Maternal/Newborn Midterm
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
What is the order of fetal development?
1. Ovum is released from the ovary
2. The ovum passes into the fallopian tube
3. Sperm and ovum meet and exchange genetic material
4. The ovum and sperm travel toward the endometrium for implantation
When does the zygotic stage occur?
Fertalization - Day 14
What are key components of the Zygotic Stage?
- Sperm and Ovum share genetic material (fertilization)
- Reaches uterine cavity 72 hrs past fertilization
- Conception occurs
When does the blastocyst stage occur?
Fertilization to Day 14
Key components of blastocyst stage
- Cell division occurs (meiosis)
* splits into ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm
- Implants into the fundus
Ectoderm
Forms the central nervous system, special senses, skin and glands
Mesoderm
Forms the skeletal, urinary,circulatory and reproductive organs
Endoderm
Forms the respiratory system, liver, pancreas, and digestive system.
When does the embryonic stage occur?
Begins at day 15 after conception and continues through the end of week 8.
Key components of Embryonic Stage
- Basic structures of all major body organs are completed (organogenesis).
- Three main structures are formed: amniotic fluid/sac, placenta, and umbilical cord.
When does the Fetal stage occur?
9th week to birth
Key Components of Fetal Stage
- Differentiation and specialization of organ structures/major systems.
Amniotic Fluid
- 1 L is expected at birth
- Is clear
- Made up of fluid from the mothers blood and fetal urine
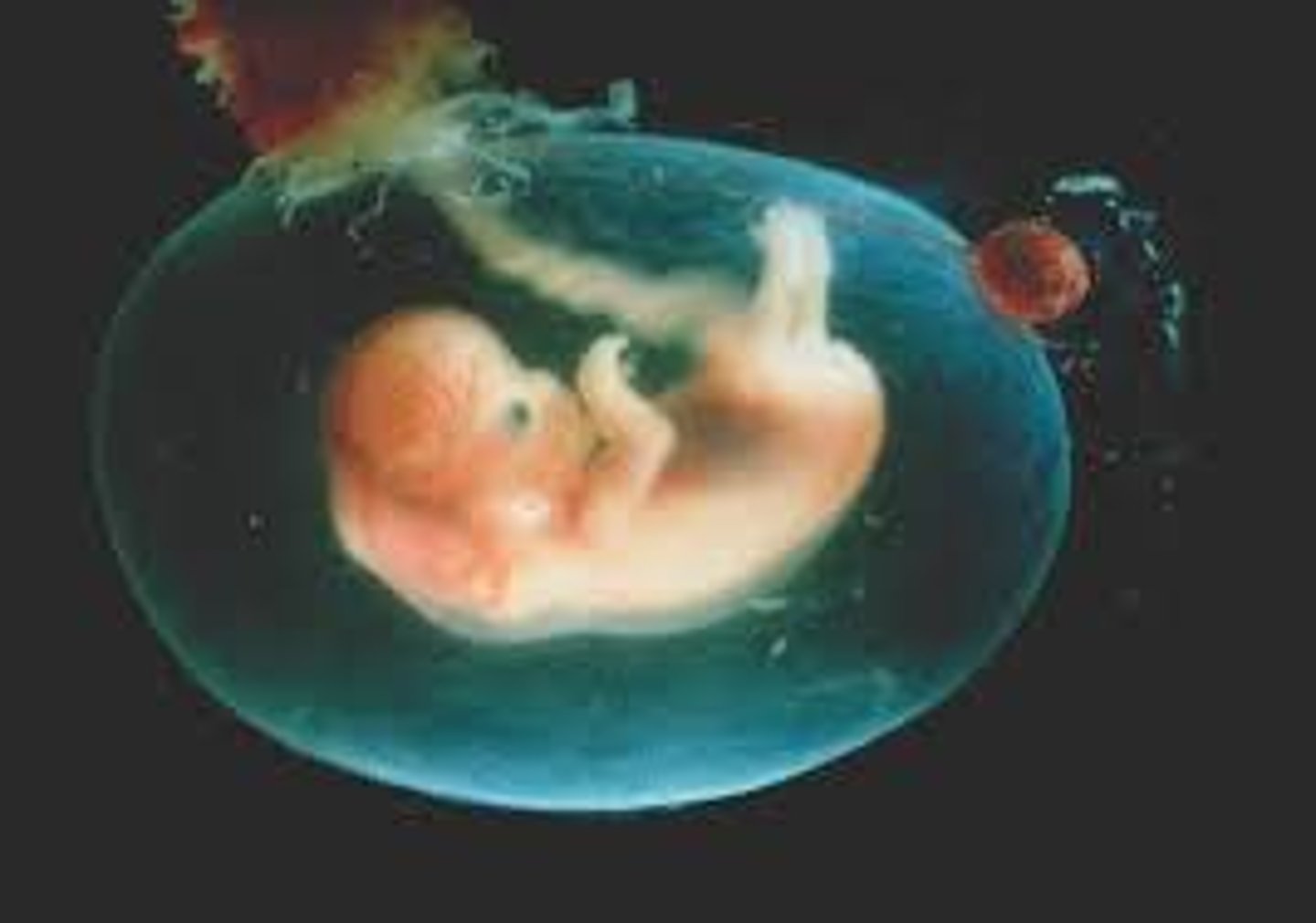
What is the term for too little fluid?
oligohydramnios
What is the term for too much fluid?
polyhydramnios
What portion of the developing embryo becomes the placenta?
Trophoblast
Where should the placenta be located within the uterus?
The Fundus
What are the functions of the placenta?
- Filtrate the blood from mom
- Provide nutrients to help the fetus grow
- Hormonal regulation
- Preparing the fetus for extrauterine environment
- Immune system protection
- Excrete waste from the fetus
- Transportation of oxygen
What portion of the developing embryo becomes the umbilical cord?
Amnion
How many veins and arteries does the umbilical cord have?
