Tietze Chapter 5 Diagnostics (Respi, Biomarkers)
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
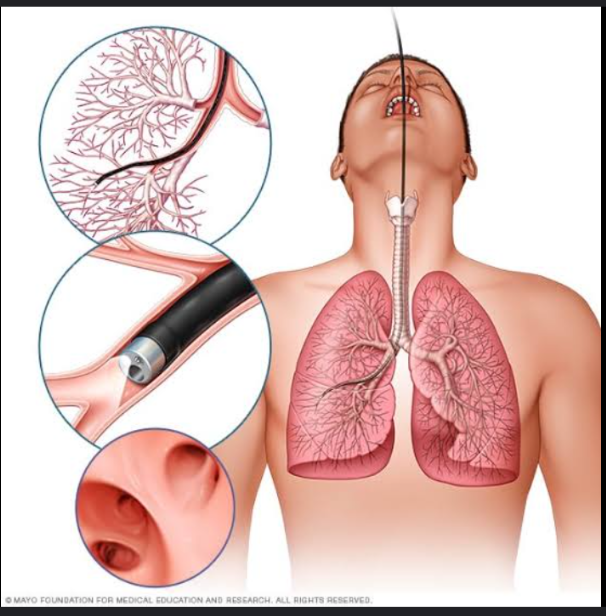
Bronchoscopy
It is used to visualize the tracheobronchial tree. A flexible bronchoscope is introduced into the tracheobronchial tree through the nose, mouth, or endotracheal or tracheotomy tube. Samples of fluid and tissue may be obtained for Gram staining, culture, and cytologic examination
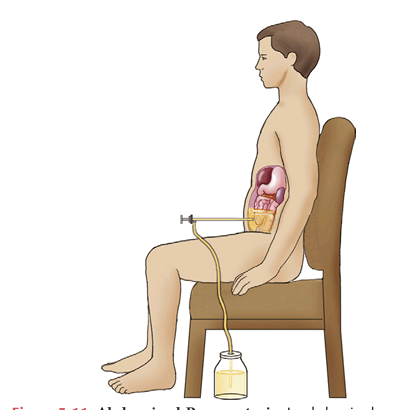
Thoracentesis
IT is the procedure that is used to obtain a sample of pleural fluid for analysis. The fluid is assessed for each of the following characteristics
Blood
Yellow
Green
Black
PLEURAL FLUID ANALYSIS
— is associated with trauma, malignancy, and pulmonary infarction.
A straw — color is associated with a transudate.
A — color is associated with biliopleural fistula.
A — color is associated with Aspergillus niger infection.
Pus
Turbid
Viscous
PLEURAL FLUID ANALYSIS
— is associated with an empyema.
A — fluid is associated with inflammatory exudates or lipids.
A — fluid is associated with mesothelioma.
Ammonia-like
Putrid
PLEURAL FLUID ANALYSIS
An — odor is associated with urinothorax.
A — odor is associated with infection with anaerobic organisms.
Spirometer
Pulmonary function testing is performed using spirometry or body plethysmography.
It detects and records changes in lung volume and flow
Body plethysmography
Pulmonary function testing is performed using spirometry or body plethysmography.
It detects changes in intrathoracic pressure and volume.
Carbon monoxide diffusing capacity
The test is a noninvasive test of lung function. DLCO is an index of the surface area available for gas exchange and is decreased in emphysema, alveolar inflammation, and pulmonary fibrosis.
Forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1)
It is the volume of air (in liters) exhaled in the first second during forced exhalation after maximal inspiration. Normally, at least 80% of the forced vital capacity (FVC) is exhaled in the first second.
It is used with the FVC to differentiate between obstructive lung disease and restrictive lung disease
Forced Vital Capacity FVC
It is the total volume of air (in liters) blown out of the lungs during forced exhalation after maximal inspiration.
peak expiratory flow rate (PEF, PEFR
IT measures the forced expiratory flow in liters per minute. It is used to monitor disease progression and response to therapy in patients with bronchospastic diseases such as asthma.
30%
PEF variability of greater than — indicates moderate to severe persistent asthma
residual volume (RV)
The — is the volume of air remaining in the lungs after forced expiration. It is measured with body plethysmography.
They are increased in diseases characterized by small airway obstruction (e.g., asthma).
Tidal volume (TV)
— is the volume of air inspired or expired in normal breathing.
Pulse oximetry
is a noninvasive transcutaneous technique used to assess oxygen saturation.
Quantitative pilocarpine iontophoresis (Sweat test)
It measures the concentration of sodium in sweat after stimulation of the sweat glands with topical pilocarpine; low-voltage current is applied to aid in the absorption of the pilocarpine.
