Biology Learning Goals - Biological molecules
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Describe the structure of a water molecule
An oxygen atom covalently bonded to 2 hydrogen atoms. It is a non-linear shape.
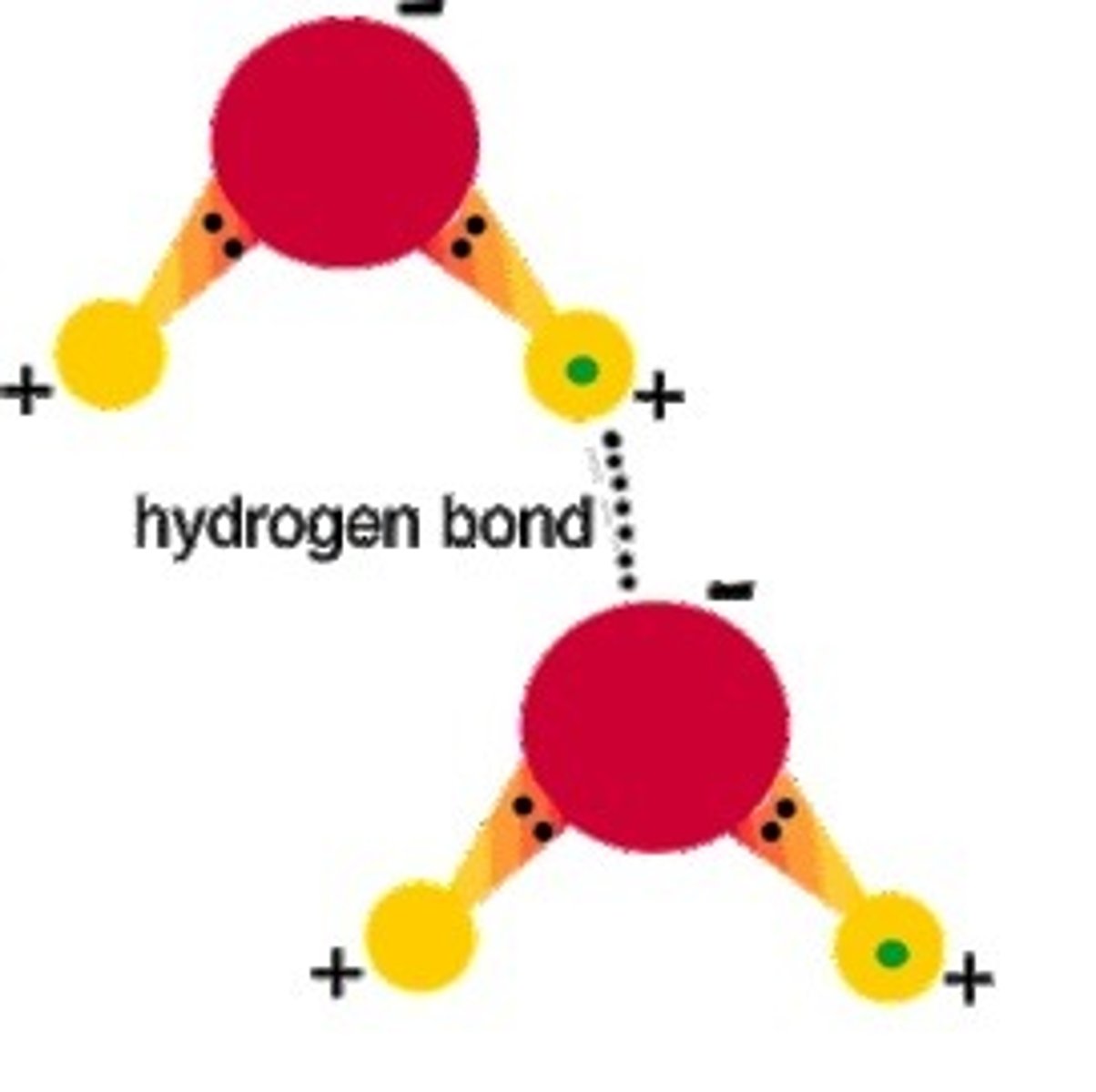
Name the bond that can link two water molecules together
Hydrogen bond
Explain what a hydrogen bond is, which types of atoms it can join together and where they occur in biology
A hydrogen bond is a weak interaction that can occur whenever molecules contain a slightly negatively charged atom bonded to a slightly positively charged hydrogen
Draw two water molecules and draw and label the bond that links them together
Define the term 'Polar'
Has 2 poles, one slightly positive the other slightly negative
Explain why water is a polar molecule
Water is a polar molecule because the oxygen atom is more attractive to electrons than hydrogen so pulls the shared electrons towards it. This causes the O to be slightly negative and the Hs to be positive.
