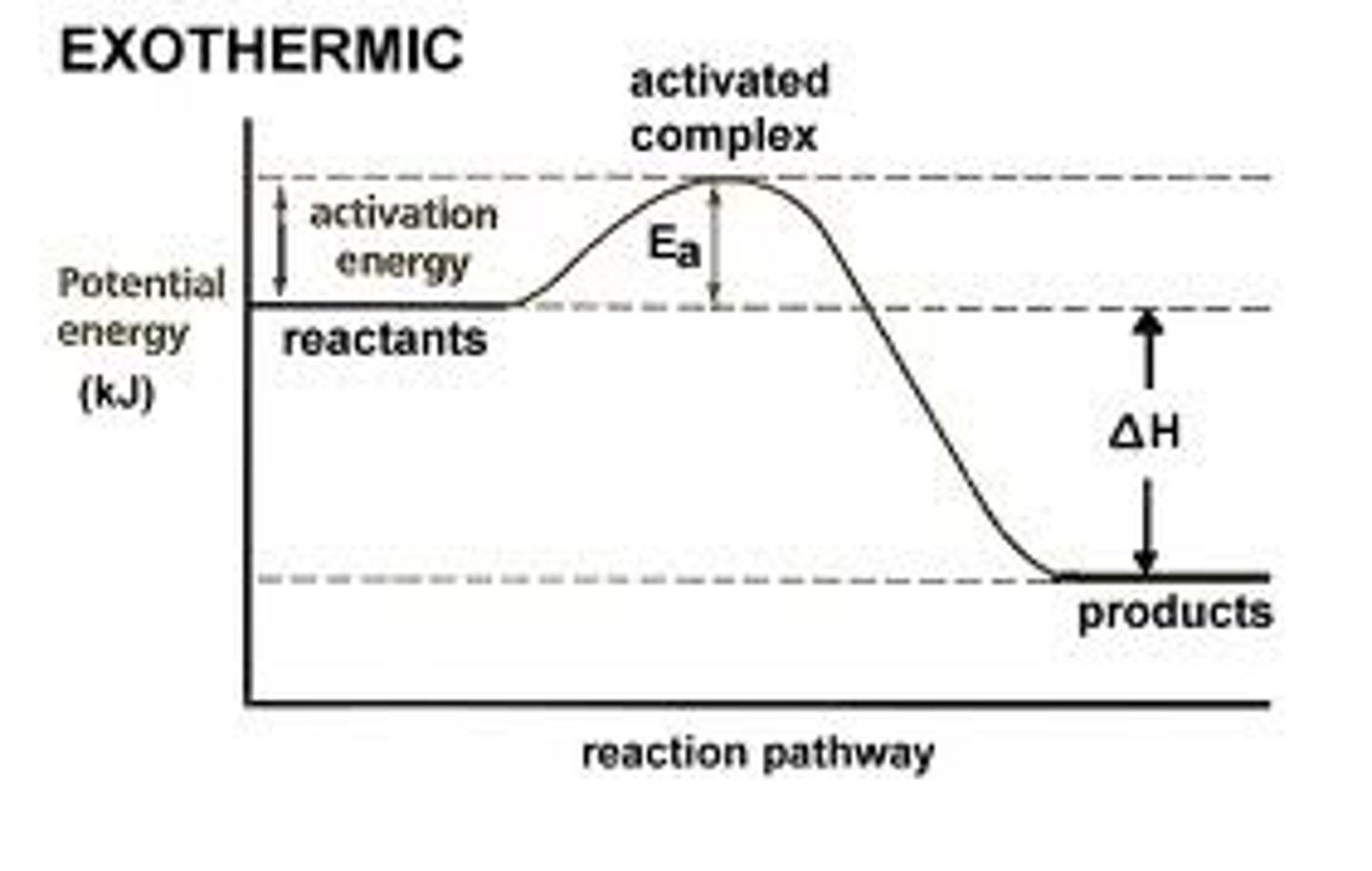
endothermic
standard conditions
100kPa
298K (25 degrees C)
1mol dm^-3
Enthalpy change of formation
the enthalpy change when 1 mole of a compound is formed from its elements in their standard states under standard conditions
enthalpy change of combustion
The energy change that takes place when 1 mole of a substance is completely combusted with oxygen in their standard states under standard conditions
enthalpy change of neutralisation
enthalpy change when one mole of water molecules are formed when an acid reacts with an alkali under standard conditions in their standard states
kelvin scale
0K =-273
calculating energy change
q=mc delta T
determine energy change of combustion
1 - calculate q in kJ
2- calculate amount of substance burnt
3- divide answer 1 by answer 2 (in kJmol^-1)
how accurate is the determination of energy change of combustion
heat lost to surroundings
incomplete combustion
evaporation of methanol from the wick
non-standard conditions
all but the last one would lead to a less exothermic result
spirit burner experiment (combustion energy change)
1 - measure out water and record initial temp.
