Biology- Chapter 12: DNA Technology and Genomics
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 12:21 PM on 5/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
1
New cards
What is the average amount of DNA that is similar between humans?
99\.9%
2
New cards
How much of human’s DNA is noncoding?
97%
3
New cards
What is noncoding DNA made up of?
* gene control sequences (ex: promoters)
* introns
* DNA located between repetitive DNA sequences
* introns
* DNA located between repetitive DNA sequences
4
New cards
Where are the repeated DNA sequences found?
at the centromeres and the end of the chromosomes
5
New cards
What are the steps in DNA identification?
* copying DNA
* cutting DNA
* sorting DNA by size
* comparing DNA
* cutting DNA
* sorting DNA by size
* comparing DNA
6
New cards
What method is used when the source of DNA is scanty, impure, or in a partially degraded state?
the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to prepare large quantities of a particular gene
7
New cards
What does the PCR method involve?
using short DNA sequences called primers to select the portion of the genome to be amplified
8
New cards
What are automated PCR machines called?
thermocyclers
9
New cards
how many molecules can the thermocycler produce in a few hours?
100 billion
10
New cards
PCR cannot replace gene cloning in cells when ___ ?
large amounts of DNA are needed
11
New cards
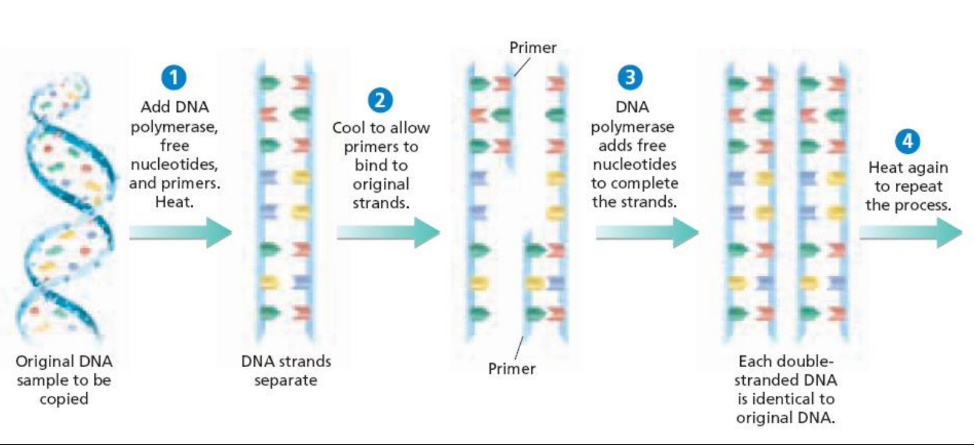
What is the DNA sample mixed with?
a heat tolerant DNA replication enzyme (DNA polymerase), DNA nucleotides, and primers that are complementary to the ends of the DNA fragment that is to be copied.
12
New cards
What is needed to start replication?
primers
13
New cards
This solution is exposed to what?
cycles of heating (to separate the DNA strands) and cooling
14
New cards
What enzyme can withstand the heat of each cycle?
the unusual DNA polymerase
15
New cards
How do scientists generate millions of copies of a single DNA fragment?
they choose a DNA fragment to copy and design primers that will bind to both ends of the fragment. DNA polymerase copies the segment between the two primers.
16
New cards
What are restriction enzymes?
they cut DNA at specific sequences
17
New cards
How long of a DNA sequence do the restriction fragments recognize?
4-8 nucleotides long
18
New cards
What are restriction fragments?
pieces of DNA produced from the restriction enzymes cutting it
19
New cards
What are “sticky ends”
2 double-stranded DNA fragments with single- stranded overhanging ends

20
New cards
Sticky ends DNA restriction fragments from ?
different sources
21
New cards
How do you add a piece of DNA from another source?
by cutting it using the same restriction enzyme
22
New cards
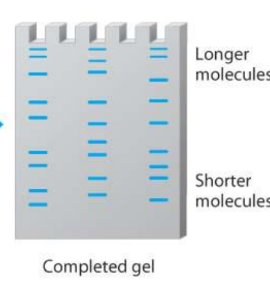
What does gel electrophoresis do?
it sorts DNA molecules by size
23
New cards
How does gel electrophoresis separate nucleic acids or proteins?
it uses a gel (a thin slab of jellylike material) as a molecular sieve
24
New cards
On what basis are the nucleic acids or proteins seperated?
size or electrical charge
25
New cards
How many steps are there to separate DNA in different mixtures?
