BIOLOGY: Chapter 8 Organelles and Transport
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Vesicle
small membrane bound organelle used for movement of material
Cell
the basic unit of all living organisms
Cell Theory
•all living things are made of cells
•cells are the basic unit of structure & function in living things
•new cells are made from existing cells
Types of cells
Prokaryotes & Eukaryotes
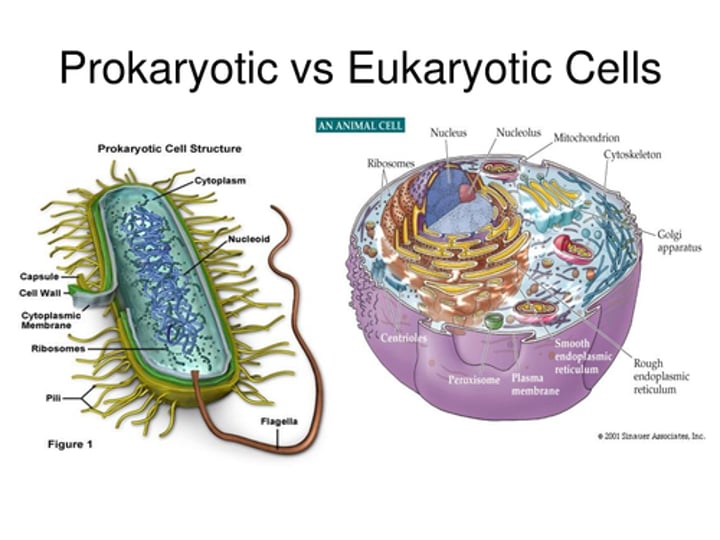
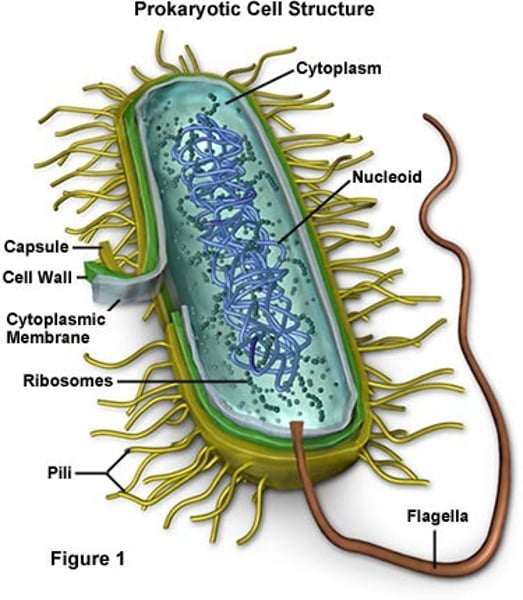
Prokaryotes
•unicellular
•no nucleus
•asexual reproduction
•example: bacteria
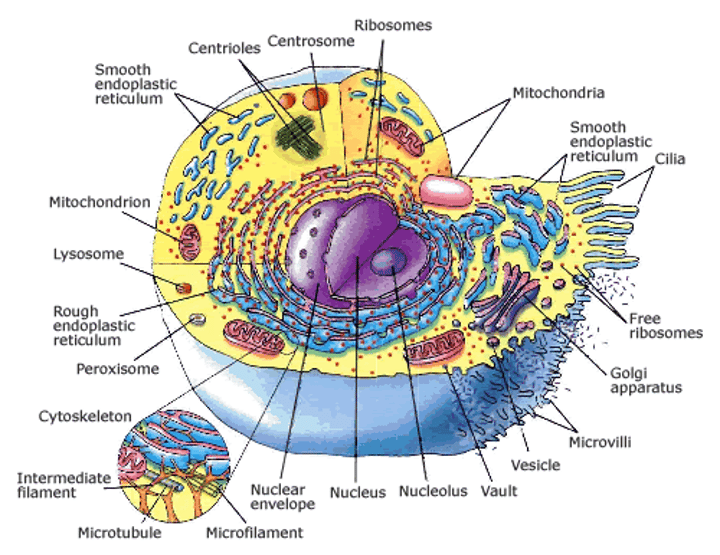
Eukaryotes
•unicellular or multicellular
•nucleus present
•organelles present
•sexual reproduction
•examples: plants, animals, people
All cells have...
cell membrane
cytoplasm
