Topic 3 - Organisms exchange substances with their environment (Biology)
1/73
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Describe the relationship between the size and structure of an organism and its surface area to volume ratio (SA:V)

How is SA:V calculated? Use an example
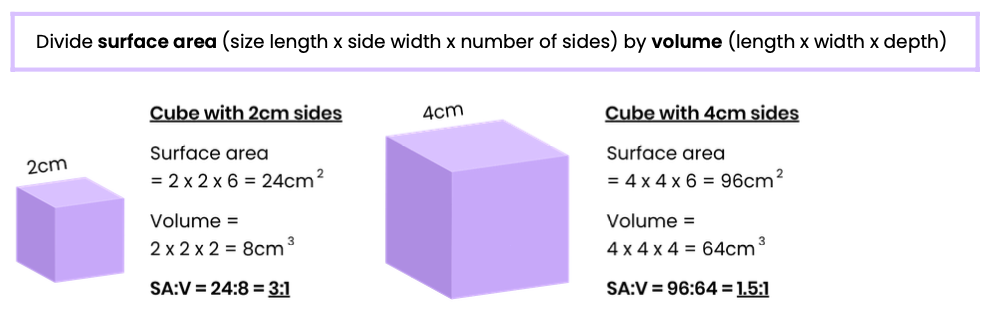
Suggest an advantage of calculating SA:mass for organisms instead of SA:V
Easier / quicker to find / more accurate because irregular shapes
What is metabolic rate? Suggest how it can be measured

Explain the relationship between SA:V and metabolic rate

Explain the adaptations that facilitate exchange as SA:V reduces in larger organisms

Explain how the body surface of a single-celled organism is adapted for gas exchange

Describe the tracheal system of an insect
Spiracles = pores on surface that can open / close to allow diffusion
Tracheae = large tubes full of air that allow diffusion
Tracheoles = smaller branches from tracheae, permeable to allow gas exchange with cells
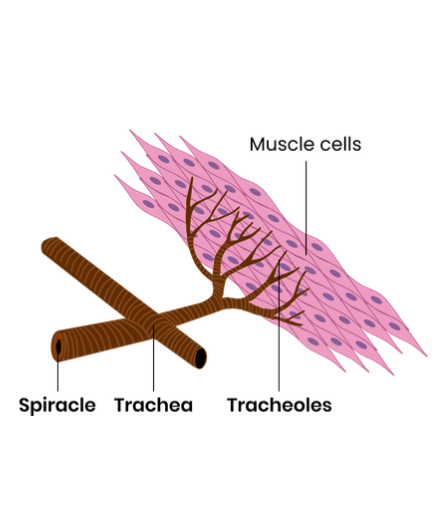
Explain structural and functional compromises in terrestrial insects that allow efficient gas exchange while limiting water loss

