Theory of Computation
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
computer systems, abstraction, decomposition, pattern recognition, algorithms, information hiding
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
define computation
processing something through mathematical/ logical/ interactive methods
define computability
measures what can/ can’t be processed
(non-computable programs = programs that can NEVER be processed)
define logical reasoning
using a set of facts to determine if new facts are true/ false
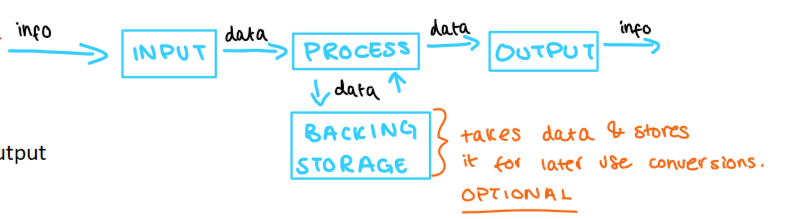
what are the basic components of a computer system?
convert human input to binary
computer processes binary data
binary data converted to ascii output
what are the 4 components that make up computational thinking
abstraction
decomposition
pattern recognition
algorithm
define abstraction
taking most important components needed to solve problem & separating them from rest
define decomposition
breaking down problem into smaller (easier to solve) sub programs
define pattern recognition
finding similar approaches to solve problem and adapt them to solve current one
define algorithm
representing solution as a sequence of steps (step by step instructions needed to solve problem)
how do computers work? basic
an algorithm is run on a computer by translating it into a sequence of computer instructions
this is converted to binary (uses switches for 1s and 0s) where computer reacts to voltages on wires
what does it mean to automate a program?
automation: idea that computer programmer turns algorithm into computer program for computer to execute
e.g. paint onto car
three types of abstraction
representational abstraction
abstraction by generalisation
problem abstraction
what is abstraction by generalisation
reducing problem by putting similar aspects of the problem into hierarchical categories
explain problem abstraction and give an example
removing unnecessary details until underlying problem is identified to see if it has already been solved
e.g. pigeon hole principle
what is representation abstraction
removing details from problem until it becomes possible to represent problem in a way that it is possible to solve
what is the purpose of user interface?
hides complexity of program
easily operate computer
users are satisfied
makes program more popular
define information hiding and describe its uses in programming
hides details of object which do not contribute to essential characteristics
In programming:
Well designed program has a solution in which source code is divided into self-contained modules. Programmer works on module so do not need to know all detail contained in other programmer modules. This makes it easier as they are local rather than global changes.
Function age(DofB as date, today as date) as integer
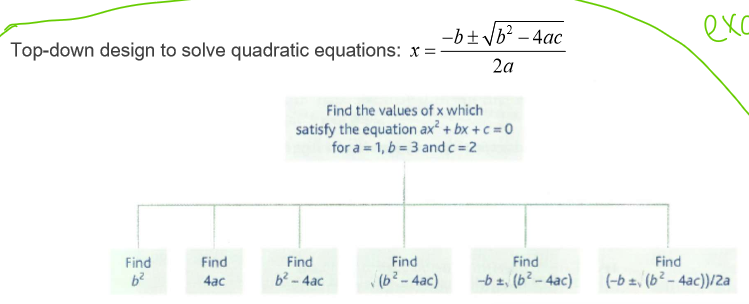
describe decomposition with an example
top-down design: modular approach where main system is at top and then broken down into smaller & smaller units
procedural decomposition: problem is divided into smaller parts and then solved independently. they are then written and tested separately before being integrated into the larger problem
benefits of using decomposition:
starting point in the aim of a project
helps users and the system analysts reach an early agreement about what the major functions should be
works through ‘logical’ design
not restricted by ‘physical’ attributes of programming language
result is more portable designs
why is procedural decomposition helpful?
makes programs more modular
easier to:
understand
debug
maintain
outline modular design:
number of small modules are written
each module has a clear objective/ specific function
each module may be a complete system in itself/ an executable file or subroutine
they are independently designed, programmed and maintained
modules are then put together in a larger structure
each module will have a single entry-entry and exit point
+ can be easier to program
- may result in an inefficient system
- project can veer towards a bottom-up design

clear advantages for using modular design
separate programmers can be working on modules individually
programmer is only concerned for their part of the system so programming is easier
flow of data can be traced far more easily through program
debugging is made easier as errors can be traced back to a single module
define computational complexity
how economic the algorithm is with time and space
why is computational complexity used?