Define the term "electronegativity" and "dipole"
Electronegativity is a measure of the tendency of an atom to attract a bonding pair of electrons.
A dipole is a molecule in which a concentration of positive electric charge is separated from a concentration of negative charge
List the roles water plays in life (at least 5)
Solvent transport medium, habitat, reactant, thermal stability, solvent
Explain why the polar nature of water allows it to be a useful solvent, transport medium, coolant and habitat
Solvent: Dissolves polar and charged molecules as charges interact with polar water molecules which cluster around them keeping them apart
Transport medium: Liquid over large temp. range as H bonds require lots of energy to break. It dissolves many molecules
Coolant: High specific heat capacity as H bonds require lots of energy to break
Habitat: Maintains a constant temp. due to energy required to break H bonds
Define the terms "hydrophilic" and "hydrophobic"
Hydrophilic: The physical property of a molecule that is attracted to water
Hydrophobic: The physical property of a molecule that is repelled by water
Define the terms "cohesion" and "adhesion".
Cohesion: Water molecules attracted to one another
Adhesion: Water molecules attracted to other substances
Describe any other properties (not related to its polar nature) water has that makes it useful for life
Transparent to light - plants growing under water can get light for photosynthesis and aquatic animals can see underwater
List examples of how water is used from across the whole diversity of life (prokaryotes and eukaryotes; plants, animals and fungi; unicellular and multicellular organisms).
Supports - keeping plant cells turgid, the hydrostatic skeletons of earthworms
Lubrication - Joints such as elbow called synovial joints have sac of synovial fluid stopping bones rubbing against each other
Bouyancy - Whales couldn't be so big etc.
Swimming - When something pushes against water there is an equal reactive force propelling forward
Reactions - Photosynthesis, hydrolysis
High surface tension allows organisms to suspend themselves at/on the surface e.g. pond skaters
Ice floats as less dense so insulates water underneath where organisms can survive
Regulating temperature and reaction conditions etc. - sweating as well as high heat capacity
Using the "polar nature of water" explain the how water can dome above the level of the glass container it is in, the shape of the meniscus in a glass measuring cylinder and capillary action in a narrow glass tube.
Dome: Cohesion between water molecules causing surface tension due to hydrogen bonds
Meniscus: Adhesion to sides of container draws molecules up.
Capillarity: Cohesion between water molecules and adhesion to other molecules explains why water moves up narrow spaces. Important for water in xylem vessels.
Define the terms "monomer", "polymer", and "macromolecule".
Monomer: Individual molecules that make up a polymer
Polymer: Long-chain molecules composed of linked (bonded) multiple individual molecules (monomers) in a repeating pattern
Macromolecule: Large complex molecules with large molecular masses
Define the terms "dimer" and "oligomer"
Dimer: a molecule consisting of two identical molecules linked together
Oligomer: a polymer whose molecules consist of relatively few repeating units
Define the terms "condensation reaction" and "hydrolysis reaction"
Condensation reaction: a reaction between two molecules to form a larger molecule and the release of a water molecule. (opposite to hydrolysis)
Hydrolysis reaction: the breakdown of a molecule into two smaller molecules requiring the addition of a water molecule (opposite to condensation)
Define the terms "metabolism", "catabolic reaction", "anabolic reaction"
Metabolism: the chemical processes that occur within a living organism in order to maintain life
Catabolic reaction: reactions of metabolism that break molecules down into smaller units. These reactions release energy.