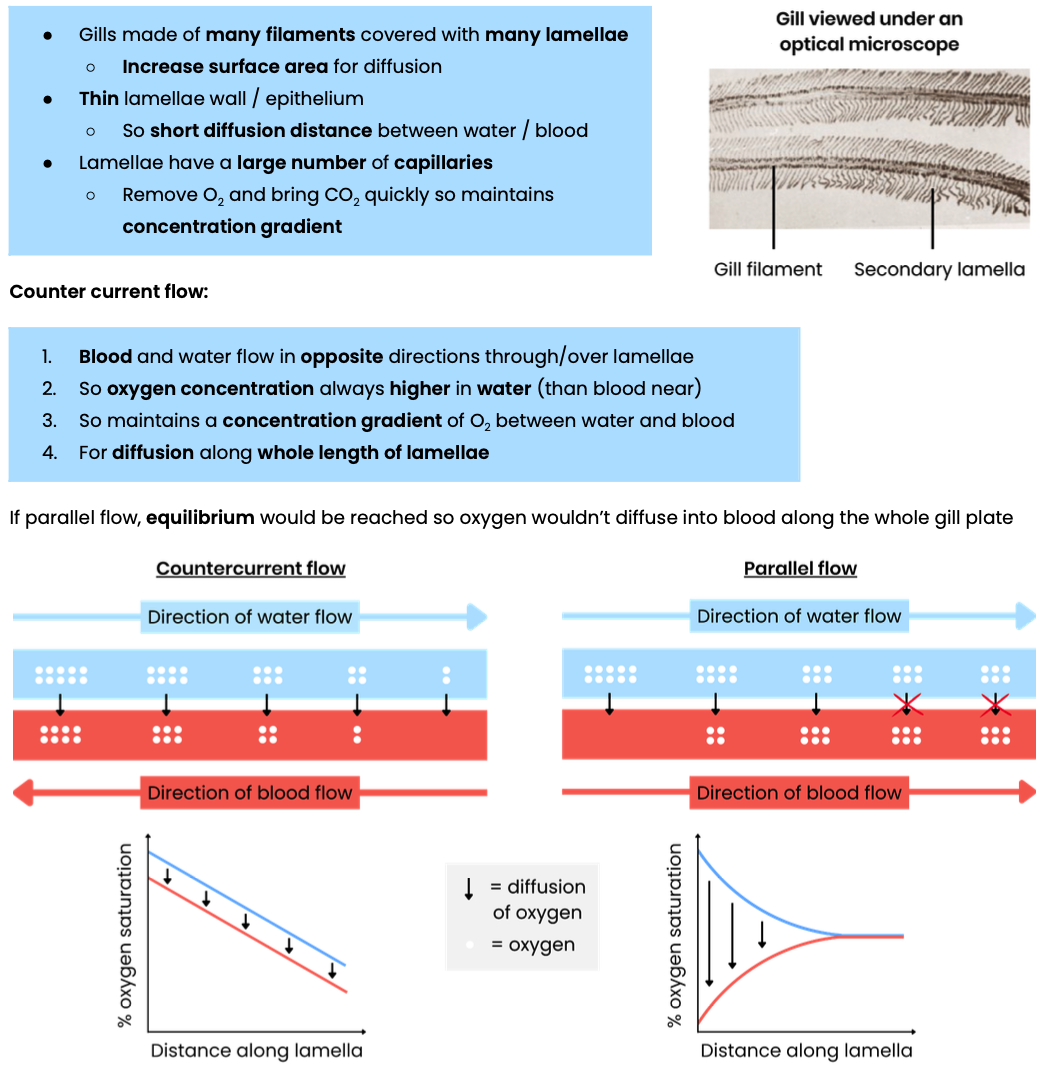
Explain how the gills of fish are adapted for gas exchange
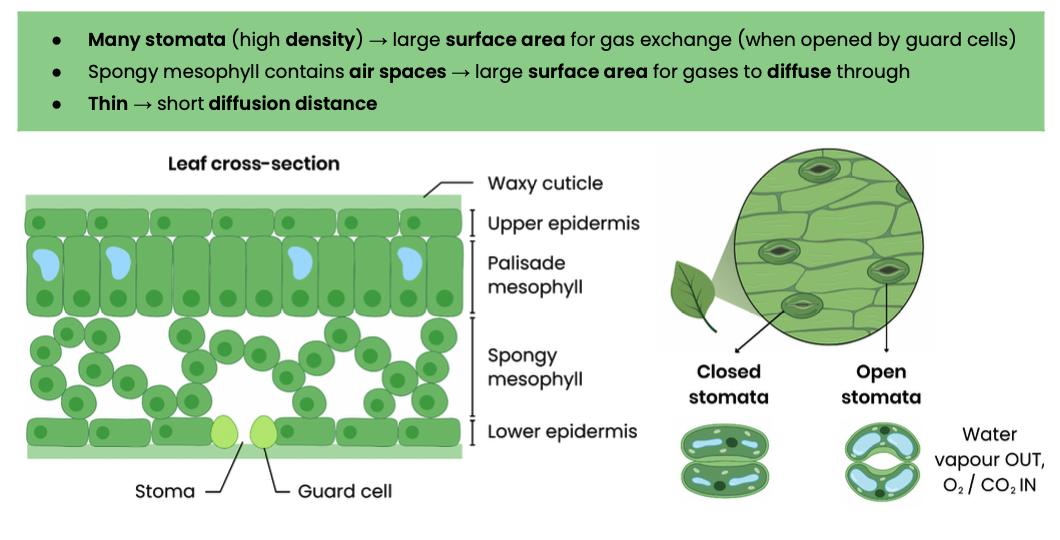
Explain how the leaves of dicotyledonous plants are adapted for gas exchange
Explain structural and functional compromises in xerophytic plants that allow efficient gas exchange while limiting water loss
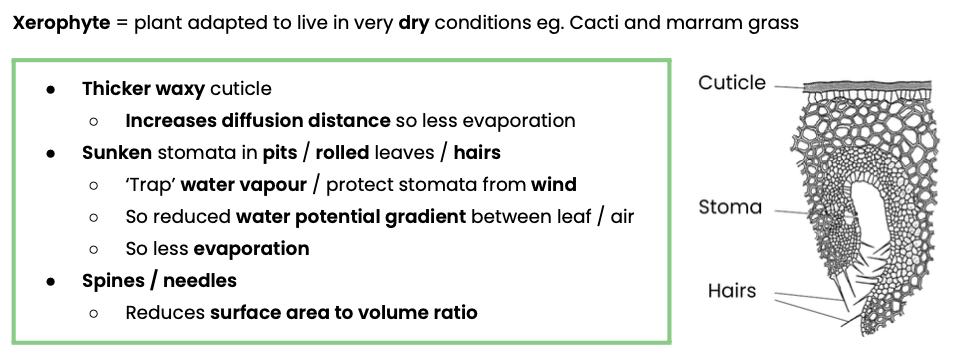
Describe the gross structure of the human gas exchange system
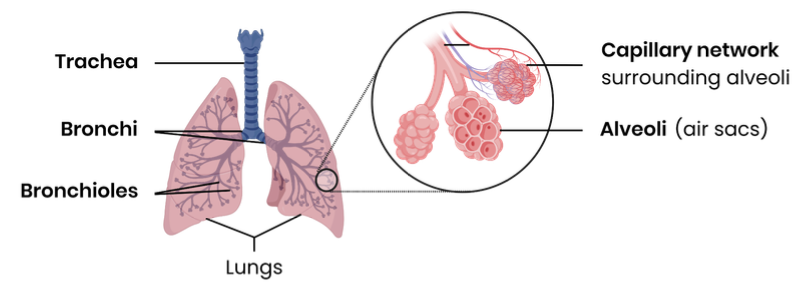
Explain the essential features of the alveolar epithelium that make it adapted as a surface for gas exchange
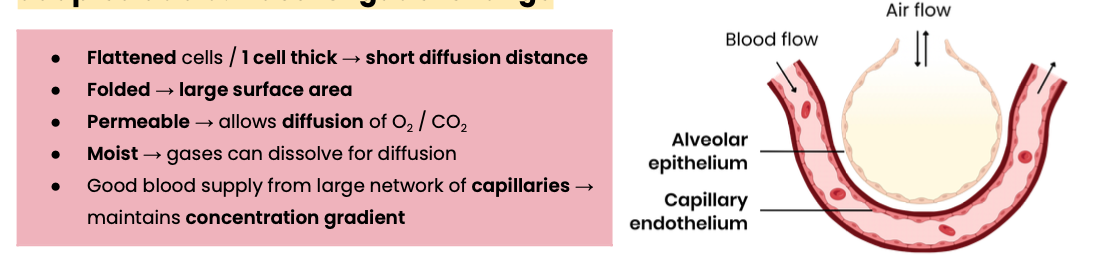
Describe how gas exchange occurs in the lung

Explain the importance of ventilation

Explain how humans breathe in and out (ventilation)
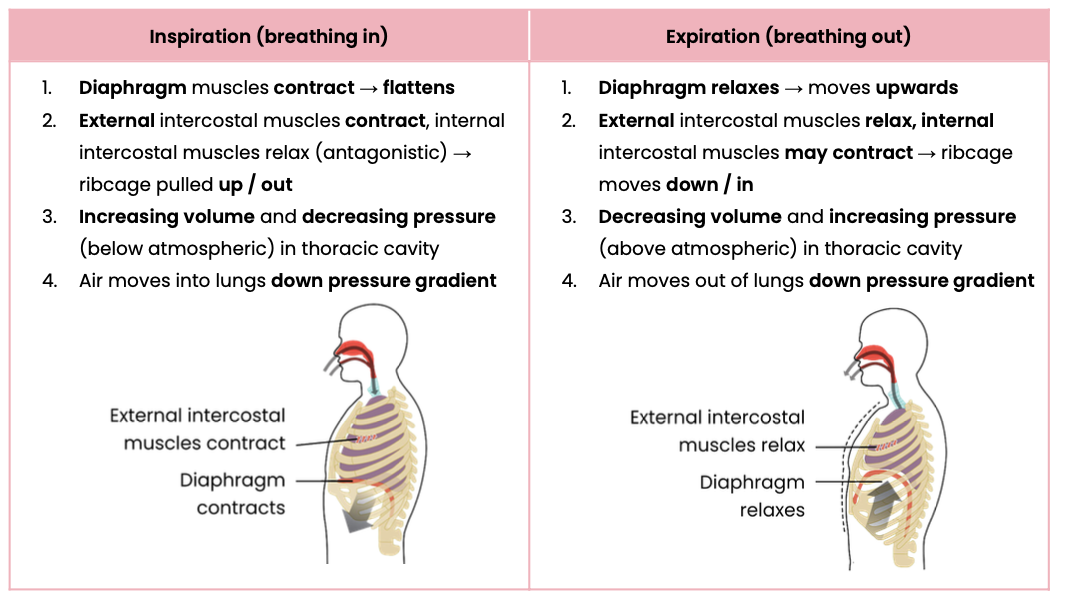
Suggest why expiration is normally passive at rest

