11.1 physical properties of group 17 elements
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
What is the colour of fluorine
Pale yellow gas
What is the colour of chlorine
pale green gas
What is the colour of bromine
Orange, brown liquid
What is the colour of iodine
Grey solid
Purple vapour
Describe the trend in volatility of chlorine, bromine and iodine
Going down the group, the boiling point of the elements increases, therefore the volatility of halogens decreases
Describe and explain the trend in the bond strength of the halogen molecules
Halogens are diatomic molecules in which covalent bonds are formed by overlapping their orbitals
In a covalent bond, the bonding pair of electrons is attracted to the nuclei on either side and it is this attraction that holds the molecule together
Going down the group, the atomic size of the halogens increases
The bonding pair of electrons get further away from the halogen nucleus and are therefore less strongly attracted towards in
Describe the trend in group 7 bond enthalpies
Bond enthalpy is the heat needed to break one mole of a covalent bond
The higher the bond enthalpy, the stronger the bond
Exception: fluorine has a smaller bond enthalpy than chlorine and brominei
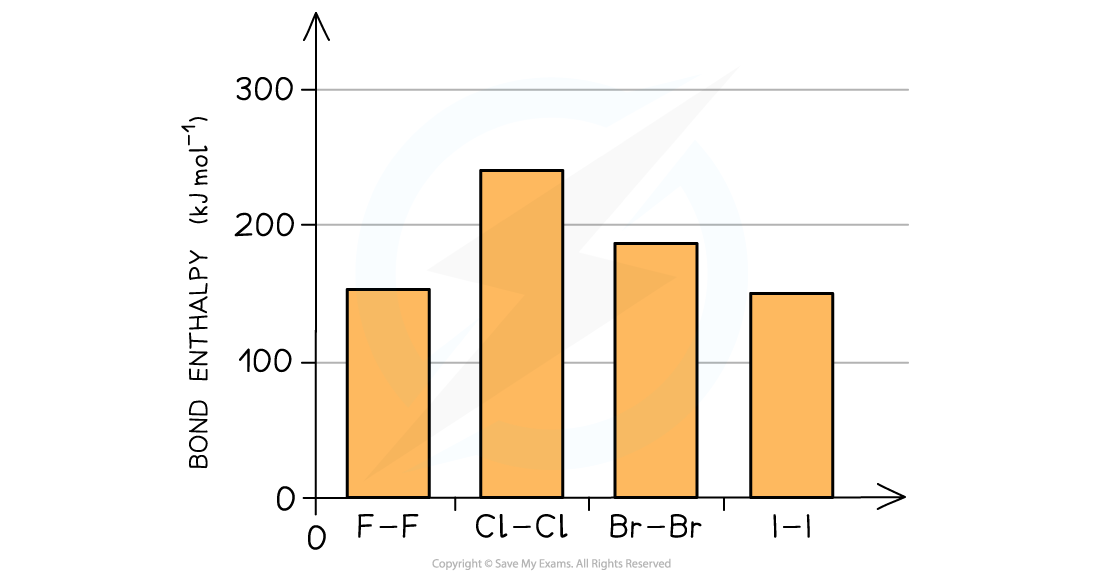
Why is fluorine an exception in bond enthalpies
Fluorine is so small that when 2 atoms of fluorine get together their lone pairs get so close that they cause significant repulsion counteracting the attracting between the bonding pair of electrons and two nuclei
Interpret the volatility of elements in terms of instantaneous dipole-induced dipole forces
The halogens are simple molecular structures with weak van der Waals’ forces between the diatomic molecules caused by instantaneous dipole-induced dipole forces
The more electrons there are in a molecule, the greater the id-id forces
Therefore, the larger the molecule the stronger the van der Waals’ forces between molecules
Therefore as you go down the group, it gets more difficult to separate the molecules and the melting and boiling points increase
As it gets more difficult to separate the molecules, the volatility of the halogens decreases going down the group
Halogens are… agents
Oxidising
How does electronegativity affect a halogen’s oxidising power?
Going down the group, atomic radii decreases
Therefore halogen’s ability to accept an electron decreases as incoming electron experiences shielding
Therefore, oxidising power decreases
Describe the reaction between fluorine and hydrogen gas
Reacts explosively, even in cool or dark conditions
Describe the reaction between chlorine and hydrogen gas
Reacts explosively in sunlight
Describe the reaction between bromine and hydrogen gas
Reacts slowly on heating
Describe the reaction between iodine and hydrogen gas
Forms an eq mixture on heating
Explain the trend in thermal stability of hydrogen halides down the group
decreases
Atomic radius of halogens increases
Overlap of outer shell with hydrogen atom gives longer bond length
The longer the bond, the weaker, and the less energy required to break it.