Anabolic reaction: reactions of metabolism that construct molecules from smaller units. These reactions require energy from the hydrolysis of ATP.
List the 4 main categories of biological molecule.
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic acids
Summarise the name of the building blocks, the name of the dimer, the name of the macromolecule, whether or not the macromolecule is a polymer, the name of the bond that links the building blocks together, the name of the reaction that joins the building blocks together, the name of the reaction that breaks the macromolecule apart, examples of the functions of the molecules and the elements that make up the molecules for carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids. Include examples of names of specific molecules where appropriate
Carbohydrates: monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides, they are polymers, glycosidic bond, condensation reaction, hydrolysis, respiration-cell wall-cell signalling etc.
Lipids: fatty acids and glycerol, (monoglyceride, diglyceride) and triglyceride, not a polymer, ester bond, condensation, hydrolysis, source of energy-membrane structure-hormones etc.
Proteins: amino acids, dipeptide, polypeptide, they are polymers, peptide bond, condensation, hydrolysis, transport molecules-enzymes-antibodies etc.
Nucleic acids: nucleotides, dinucleotide, polynucleotide, they are polymers, phosphodiester bond, condensation, hydrolysis, genetic material-protein synthesis etc.
Define the terms "single bond" and "double bond"
single bond: a chemical bond in which one pair of electrons is shared between two atoms