Suggest how different lung diseases reduce the rate of gas exchange

Suggest how different lung diseases affect ventilation

Suggest why people with lung disease experience fatigue
Cells receive less oxygen → rate of aerobic respiration reduced → less ATP made
Explain the difference between correlations and causal relationships

Describe the digestion of starch in mammals
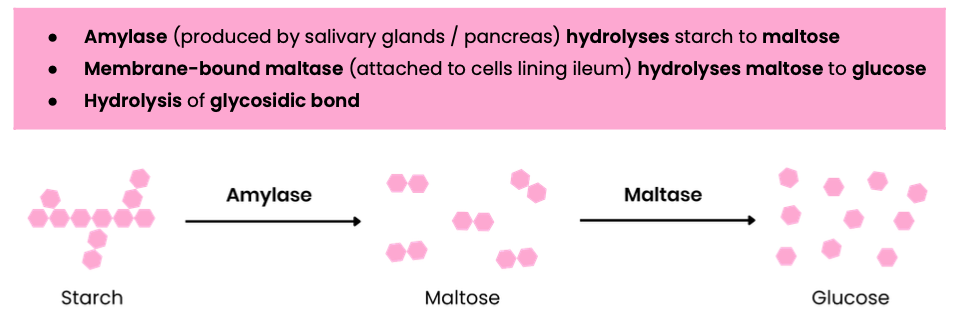
Describe the digestion of disaccharides in mammals

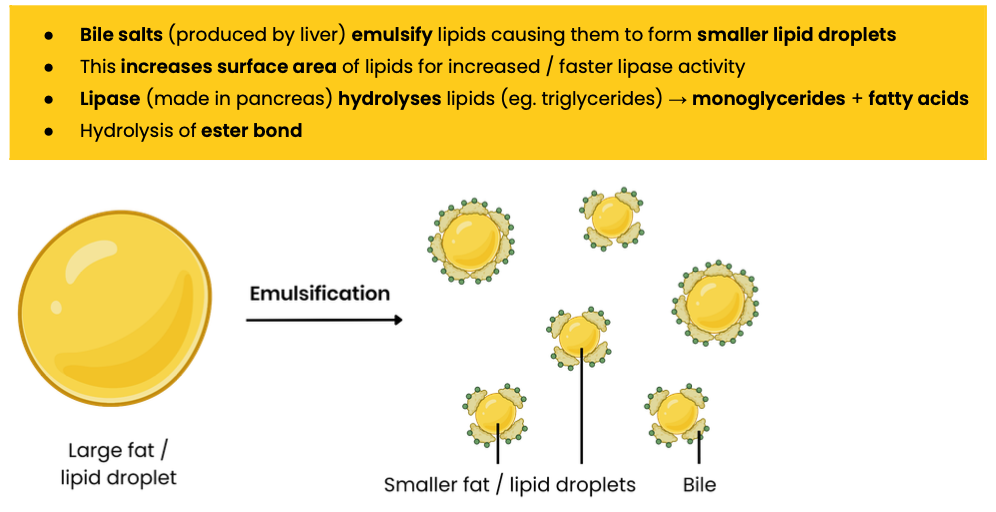
Describe the digestion of lipids in mammals, including action of bile salts
Describe the digestion of proteins by a mammal

Suggest why membrane-bound enzymes are important in digestion

Describe the pathway for absorption of products of digestion in mammals
Lumen (inside) of ileum → cells lining ileum (part of small intestine) → blood
Describe the absorption of amino acids and monosaccharides in mammals
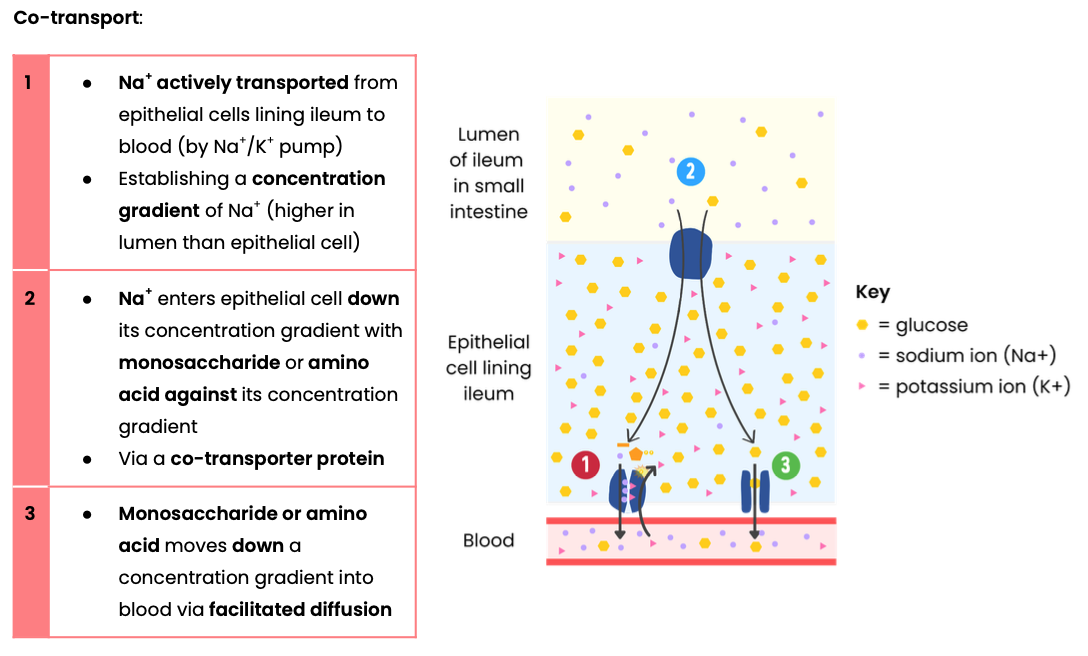
Describe the absorption of lipids by a mammal, including the role of micelles