ribosomes
DNA
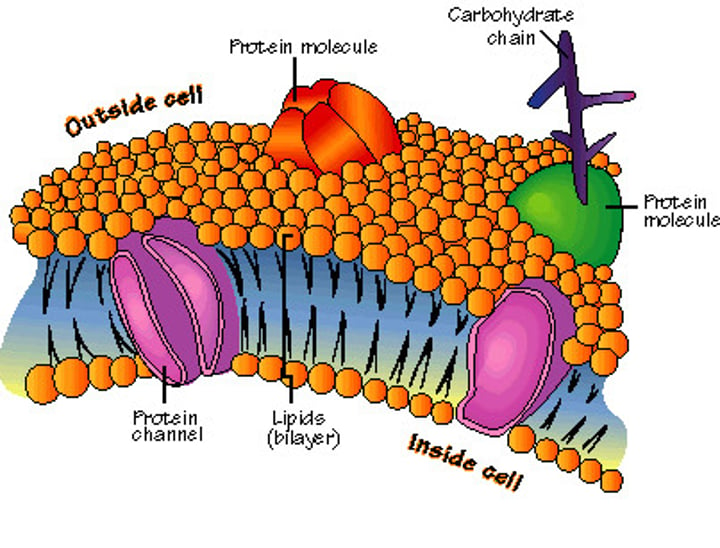
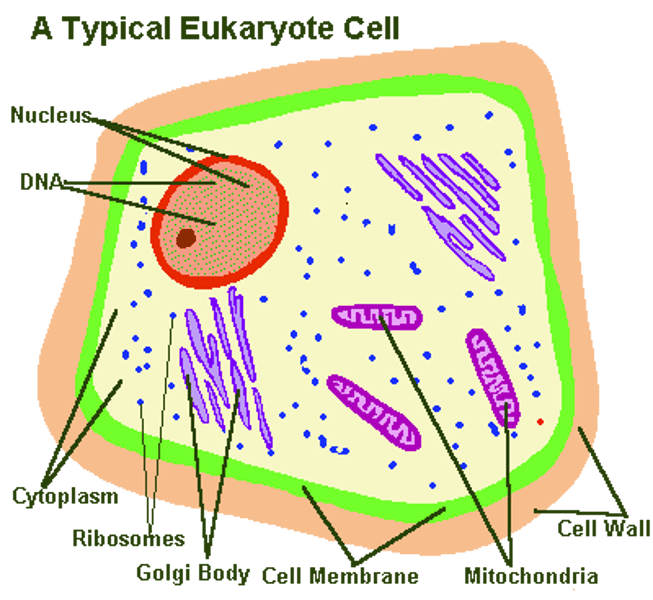
Cell membrane
•the "skin" of the cell
•protects cell from outside environment
•regulates flow of water, nutrients, & waste
•made of mostly of phospholipid bilayer
•described as "fluid mosaic model"
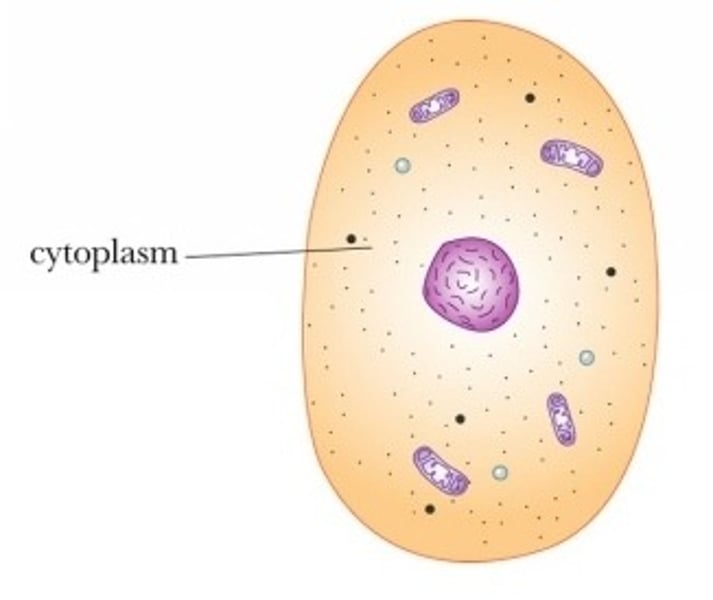
Cytoplasm
•material inside the membrane
•contains many important structures
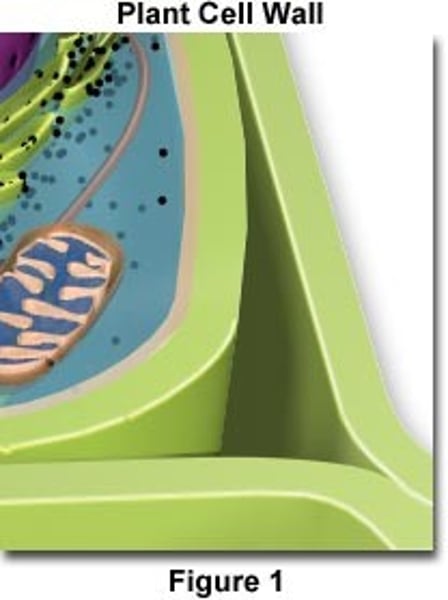
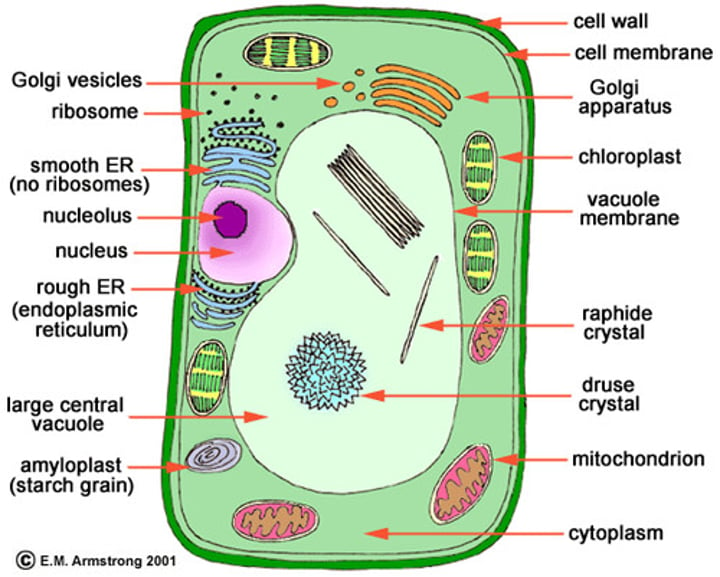
Cell wall
•plant, fungi, bacteria, arcaea cells
•found outside cell membrane
•supports & protects cell
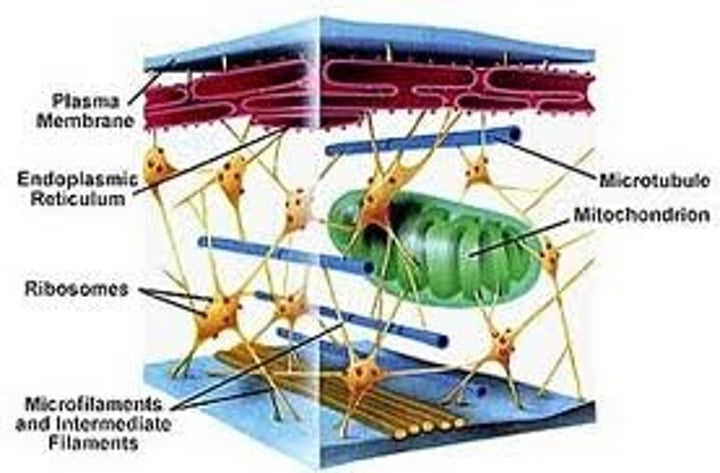
Cytoskeleton
•maintains shape
•movement
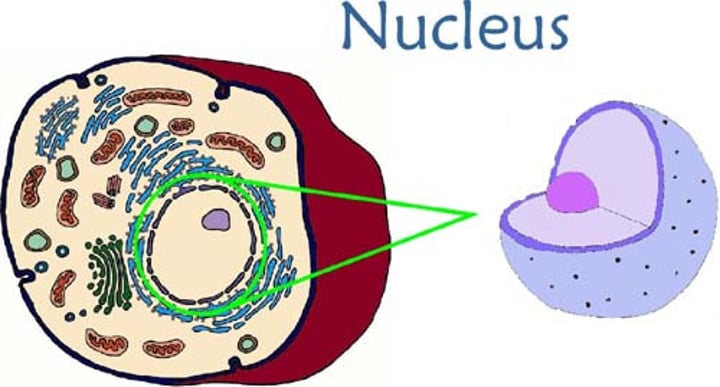
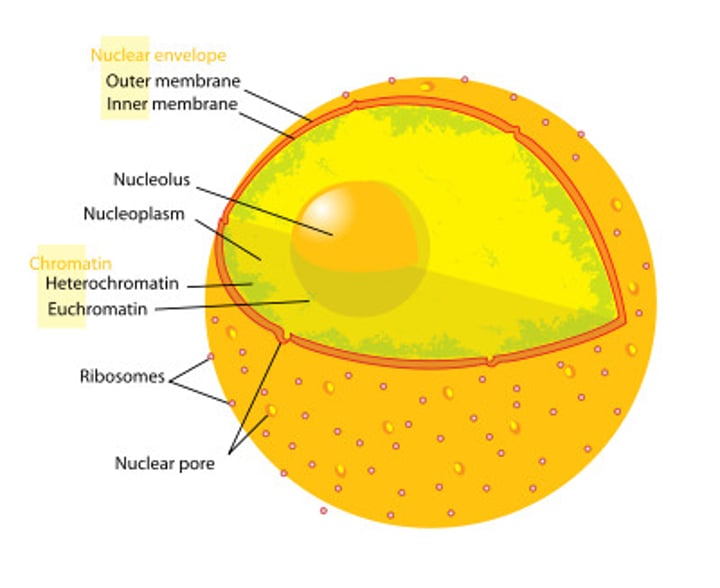