- 1 vein
- 2 arteries
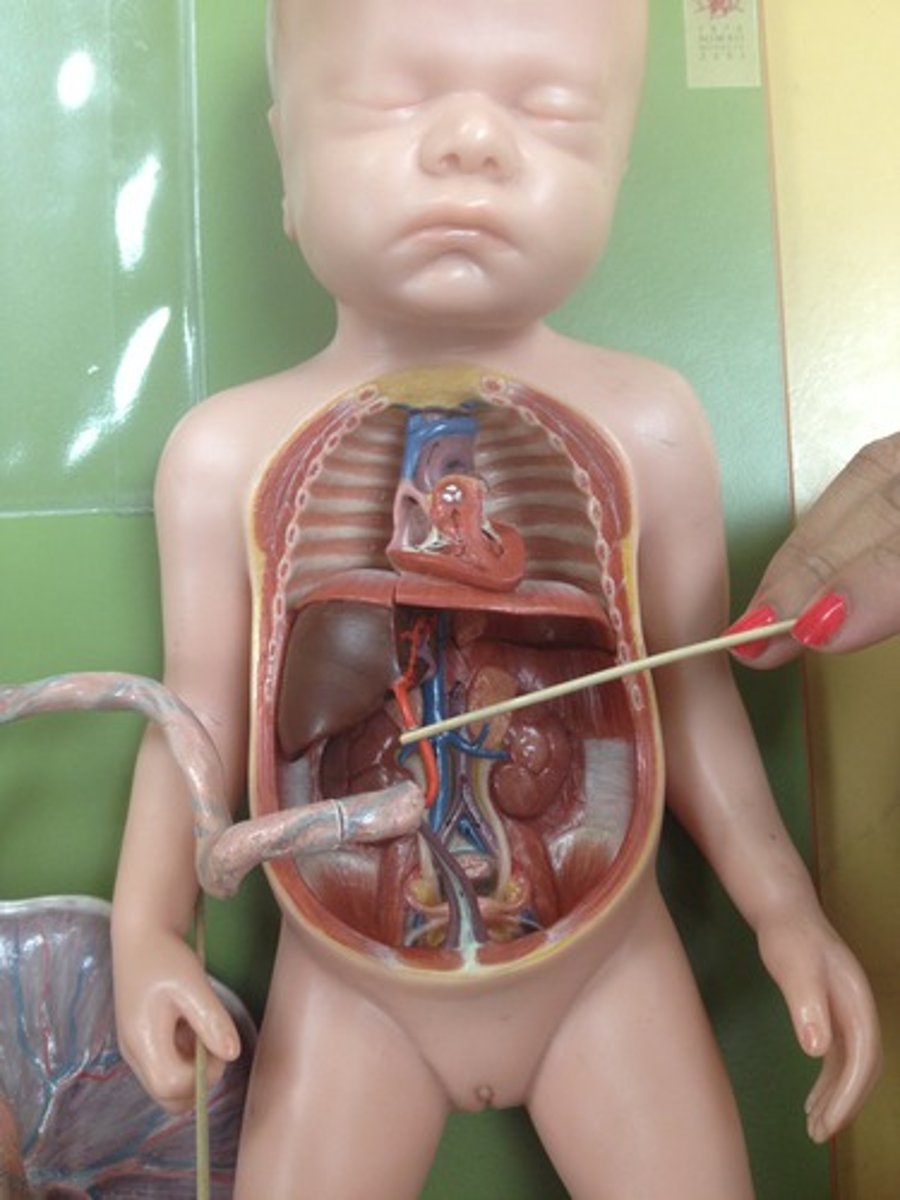
Fetal Circulation
- Veins carry oxygenated and nutrient rich blood from the placenta to the fetus.
- Arteries carry deoxygenated blood from the fetus to the placenta.
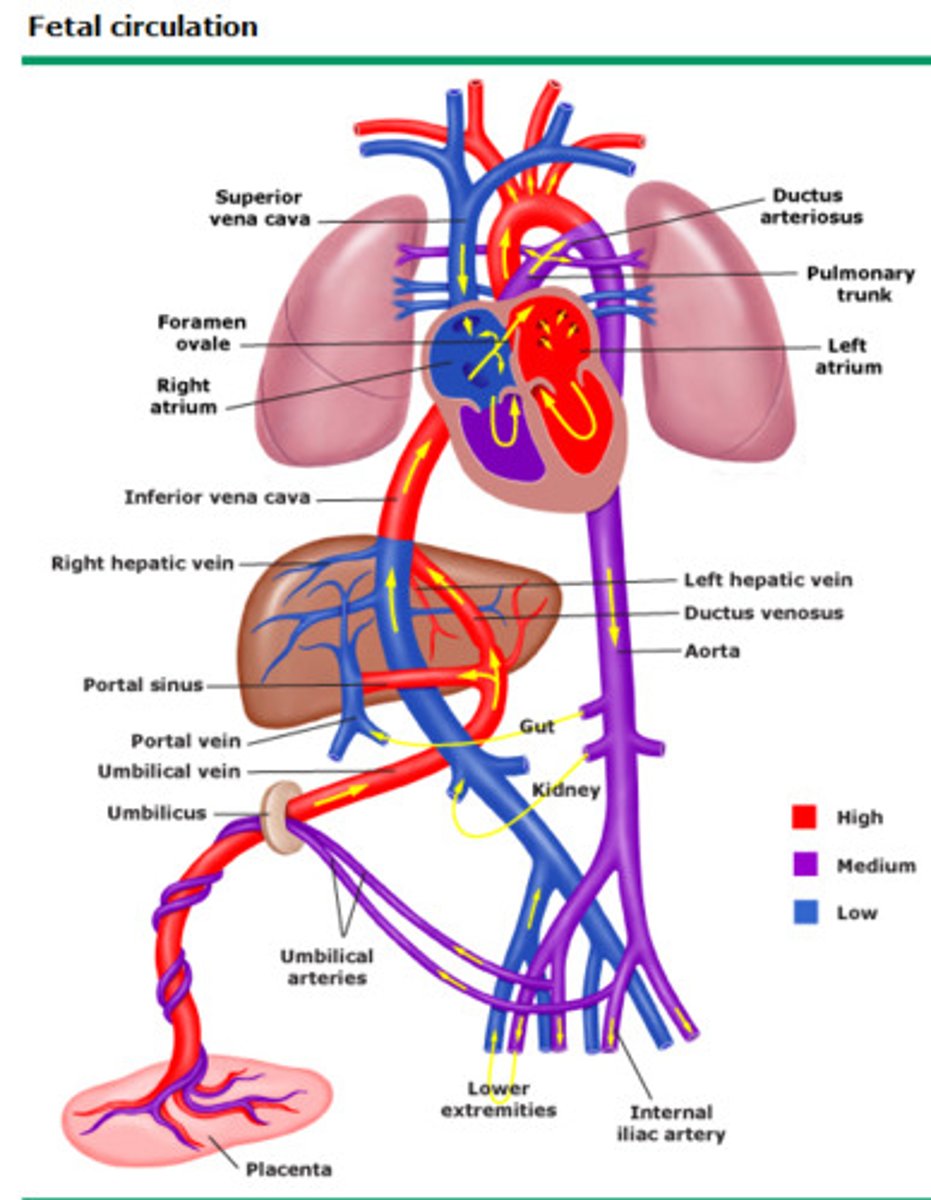
Foramen ovale
- Bypasses the right ventricle and is an opening between the right and left atrium
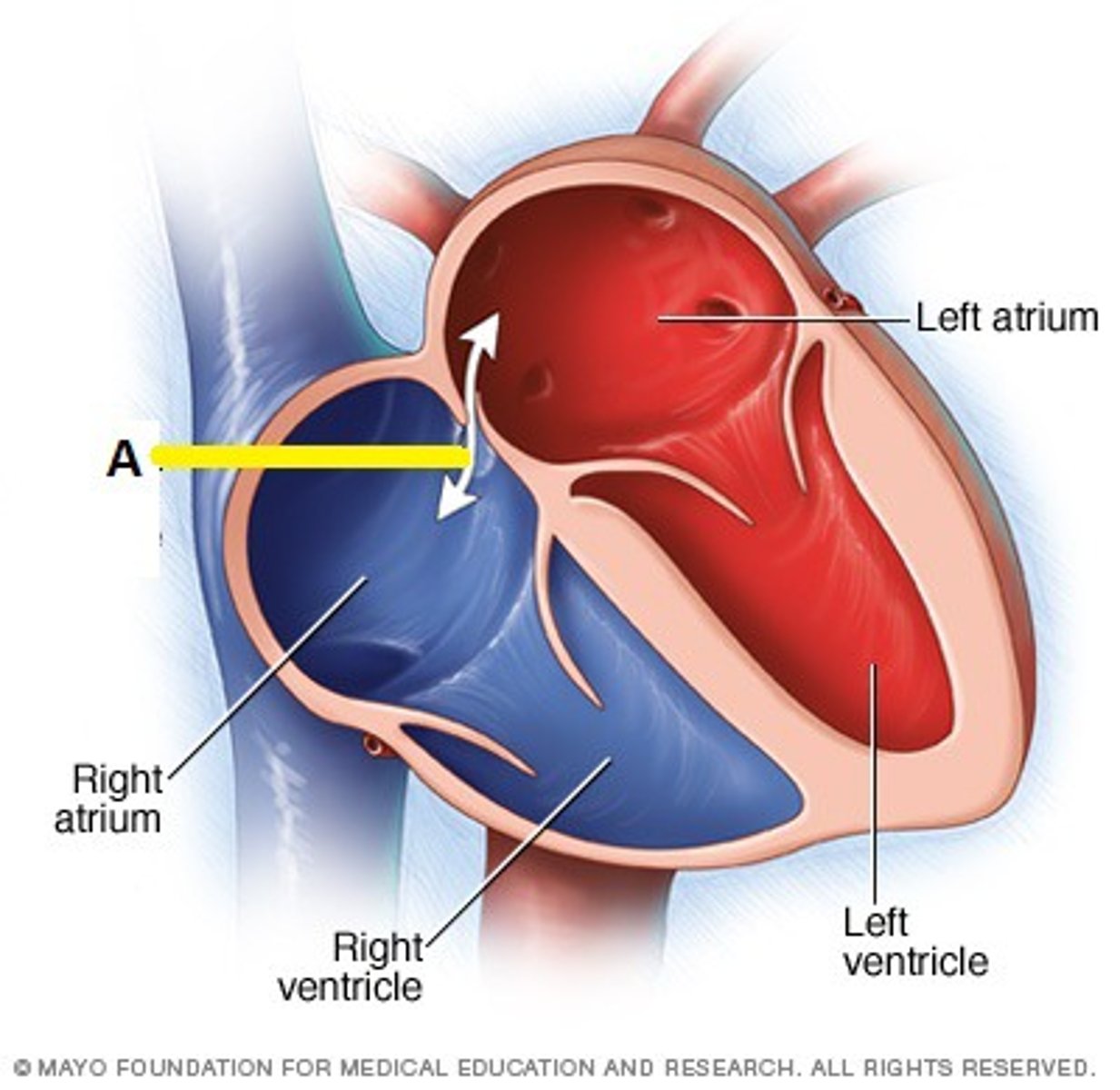
When the holes close they become...
Unuseable ligaments
Ductus Arteriosus
- Bypasses the lungs and connects the main pulmonary artery to the descending aorta.
Ductus Venosus
- Bypasses the liver and connects the umbilical vein to the inferior vena cava
Presumptive Signs of Pregnancy - definition
Signs that the mother can perceive
Presumptive Signs and Symptoms
- Absence of menstruation
- Consistent nausea
- Fatigue
- Breast tenderness
- Urinary frequency
Probable Signs of Pregnancy
- Signs that can be detected on physical examination by a healthcare provider
Probable Signs and Symptoms
- Softening of the lower uterine segment or isthmus (Hegar sign).
- Softening of the cervix (Goodell sign).
- Bluish-purple coloration of the vaginal mucosa and cervix (Chadwick sign).
- Changes in shape and size of the uterus.
- Abdominal enlargement
- Braxton Hicks contractions
- Ballottement -examiner pushes against the women's cervix during a pelvic examination and feels a rebound from the floating fetus.
- Pregnancy test
Positive Signs of Pregnancy
Usually within 2 weeks after missed menses,enough subjective symptoms are present so that a woman can be reasonable sure she is present
Positive Signs and Symptoms
- Visualizing the fetus by ultrasound
- Palpating for fetal movements
- Hearing a fetal heart beat
What are the anatomical landmarks used when measuring fundal height?
- Symbis Pubis
- Fundus
Where should the fundus be felt at 20 wks gestation?