Describe the role of red blood cells & haemoglobin (Hb) in oxygen transport

Describe the structure of haemoglobin

Describe the loading, transport and unloading of oxygen in relation to the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve
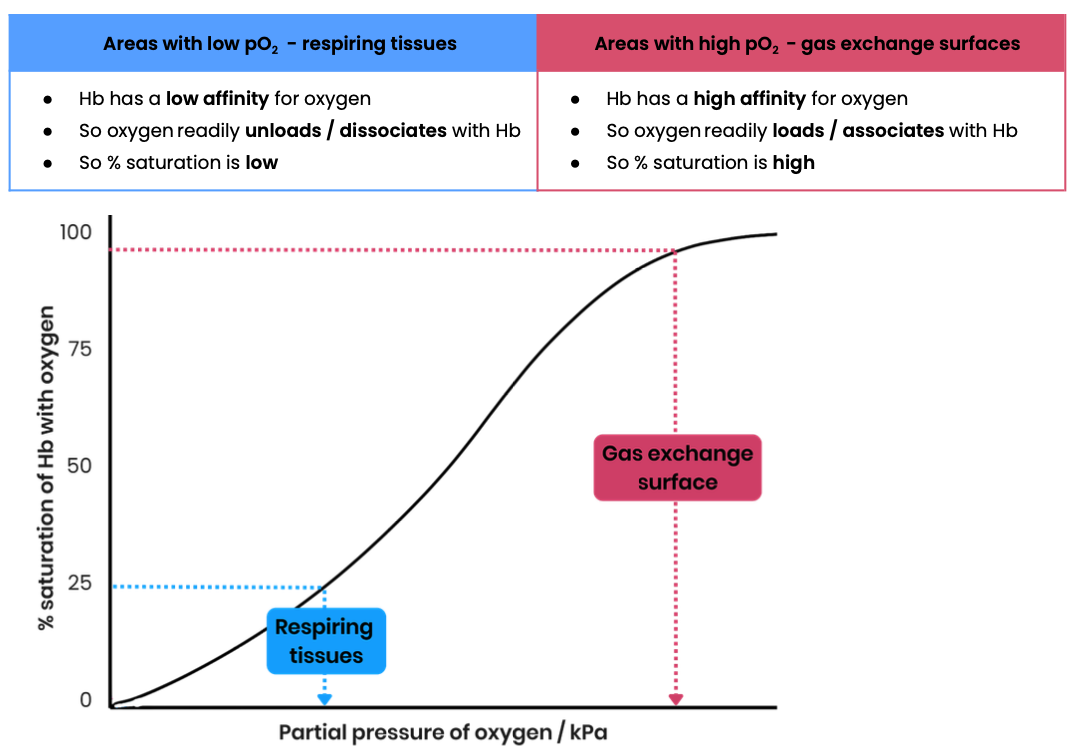
Explain how the cooperative nature of oxygen binding results in an S-shaped (sigmoid) oxyhaemoglobin dissociation curve

Describe evidence for the cooperative nature of oxygen binding

What is the Bohr effect?

Explain effect of CO2 concentration on the dissociation of oxyhaemoglobin
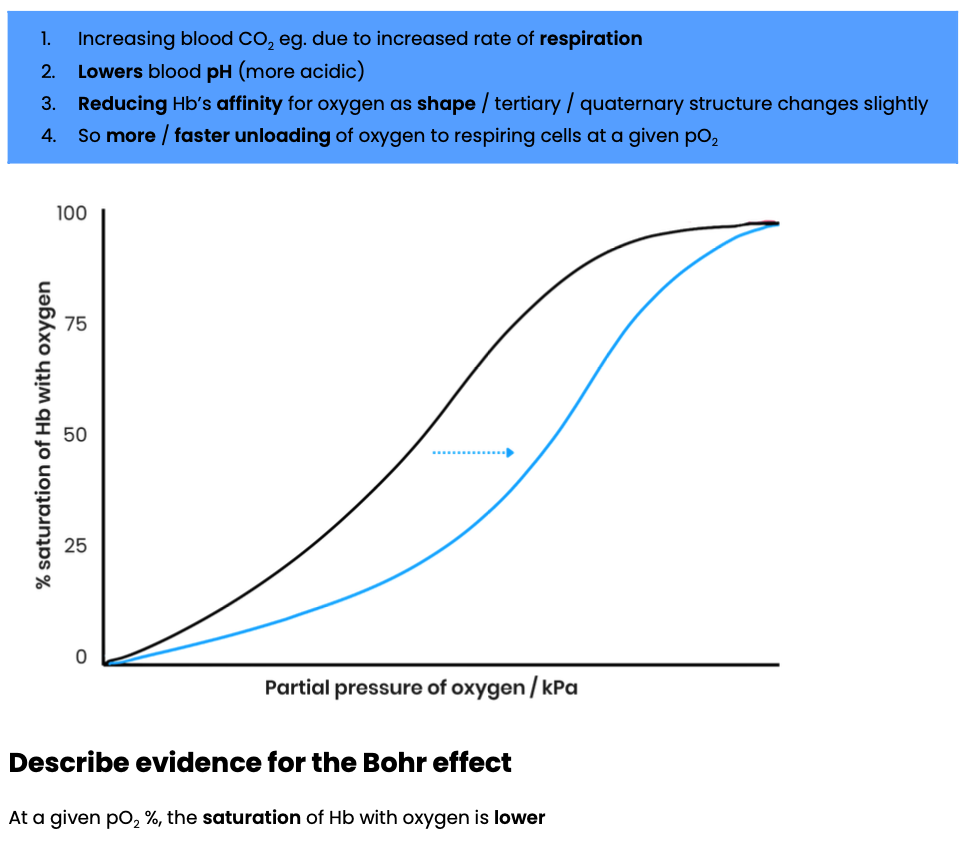
Explain the advantage of the Bohr effect (eg. during exercise)