2- weigh before and after adding methanol to spirit burner
3- place burner under beaker and light
4- after a bit stop experiment and immediatly record the temp. of the water
5- reweigh spirit burner
determining the enthalpy change of reaction
1- calculate q in the solution in kJ
2- calulate the amount in mol of the substance not in excess
3- divide 1 by 2 in kJmol^-1
Average bond enthalpy
The energy required to break one mole of a specified type of bond in a gaseous molecule
delta H +
endothermic, breaking bonds
delta H -
exothermic, making bonds
Why are bond enthalpies always endothermic?
Because energy has to be supplied in order to break the bonds
How can you calculate an average bond enthalpy?
Take An average of actual bond enthalpies in different environments
Why is bond breaking endothermic?
Energy must be supplied to break existing bonds
Why is bond making exothermic?
Energy is released when new bonds are formed
What are the limitations of using average bond enthalpies?
The actual energy involved in breaking and making individual bonds would be slightly different
Why would it be difficult to measure the enthalpy change of this reaction:
4C + 5 H2 = C4H10
Because carbon and hydrogen react to produce many products, so C4H10 would only be one of the many products formed.
Suggest reasons why standard enthalpy changes of combustion determined experimentally are less exothermic than calculated theoretical values?
- heat released to surroundings
- incomplete combustion
- substances may not be present in standard states
It's difficult to determine the standard enthalpy change of formation of hexane directly - suggest why?
- Many different hydrocarbons would form
- activation energy too high
- reaction too slow
- They don't react together
list important processes where hydrogen is used?
production of margarine, ammonia, Haber process
The student looked in a textbook and found that the actual value for the standard enthalpy change of combustion of propan-1-ol was more exothermic than the experimental value - suggest why?
-elements might not be in their standard states
-water evaporates
-thermal capacity of beaker ignored