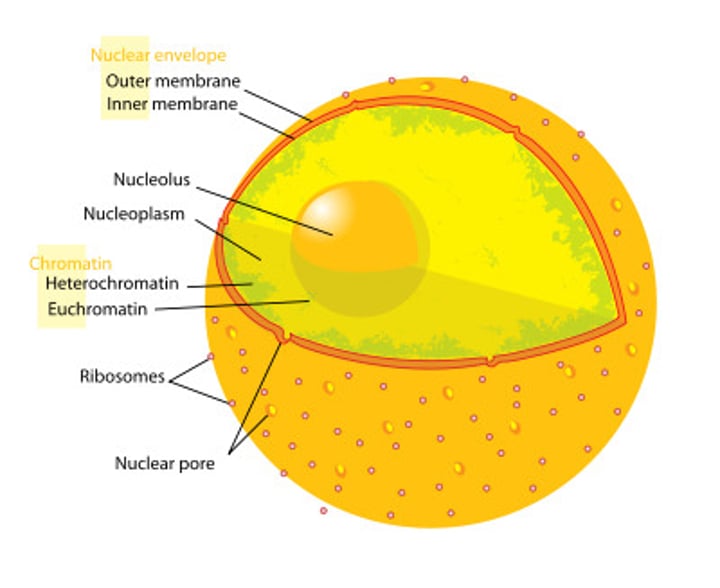
Nucleus
•the "brain" of the cell
•controls cell functions
•contains DNA
•surrounded by nuclear envelope
•contains nucleolous
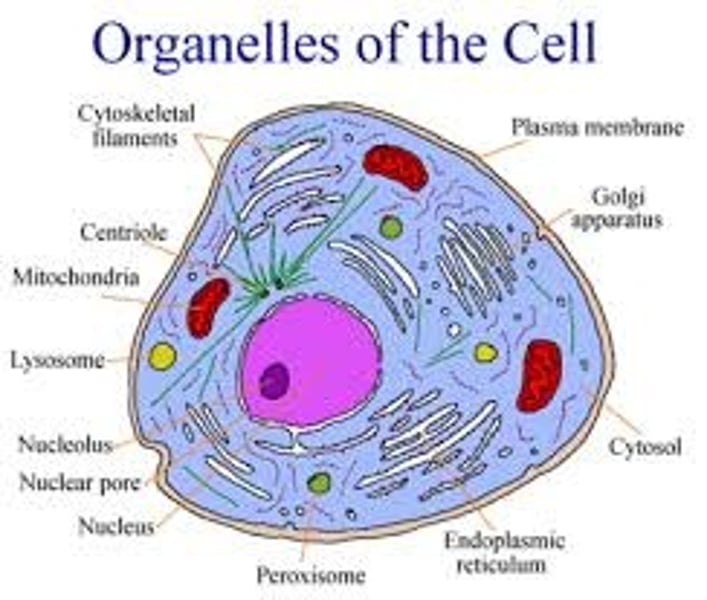
Organelles
•"little organs"
•specialized parts of the cell
•examples: ribosomes, mitochondria, chloroplasts, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vacuoles.
all eukaryotes
nucleus are found in...
nucleolus
makes ribosomes
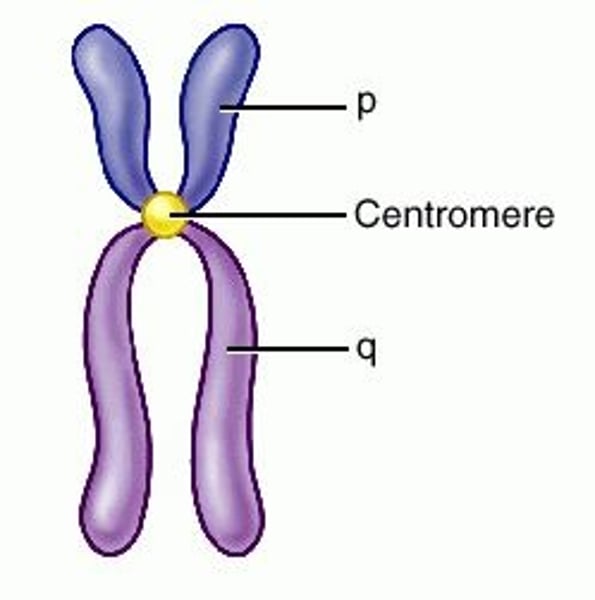
chromosomes
•genetic info
•holds DNA
•visbile DNA during mitosis and meiosis
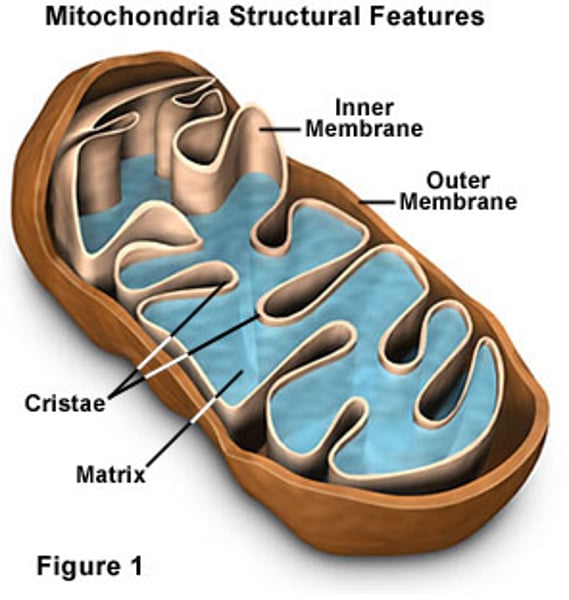
mitochondria
cellular respiration to create ATP
ribosomes
makes proteins, found in all cells
float in cytoplasm or on Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
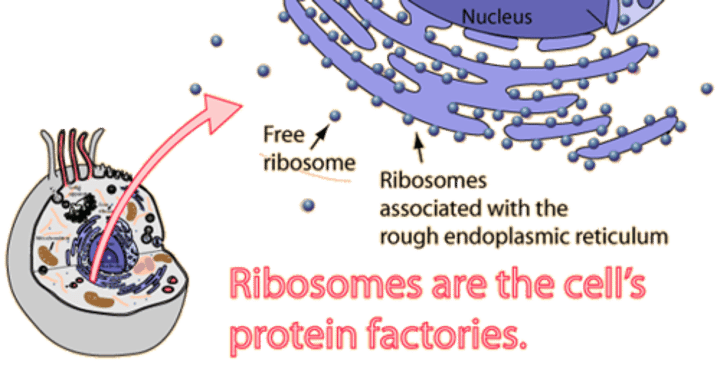
