Biology/Ecology Study Guide
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/28
Last updated 3:35 AM on 2/17/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
1
New cards
Cell Cycle Order
Interphase, Mitosis, and Cytokinesis
2
New cards
Mitosis Order
Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, and Anaphase
3
New cards
Interphase
* DNA is copied in S Phase
* Nuclear Membrane Still Exists
* DNA is Chromatin
* Nuclear Membrane Still Exists
* DNA is Chromatin
4
New cards
Prophase
* Spindle Fibers start forming
* Chromatin is Chromosomes
* Nuclear Membrane disappears
* Chromatin is Chromosomes
* Nuclear Membrane disappears
5
New cards
Metaphase
* Chromosomes line up
* Spindle Fibers connect
* Spindle Fibers connect
6
New cards
Anaphase
* Chromosomes are pulled apart
7
New cards
Telophase
* The Nuclear Membrane comes back
* Spindle Fibers leave
* Chromosome → Chromatin
* Spindle Fibers leave
* Chromosome → Chromatin
8
New cards
Incomplete Dominance
* Not completely dominant
* Example: black, white, gray| red, white, pink
* Example: black, white, gray| red, white, pink
9
New cards
Codominance
* Equally Dominant
* Example: Speckled Black and White| Blood Types
* Example: Speckled Black and White| Blood Types
10
New cards
Colorblindness
* X-Linked Recessive
* The inability to distinguish certain colors
* The inability to distinguish certain colors
11
New cards
Hemophilia
* X-Linked Recessive
* A rare disorder in which the blood doesn't clot in a typical way because it doesn't have enough blood-clotting proteins.
* A rare disorder in which the blood doesn't clot in a typical way because it doesn't have enough blood-clotting proteins.
12
New cards
Cystic Fibrosis
* Autosomal Recessive
* Cystic fibrosis affects the cells that produce mucus, sweat, and digestive juices. It causes these fluids to become thick and sticky. They then plug up tubes, ducts, and passageways.
* Cystic fibrosis affects the cells that produce mucus, sweat, and digestive juices. It causes these fluids to become thick and sticky. They then plug up tubes, ducts, and passageways.
13
New cards
Sickle Cell Anemia
* Autosomal Recessive
* A group of disorders that cause red blood cells to become misshapen and break down.
* Abnormal Hemoglobin
* A group of disorders that cause red blood cells to become misshapen and break down.
* Abnormal Hemoglobin
14
New cards
Albinsim
* Autosomal Recessive
* affects the production of melanin, the pigment that colors skin, hair, and eyes.
* affects the production of melanin, the pigment that colors skin, hair, and eyes.
15
New cards
Phenylketonuria
* Autosomal Recessive
* A rare inherited disorder that causes an amino acid called phenylalanine to build up in the body.
* No diet soda
* A rare inherited disorder that causes an amino acid called phenylalanine to build up in the body.
* No diet soda
16
New cards
Huntington’s Disease
* Autosomal Dominant
* An inherited disorder that causes nerve cells (neurons) in parts of the brain to gradually break down and die.
* An inherited disorder that causes nerve cells (neurons) in parts of the brain to gradually break down and die.