7
26
New cards
What is the first step?
Restriction enzymes are used to prepare DNA fragments in each mixture
27
New cards
What is the second step?
A sample of each mixture is placed in a well at one end of a flat, rectangular agar gel slab
28
New cards
What is the third step?
A negatively charged electrode from a power supply is attached near the DNA-containing end of the gel, and a positive electrode is attached near the other end.
29
New cards
What is the fourth step?
the DNA molecules all travel through the gel toward the positive pole.
30
New cards
Are DNA molecules negatively charged?
yes
* because of their phosphate groups
* because of their phosphate groups
31
New cards
What is the fifth step?
As they move, the polymer fibers within the gel slows down the movement of the longer molecules more than it does shorter ones, separating them by length.
32
New cards
What is the sixth step?
After about 1⁄2 hour the electrodes are disconnected
33
New cards
What is the seventh step?
gel electrophoresis separates a mixture of DNA molecules into bands
34
New cards
Are these bands of DNA the same length?
yes
* the shorter molecules are towards the bottom
* the shorter molecules are towards the bottom
35
New cards
What are restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs)?
The differences in restriction fragments produced in this way
36
New cards
How many base pairs are different between two people?
3 million
37
New cards
What does electrophoresis allow us to see?
Similarities as well as differences between
1. mixtures of restriction fragments belonging to the same individual
2. the base sequences in DNA from two individuals.
1. mixtures of restriction fragments belonging to the same individual
2. the base sequences in DNA from two individuals.
38
New cards
How do you permanently preserve DNA fragments that are isolated by gel electrophoresis?
the pieces of DNA are transferred or ‘blotted’ out of the fragile gel onto a nylon membrane
39
New cards
How many steps are there to make a DNA fingerprint?
5
40
New cards
What is the first step?
A positively charged nylon membrane is placed over the gel and the negatively charged DNA fragments are transferred to membrane
41
New cards
What is the second step?
DNA is then ‘unzipped’ to produce single strands of DNA
42
New cards
What is the third step?
Biologists incubate the nylon membrane with radioactive probes. They can prepare a nucleic acid probe complementary to the DNA of interest and label it radioactively.
43
New cards
What is the fourth step?
A sheet of X-ray film placed over the gel will be exposed only where the desired DNA is on the gel.
44
New cards
What is a fingerprint?
The resulting pattern of bands
45
New cards
What is the fifth step?
To compare two or more different DNA fingerprints the different DNA samples are run side-by-side on the same electrophoresis gel
46
New cards
What are probes?
small fragments of minisatellite DNA tagged with radioactive phosphorous
47
New cards
When can the information be used to synthesize a short single strand of DNA with the complementary sequence?
When at least part of the nucleotide sequence of a gene is already known or can be guessed
48
New cards
What is the DNA labeled with?
a radioactive isotope or fluorescent dye
49
New cards
What is a nucleic acid probe?
This labeled, complementary single-stranded nucleic acid molecule
50
New cards
What is n.a.p. used for?
to find a specific gene or other nucleotide sequence within a mass of DNA
51
New cards
What do the probes hydrogen bond to?
the complementary sequence in the targeted DNA
52
New cards
What is this method used for?
detecting genes/specific DNA pieces depend on base pairing between the gene/DNA piece and a complementary single strand sequence on another nucleic acid molecule, either DNA or RNA.
53
New cards
What can happen once the researcher identifies a colony carrying the desired gene?
the cells can be grown further and the gene of interest (and/or its protein product) isolated in large amounts
54
New cards
What are minisatellites?
short sequences (10-60 base pairs long) of repetitive DNA that show greater variation from one person to the next than other parts of the genome
55
New cards
What is this variation exhibited in?
stutters or VNTRs
56
New cards
How many VNTR loci does DNA fingerprinting usually compare?