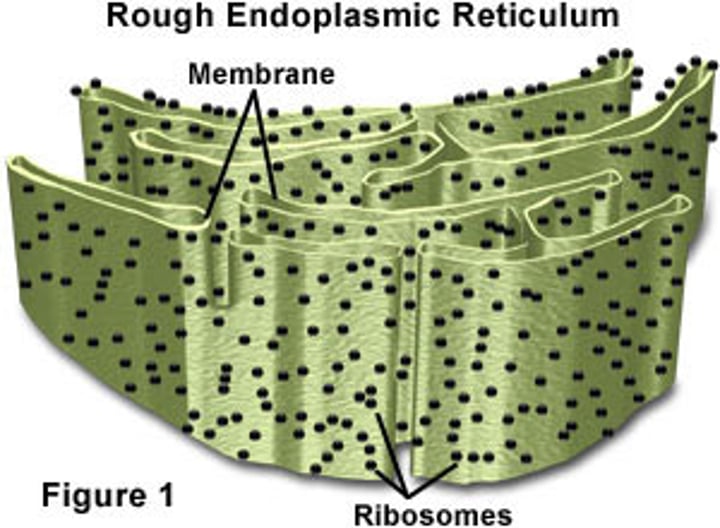
rough ER
•has ribosomes
•makes & transports proteins
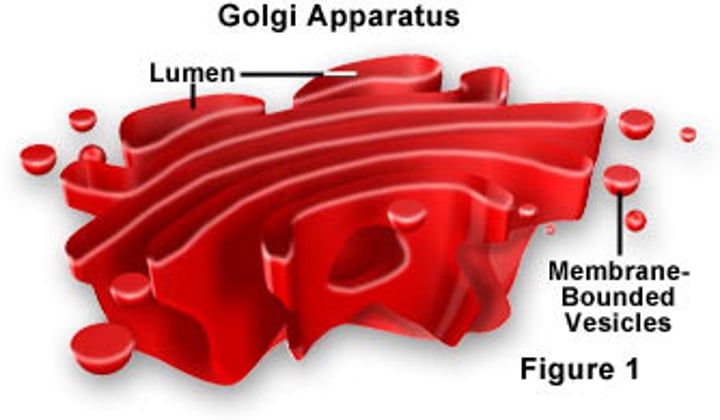
golgi apparatus
packages proteins and lipids
short term storage of material
smooth ER
•no ribosomes
•detoxify cells of drugs and alcohol
•makes & transports lipids and carbs
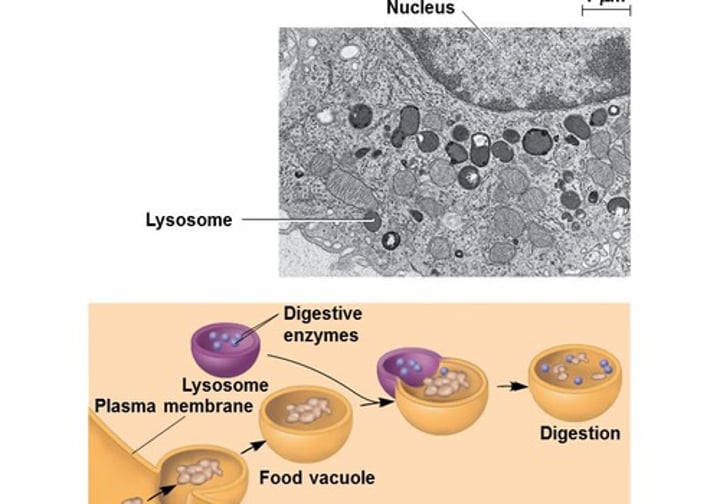
lysosomes
•contains enzymes that break down & recycle waste
cytoplasm
•contains cell structures
•jelly like fluid
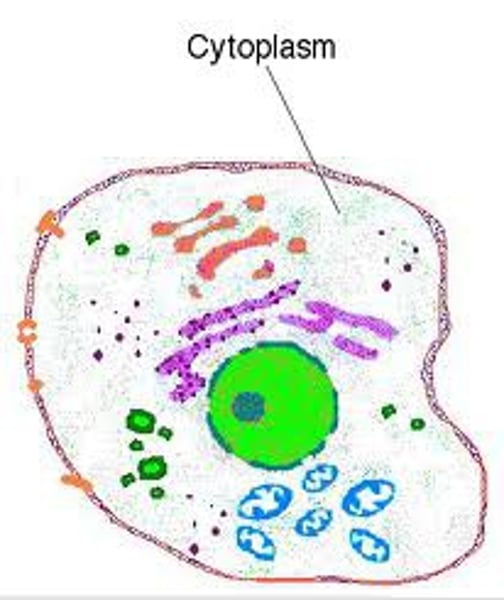
all cells
cytoplasm is found in...
nuclear envelope
covers nucleus
eukaryote plant (and plant-like protist) cells
chloroplast are found in...
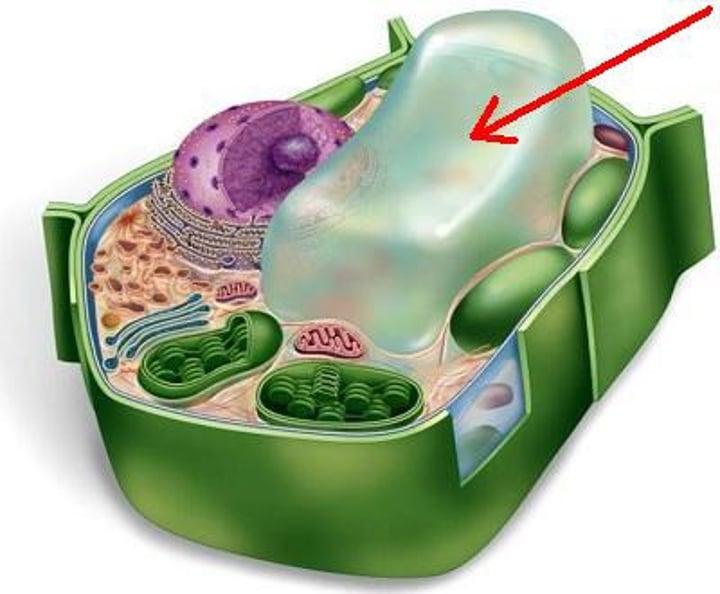
vacuole
storage of material
what types of cells are cell membranes found in?