17
New cards
Homologous Chromosomes
Same genes, different alleles
18
New cards
Diploid Cells
* Homologous Pairs
* Makes Body Cells
* 2n
* Makes Body Cells
* 2n
19
New cards
Haploid Cells
* One of each
* Sex Cells
* n
* Sex Cells
* n
20
New cards
Meiosis I
Homologous Chromosomes are separated reducing chromosome numbers in half
21
New cards
Meiosis II
Sister Chromatids are separated making four haploid gametes
22
New cards
Trisomy 21
* Down Syndrome
* During Anaphase II, split wrong
\
* During Anaphase II, split wrong
\
23
New cards
Nondisjunction
Chromosomes did not separate during Meiosis
24
New cards
Klinefelter’s Syndrome
* Nondisjunction
* Male
* Doesn’t go through puberty
* Male
* Doesn’t go through puberty
25
New cards
Turner’s Syndrome
* Monosomy, missing one copy
* Female
* Doesn’t go through puberty
* Female
* Doesn’t go through puberty
26
New cards
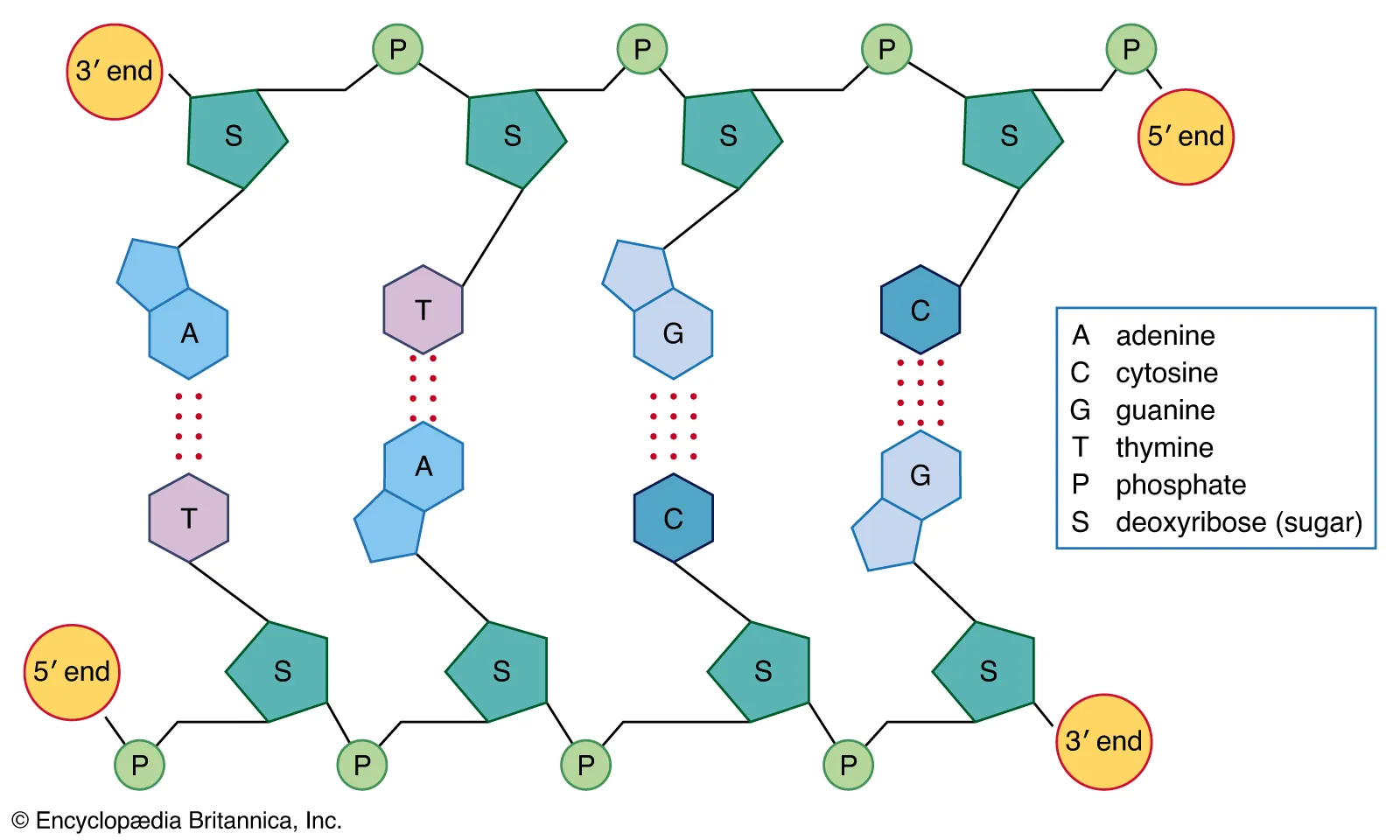
Base Pairs
* Adenine → Thymine
* Cytosine → Guanine
* The “rungs” of DNA structure
* Cytosine → Guanine
* The “rungs” of DNA structure
27
New cards
Hydrogen Bonds
hold together Base pairs
28
New cards
What does DNA stand for?
Deoxyribonucleic acid
29
New cards
DNA Structure
see image