allows us to compare algorithms as there may be multiple algorithms for achieving a solution to a problem and they may vary considerably in their speed and use of memory
time complexity
algorithm indicates how fast it runs
space complexity
algorithm indicates how much memory algorithm needs (memory footprint)
worst case complexity
algorithm takes longest time or greatest workload
best case complexity
algorithm takes shortest time or smallest workload
how is average case complexity calculated
calculating arithmetic mean for all possible inputs
describe the 2 ways of measuring complexity of algorithm and evaluate
algorithm written in programming language an then run on computer and timed
CRUDE way because it is dependent on:
speed of computer
efficiency of programming language
length of list
measure speed of algorithm
better because it’s based on number of operations it requires to be carried out
how come the length of list (data) and algorithm is important factor of time complexity?
if we have a bubble sort for 5 numbers, it's efficient. If we have a bubble sort for 1 million numbers, it's not efficient.
therefore, the length of the list is an important factor.
how to calculate execution time in algorithms: BASIC RULES
number of times loops repeat relates to size of input, denoted by n
when statements are simply evaluated sequentially by computer, it takes constant amount of time to execute, denoted by k
easy to count few instructions but when it becomes more complex we calculate time complexity using operation of algorithm
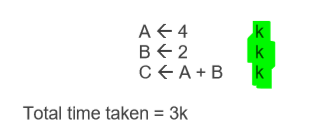
how to calculate execution time in algorithms: FOR LOOPS
For loop condition is executed n+1 times since it requires one extra check to see whether terminating condition has been satisfied
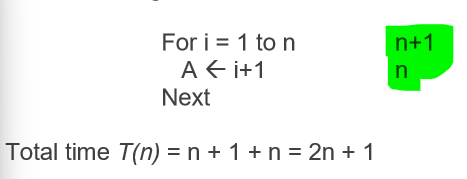