•all cells
centrioles
helps with cell division
Semi-permeable
allow certain nutrients and molecules in or out
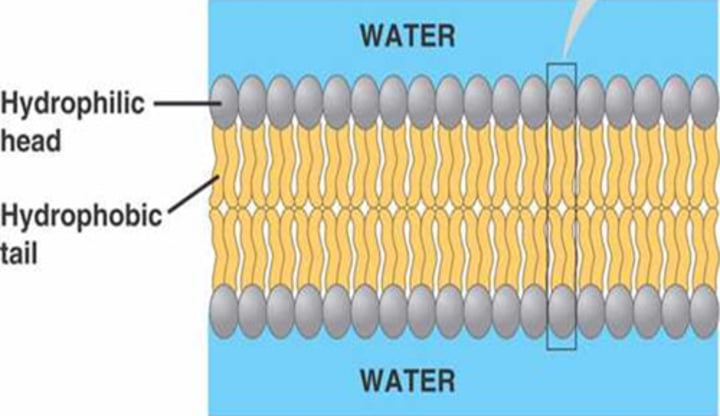
Main parts of Cell Membrane:
•phosopholipid bilayer
•protein channel
•carbohydrates
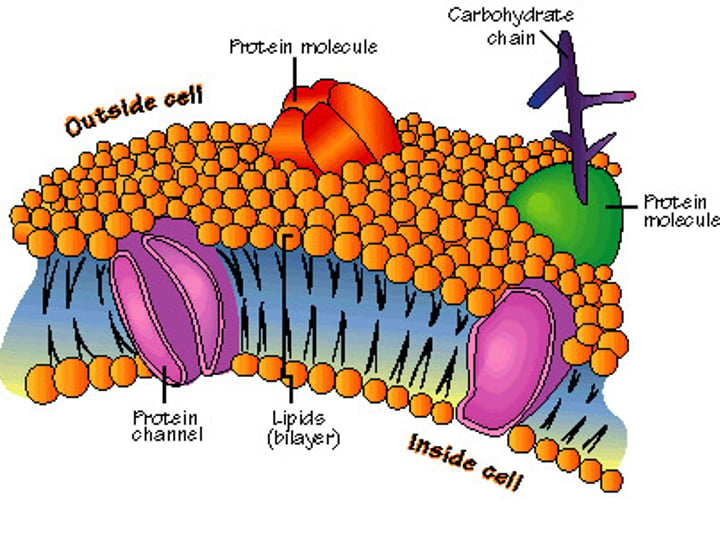
Phosopholipid Bilayer
the core of the membrane, form a strong barrier b/w cell and the outside
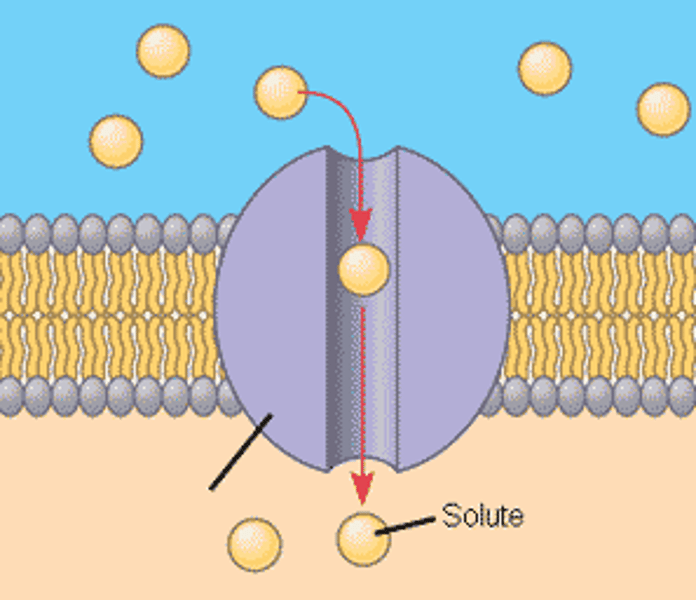
Protein Channel
Forms channel to move material through the membrane
Concentration
how much solutes are in a give volume
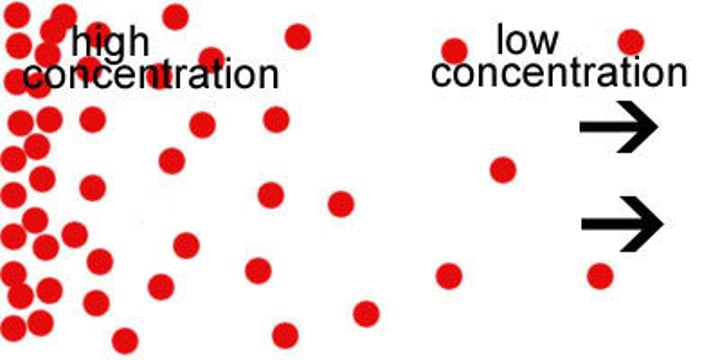
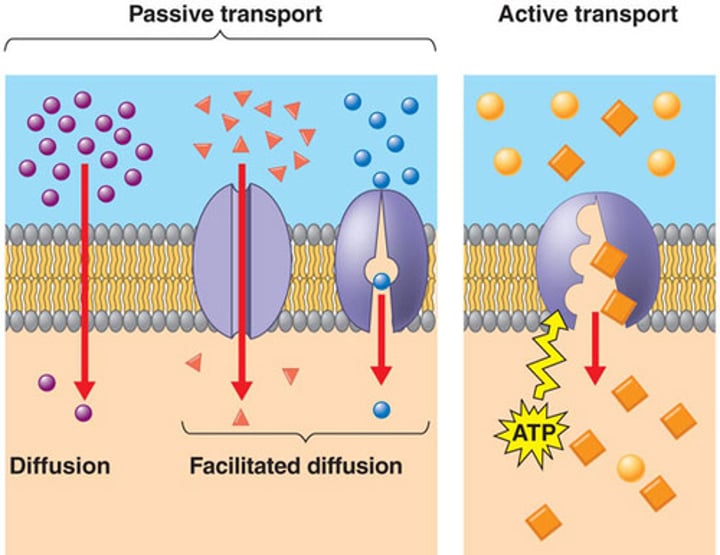
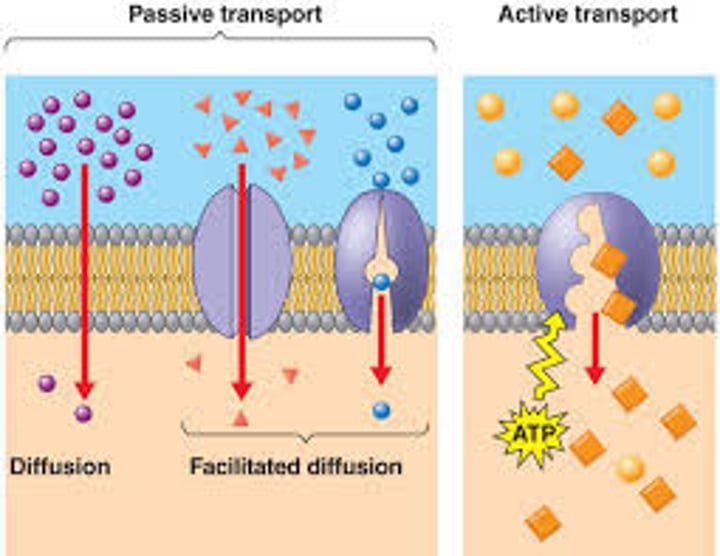
Passive transport
Movement from an area of high concentration to areas of low concentration (getting less crowded), does not use energy
