economic world - nigeria
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Define development.
Progress of a country.
Define the following terms and give an example if needed: HIC, NEE, LIC, BRIC, MINT.
HIC - High Income Country (UK)
NEE - Newly Emerging Economy (Nigeria)
LIC - Low Income Country (Ethiopia)
BRIC - Brazil, Russia, India, China
MINT - Mexico, Indonesia, Nigeria, Turkey
What is GDP?
Gross Domestic Product - total value of goods and services produced within a country in a year.
What is GNI?
Gross National Income - the total income earned by a country's people and businesses,
What is HDI?
Human Development Index - A development measure, which uses life expectancy, literacy rates, and GDP. 1 is the highest and 0 is the lowest.
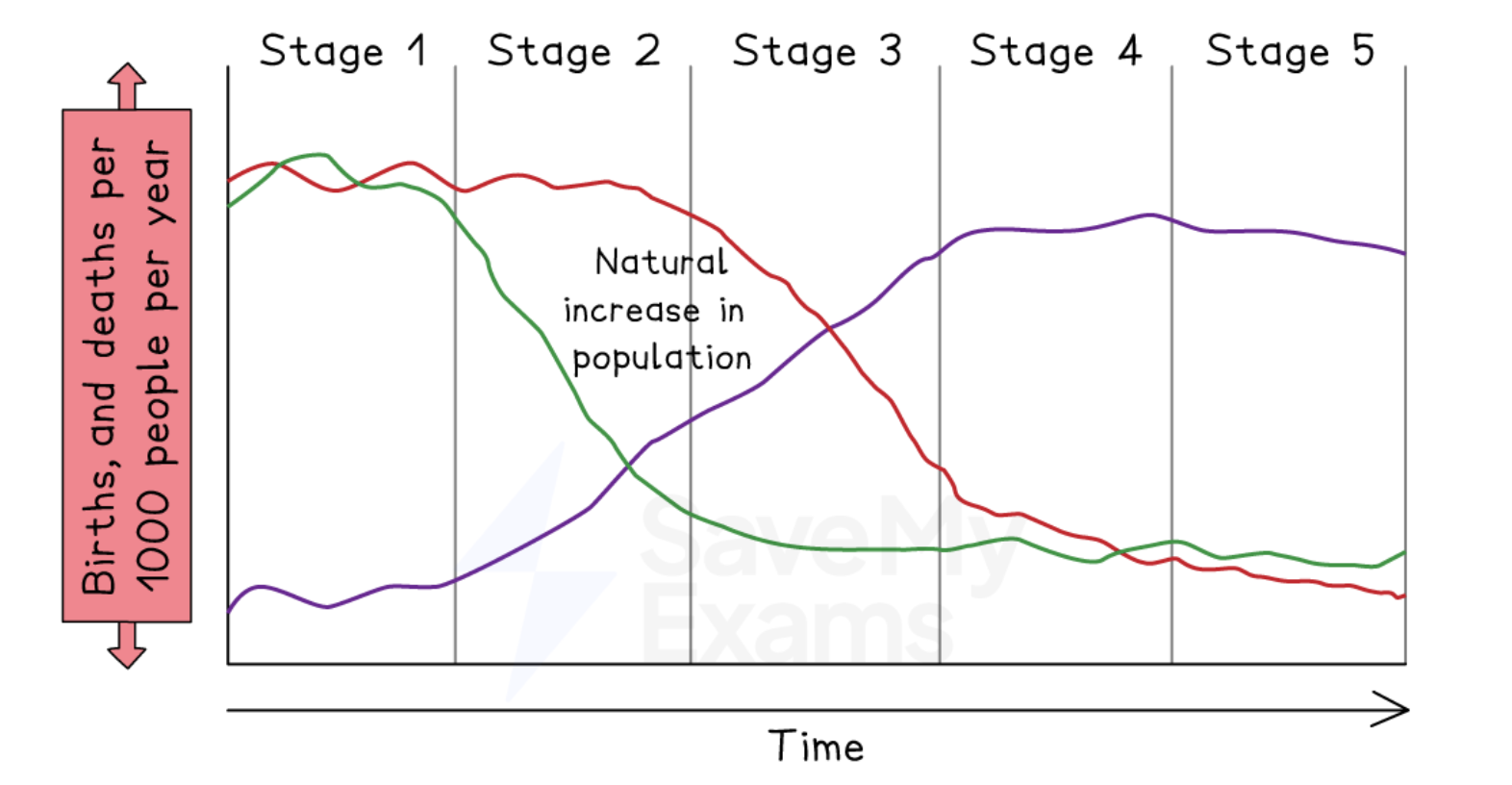
Describe the DMT (3 points)
Demographic Transition Model:
Shows how the population, BR, and DR fluctuate at each stage of development.
UK is around stage 4, while LICs would be stage 1.
Fluctuation at stage 1 shows poor health.
What are the four categories of causes of uneven development?
Historical (colonisation)
Physical (location or lack of resources)
Economic (global trade policies)
Political (corruption or conflict)
What are the four effects of uneven development?
Economic (income) - this usually kickstarts the others.
Physical (food and nutrition)
Social (family)
Happiness (wellbeing, social life)
Define development gap.
The disparity of wealth between the world’s richest (HICs) and poorest countries (LICs).
What are the strategies to reduce the development gap? (3 points)
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) - 17 separate goals made in ‘15 by the UN to end global poverty.
FairTrade - Ensures farmers receive a fair wage and good working conditions. FairTrade premium also supports the entire community.