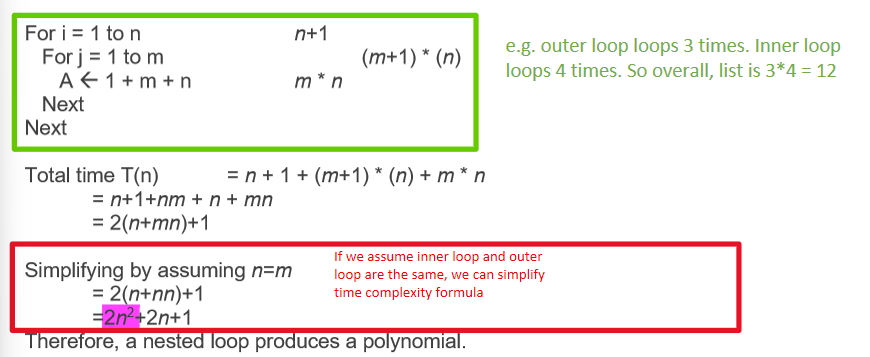
how to calculate execution time in algorithms: FOR LOOPS
execution times within inner FOR loop will be multiplied by those of outer loop. this produces a polynomial
Basic operation
operation contributing most total running time
asymptotic behaviour
idea that as amount of data changes, difference between two algorithms increases
in mathsy terms: behaviour of function f(n) for very large values of n
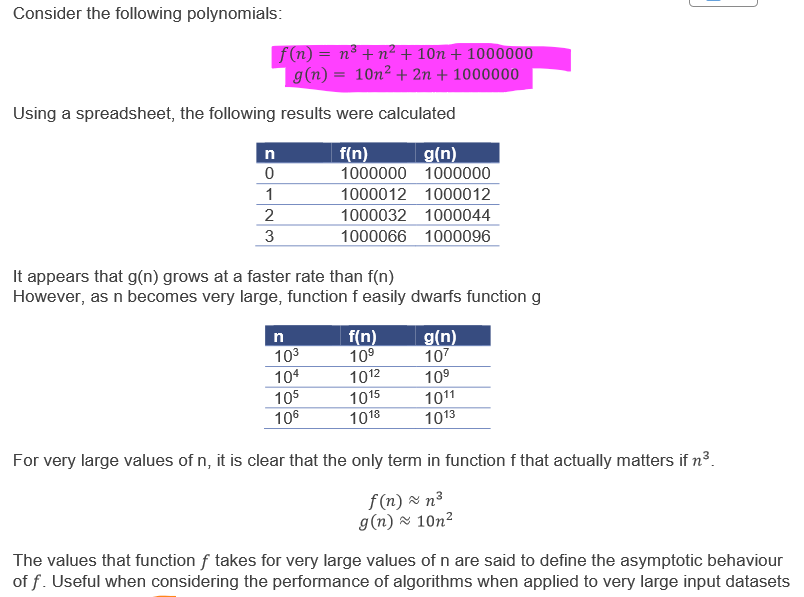
what is Big O notation
analysis of an time complexity considering worst-case scenario and provides notation for upper bound running of a function
state the functions & Big O notation for:
linear
polynomial
exponential
logarithmic
exponential:
function: y = 2x
Big O notation: O (an) e.g. O (3n)
polynomial:
function: y = 2x2
Big O notation: O (na) e.g. O (n3)
linear:
function: y = 2x
Big O notation: O (n)
logarithmic:
function: y = log10 x
Big O notation: O (log n)
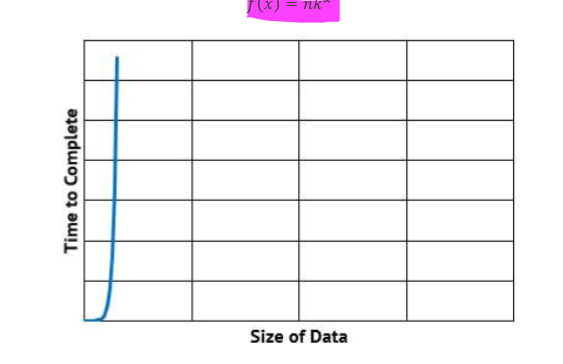
exponential time algorithms:
take very long time to compute
growth takes form Kx, where K is constant and x = 1,2,3….
e.g. recursive Fibonacci numbers & recursive factorial calculations
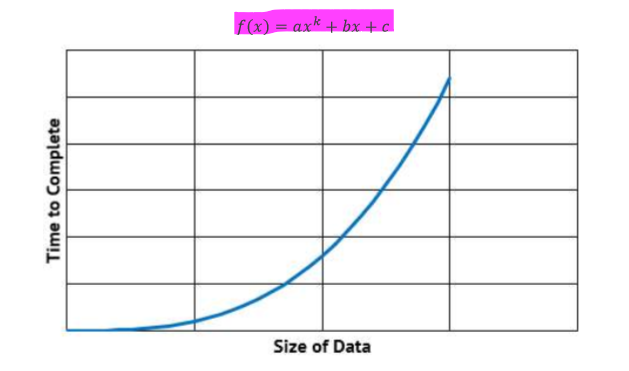
polynomial time algorithms
mostly use nested loops
growth has form xk where K is a constant and x = 1,2,3…
e.g. bubble and insertion sorts
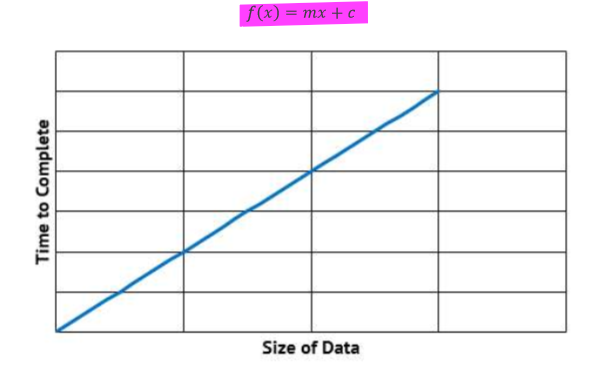
linear time algorithms
go through data step by step
growth has mx + c (← normal calculation for gradient of line we learnt in gcse math)
e.g. linear search
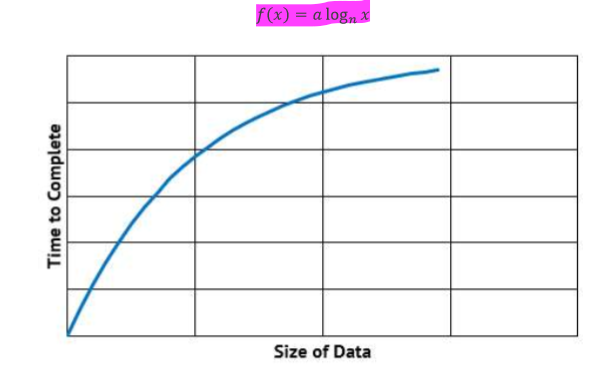
logarithmic time algorithms
EXECUTION time does NOT increase as fast as IPUT size
n is halved each cycle since log2 is used to see how many times we can multiply number by 2 until answer is reached