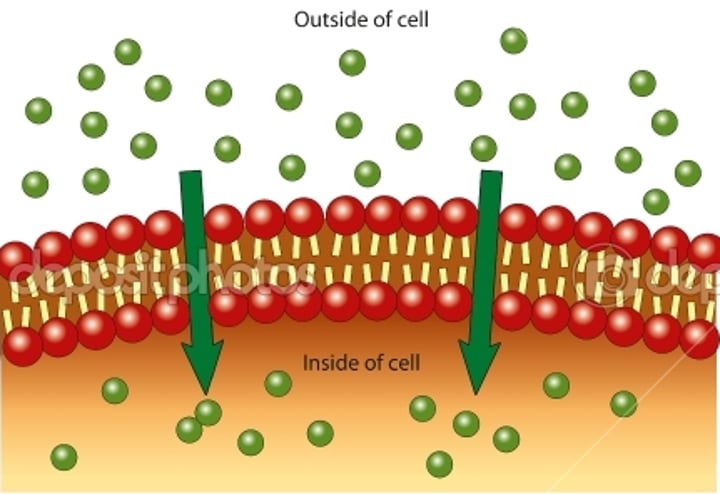
Types of passive transport
Simple Diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion
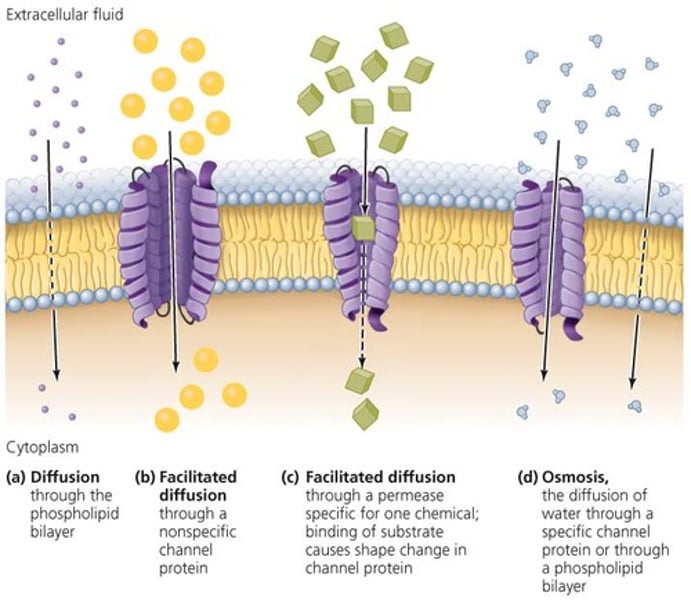
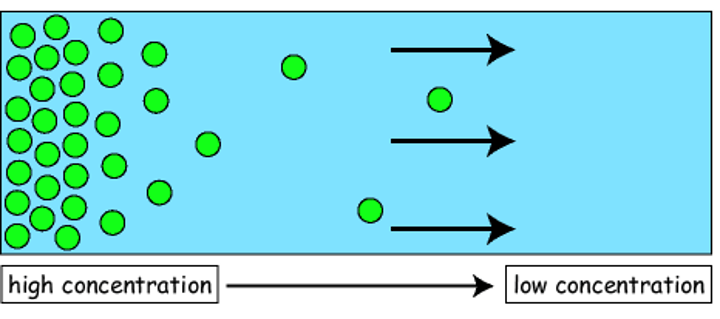
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from hight concentration to low concentration (along concentration gradient)
Facilitated diffusion
Molecules that are too large to pass through the cell membrane go through protein channels, does not use energy (ATP)
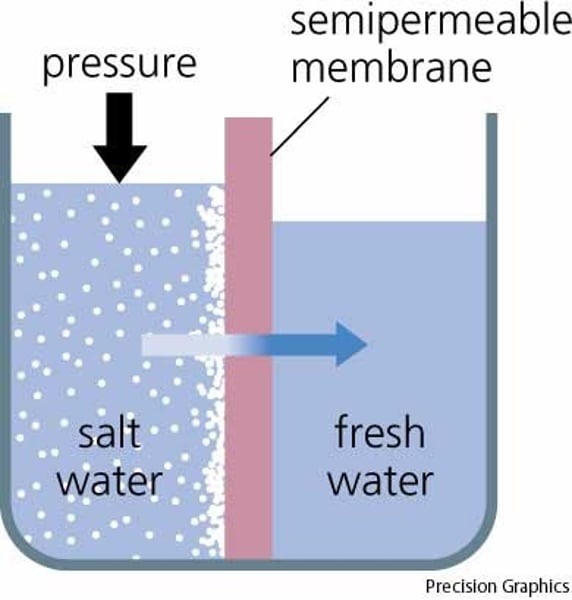
Osmosis
The diffusion of water
Types of solutions
•hypotonic
•isotonic
•hypertonic
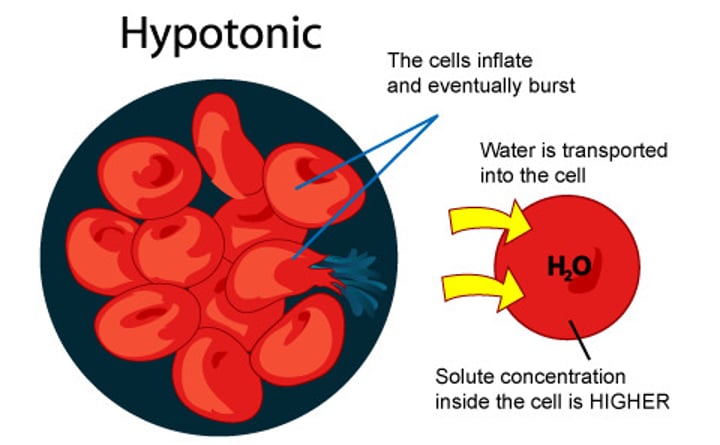
Hypotonic
Lower solute concentration than hypertonic solution. If cell placed into hypotonic solution the cell will swell and could bust.
