Class 8 (integumentary, pressure injury, nursing care planning)
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
What are the subjective/symptom analysis of integumentary
skin changes, pruritus (itching), rashes, lesions, ecchymosis (bruises), changes to a mole, hair loss, nail changes
Notice widespread or localized color changes
erythema: redness
cyanosis: bluish
pallor: white
jaundice: yellow
What should you assess for abnormal skin tone
color/pigmentation even all over body, changes in freckles, moles, birthmarks, bruises
How should you palpate skin temp
use backs (dorsa) of own hands, palpate bilaterally (upper/lower extremities)
What is maceration
excessive moisture
What is normal skin
smooth and dry with minimal perspiration and oiliness
what is diaphoresis
excessive or abnormal sweating
how do you palpate texture
use palms of hands or fingertips, assess for smoothness, roughness, thickness, tightness, induration, softness
how do you palpate skin thickness
use palms of hands or fingertips
what is a healthy finding of skin thickness
epidermis is uniformly thin over most of body, thickened areas on palms/soles are normal
What is a bony prominence
any point on the body where the bone is immediately below skin surface
what is erythema
redness of skin due to congestion of the capillaries
What does erythema look like in pale, ivory, beige skin
red, bright pink
what does erythema look like in very dark skinned (difficult to see)
purplish tinge or darkened area, palpate for incr warmth with inflammation, taut skin, induration (hardening of deep tissue)
What should you asses for blanching
blanchable redness is normal, non-blanchable is 1st stage of pressure ulcer development
What is skin mobility
ease of skin to rise
what is tugor
skin ability to return to place promptly when released
what is skin mobility and turgor used to assess
elasticity of skin and hydration status
where do you assess mobility and turgor
anterior chest or forearm do NOT use back of hand
exudate (byproduct of wound healing:
serous: clear liquid (blister)
sero sanguineus: liquid with blood
sanguineus: bloody
pustulant/purulent: pus (infected)
ABCDE for skin cancer (moles) is
A smmetry
B order
C olor
D iamter
E volving
Normal age related skin lesions consist of
senile/solar purpura, solar lentigines (liver or age spots) , seborrheic keratosis
What are healthy nails
pink, translucent, smooth, firm, well rounded, convex, nail angle of 160 degrees, good adherence to nailbed
What is nail clubbing
bulging of nail base leading to abnormal curvature of nail, associated with chronic decreased oxygen levels
How do you assess for clubbing
-flex 1st phalangeal join of L&R back to back
- raise fingers to eye level
- positive - no diamond shape space
Pressure injury ulcer is
localized damage to skin/underlying soft tissue over a boney prominence or related to a medical or other device
Pressure injuries are avoidable
True
What is the development of pressure injury
1) contact b/w boney prominence and surface creates friction, superficial and seen
2) movement creates shearing force, deeper tissue damage
3) moisture creates risk of breakdown
4) pressure decreases circulation to area
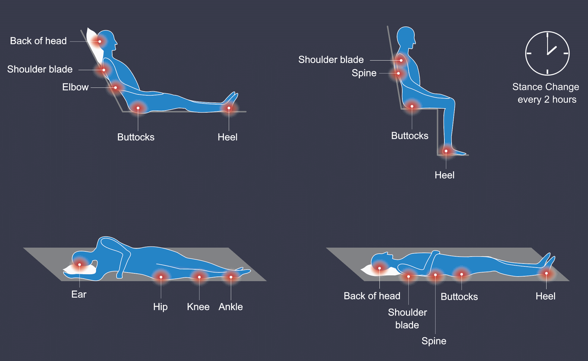
common places for pressure injuries
refer to picture
Stage 1 pressure injury
Non-blanchable erythema of intact skin
Stage 2 pressure injury
Part-thickness skin loss with exposed dermis.