Midline at the umbilicus
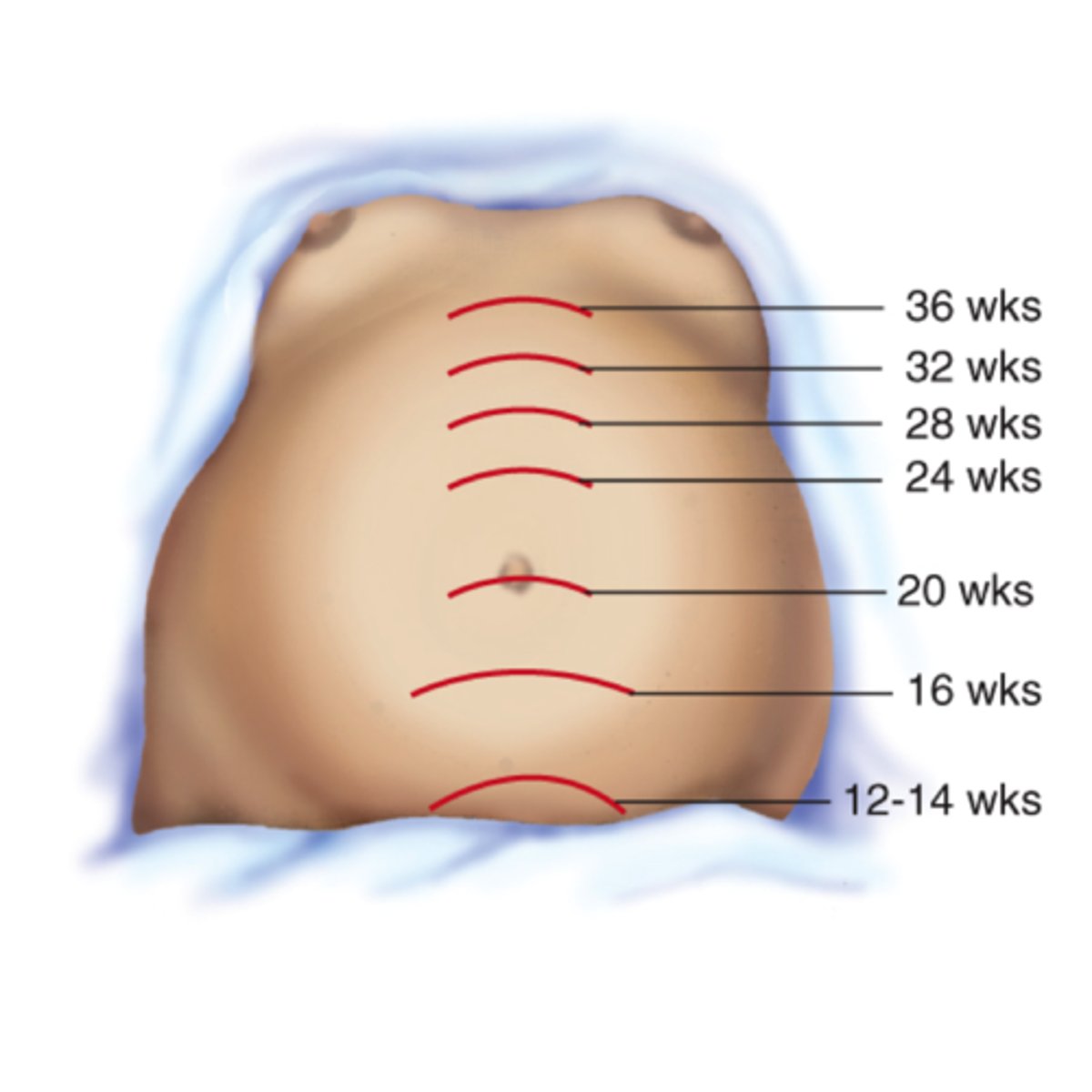
What are reasons why the fundal height may be above the expected reference range?
- Multiple gestation
- Polyhydramosis
- Fetal macrosomia
- Large for gestational age (LGA)
What are reasons why the fundal height may be below the expected reference range?
- Oligyhrdamosis
- Small for gestational age (SGA)
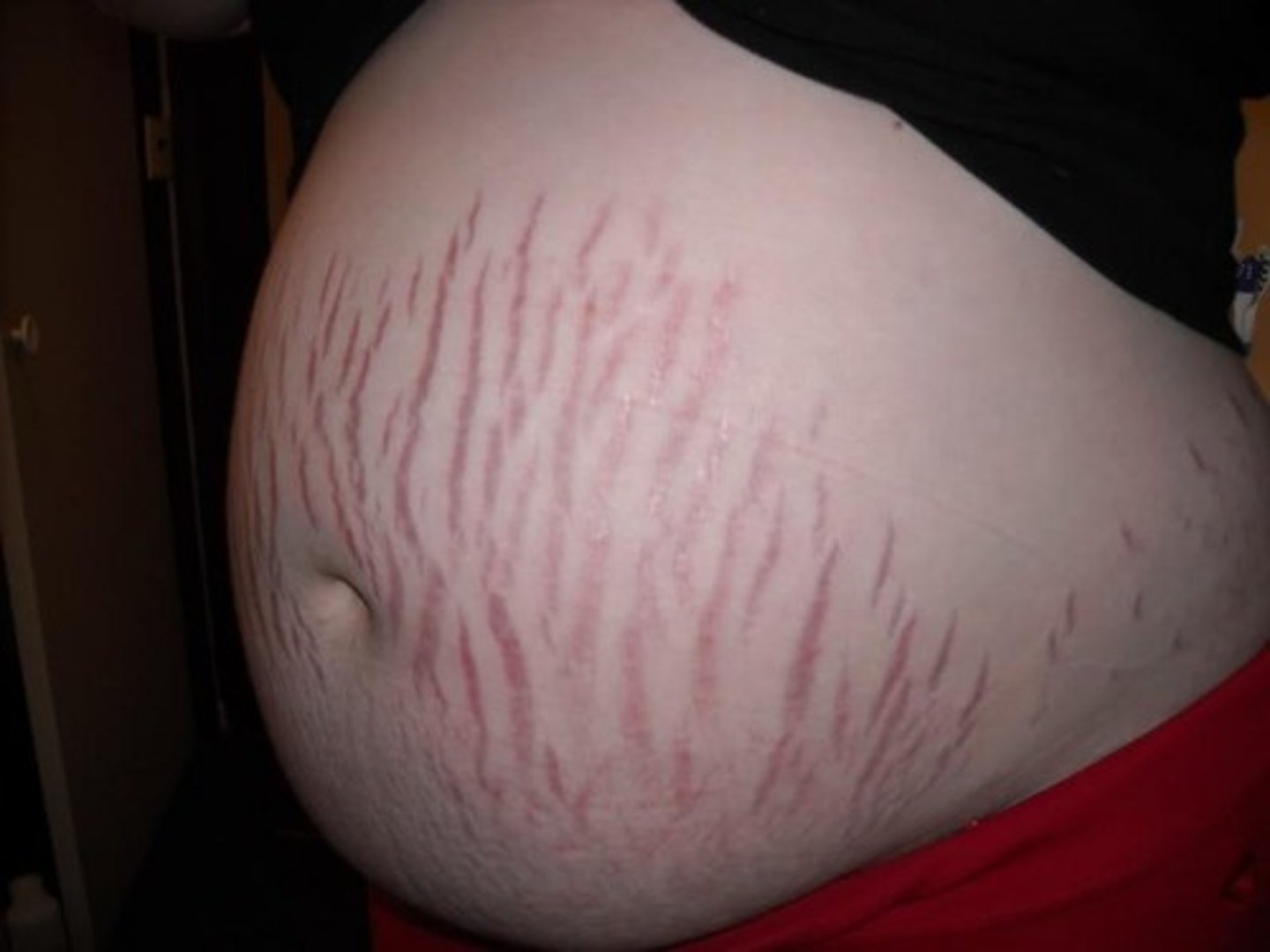
Striae Gravidarum
- AKA stretch marks
- DOES NOT go away, will fade.
