EUKARYOTIC CELLS
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
eukaryotic cells
Membrane-bound nucleus that houses dna
Specialized organelles
prokaryotes
what were the first cells ?
archaea
eukaryotes are most closely related to ____
Nucleus—> Endomembrane System—> Mitochondrion—>Chloroplast
how did the eukaryotic cell develop?
nucleus, endoplasmic reitculum, and golgi apparatus
the __________ is believed to have EVOLVED by the invagination of the plasma membrane. The invagination process also explains origins of ________ and _________.
mitochondria and chloroplasts
energy organelles like _________ and ____ may have originated when larger cells engulfed smaller prokaryotic cells
endosymbiotic theory
is the name of the hypotheses that eukaryotic cells would have benefited from the ability to utilize oxygen or synthesize organic food
endomembrane system
- Organelles that communicated with one another
Via membrane channels
Via small vesicles
how did the endomembrane system communicate?
energy-related organelles
Mitochondria and chloroplasts
Independent and self-sufficient
endomembrane system and energy related organelles
two classes of organelles
nucleus
Command center of cell,
nuclear envelope
Consists of a DOUBLE-LAYER membrane
nuclear pores
permits exchange between nucleoplasm and cytoplasm
chromatin
contains nucleic acids and proteins
dark nucleolus
composed of rRNA
ribosomes
Composed of rRNA
Consist of a large subunit and a small subunit
nuecleolus
subunits are made in the ____
endoplasmic reticulum and cytoplasm
ribosomes may be located in the _____ and ____
polyribosomes
ribosomes can be located in the cytoplasm in singly or groups called ____
ribosomes
Site of protein synthesis in the cell
In the process of transcription and translation:
endomembrane system
Series of intercellular membranes that compartmentalize the cell.
endoplasmic reticulum, nuclear envelope, golgi apparatus, and vesicles
parts of the endomembrane system
endoplasmic reticulum
A system of membrane channels and saccules ( flattened vesicles) continuous with the outer membrane of the nuclear envelope
saccules
flattened vesicles
rough er
Studded with ribosomes on cytoplasmic side
Has the capacity to produce proteins
Modifies and processes proteins
Adds sugar to protein
Results in glyco proteins
I. important in cell functions
smooth er
No ribosomes
Synthesis of lipids
In tests, testosterone is produced by smooth ER
Site of various synthetic processes, detoxification, and storage
The liver, with abundant smooth ER, detoxifies drugs
golgi apparatus
Consists of flattened, curved saccules
.
Modifies proteins and lipids with “signal” sequences
Receives vesicles from ER on cis (or inner) face
After modification, prepare for “shipment” and packages proteins and lipids in vesicles that leave Golgi from the trans (or outer) face.
exocytosis
exported from the cell
vesicles
production of specific molecules takes place in or on organelles by enzymes in membranes
vesicles
Products are transported around the cell by _____
sacs made of membranes
vesicles are ________________
cytoskeletal network
vesicles move around using the _____
lysosomes
membrane-bound vesicles (not found in plants)
produced by the golgi apparatus
contain powerful hydrolytic digestive enzymes and are highly acidic
digests large molecules into simpler subunits
recycle cellular resources
in white blood cells, they engulf pathogens
microbodies
contain specialized enzymes to perform special metabolic functions
vacuoles
membranous sacs that are larger than vesicles
store materials that occur in excess
others are very specialized
central vacuole
accounts for 90% of the volume in some cells in plants
vacuole
storage of water, nutrients, pigments, and waste products
vacuole
development of turgor pressure
toxic substances used for protection from herbivores
some functions performed by lysosomes in other eukaryote
chloroplast
bounded by double membrane
serve as sites of photosynthesis
thylakoids
disc like things in the chlorplast
grana
stacked thylakoids
stroma
chloroplast suspended in semi fluid
mitochondria
smaller than chloroplast
numbers vary with metabolic activities and energy requirements of cells
matrix
inner membrane surrounds ____ in mitochondria
matrix
inner semifluid substance containing respiratory enzymes
cristae
matrix convoluted (folded) to form ____
cytoskeleton
maintains cell shape (similar to the bones and muscles of an animal)
assists in movement of cell and organelles
makes internal transport possible
actin filament
intercellular traffic control, muscle contraction, animal cell division

intermediate filament
support nuclear envelope, cell-cell junctions
microtubules
distributes chromosomes during cell division

centrioles
short, hollow cylinders
one pair per animal cell
located in centrosome only
27 microtubules, nine overlapping triplets
centrioles are composed of ____ microtubules arranged into ____ overlapping ____
Cilia and Flagella
hairlike projections from the cell surface that aid in eukaryotic cell movement
flagella
outer covering of plasma membrane
inside this is a cylinder of 18 microtubules arranged in 9 pairs
in the center are two single microtubules
false; cilia are much SHORTER than flagella
T OR F: in eukaryotes, cilia are much longer than flagella
cilia
move in coordinated waves like oars
flgaella
move like a propeller or corkscrew
plasma membrane
separates internal cytoplasm from the external environment of the cell
allows sometimes incompatible chemical reactions to occurs simultaneously
phospholipid bilayer
external surface lined with hydrophilic polar heads
cytoplasmic surface lined with hydrophilic polar heads.