-combustion could be incomplete
-propan-1-ol evaporates
hess' law
If a reaction can take place by more than one route and the initial and final conditions are the same, the total enthalpy change is the same for each route.
working out enthalpy changes
1 - construct enthalpy cycle, elements at the bottom, reactants on the left, products on the right
2 - add values of known enthalpys and calculate unknown enthalpy
buildings form up, and burn down
rate of chemical reaction
measures how fast a reactant is being used up or how fast a product is being formed
rate of reaction
change in conc. over time
The rate of a chemical reaction depends on
temperature
concentration
catalyst
surface area of solid reactants
reason for ineffective collision of particles
not the correct orientation
not sufficient energy to overcome activation energy barrier
increasing the conc. affect on the rate
increases the number of particles in the same volume, they are closer together and collide more frequently in a given period of time, therefore more successful collisions per unit of time
increasing pressure of a gas affect on rate
conc. of gas molecules increase as the same number of molecules fill a smaller volume, they are closer together and collide more frequently in a given period of time, therefore more successful collisions per unit of time
monitor gas production
or measuring cylinder, measured at timed intervals
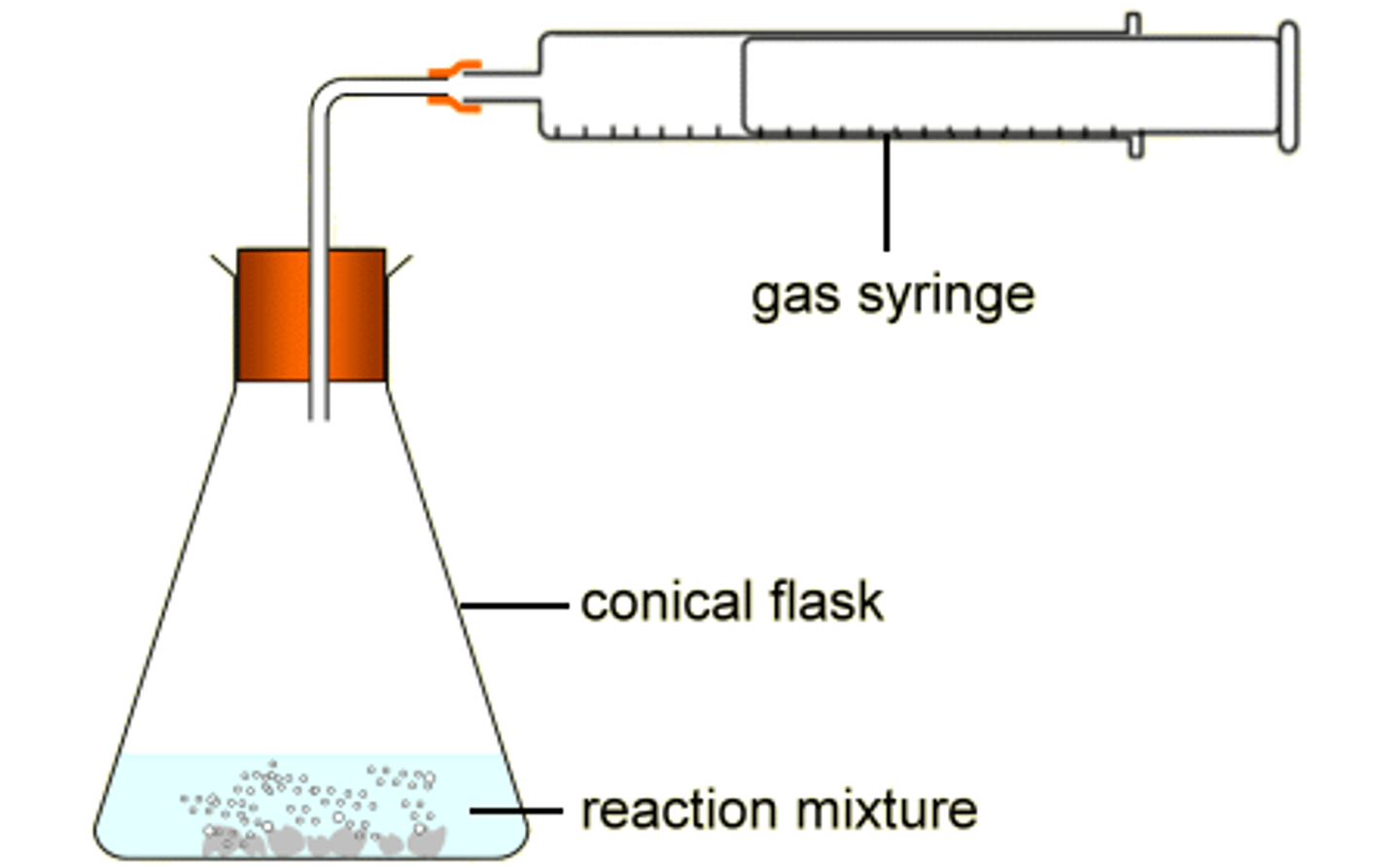
catalyst
changes the rate of reaction without undergoing any permanent change
homogeneous catalyst
In the same state as the reactants, it reacts to form an intermediate
heterogeneous catalyst
Different physical state to reactants, they are absorbed onto the surface of the catalyst where the reaction takes place- then deabsorbed
dynamic equalibrium
rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the backward reaction
Le Chatelier's Principle
States that if a stress is applied to a system at equilibrium, the system shifts in the direction that minimise the stress.
Effect of catalyst on equilibrium
no effect, merely speeds up the rates of the forward and reverse equally