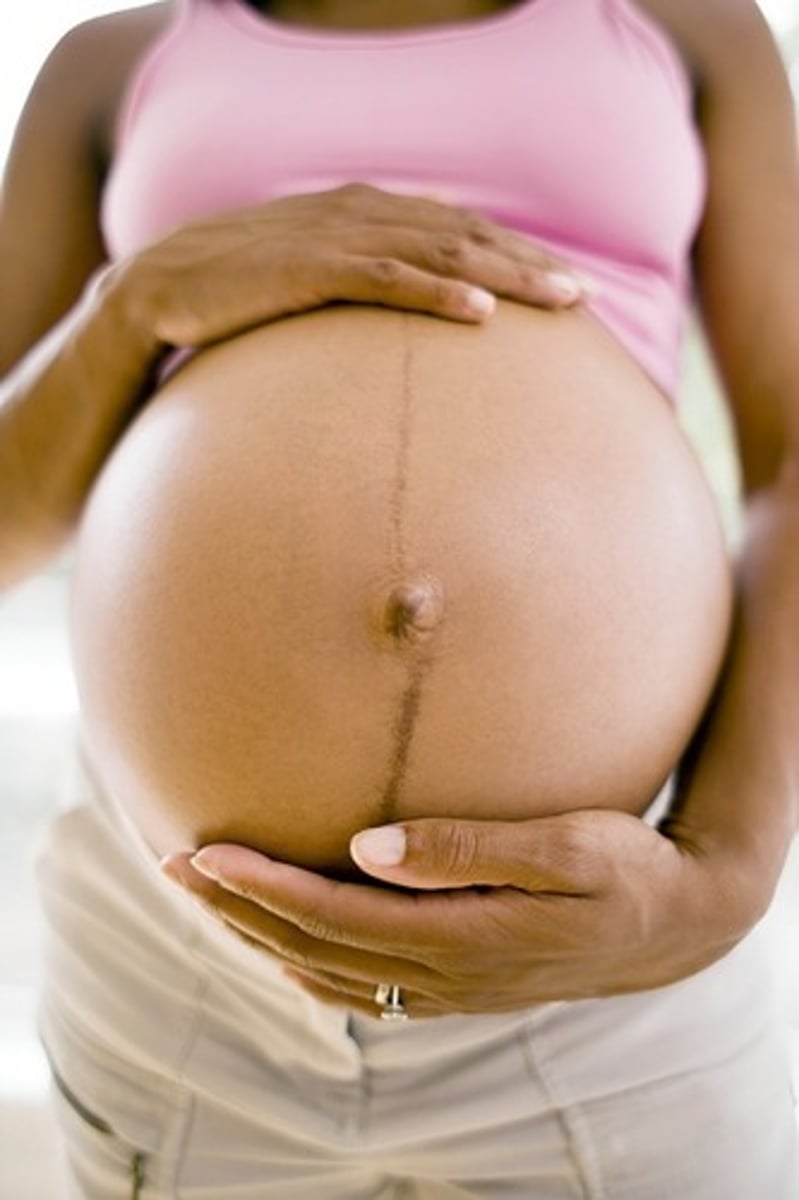
Linea Nigra
- Will go away

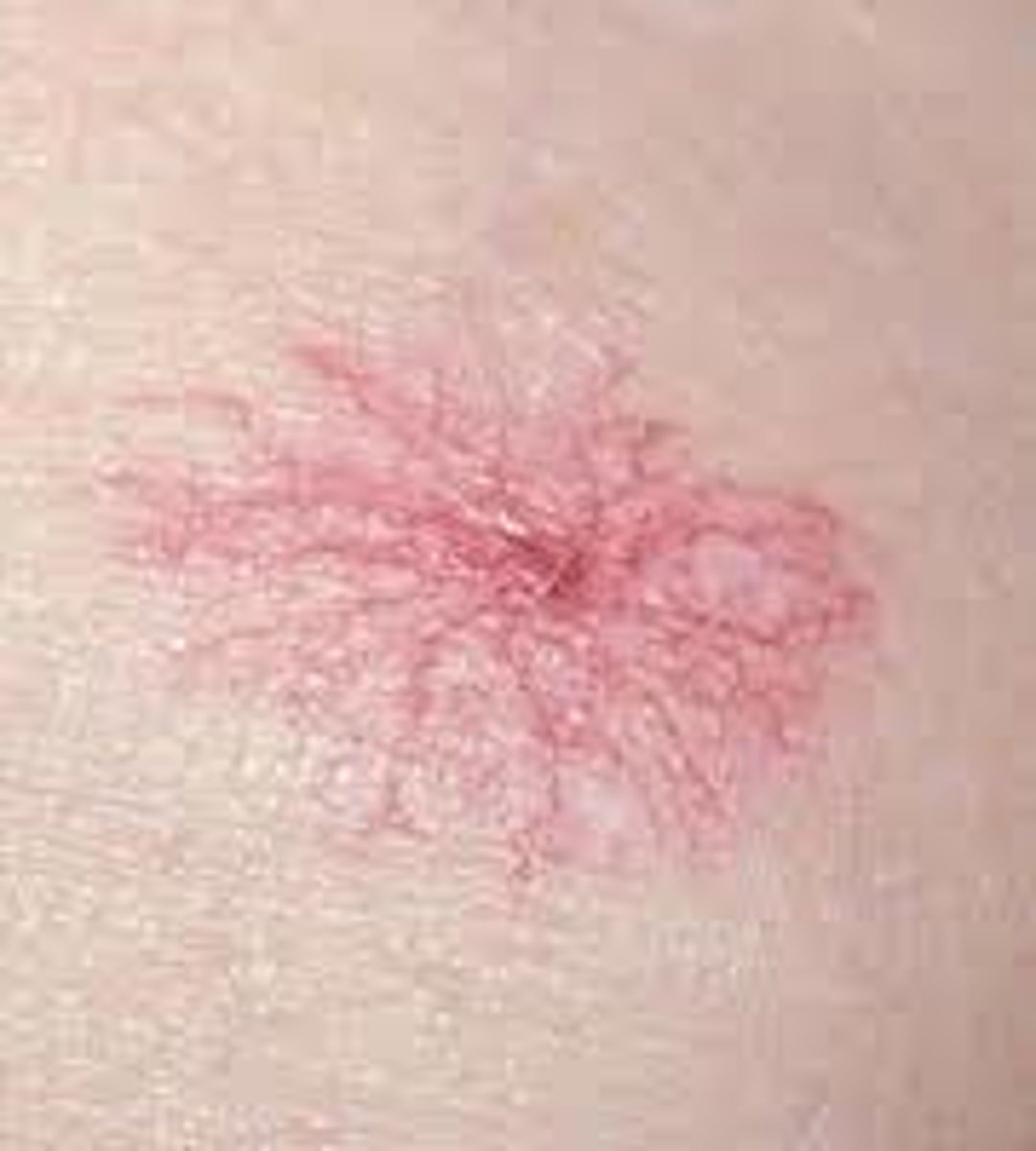
Vascular Spiders
- Common in pregnancy because of increased estrogen and may resolve after childbirth
