Fluid & Electrolytes
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
What are the main functions of water in the body?
Transporting nutrients and wastes, hormones, enzymes, facilitating metabolism, acting as a solvent, maintaining body temperature, aiding digestion, and serving as a tissue lubricant.
What percentage of total body water is intracellular fluid (ICF)?
70%
What percentage of total body water is extracellular fluid (ECF)?
30%
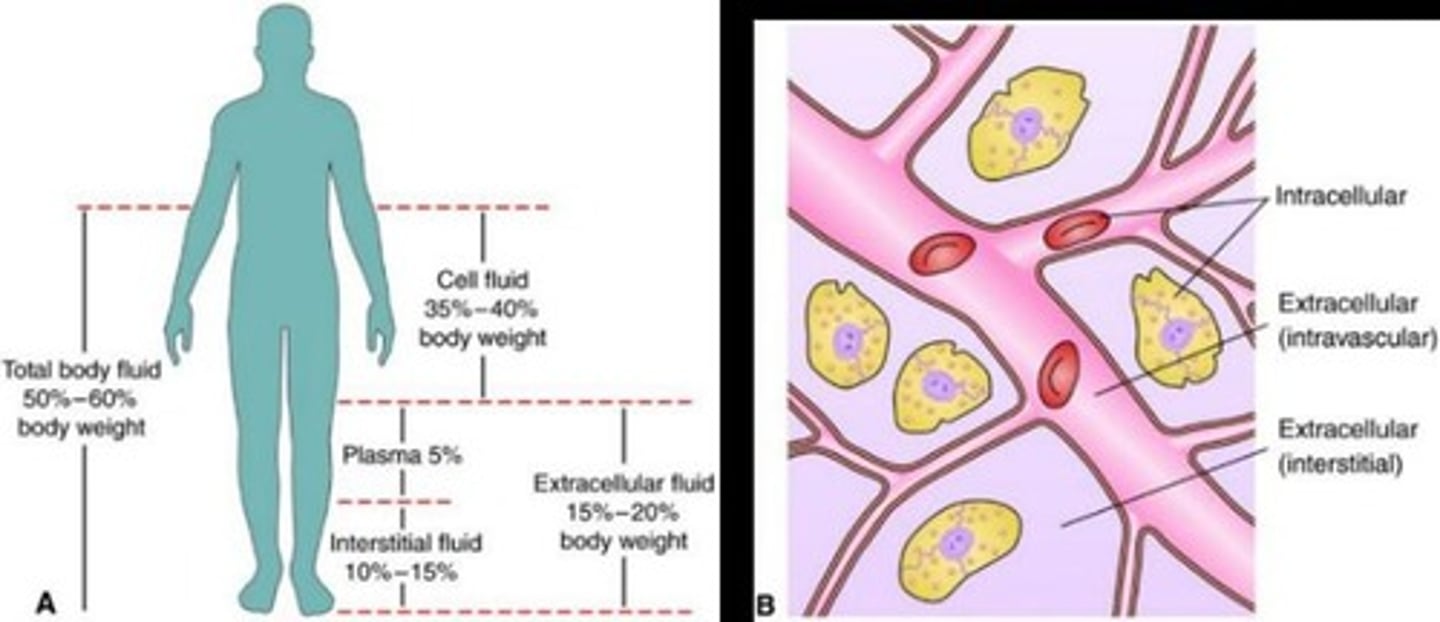
What factors influence variations in fluid content in the body?
Age, gender, and amount of fat cells; infants have more body fluid and ECF than adults.
What is the normal range of total body water as a percentage of body weight in a healthy adult?
50% to 60%
What are cations and anions in the context of electrolytes?
Cations are positively charged ions, while anions are negatively charged ions.
What is homeostasis in relation to electrolytes?
It is the balance where total cations equal total anions.
What is osmosis?
The movement of water from an area of lesser solute concentration to greater concentration until equilibrium is reached.
