CHEM120 Exam 3
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 15 & 16
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
What is the general formula for carbohydrates?
CnH2nOn
What is the difference between a monosaccharide, disaccharide, and polysaccharide?
Mono = 1 sugar, di = 2 sugars linked, Poly = many sugars linked
What are the two functional groups in all monosaccharides?
Hydroxyl (-OH) and carbonyl (C=O)
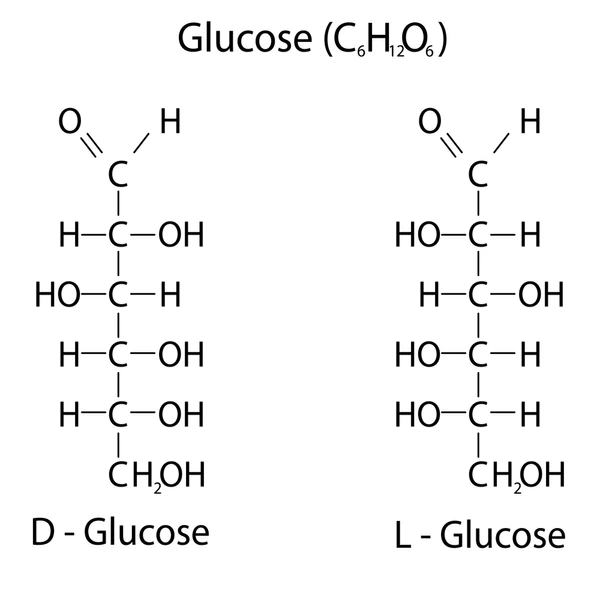
How do you determine if a sugar is a D or an L?
Look at the penultimate carbon; OH on the right = D, left = L
penultimate carbon
the second-to-last carbon atom in a carbon chain
Enantiomers vs Diastereomers
Enantiomers = mirror images
Diastereomers = non-mirror stereoisomers
Define Chiral Carbon
Carbon with 4 different groups attached
How are enantiomers drawn in a Fisher Projection?
As mirror images with opposite configurations at all chiral centers
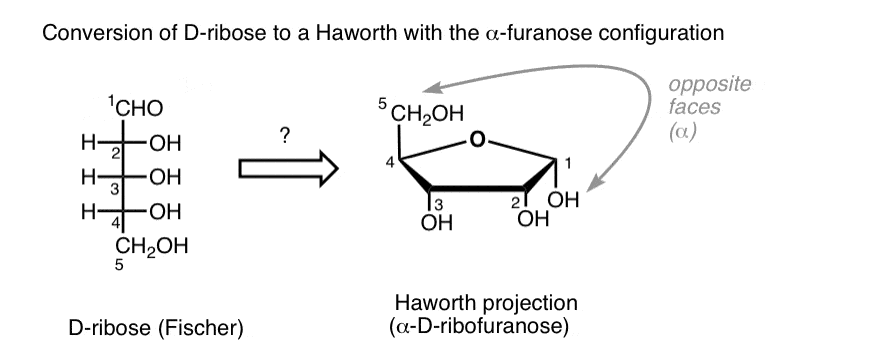
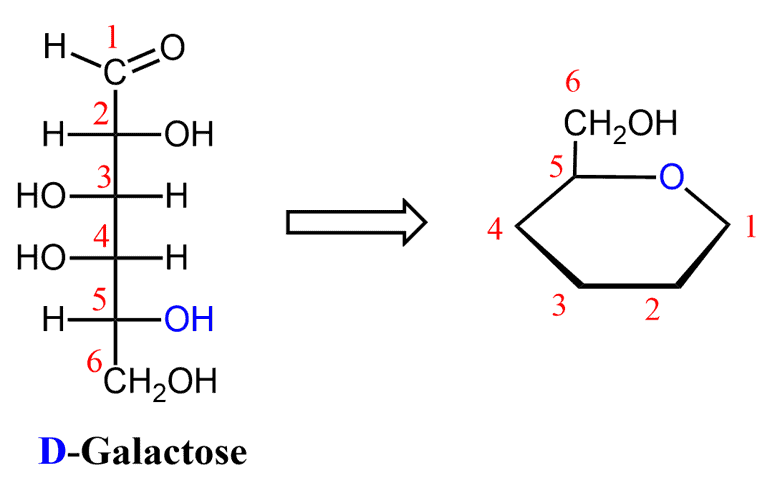
What reaction creates a cyclic monosaccharide?
Intramolecular reaction forming a hemiacetal (C=O + OH)
a- vs B-anomer difference
a = OH opposite side from CH2OH; B = OH same side
What is the anomeric carbon
The carbon derived from the carbonyl carbon during ring formation
D-Glucose
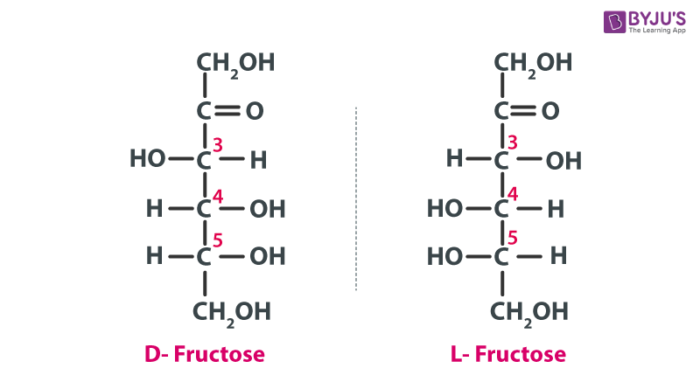
D-fructose
D-Ribose
D-Galactose
Functional Group of Carboxylic Acids
-COOH
Functional group of Esters
-COOR
Suffix for acids
-oic acid
Suffix for esters
-oate
how to name esters?
Alkyl + Acid part (-oate)
Example: Methyl Benzoate
Why do carboxylic acids have high boiling points?
Strong H-bonding and dimer formation
Can esters hydrogen bond with each other
No. Therefore they have a lower boiling points
Solubility trend for carboxylic acids
small chains = soluble; large chains = less soluble
What is saponification?
Base-catalyzed ester hydrolysis producing soap
Esterification reaction
Acid + Alcohol <> ester + water (H+ catalyst)
Acid hydrolysis of an ester
Ester + H2O → acid + Alcohol
Base hydrolysis of an ester
Ester + NaOH → carboxylate salt + alcohol