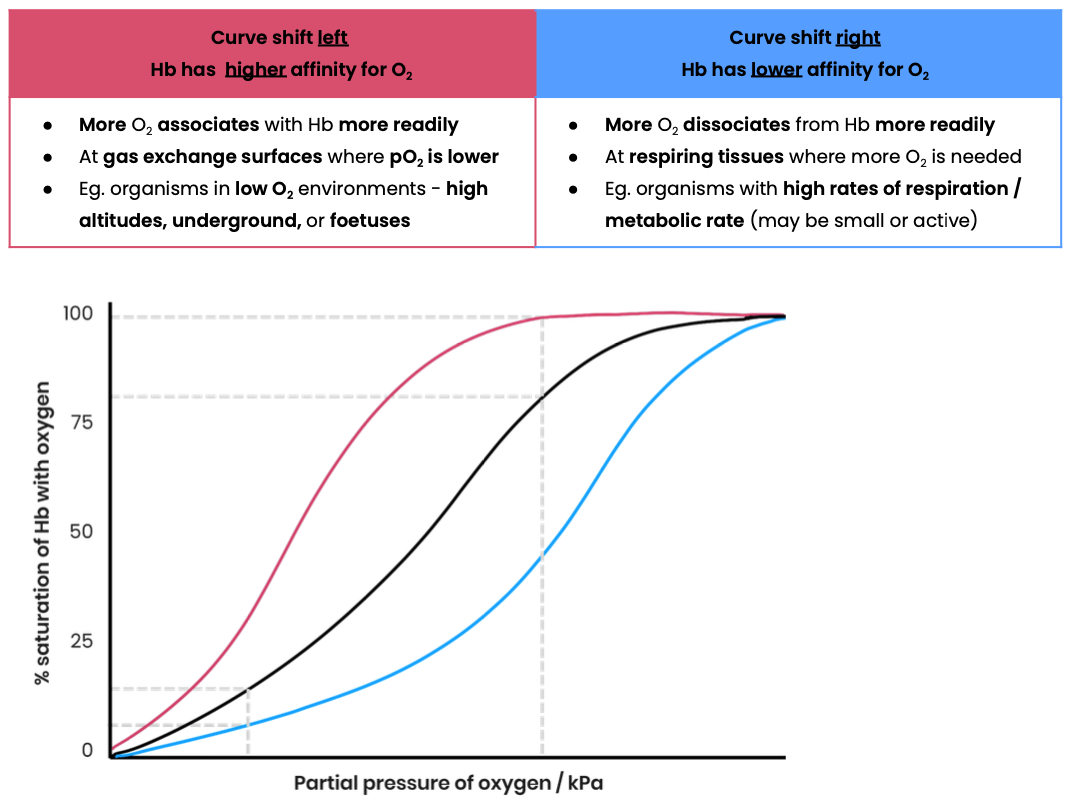
Explain why different types of haemoglobin can have different oxygen transport properties
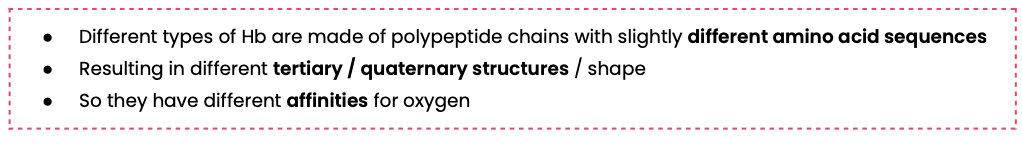
Explain how organisms can be adapted to their environment by having different types of haemoglobin with different oxygen transport properties
Organisms may evolve various types of haemoglobin to optimize oxygen transport based on specific environmental conditions such as altitude, activity level, or habitat, allowing for more efficient survival and function.
Describe the general pattern of blood circulation in a mammal
Closed double circulatory system - blood passes through heart twice for every circuit around body:

Suggest the importance of a double circulatory system

Draw a diagram to show the general pattern of blood circulation in a mammal, including the names of key blood vessels
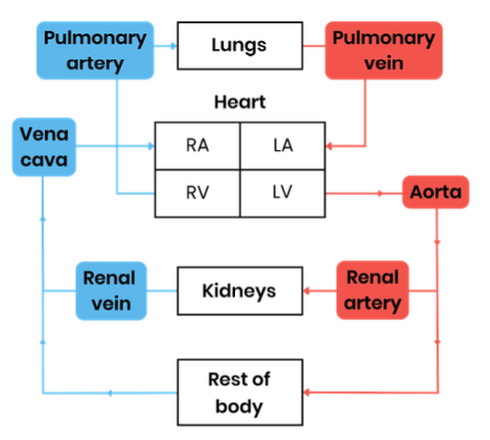
Name the blood vessels entering and leaving the heart and lungs
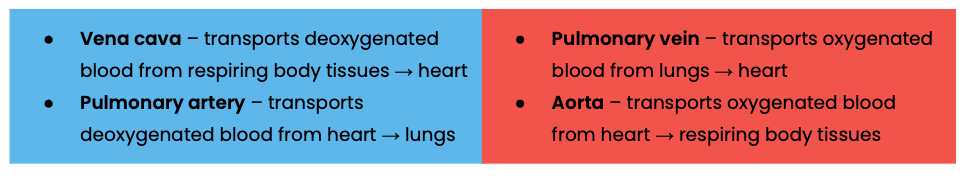
Name the blood vessels entering and leaving the kidneys

Name the the blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood to the heart muscle
Coronary arteries - located on surface of the heart, branching from aorta
Label a diagram to show the gross structure of the human heart (inside)
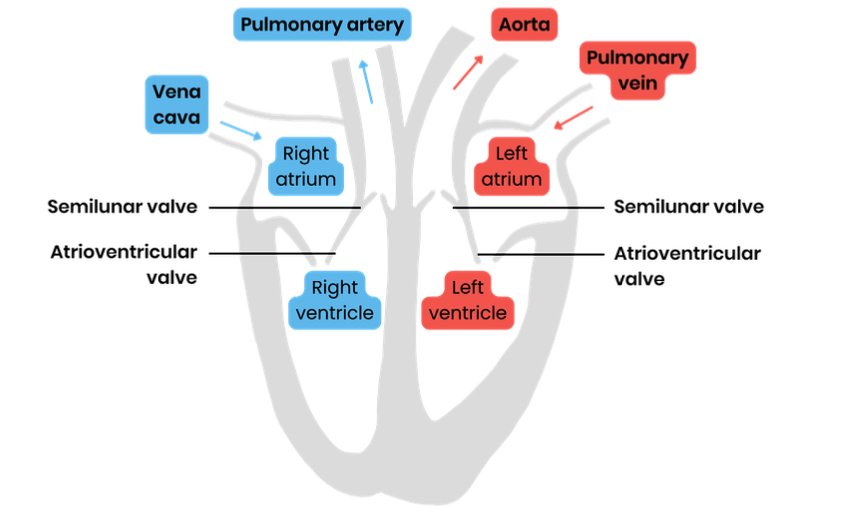
Suggest why the wall of the left ventricle is thicker than that of the right