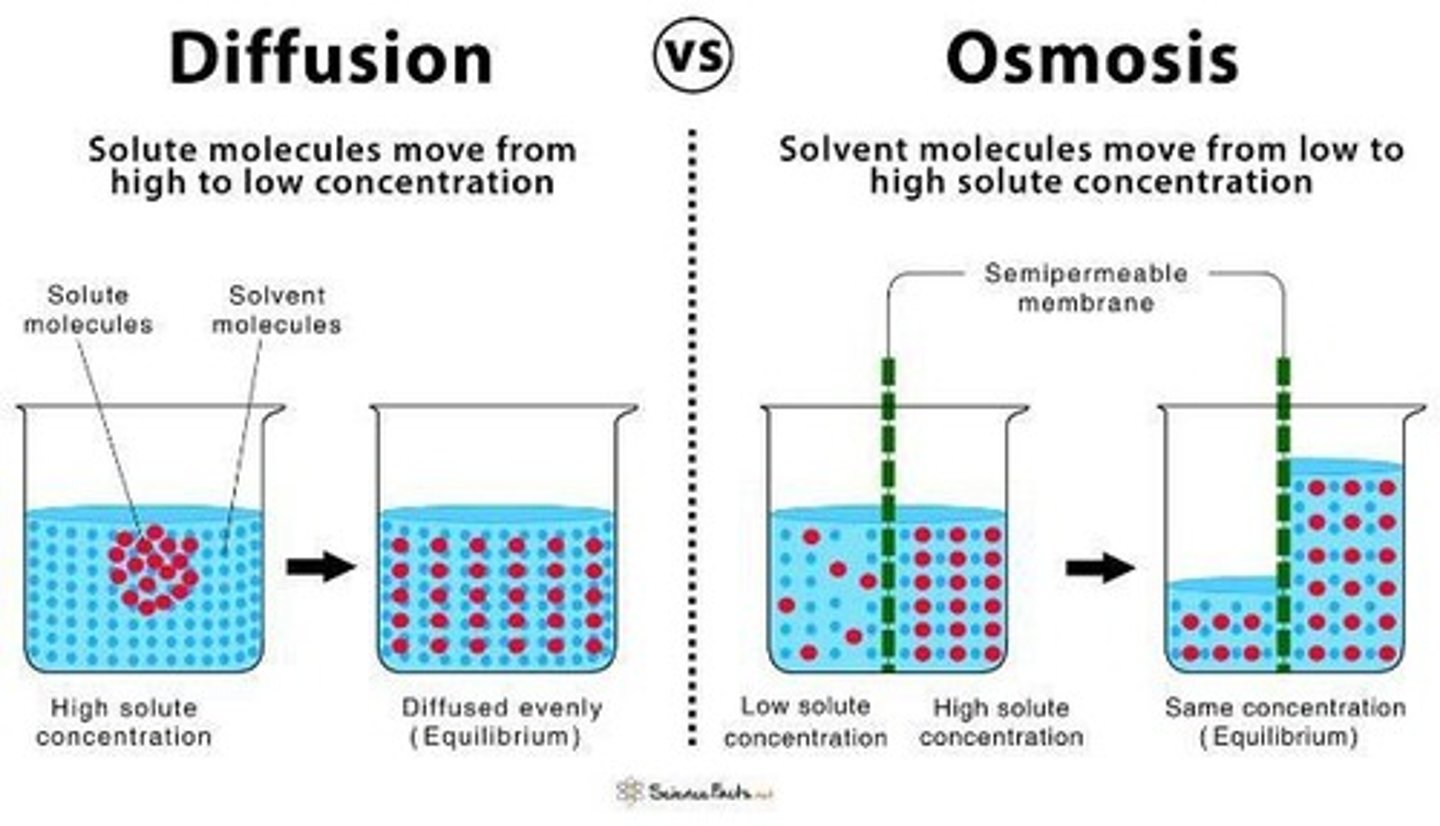
What is the difference between isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic solutions?
Isotonic solutions have the same osmolarity as plasma; hypotonic solutions have fewer solutes than plasma (causing cells to swell); hypertonic solutions have more solutes than plasma (causing cells to shrink).