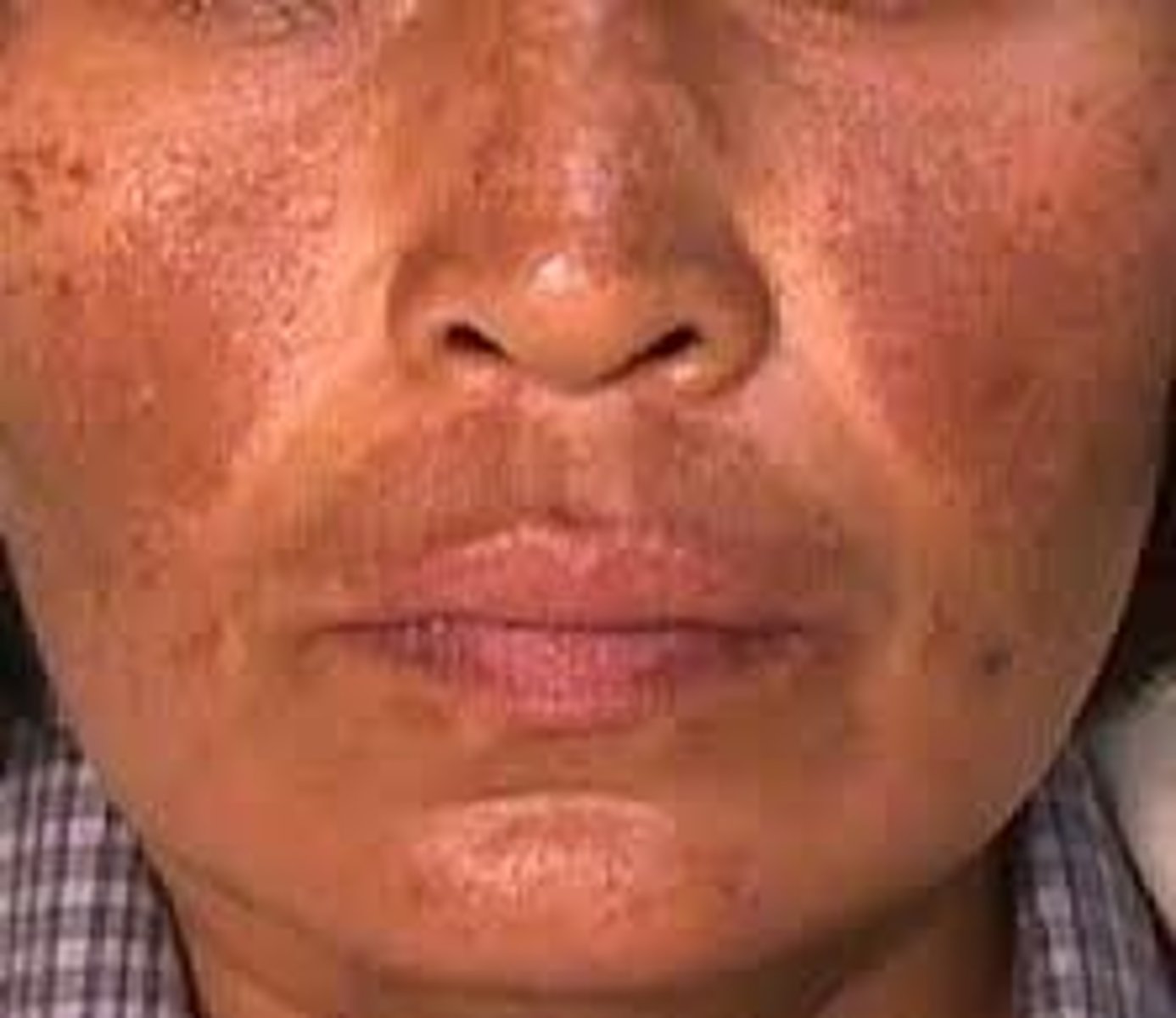
Hyperpigmentation
- AKA Melasma
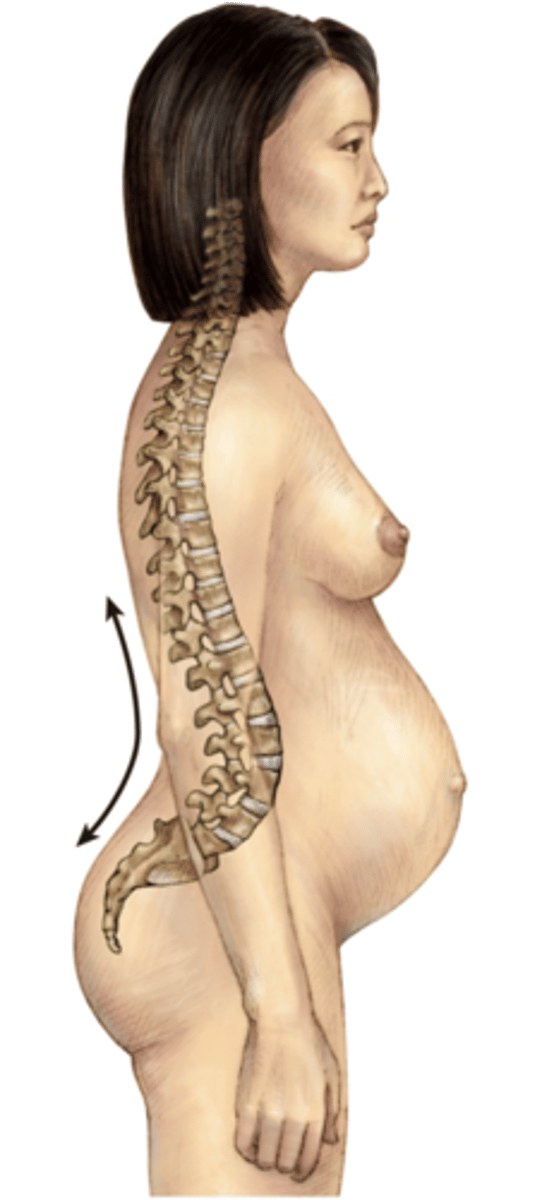
Lordosis
abnormal increase in the forward curvature of the lumbar spine
Why does increased urination occur at the beginning of pregnancy?