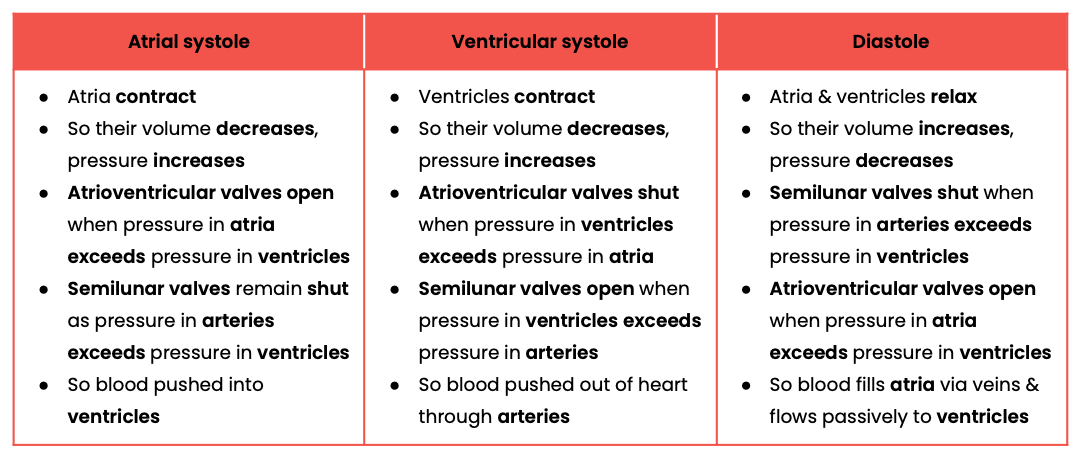
Explain the pressure & volume changes and associated valve movements during the cardiac cycle that maintain a unidirectional flow of blood
Explain how graphs showing pressure or volume changes during the cardiac cycle can be interpreted, eg. to identify when valves are open / closed
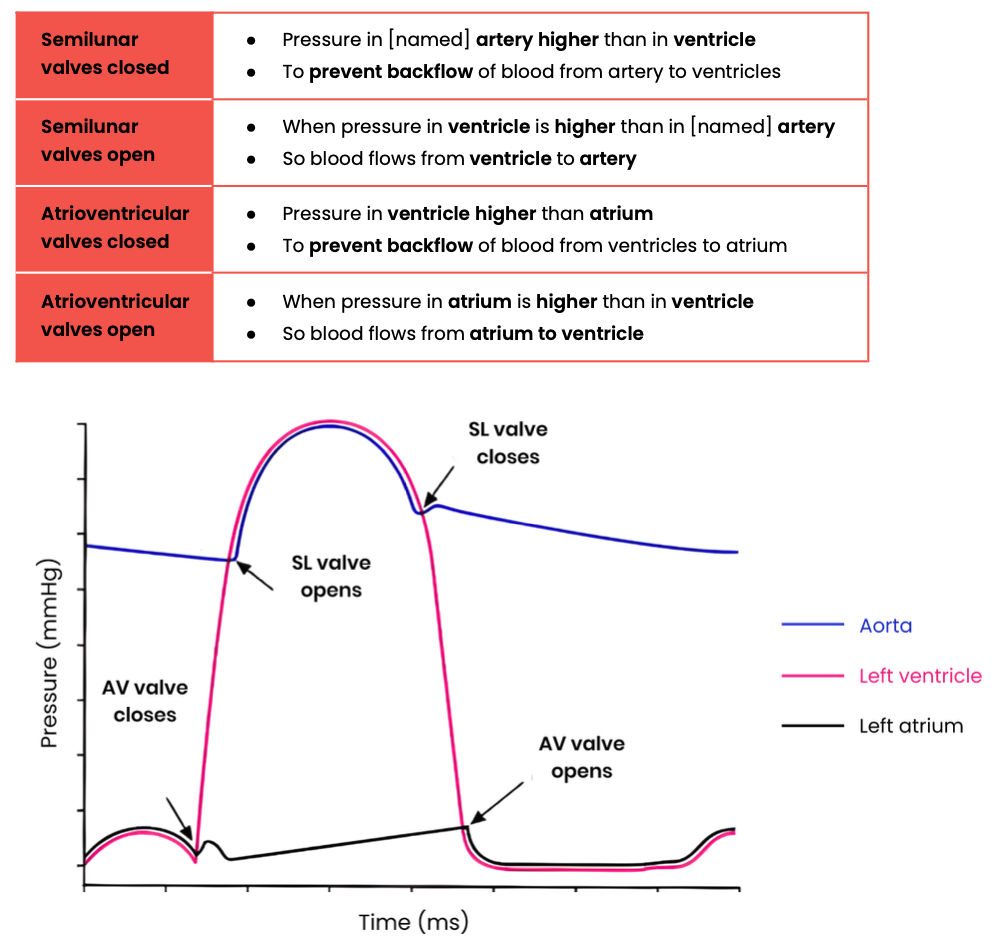
How can heart rate be calculated from cardiac cycle data?

Describe the equation for cardiac output

Explain how the structure of arteries relates to their function
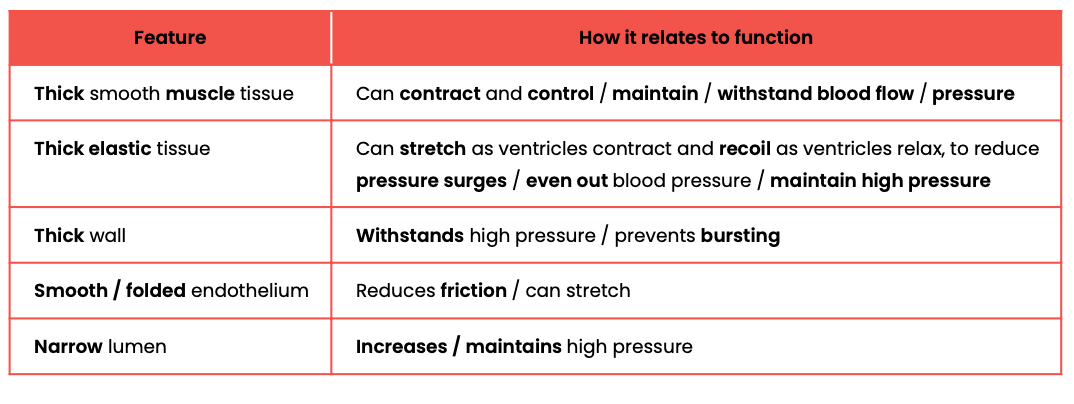
Explain how the structure of arterioles relates to their function

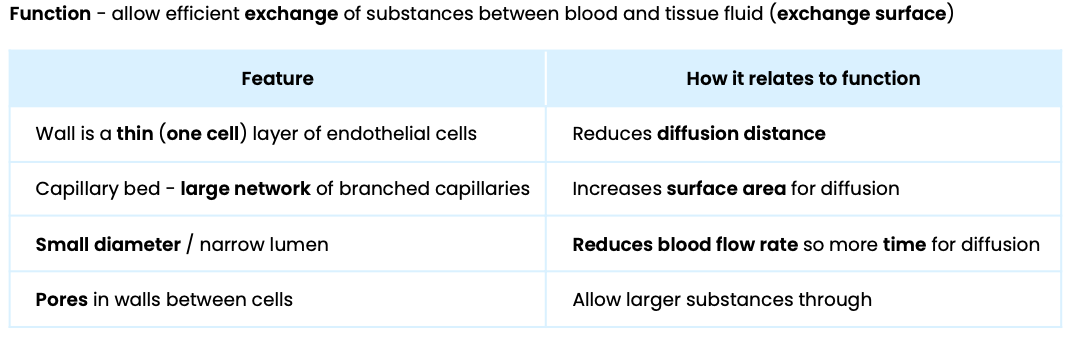
Explain how the structure of capillaries relates to their function
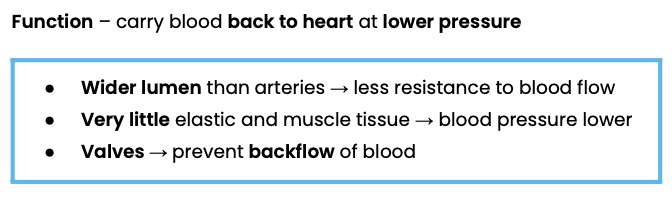
Explain how the structure of veins relates to their function
Explain the formation of tissue fluid