What are examples of isotonic IV fluids?
0.9% Normal Saline (NS) and Ringer's Lactate (RL).
What are the major functions of sodium in the body?
Regulates volume of body fluids and is involved in conduction of neurological impulses.
What are the symptoms of hyponatremia?
Headache, nausea, vomiting, confusion, muscle twitching, weakness, irritability.
What are the symptoms of hypernatremia?
Extreme thirst, restlessness, dry tongue, disorientation, lethargy.
What is the normal reference range for potassium levels in adults?
3.5-5.3 mmol/L
What are the symptoms of hypokalemia?
Muscle weakness, leg cramps, fatigue, cardiac irregularities.
What is the treatment for hyperkalemia?
Kayexalate (a cation exchange resin) or other prescribed therapies.
What is the normal reference range for calcium levels in adults?
8.6 - 10 mg/dL
What are the symptoms of hypocalcemia?
Muscle cramps, tetany, irritability, seizures, arrhythmias.
What is the primary buffer system in the body?
Bicarbonate.
What is the role of magnesium in the body?
Involved in metabolism of carbohydrates and proteins, and vital enzyme functions.
What are common causes of electrolyte imbalances?
Illness, burns, trauma, and medications.
What is the significance of the panic values for sodium?
Panic values are <125 mmol/L or >150 mmol/L, indicating severe imbalances.
What are the three components of calcium in the body?
Protein-bound, ionized (free), and complexed.
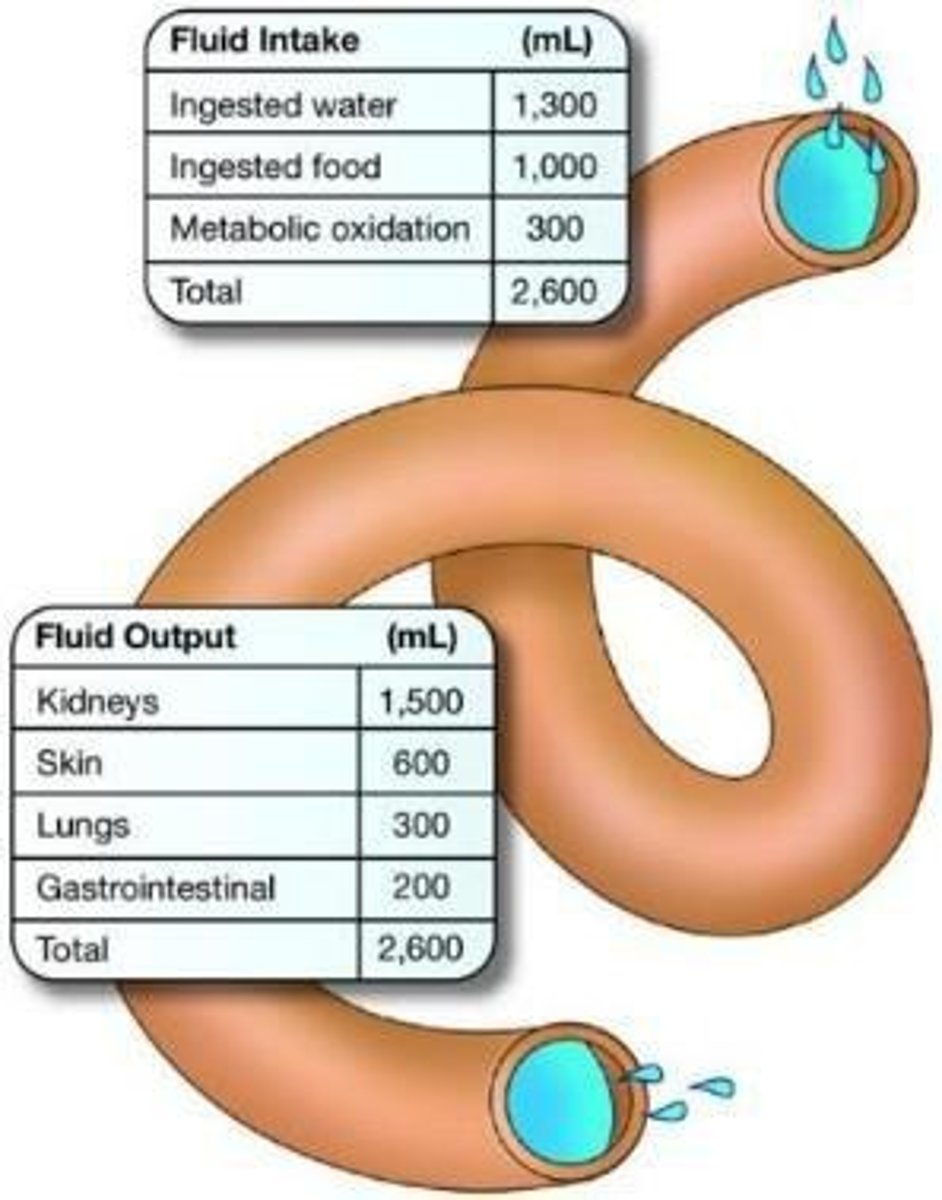
What is the primary source of fluids for the body?