e.g. binary search & binary tree search
constant time algorithm
time complexity remains same regardless of number of inputs
e.g. finding first item in list
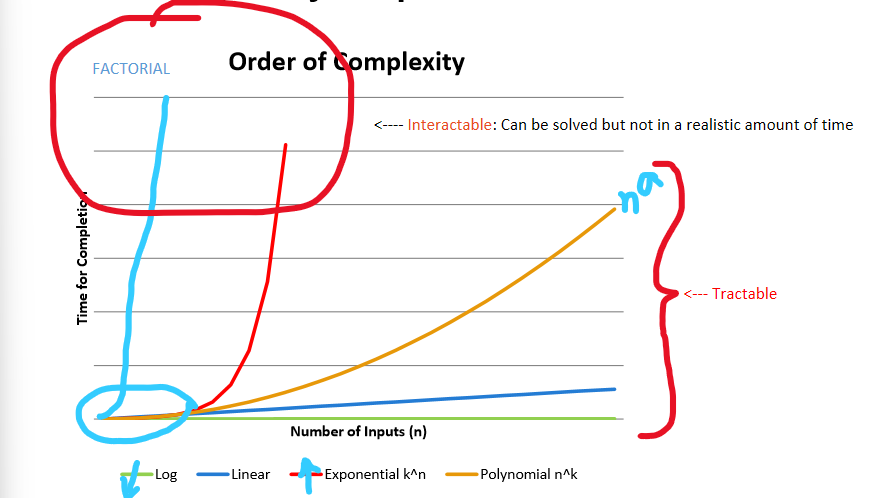
draw the order of complexity graph:
most time consuming/ worst case scenario
factorial
exponential
polynomial
linear
logarithmic
least time consuming/ best case scenario
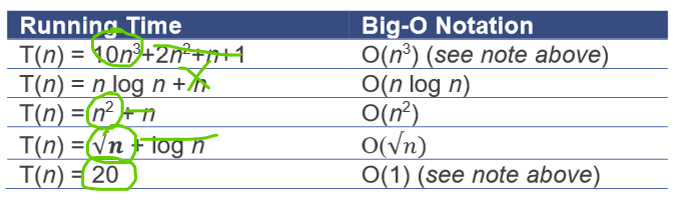
Big-O Rules:

how to express functions as Big-O
only look at section that changes most significantly, make rest redundant
take off term from function which would give largest number
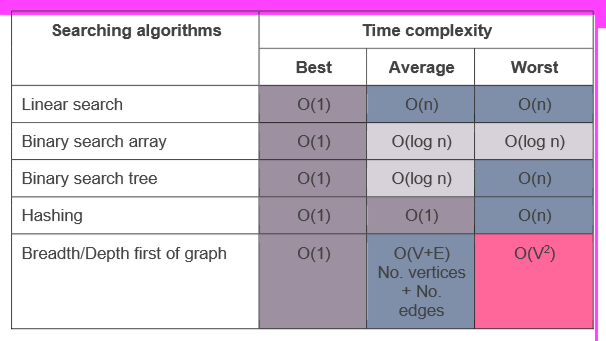
state the best/ave./wost case time complexity for searching algorithms
state the best/ave./wost case time complexity for sorting algorithms

define tractable problems + state an example
problem that can be solved in acceptable amount of time
e.g. searching ordered list
define intractable problems + state an example
problems that can be solved but not in an acceptable time frame
e.g. travelling salesman (has to travel between cities. distance between each pair of cities is known. he must visit each city once and return to start point. must calculate shortest route)
how are interactable problems tackled?
programmer produces heuristic algorithm
what are heuristic algorithms
method for producing a “rule of thumb“ to produce an acceptable solution to common sets of data and interactable programs within acceptable time frame
unlikely to produce optimal results but can produce results which are satisfactory in acceptable time frame
computable problems
problems that have effective procedure/ algorithm to solve them. contain finite set of instructions
non computable problems
never be able to be solved using a computer, irrespective of processing power
e.g. halting problem