5-13
57
New cards
DNA fingerprinting simultaneously does what?
detects lots of minisatellites in the genome to produce a pattern unique to an individual
58
New cards
What are the odds that 2 people will share a DNA profile produced by 13 VNTR loci?
1 in a 100 billion
59
New cards
What does VNTR stand for?
variable number tandem repeats
60
New cards
What are length polymorphisms?
The non-coding DNA segments that vary in their length
61
New cards
What are some length polymorphisms made out of?
short repeating sequences of DNA nucleotides
62
New cards
What are VNTRs?
The nucleotides that repeat few or many times in tandem (one after another) in length polymorphisms
63
New cards
Is the amount of tandam repeats in a specific loci in DNA the same for everyone?
no, that’s why it is used for DNA identification
64
New cards
What does recombinant DNA technology do?
combines genes from different sources–even different species–into a single DNA molecule
65
New cards
How do researchers create recombinant DNA?
by inserting desired genes into plasmids

66
New cards
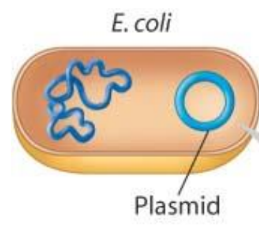
What are plasmids?
small, circular DNA molecules that replicate separately from the much larger bacterial chromosome
67
New cards
Are plasmids required for cell reproduction or growth?
no
68
New cards
What genes do plasmids carry?
genes that cause the bacterium to cause diseases or provide resistance against antibiotics.
69
New cards
What happens when DNA from another source is introduced to the plasmid?
they hydrogen bond with the plasmid DNA
70
New cards
How are the bonds made permanent?
DNA ligase forms covalent bonds between adjacent nucleotides
71
New cards
How many times is the plasmid cleaved?
one
72
New cards
the restriction enzymes creates sticky ends on what?
both the human DNA fragments and the plasmid
73
New cards
What is transformation?
A process by which bacteria take up DNA from the surrounding
74
New cards
The bacteria reproduces to produce what?
a clone of cells
75
New cards
How can cloned genes be used?
directly or to manufacture protein products
76
New cards
What is a cloning vector?
they copy genes and move them from one organism to the next
77
New cards
Can plasmids be used as cloning vectors?
yes
78
New cards
the restrction enzyme makes ___ of human DNA fragments
millions
79
New cards
What is the genomic library?
The entire collection of all the cloned DNA fragments from a genome
80
New cards
What are vectors?
short pieces of DNA that are capable of replicating on their own when inside a cell
* they’re used for cloning
* can be bacterial plasmids or phages
* they’re used for cloning
* can be bacterial plasmids or phages
81
New cards
How is a phage used?
The DNA fragments are inserted into phage DNA molecules. The recombinant phage DNA can then be introduced into a bacterial cell through the normal infection process.
82
New cards
What happens to the phage inside the cell?
The phage DNA replicates and produces new phage particles, each carrying the foreign DNA. A collection of phage clones can constitute a second type of genomic library.
83
New cards
How do they identify the clone with the desired gene?
* with testing the protein product or
* viewing it under UV light or exposing it to photographic film, the probe glows and reveals its location.
* viewing it under UV light or exposing it to photographic film, the probe glows and reveals its location.
84
New cards
How does reverse transcriptase help make cloned genes?
it makes complementary DNA which is shorter due to the lack of introns
85
New cards
What are cDNA libraries used for?
studying genes responsible for specific functions in a specific cell
86
New cards
What is the Human Genome Project?
an effort to map the human genome in total detail by determining the entire nucleotide sequence of human DNA
87
New cards
What are bacteria used for?
to manufacture protein products on a large scale because plasmids and phages are readily available and can be grown rapidly and cheaply
88
New cards
What are sheep cells used for?
they add glycoproteins to the initial ones made in bacteria
89
New cards
What is a GMO?
an organism that has acquired 1 or more genes by artificial means rather than through normal breeding methods