Ingested liquids, food, and metabolic byproducts.
What is the normal reference range for bicarbonate levels in the body?
22-26 mmol/L (not explicitly stated in the note but commonly known).
What are the treatments for hypercalcemia?
Calcium supplements orally or IV Calcium gluconate or Calcium chloride, adequate hydration, and Biphosphonates (e.g., Zoledronic acid).
What are common symptoms of hypercalcemia?
Lethargy, muscle weakness, hyporeflexia, decreased muscle tone, polyuria, polydipsia, urinary calculi, arrhythmias, and cardiac arrest.
What is the reference value for magnesium in adults?
1.5-2.5 mg/dL.
What are the symptoms of hypomagnesemia?
Neuromuscular irritability, weakness, tremors, dizziness, cardiac irritation, mood changes, tetany, and convulsions.
What is the treatment for hypermagnesemia?
IV Calcium gluconate, Lasix, Glucose, and insulin.
What is the panic value for phosphorus?
<1.5 mg/dL.
What are the symptoms of hyperphosphatemia?
Tingling around the mouth, fingertips, delirium, numbness, muscle cramps, and tetany.
What is the reference value for chloride?
97-107 mEq/L.
What are the symptoms of hypochloremia?
Hyperexcitability of muscles, tetany, hyperactive deep tendon reflexes, and muscle cramps.
What is the normal range for a platelet count?
150,000-400,000/mm3.
What does an increased BUN and creatinine level indicate?
Kidney dysfunction.
What is the normal range for white blood cell (WBC) count?
4,500 - 11,000/mm3.
What does leukocytosis indicate?
WBC count >11,000, which can suggest infection, inflammation, or tissue necrosis.
What is the panic value for sodium?
>145 mEq/L.
What symptoms are expected in a client with elevated sodium levels?
Changes in level of consciousness, elevated respiratory rate, extreme thirst, and dry oral mucous membranes.
What is the therapeutic range for Prothrombin Time (PT)?
1.5-2 times the normal value, which is 11.2-12.5 seconds.
What does an increased BUN with normal creatinine suggest?
Dehydration.
What is the significance of creatinine clearance?
It is a more accurate measure of renal function used when renal disease is suspected.
What is the normal range for total cholesterol?
<200 mg/dL.
What is the role of phosphorus in the body?
Essential for building strong bones and teeth, and crucial for energy storage and usage.
What is the treatment for hypophosphatemia?
Oral phosphates, IV phosphates, and dietary control.
What does the term 'azotemia' refer to?
An increase in nitrogenous waste products in the blood, often indicating kidney dysfunction.
What is the significance of monitoring trends in lab values?
It provides a more complete picture of a patient's condition and helps identify changes over time.
What is the normal range for triglycerides?
<150 mg/dL.
What are the symptoms of hyperchloremia?
Tachypnea, lethargy, altered mentation, weakness, and extreme thirst.