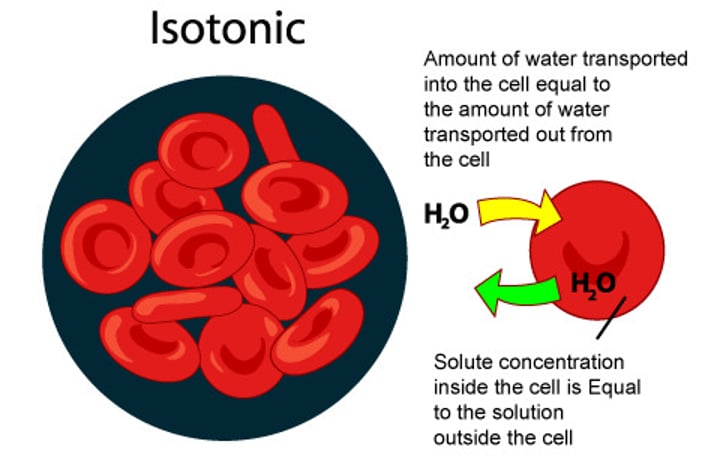
Isontonic
the solution outside has the same concentration as the solution inside the cell
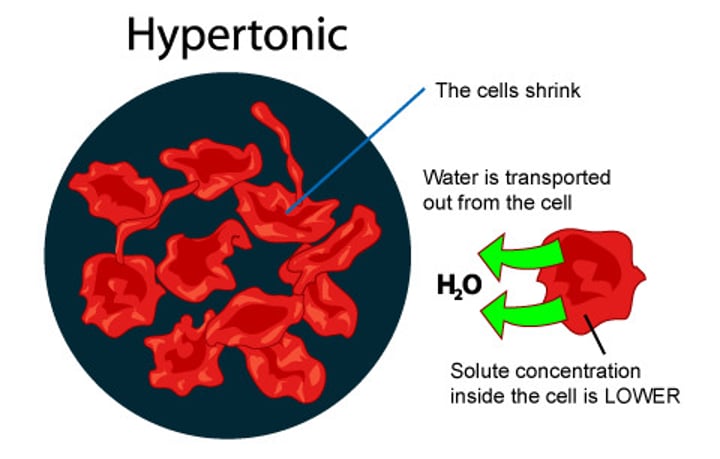
Hypertonic
Higher solute concentration than hypotonic solution. If cell placed into hypertonic solution the cell will lose water and shrink .
chromatin
Invisible DNA found within the nucleus.
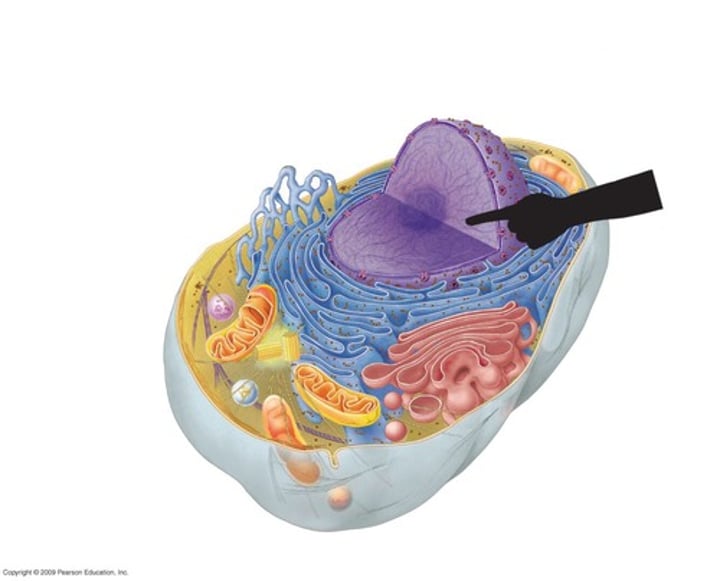
Cell Membrane
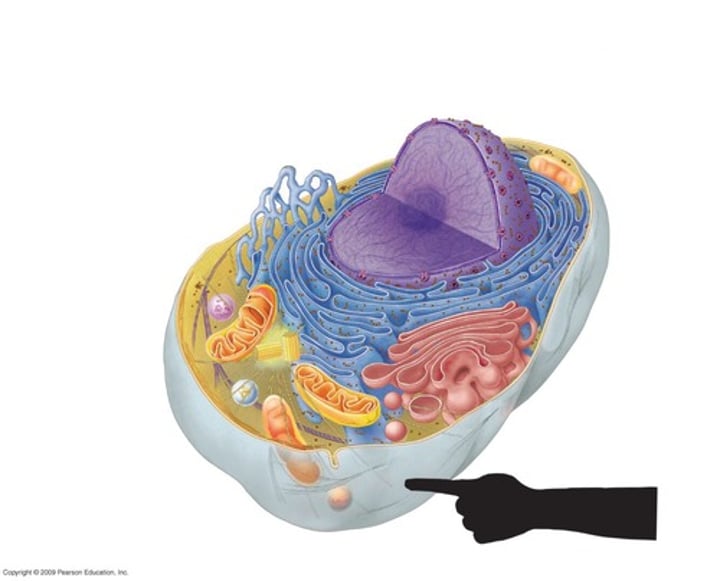
Golgi Apparatus
The UPS of the cell. Packages proteins, lipids and carbohydrates for secretion out of the cell or to transport to other parts of the cell.