Microfinance - People donate to farmers to invest in themselves and their business and pay it back over-time. Empowers individuals.
What are TNCs?
Transnational Corporation - e.g. Apple or Microsoft.
What are the positives and negatives of TNCs in lowly-developed countries?
P - Job opportunities, FDI, improvement of services and roads.
N - Exploitation of workforce, environmental pollution, leakage of income.
What is FDI?
Foreign Direct Investment
Case Study: Where in Nigeria is an example of a TNC causing advantages and disadvantages? (7 points)
Shell: Bodo Village, Nigeria
invested billions in oil extractions and infrastructure
Supports over 8,000 Nigerian people directly and indirectly
Large oil leak in 2008
Caused water and soil contamination - which affected the local area’s drinking water
Massive loss of fish population
Lack of accountability for many months
500,000 barrels approx spilt, but they claimed it was only 4000 initially.
What are some consequences of uneven development? (2 points).
Migration - Young people seek a better quality of life elsewhere.
Brain Drain - When highly skilled people are attracted to work somewhere else, causing the country’s economic development to decrease.
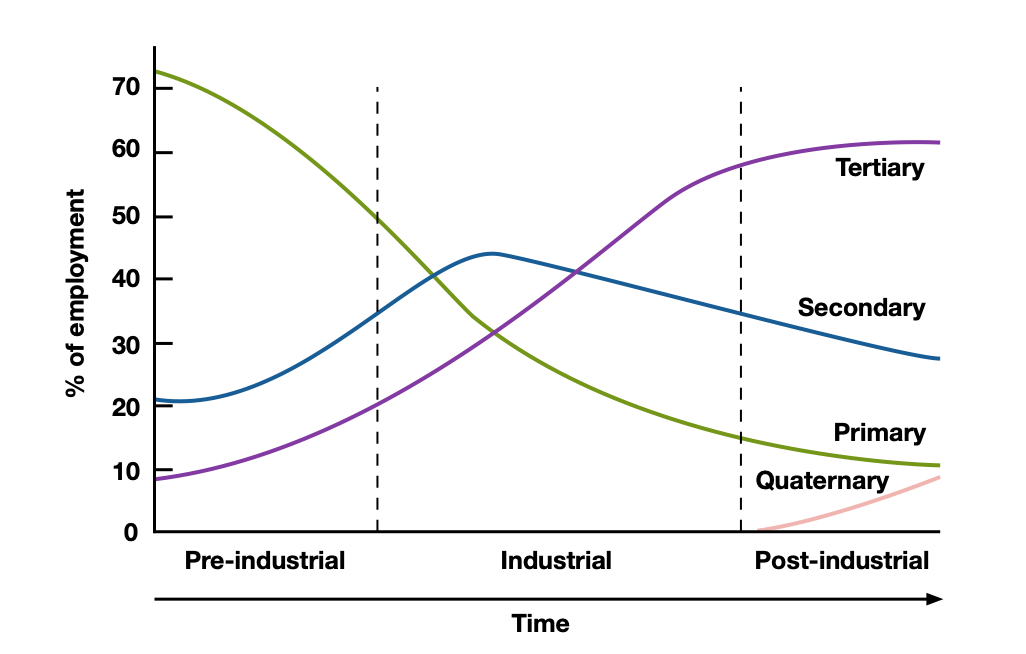
Describe the employment structure graph. (6 points)
Shows the percentage of jobs across the four work sectors.
Primary sector is agriculture.
Secondary sector is manufacturing.
Tertiary sector provides services for people (retail)
Quaternary sector is subject-specific jobs (IT)
LICs are heavily pre-industrial, while HICs like London are heavily post-industrial.
Where is Nigeria located?
West Africa, bordering countries such as Cameroon.
How is Nigeria regionally important? (5 points)
One of the fastest-growing economies in Africa
The variety of rainy and dry seasons allows it to have the highest farm output in Africa
Nigeria is the most populous African nation (over 230mill people)
Diverse economy
Imports telephones
How is Nigeria globally important? (4 points)
GDP of $440 billion in 2021
One of the world’s biggest oil exporters - around 2 million barrels exported each day
Nigerian film industry Nollywood has overtaken Hollywood to become the world's second-largest film industry
Main exports are rubber, cocoa, cotton and oil
Oil accounts for // % of Nigeria’s GDP.
14
What is ‘tied aid’?
When the country giving aid expects something in return, for example trade in the future.
What are the four types of aid?
Development Aid - Long-term aid to promote progress, e.g. from the World Bank and the EU.
Emergency Aid - Short-term aid during an emergency, usually after a disaster.
Bilateral Aid - Direct aid from one country to another, e.g. from the UK to Nigeria, but often tied aid.
Multilateral Aid - Richer countries giving money to international organisations (like the World Bank) to distribute to lower income countries.
Name some disadvantages of international aid.
May not reach the people who need it due to corruption.
Countries may become over-dependent on aid.
Food and water can become more expensive.
What is a key project that was started in Nigeria thanks to aid?
Anti-mosquito nets, provided by ‘Nets for Life’.
Why is aid needed in Nigeria?
60% of the population live on $1/day, and there are high wealth disparities within the country.
What effects has aid had on Nigeria?
Increased years of schooling for children.
Life expectancy increased from 45 to 55 in 2020.
Higher access to safe drinking water in rural areas.
Over 70% of Nigeria now own a mobile phone.
What Asian county has invested into and made a trade relationship with Nigeria?
China.