Explain the return of tissue fluid to the circulatory system
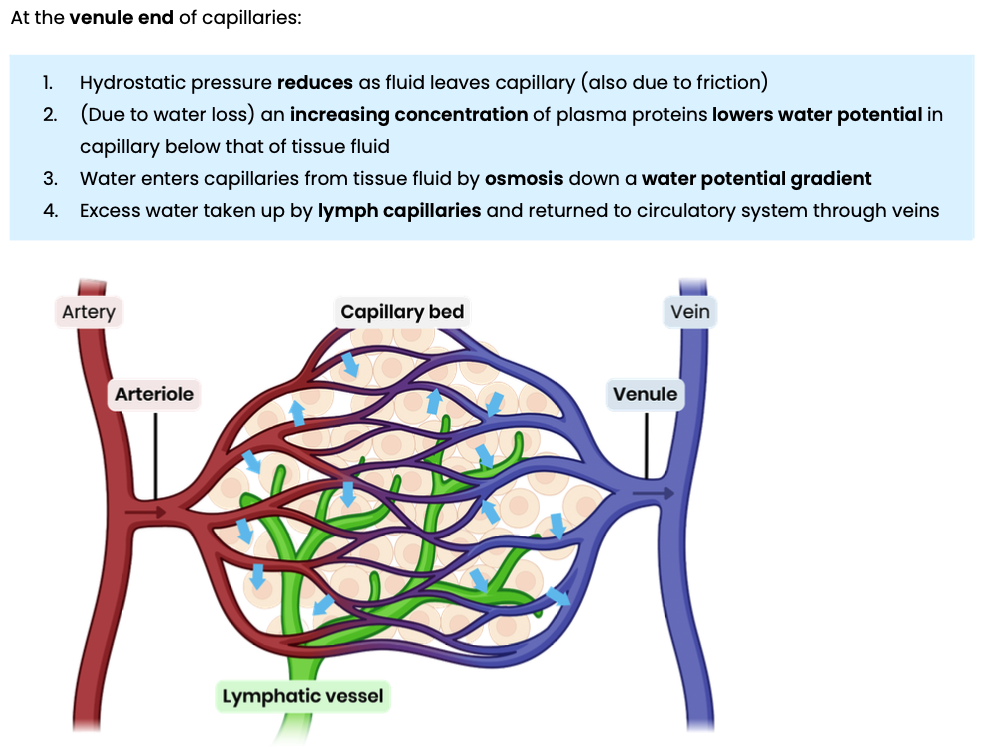
Suggest and explain causes of excess tissue fluid accumulation