double bond: a chemical bond in which two pairs of electrons are shared between two atoms
State the elements present in carbohydrates
Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen
State the general formula of carbohydrates
(CH2O)n
Define the term "monosaccharide", "disaccharide" and "polysaccharide"
Monosaccharide: A single sugar molecule
Disaccharide: A molecule comprised of two monosaccharides joined by a glycosidic bond
Polysaccharide: A polymer made of many sugar (monosaccharides) monomers
Define the term "pentose sugar" and "hexose sugar"
Pentose - a monosaccharide composed of 5 carbons
Hexose - a monosaccharide composed of 6 carbons
Define the term "triose sugar" and name an example
Triose - monosaccharide composed of 3 carbons
E.g. glyceraldehyde
Describe what is meant by a "furanose ring" and a "pyranose ring"
Furanose ring - 5 membered ring e.g. fructose
Pyranose ring - 6 membered ring e.g. glucose
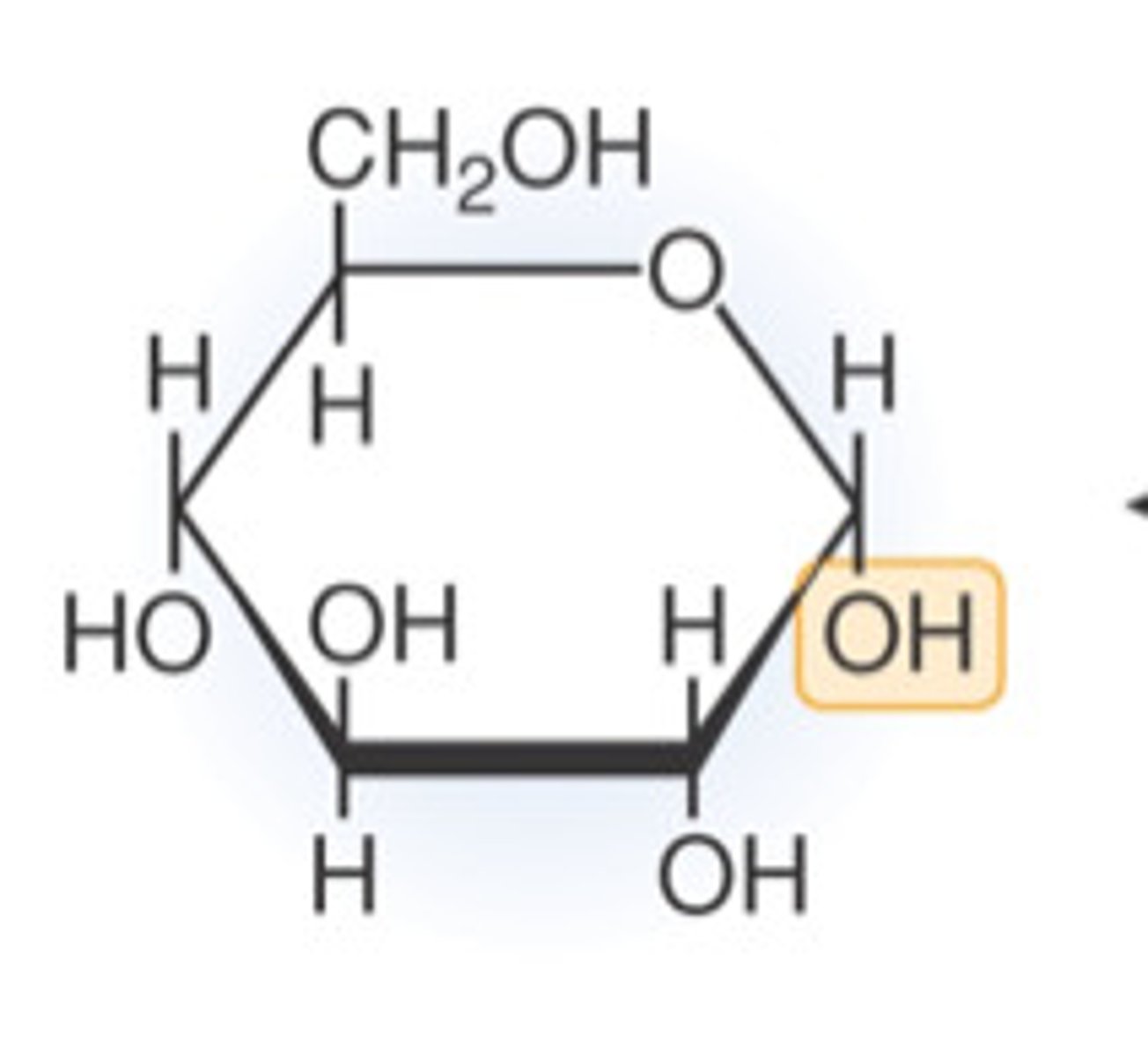
Draw a molecule of alpha-glucose
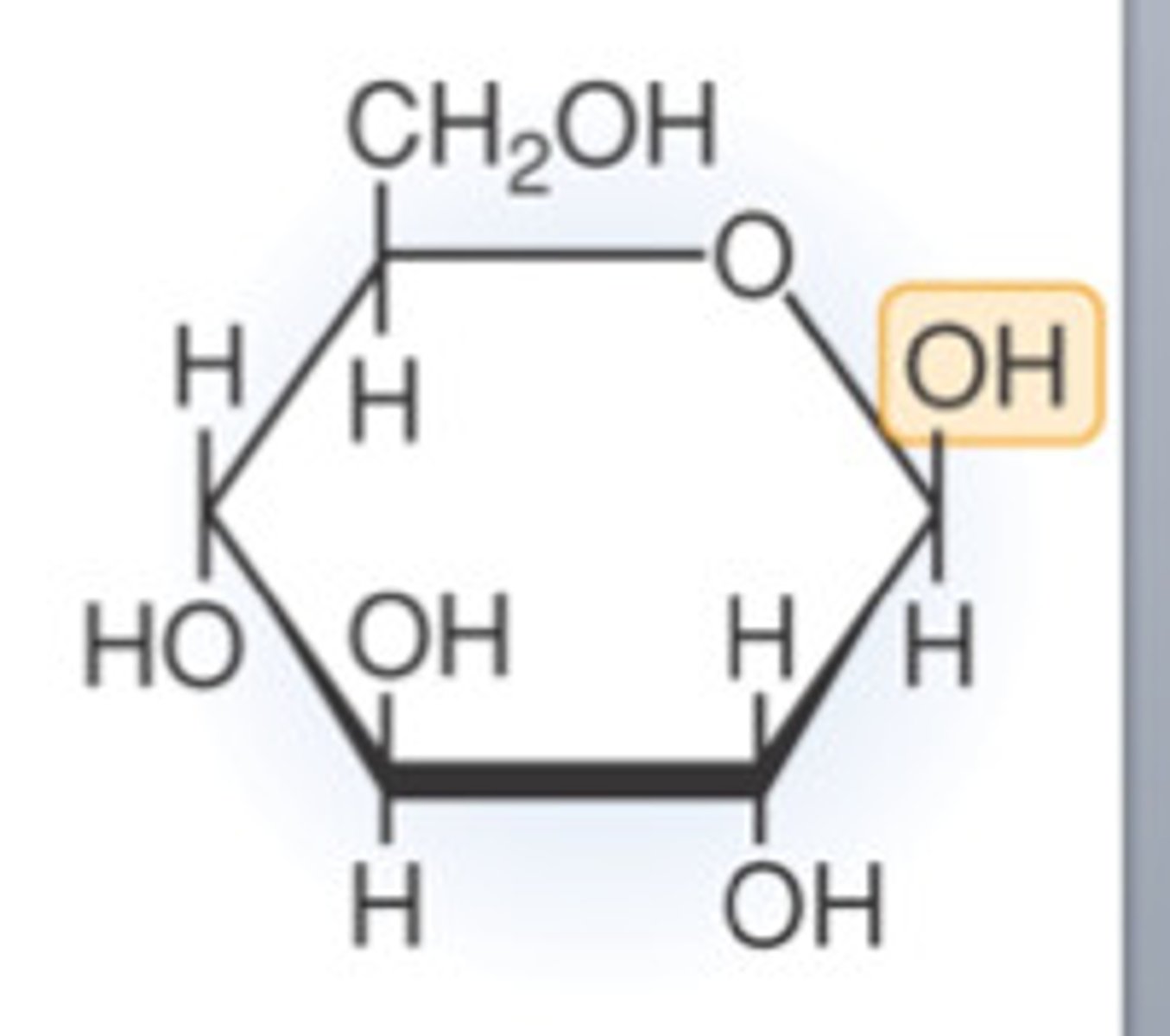
Draw a molecule of beta-glucose
Draw a molecule of ribose
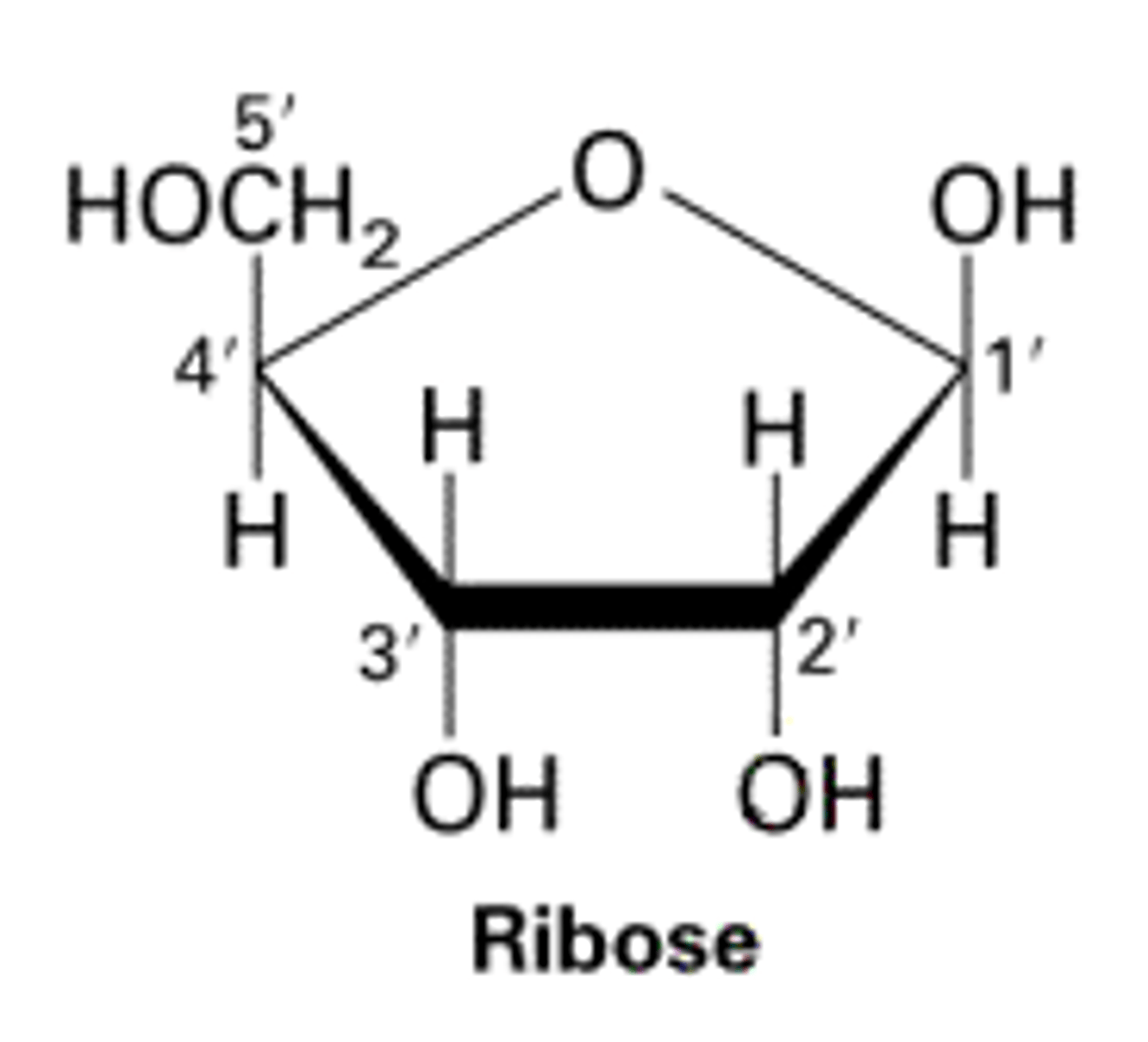
Define the term "isomer"
Molecules with the same molecular formulae but different structural formulae (same atoms but arranged differently)
Describe the difference between alpha- and beta-glucose
The hydrogen and hydroxyl groups on carbon 1 are reversed.
Describe the differences between alpha glucose and ribose
Glucose is pyranose but ribose is furanose
Glucose used in starch and glycogen
Ribose used in RNA
List 3 examples of disaccharides and for each state which monosaccharides they are composed of
Sucrose - alpha-glucose and fructose