- Hormonal changes
- Increasing size of uterus
Why does increased urination occur at the end of pregnancy?
The uterus is compressing the bladder from the increased size of the baby
Why doe the gums become hyperemic, swollen, and friable?
- Increase in blood flow
- Increase in vascularization
Why do the joints become more relazed and painful throughout pregnancy?
- Due to the hormone relaxin
- This helps to accommodate the growing fetus
What are common assessment findings of a DVT?
- Increased warmth
- Redness
- Increased calf size
- Calf pain/tenderness
What are some possible education to provide about DVT
- May occur due to increased blood volume and clotting factors.
- Have them increase movement/moving
- Wear compression socks to help
What nutrient helps prevent neural tube defects of the fetus?
Folic Acid
What education should be provided to women who are of childbearing age?
- They should be taking a multivitamin that includes folic acid
What is the expected weight gain for someone with an average BMI during pregnancy?
25-35 lbs
What is the expected weight gain for someone with a low BMI during pregnancy?
28-40 lbs
What is the expected weight gain for someone with a higher BMI during pregnancy?
15-25 lbs
Nageles Rule
Subtract 3 months
Add 7 days
Factor in the year
GTPAL
G - Gravida (# of pregnancies)
T - Term (# of infants >37 wks)
P - Preterm (# of infants <37 wks)
A - Abortion (# of births < 20 wks)
L - Living (# of currently living children)
RH Factor that is Bad
Mom (-) and Baby (+)
What is significant about the RH factor and pregnancy
- RH is the rubella factor
- It helps determine in future pregnancies if there is a risk for maternal-fetal incompatibility.
What does a positive versus negative rubella titer indicate?
- Positive means the mom has immunity
- Negative means the mom is nonimmune and needs MMR vaccine after pregnancy.
When/How is GBS collected?
- When the mom is 36/37 wks pregnant
- Collected by a vaginal/rectal swab
What does a positive GBS swab indicate?
- The baby has a higher risk of developing an infection when being delivered.
What is a NST?
- Non reactive stress test
- It is done for 20-40 minutes
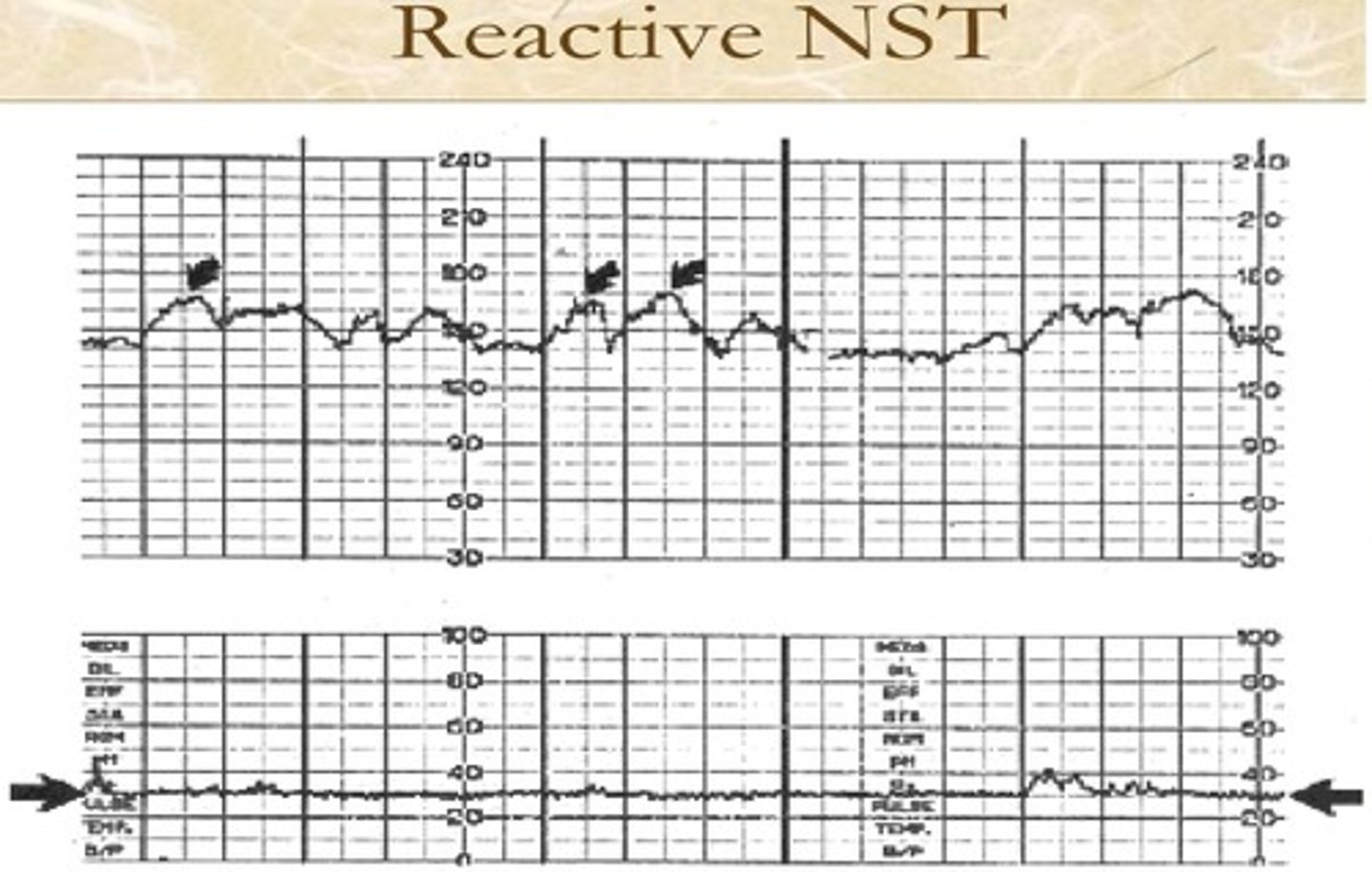
What are the results of a NST?