It is used in the diagnosis of cystic fibrosis.
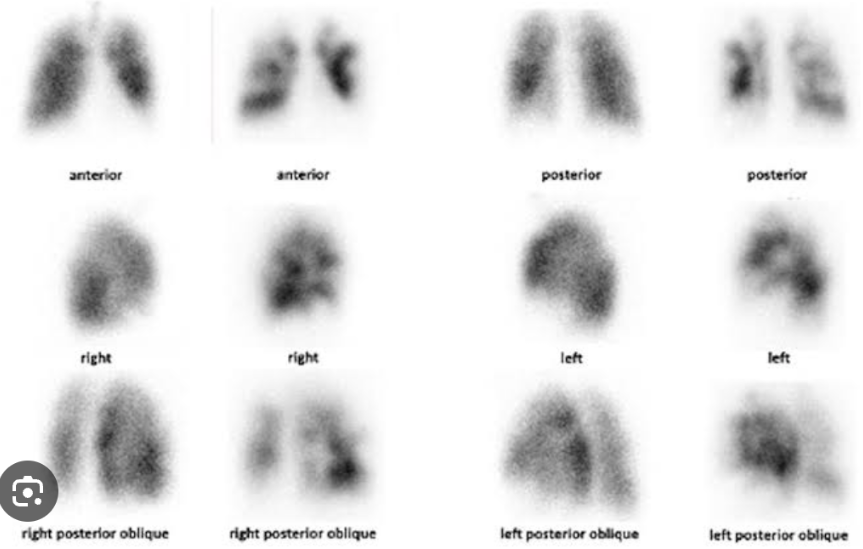
Ventilation/Perfusion Scanning
It is used to compare ventilation and perfusion. Images of the airways taken after the inhalation of radiolabeled tracers are compared with images of the pulmonary vasculature taken after the injection of contrast agents.
Normally, ventilated and perfused areas match. This test is commonly used to identify pulmonary emboli.
BIomarker
a characteristic that is measured and evaluated as an indicator of normal biologic processes, pathogenic processes, or pharmacologic response to a therapeutic intervention.”
In the broadest sense, it is any clinical biologic measure
Proximal biomarker
biomarker that occurs early in the pathophysiologic cascade
Distal biomarker
biomarker that occurs late in the pathophysiologic cascade
Preventive biomarker
biomarker that prospectively identifies risk of disease
Diagnostic biomarker
biomarker that identifies the disease before any clinical signs or symptoms appear
Prognostic biomarker
biomarker that stratifies the risk of disease progression
Predictive biomarker
biomarker that prospectively identifies patient response to therapy
Surrogate end point biomarker
biomarker that substitutes for a clinical end point
CK MB
Troponins
Well-established cardiac biomarkers for detecting an acute myocardial infarction (AMI) include
Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP), Brain natriuretic peptide (BNP)
—, secreted by the heart, regulate blood pressure and body fluid balance by antagonizing the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and the sympathetic nervous system.
C-reactive protein CRP
—, a protein synthesized by the liver in response to cytokine stimulation, reflects ongoing inflammation and is predictive of increased risk of AMI.
QT interval prolongation
often precedes potentially fatal ventricular arrhythmias but has low sensitivity and specificity for torsades des pointes (TDP
CEA
Alpha fetoprotein
PSA
CA125
CA19-9
CANCER BIOMARKERS
Colorectal cancer
Primary liver carcinoma
Prostate cancer
Ovarian carcinoma
Pancreatic/gastric carcinoma
BRCA1
BRCA2
These gene mutations are used as screening markers to identify patients at increased risk for developing breast and ovarian cancer.
Serum BUN
Creatinine
What are the well established kidney biomarkers
Cystatin C
is a cysteine protease inhibitor that is freely filtered by the glomeruli, resorbed in the proximal tubule, and not affected by muscle mass, age, or race.
Serum levels may predict glomerular function better than serum creatinine concentration.
Kidney injury molecule 1 (Kim1)
IT is a renal tubular protein and is a very early indicator of kidney damage.
Neutrophils gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL)
It is one of the proteins found earliest in the blood and urine after acute kidney injury.
IL-18
It is a specific early marker of acute tubular necrosis.
CSF levels of Tau protein
These may be useful for identifying patients with mild cognitive impairment that may progress to Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
Endotoxin
TNF
IL-6
Procalcitonin (PCT)
CRP
Although more than 100 biomarkers have been identified as potentially useful indicators of sepsis, none is currently sensitive or specific enough to be clinically applicable.17 Biomarkers of interest include: