4.3 Fundamentals of Algorithms (Combined)
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
What is meant by graph-traversal?
The process of visiting each vertex in a graph
What are the types of graph traversal algorithms?
- Depth-first
- Breadth-first
How is a graph traversed using depth-first?
Each branch of the graph is fully explored before backtracking and exploring the next
How is a depth-first traversal implemented?
- A stack keeps track of the last node visited
- A list holds the names of the node which have already been visited
- Makes use of the call stack and recursion
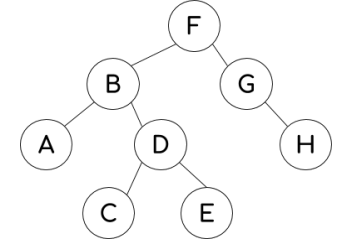
What would the order of nodes be when traversing this graph using depth-first?
F B A D C E G H
What are some applications of depth-first traversal?
- Job scheduling where jobs have to be completed before others can begin
- Finding a path between two vertices
- Solving puzzles (e.g. navigating a maze)
How is a graph traversed using breath-first traversal?
All nodes adjacent to another are visited before moving to the next
How is a breadth-first traversal implemented?
- A queue keeps track of the nodes to be visited
- A list stores the nodes that have been visited
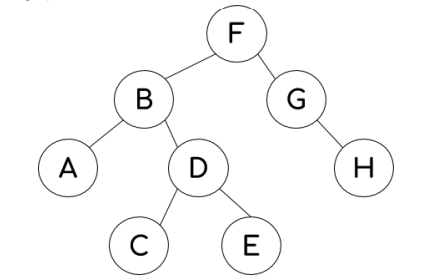
What would the order of nodes be when traversing this graph using breadth-first?
F B G A D H C E
What are some application of breath-first traversal?
- Finding the shortest path between two points
- Web-crawlers
- Facebook friend suggestions
What is the time complexity of traversals in a sparse graph?
O(n)
What is the time complexity of traversals in a graph with the maximum number of edges?
O(n²)
What is tree-traversal?
The process of visiting/updating/outputting each node in a tree
→ Must start at the root
What are the types of tree traversal algorithms?
- Pre-order
- In-order
- Post-order
How is a tree traversed using pre-order?
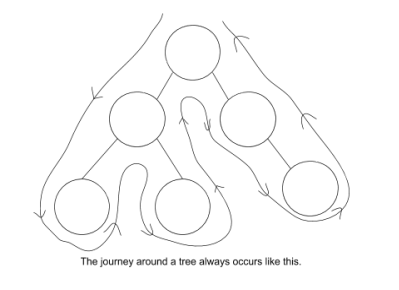
What is pre-order traversal used for?
Copying a tree
→ Can be performed on any tree
How is a tree traversed using in-order?
Traverse the nodes in ascending order
→ Can only be performed on binary trees
What is in-order traversal used for?
- Traversing binary search trees
- Alphabetising
How is a tree traversed using post-order?
Starts from the left and works up and round the tree
What is post-order traversal used for?
- Make infix to RPN conversions
- Make postfix expressions from expression trees
What is an algorithm?
A set of instructions which completes a task in a finite time and always terminates
What is a searching algorithm?
An algorithm to:
- Find the location of an item in a data structure
- Verify the presence of the item
What are the types of searching algorithm?
- Linear search
- Binary search
- Binary tree search
How does a linear search work?
Each item in the list is checked in sequence until the item is found or all items have been checked
→ Compared with the search term
→ Can be performed on any unordered list
Why are linear searches rarely used?
High time complexity - O(n)
How does a binary search work?
- Midpoint in the list is found
- Determine if the target is higher or lower than the midpoint
- This is repeated until the item is found or the list cannot be divided further
Ordered lists only
What is the time complexity of a binary search?
O(log n) - The list is halved with each search
How does a binary tree search work?
Identical to a binary search except it is conducted on a binary tree
What is a binary tree?
A rooted ordered tree in which each node has a maximum of two children
What is the time complexity of a binary tree search?
O(log n)
What is a sorting algorithm?
An algorithm that sorts elements of an array into a specific order
What are the key sorting algorithms?
- Bubble sort
- Merge sort
How does a bubble sort work?
- Items compared in pairs and swapped if they are in the wrong position
- Passes made until the list is fully ordered
What is the time complexity of a bubble sort?
O(n²) - very inefficient
How does a merge sort work?
Divide and conquer algorithm
- List is split into sub-lists until each list contains one item
- List reformed until one ordered list
What is the time complexity of a merge sort?
O(n log n)
What is an optimisation algorithm?
An algorithm that finds the best possible solution to the problem posed
What is an example of an optimisation algorithm?
Dijkstra’s algorithm
What does Dijkstra’s algorithm do?
Finds the shortest path from a starting node to every other node in a graph/network
→ Keeps track of visited nodes with a priority queue
What are some applications of Dijkstra’s algorithm?
- To calculate shortest paths (e.g. satellite navigation systems)
- Routing of packets in a network
What does it mean if a problem is computable?
If an algorithm can solve every instance of the problem in a finite number of steps
What does it mean if a program is soluble?
It is able to be solved
What makes a problem insoluble?
It cannot be solved
→ Includes solutions which would take millions of years
What does it mean if a problem is intractable?
It is unable to be solved in a reasonable time
What is an example of a famous intractable problem?
The Travelling Salesman Problem
→ Finding the shortest distance to visit every node on a graph exactly once
What are the time complexities of intractable problems?
- O(n!)
- O(2^n)
What are the time complexities of tractable problems?
- O(n)
- O(n²)
- O(n^a)
- O(log n)
What is meant by a heuristic method?
One which attempts to find a solution which may not be perfect but is adequate for its purpose
What are some examples of heuristic methods?
- Common sense
- Educated guess
- Gut feeling
What are the essential characteristics of a recursive routine?
- A stopping condition/base case
- The routine must call itself for input values other than the stopping condition
- Stopping condition must be reached after a finite number of calls
How is the call stack used in recursive algorithms?
Every time a subroutine is called, the return address is added to the call stack
→ The algorithm will ‘unwind’ automatically as the call stack is popped off
This is filler
This is filler
This is filler
This is filler