- Non reactive (NO accelerations)
- Reactive (Accelerations)
Accelerations
- An increase in fetal HR in a 15 by 15 section.
Contraction Stress Test
- Helps determine if the baby will be able to tolerate the stress of labor.
- Performed by having the client lightly brush their palm across the nipple for 2 min and have them stop when a contraction begins.
- A pattern of at least three contractions within a 10-min time period with duration of 4 to 6 seconds each must be obtained to use for assessment data
Indications of CST
- Positive
* Indicated with late decelerations with 50% or more of the contractions.
* Indicated uteroplacental insufficiency and may suggest cord compression.
- Negative
NORMAL
* within a 10-min period, with at least three uterine contractions, there are no late decelerations of the FHR.
What are some contraindications to a CST?
- Placenta previa
- Previous c-section w/a classical incision
- Vasa previa
- Multiple gestations
- Fetal incompetence
Biophysical Profile
- A test that asses wellbeing of the baby
Components of a BPP
- Body Movements
- Muscle Tone
- Breathing
- Amniotic fluid
- Fetal Heart Rate
Body Movements
Three or more discrete limb or trunk movements
Muscle Tone
One or more instances of full extension and flexion of a limb or trunk
Fetal Breathing
One or more fetal breathing movements of more than 30 seconds
Amniotic Fluid volume
One or more pockets of fluid measuring 2 cm
Fetal Heart Rate
110 -160 (WNL)
What does the scoring of a BPP mean?
Overall, a score of 8-10 is considered normal if the amniotic fluid volume is adequate.
- A score of 6 or below is suspicious, possible indicating a compromised fetus; further investigation of fetal well-being is needed.
Amniocentesis
A needle puncture in which is used to confirm a fetal abnormality when other screening tests detect a possible problem
Describe the procedure to the patient
- Have them empty their bladder, and place them in semi fowler's position with a wedge under one hip.
- Using an ultrasound, they will insert a needle through the abdominal cavity into the amniotic sac and obtain an aspiration of amniotic fluid.
Premonitory Signs of Labor
- Spontaneous Rupture of Membranes (SROM)
- Nesting
- Braxton Hicks (False contractions)
- Cervical changes
- Bloody show
- Lightening
SROM
- Initiation of labor
- prolonged ROM = infection risk
- assess FHR STAT
- fetal risk
Assessing Amniotic Fluid
- Color: clear/yellow tinge
- Consistency: watery
- Odor: little to no odor
- Amount: 700-1,00 mL
- Confirmation: Nitrazine (swab of vaginal canal)
Nesting
Sudden surge of energy
Braxton Hicks
- False contraction
- irregular
- upper abdomen
- can be relieved with activity or rest
Cervical changes
- Dilation
- Effacement
Bloody Show
- Loss of mucus plug
- Discharge is pink/mucus
Lightening
- Softening of cervix and baby descends
What is the only indication of true labor?
Cervical change
Where do you place the ultrasound transducer?
On the fetal back
What does VEAL CHOP mean?
V - Variable Decelerations
C- Cord compression
E- Early decels
H- Head compression
A- Accelerations
O- OKAY!!
L - Late decels
P- Placental insufficiency
What are the priority interventions for Variable Decels?
- Position on left lateral side
- Perform vaginal exam
What are the priority interventions for Early Decels?
- No interventions
- Continue to watch FHR
What are the priority interventions for Acclerations
- No interventions needed
What are the priority interventions for Late Decels?
- Position on left lateral side
- Turn of pitocin
- IV bolus
- Oxygen via nonrebreather
What is an Amniotomy?
Artificial rupture of membranes
What are immediate actions following an amniotomy?
- Monitor FHR, sig. depression may indicate cord prolapse
- Check patient
- Look at amniotic fluid (color, amount, odor)
What are possible complications of prolonged rupture of membranes?
- Infection
- Fetal distress
Stages of Labor
- Stage 1: latent vs active
- Stage 2: Pushing
- Stage 3: Placental delivery
- Stage 4: 2 hours post delivery of placenta
Stage 1 - Latent Phase
- 0 to 5 cm dilated
- contractions are irregular, mild, moderate
- frequency is 5-30 minutes
- duration is 30-45 seconds
- physical: bloody show, mucus plug; can walk and talk through contractions
- psychological: self-focused; apprehensive
Stage 1 - Active Phase
- 6 to 10 cm dilated
- contractions are regular, moderate-strong
- frequency is 3 to 5 mins
-lasts 40 to 90 seconds
- physical: increase in bloody show; irritable; severe pain; nausea/vomiting, urge to push
- psychological: serious; helpless; anxious; inward-focus
Stage 2
- Full cervical dilation and effacement to birth of the newborn.
- Physical: "pushing", burning sensation of perineum, urge to defecate, shaking, perineal lacerations, episiotomy
- Psychological: cooperative; focused; sense of relief with pushing
Stage 3
- Delivery of the placenta
* should be delivered 5-30 minutes following delivery of neonate.
- Monitor VS every 15 minutes
- Do fundal assessments
- Administer oxytocics IMMEDIATELY after placental expulsion
Stage 4
- Maternal homeostasis
* About 2 hrs from placental delivery
- VS monitored every 15 mins for 2 hrs
- Fundal assessment every 15 mins for 1 hr
- Encourage voiding
- Rest, recovery, nutrition
Which incision type would be contraindicated for a VBAC?
- Classical incision
What are adverse effects of epidural administration?
- Hypotensive
- Resp. Depression
Comfort measures for the perineum after delivery
- Sitz baths
- Cold compresses
- Tuck Pads
- Perineal bottle
- Diapers/pads
- Position changes
- Inflatable donut