What is a risk factor? Give examples for cardiovascular disease

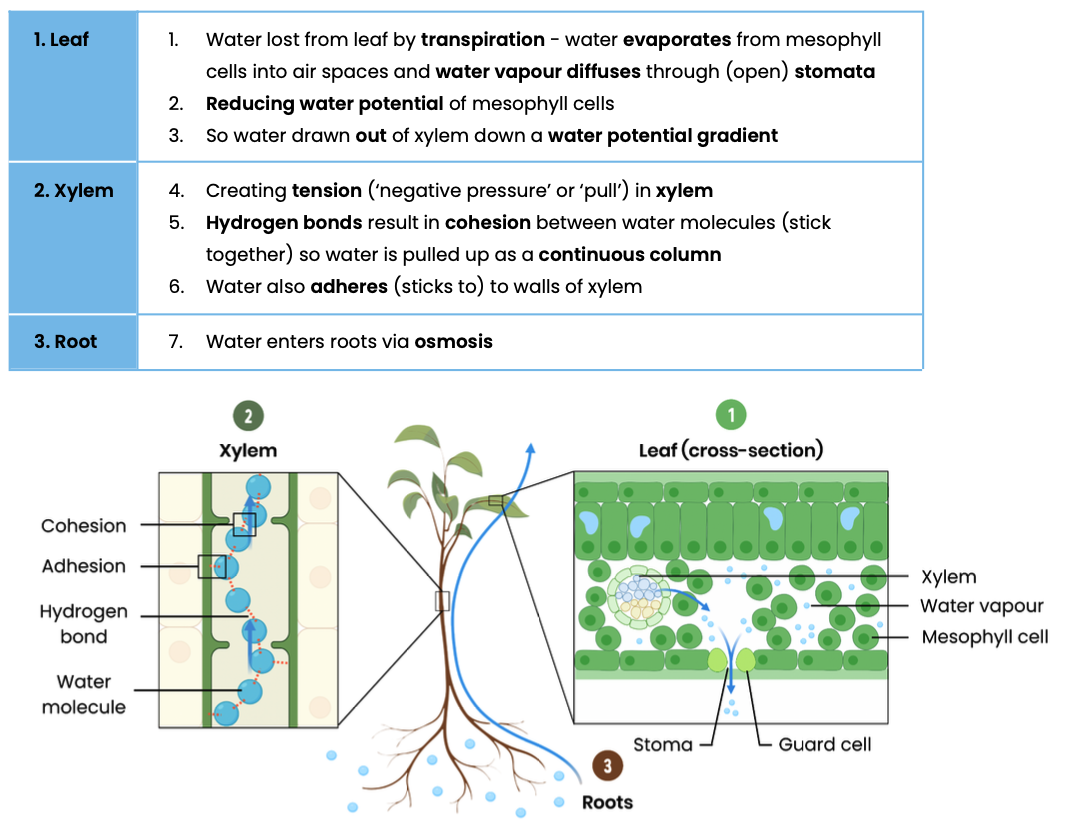
Describe the function of xylem tissue

Suggest how xylem tissue is adapted for its function

Explain the cohesion-tension theory of water transport in the xylem
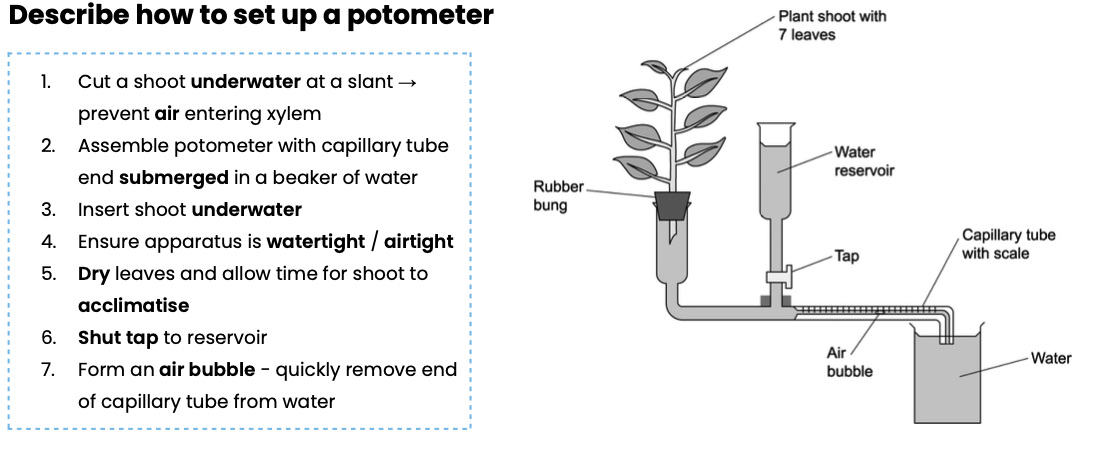
Describe how to set up a potometer
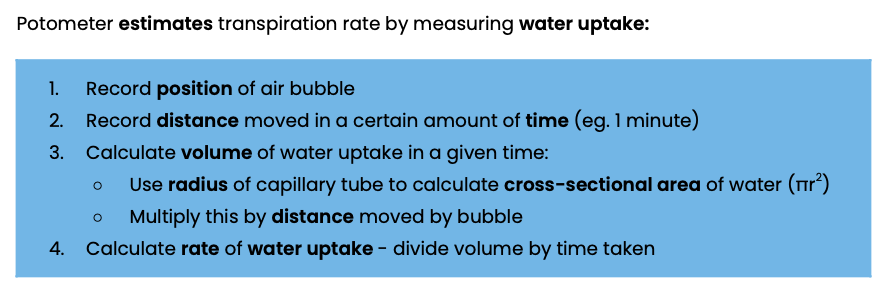
Describe how a potometer can be
used to measure the rate of transpiration
Describe how a potometer can be used to investigate the effect of a named environmental variable on the rate of transpiration

Suggest limitations in using a potometer to measure rate of transpiration

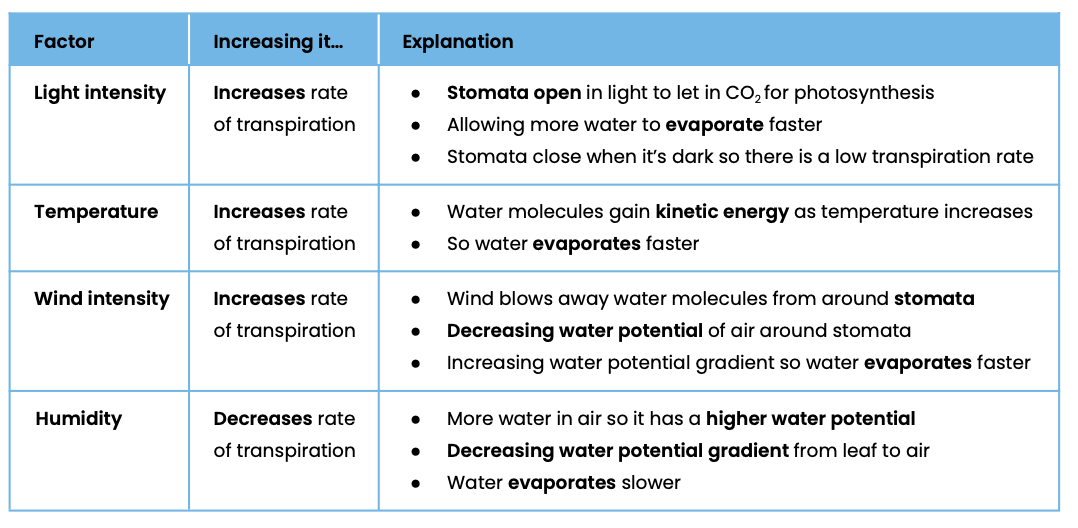
Suggest how different environmental variables affect transpiration rate
Describe the function of phloem tissue
Transports organic substances eg. sucrose in plants
Suggest how phloem tissue is adapted for its function

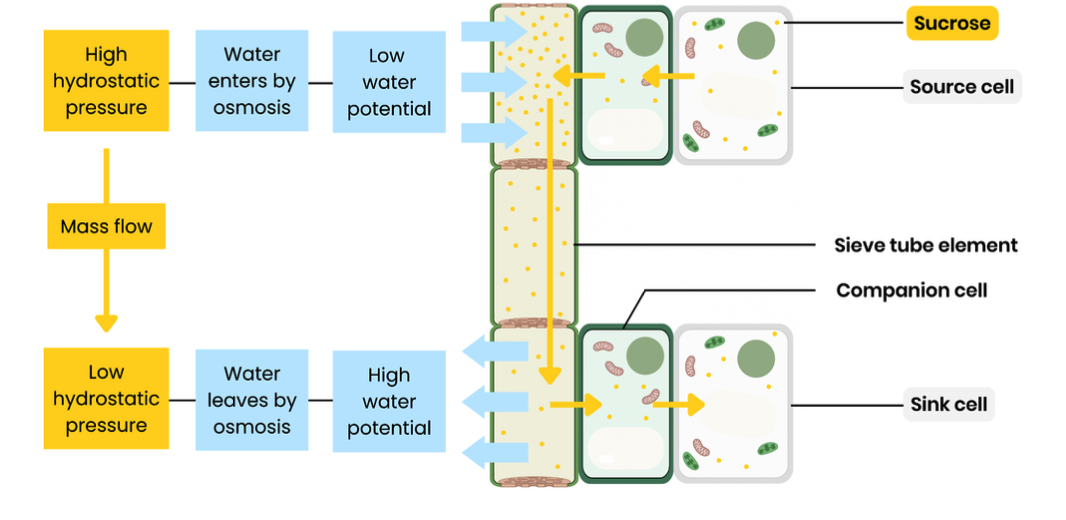
What is translocation?
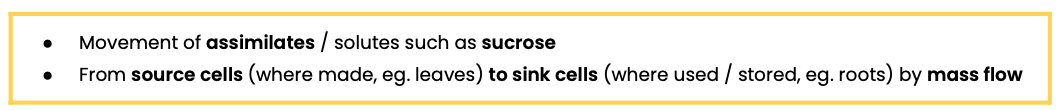
Explain the mass flow hypothesis for translocation in plants
At source, sucrose is actively transported into phloem sieve tubes / cells
By companion cells
This lowers water potential in sieve tubes so water enters (from xylem) by osmosis
This increases hydrostatic pressure in sieve tubes (at source) / creates a hydrostatic pressure gradient
So mass flow occurs - movement from source to sink
At sink, sucrose is removed by active transport to be used by respiring cells or stored in storage organs
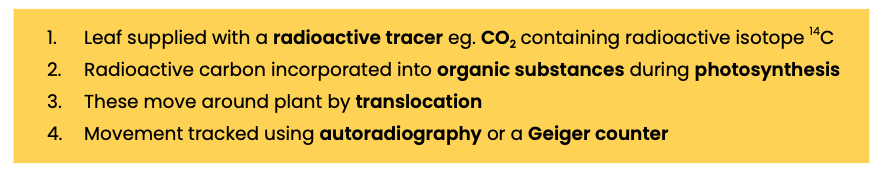
Describe the use of tracer experiments to investigate transport in plants
Describe the use of ringing experiments to investigate transport in plants