Maltose - two alpha-glucose
Lactose - alpha-glucose and galactose
State the properties and functions of glucose, fructose, galactose, maltose, sucrose and lactose. For each also state where they occur.
Glucose - monosaccharide used in respiration and to make polymers such as starch
Fructose - hexose sugar commonly found in fruit
Galactose - another hexose sugar
Maltose - found in barley
Sucrose - found in sugar cane and beet
Lactose - found in milk
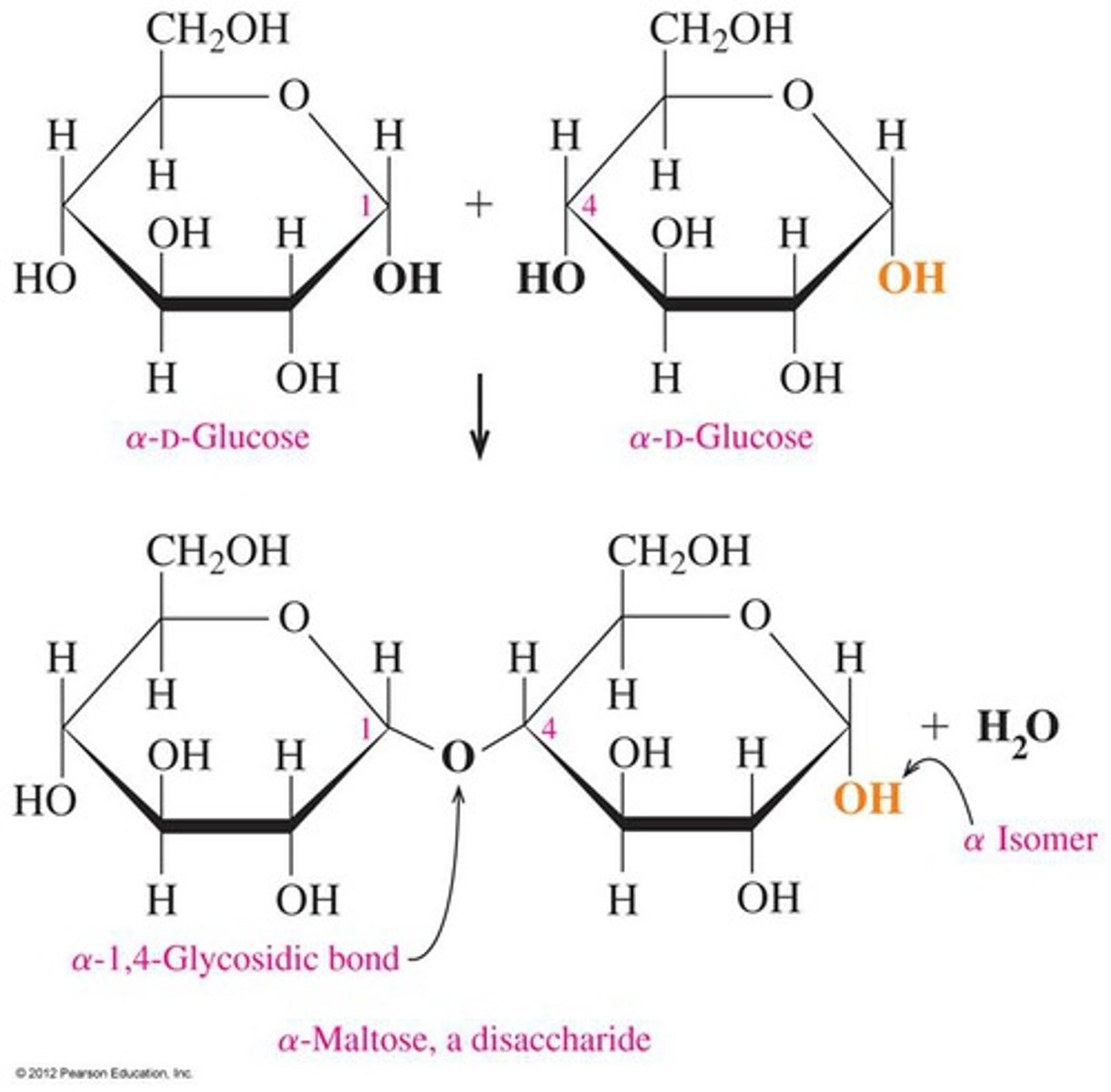
Draw a labelled diagram demonstrating how two molecules of glucose form a disaccharide in a condensation reaction, showing the location of a 1,4-glycosidic bond and from where a water molecule is generated
Condensation reaction involves hydroxyl groups on carbons 1 and 4. Water is lost and the bond is formed by the remaining oxygen atom.