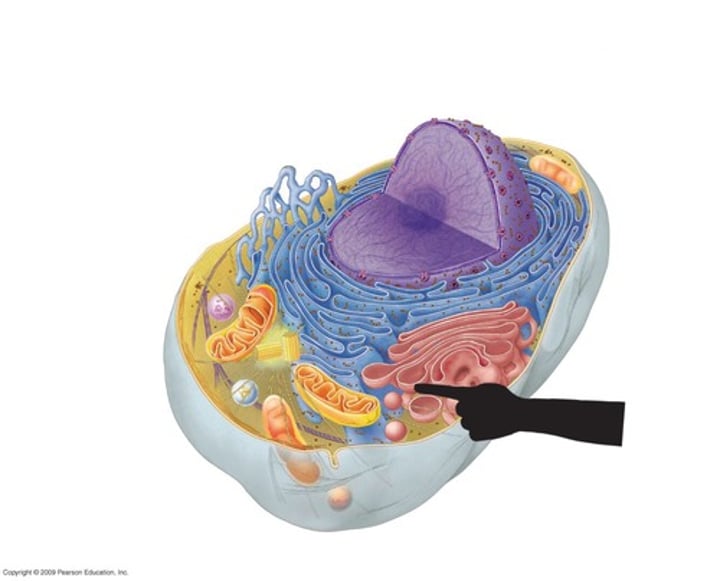
Active Transport
Movement from an area of low concentration to areas of higher concentration (getting more crowded), uses energy, examples: sodium/potassium pump, endocytosis, exocytosis
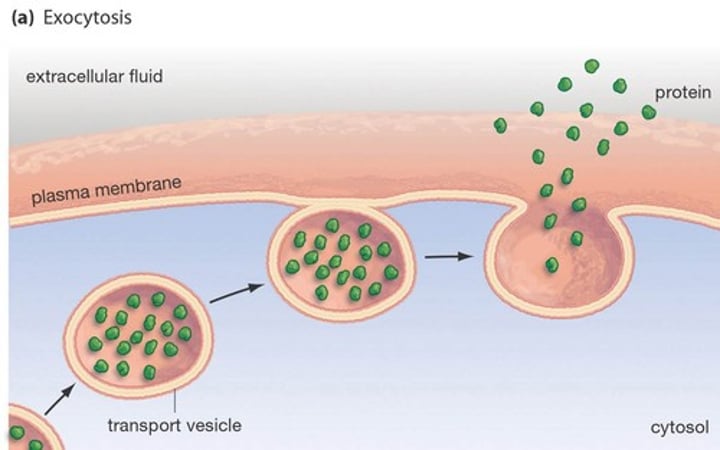
Exocytosis
•type of active transport
•when a vesicles fuses with the cell membrane to take material out of the cell
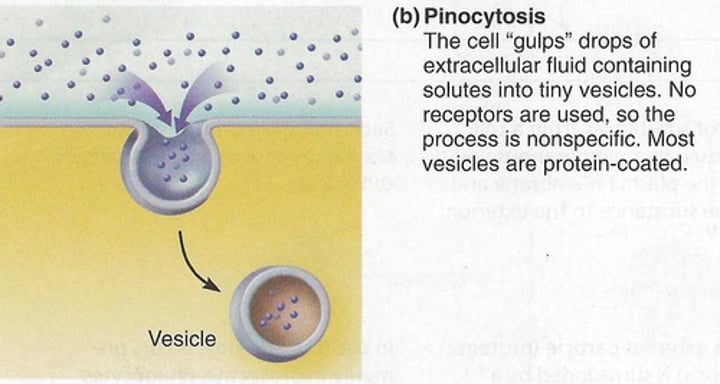
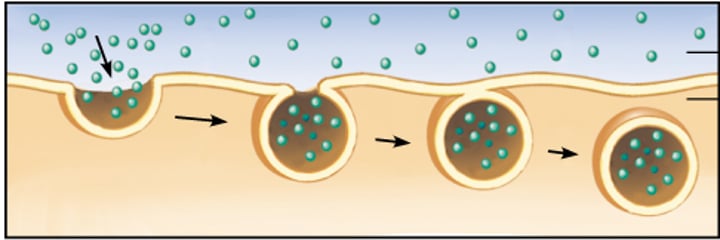
Endocytosis
•type of active transport
•brings material into the cell when a pocket is the membrane breaks off forming a vesicle
Types of Endocytosis:
•phagocytosis
•pinocytosis
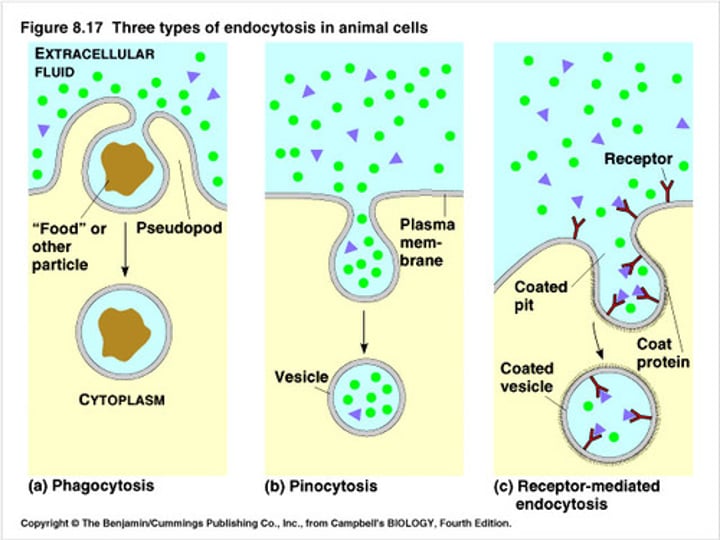
Phagocytosis
•large solid particles taken in
•type of Endocytosis
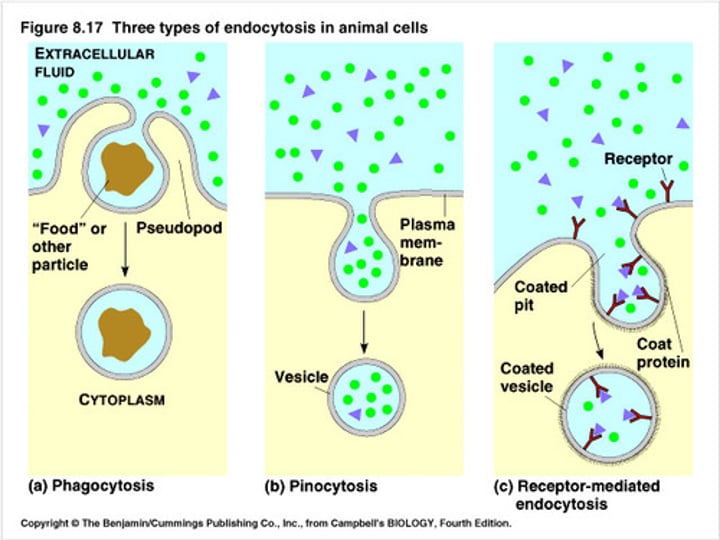
Pinocytosis
•small particles taken in
•type of Endocytosis