Stage 3 pressure injury
Full-thickness skin loss to subcutaneous layer, may have undermining or tunneling; fat may be visible
Stage 4 pressure injury
Full-thickness skin and tissue loss to tendon, cartilage or bone, undermining or tunneling; muscle/bone may be visible
Unstageable pressure injury
obscured full-thickness of tissue loss
Deep tissue injury
persistent non-blanchable deep red, maroon and purple discoloration, intact or non intact skin
What is slough
yellow or white material (dead tissue) in wound bed, by product of inflammatory phase of wound healing
unstageable vs suspected deep tissue injury (SDTI)
Unstageable
Obscured full-thickness tissue loss
Suspected Deep Tissue Injury (SDTI)
Deep tissue injuring presented as persistent non-blancheable, deep maroon or purple discoloration to intact or non-intact skin
When should you assess for pressure injury
on admission (24 hrs of arrival), once every shift, when pericare completed, during position changes/turning, every bath, assess for persistent moisture or medical devices, bony prominences, assess for risk (braden scale), focus on elements that help guide skin assessment
What is the braden scale
determine risk for developing pressure ulcers (sensory perception, moisture, activity, mobility, nutrition, friction and shear)
what are the 6 components of the braden scale
Sensory Perception
Moisture
Activity
Mobility
Nutrition
Friction & Shear
How do you intervene immobility
turn/reposition every 2 hours
How do you intervene mositure
assess, provide pericare, avoid diapers, toileting shcedules, dry after bathing, barrier creams
how do you intervene nutrition
adequate feeding, intake, and protein
how do you intervene friction and shear
waffle mattresses, booties, lifting devices, ambulation, pressure relieving surfaces
What are the 3 focuses of nursing diagnosis
1) Determine client/family responses to human problems, level of wellness, and need for assistance;
2) Provide physical care, emotional care, teaching, guidance, and counseling;
3) Implement interventions aimed at prevention and assisting the client to meet his or her own needs and health-related goals.
Arriving at a diagnosis process
Cluster data (S/O, pt history, current symptoms) -> analysis (abnormal, risk, concern) -> identify areas of need (concern about _, pt needs additional _, risk for _) -> elect diagnosis
what is NANDA international
Identified domains -> conducted research -> identified best interventions and outcomes
creates standards, improves consistency, provides for evidence based nursing actions
What are the 3 types of nursing diagnosis?
problem, risk, and health promotion based
What is a problem based diagnosis
1) undesirable situation exists, problem
2) problem related to measurable, observable, reported fact
3) pt actively experiencing sign or symptom, evidence
what is a risk based nursing diagnosis
1) reason to believe problem may result; risk
2) concern is related to circumstances, evidence, observed behaviors
3) there is no active symptom or complain but has risk factors
what is health promotion based nursing diagnosis
1) readiness or expressed desire to improve (promote) health
2) evidence exists to support claim or readiness
Components of a problem
P: problem statement/NANDA-I diagnostic label
RELATED TO (r/t)...
E: etiology/related factors
AS EVIDENCED BY (aeb)...
S: defining characteristics/signs & symptoms
NANDA-I label
A concise term or phrase that represents a pattern of related cues. The nursing diagnosis label is taken from the official NANDA-I list.
What is an example of a NANDA-I label
qualifier: decreased
health problem/focus of diagnosis: cardiac output
Etiology/related factors
factors that are related to a cause or contributor to the problem, pathophysiological, treatment related, situational, maturational, secondary to statements
"as evidenced by" statement (risk factors):
NANDA label r/t _____ (etiology) aeb ______ (min 2 defining characteristics [signs/symptoms])
Defining characteristics
as evidenced by, clusters of signs and symptoms (2 or more) that the nurse identified in the assessment
actual nursing diagnosis vs risk nursing diagnosis
risk:
- do not have related to statements
- only lists risk factors
- risk factors are written following the phrase "aeb"
- risk factors are written following a colon ":"
What is an example of the use of aeb and :
Risk for impaired skin integrity aeb excessive moisture and immobility
Risk for impaired skin integrity: excessive moisture and immobility
Planning phase
3rd phase: "how to manage the problem" consists of writing pt centered goals and measurable expected outcomes, nursing interventions to achieve expected outomces, rationale using evidence (research) to support interventions
The writing expected outcomes goals is
S pecific
M easurable
A ttainable
R ealistic
T imed
"outcomes are pt focused, pt will..."
What is an example of SMART outcome statement (patient-centere)
Target client + verb + measurable outcome + timeframe
E.g.: The patient will be able to eat at least 60% of each meal by the end of the week
For nursing interventions should note that
Interventions are NURSING based and begin with the statement "Nurse will"
Implementation is
4th phase: actual initiation and implementation of nursing care plan, putting plan into action
Evaluation is
5th phase: "did the plan work", examine results, compare achieved effects with goals and expected outcomes, revise care plan