non polar hydrophobic, fatty acids tails sandwiched in between
periphreal protein
are found on the inner membrane surface (protein)
integral protein
are partial or wholly embedded (trans membranes) in the membrane (protein)
carbohydrate chains
contribute to cell’s fingerprint
important in tissue transplantation and blood transfusions
glycorpoteins
proteins with attached carbohydrate chains
glycolipids
lipids with attached carbohydrate chains
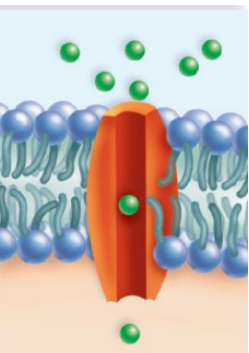
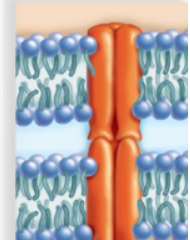
channel protein
KIND OF PROTEIN: allows a particular molecule or ion to cross the plasma membrane freely.
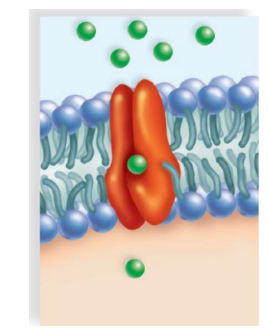
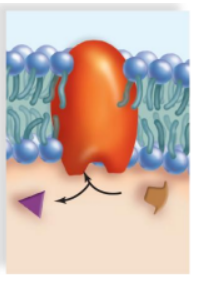
carrier protein
KIND OF PROTEIN: selectively interacts with a specific molecule or ion so that i can cross the plasma membrane. Glucose transporters move glucose in and out of the various celll types in the body.
the inability of some persons to use energy for sodium potassium transport has been suggested as the cause of their obesity
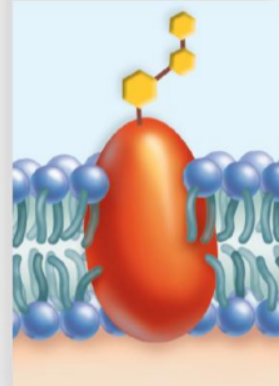
cell recognition protein / glycoprotein
KIND OF PROTEIN:the MHC (major histocompatibility. complex) glycoproteins are different for each person, so organ transplants are difficult to achieve. Cells with foreign MHC glycoproteins are attacked by white blood cells responsible for immunity.
receptor protein
KIND OF PROTEIN:Is shaped in such a way that a specific molecule can bind to it. Some forms of dwarfism result not because the body does not produce enough growth hormone, but because their plasma membrane growth hormone receptors are faulty and cannot interact with growth hormone
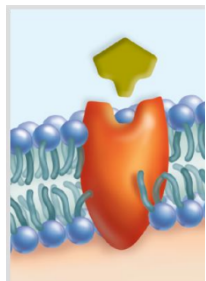
enzymatic protein
KIND OF PROTEIN:Catalyzes a specific reaction. The membrane protein adenylate cyclase, is involved in ATP metabolism. Cholera bacteria release a toxin that interferes with the proper functioning of adenylate cyclase; sodium (Na+) and water leave intestinal cells and the individual may die from severe diarrhea
junction proteins
KIND OF PROTEIN:Tight junctions join cells so that a tissue can fulfill a function, as when a tissue pinches off the neural tube during development. Without this cooperation between cells, an animal embryo would have no nervous system
true
T OR F: plasma membrane is selectively permeable
concentration gradient
Move from an area where they are in high concentration to an area of low concentration
aquaporins
speed up water transport across membrane
carrier proteins
The movement of ions and polar molecules across the membrane is often assisted by which kind of proteins
Exocytosis
fusion of a vesicle with the plasma membrane moves a particle outside the membrane
Active transport
Some molecules must move against their concentration gradient with the expenditure of energy
Endocytosis
vesicle formation moves particle to inside the plasma membrane
diffusion
is the net movement of molecules down a concentration gradient. Molecules move both ways along the gradient, but net movement is from high to low concentration.
Temperature, pressure, electrical currents, and molecular size
what are the 4 things that affect the rate of diffusion.
osmosis
Special case of diffusion
Focuses on solvent movement rather than solute
Diffusion of water across a SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE MEMBRANE
osmotic pressure
is the pressure that develops due to osmosis.
Isotonic Solutions
Solute and water concentrations are equal on both sides of cellular membrane
There is no net gain or loss of water by the cell
hypotonic
Concentration of solute in the solution is lower than inside the cell.
Cells placed in hypotonic solution will swell
Cause turgor pressure in plants
May cause animal cells to lyse (rupture)
hypertonic solution
Concentration of solute is higher in the solution than inside the cell
Cells placed in a hypertonic solution will shrink
Crenation in animal cells
Example: red blood cells placed in a hypertonic solution
Plasmolysis in plant cells
bulk trasnport
Macromolecules are transported in or out of the cell inside vesicles
Endocytosis
cells engulf substances into a pouch which becomes a vesicle
Exocytosis
vesicles fuse with plasma membrane and SECRETE contents
phagocytois
large, solid material is taken in by endocytosis
example : human white blood cells can engulf debris or viruses
pinocytosis
vesicles from around a liquid or very small particles (cell drinking)
Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis
specific form of pinocytosis using receptor proteins and a coated pit.