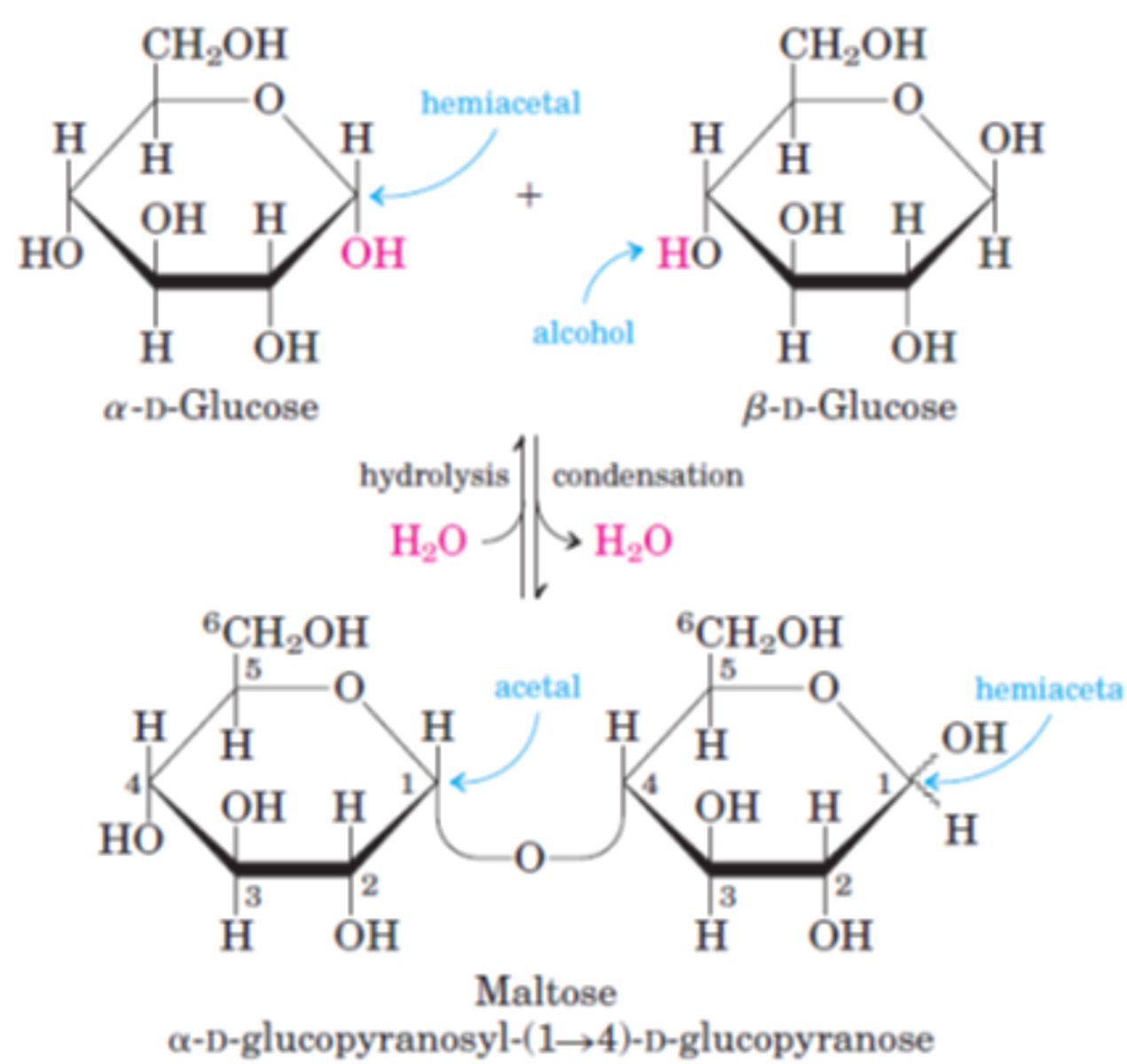
Describe, using a diagram, how hydrolysis of maltose occurs and why water is needed
Glycosidic bond is broken by the addition of water. Catalysed by enzymes at 35-40°C or by being boiled with an acid for acid hydrolysis
Explain why alpha-glucose links together to form starch whereas beta-glucose links together to form cellulose
Due to the arrangement of the hydrogen and hydroxyl groups on carbon-1...
The 1-4 glycosidic bonds using alpha mean all the monomers are the same way up, but with beta each is rotated 180° from the last.
List the two different polysaccharides that make up starch.
Amylose (1-4 bonds only) and Amylopectin (mainly 1-4 but some 1-6)
Explain with the use of diagrams why glycosidic bonds are called 1,4 or 1,6
Whether they are between the OH groups on carbons 1 and 4 or 1 and 6.
Describe the structure of a cellulose fibre
Several cellulose molecules produce a microfibil
Several microfibrils hydrogen bonded together produce a macrofibril
Macrofibrils are laid down in layers to form cell wall etc.
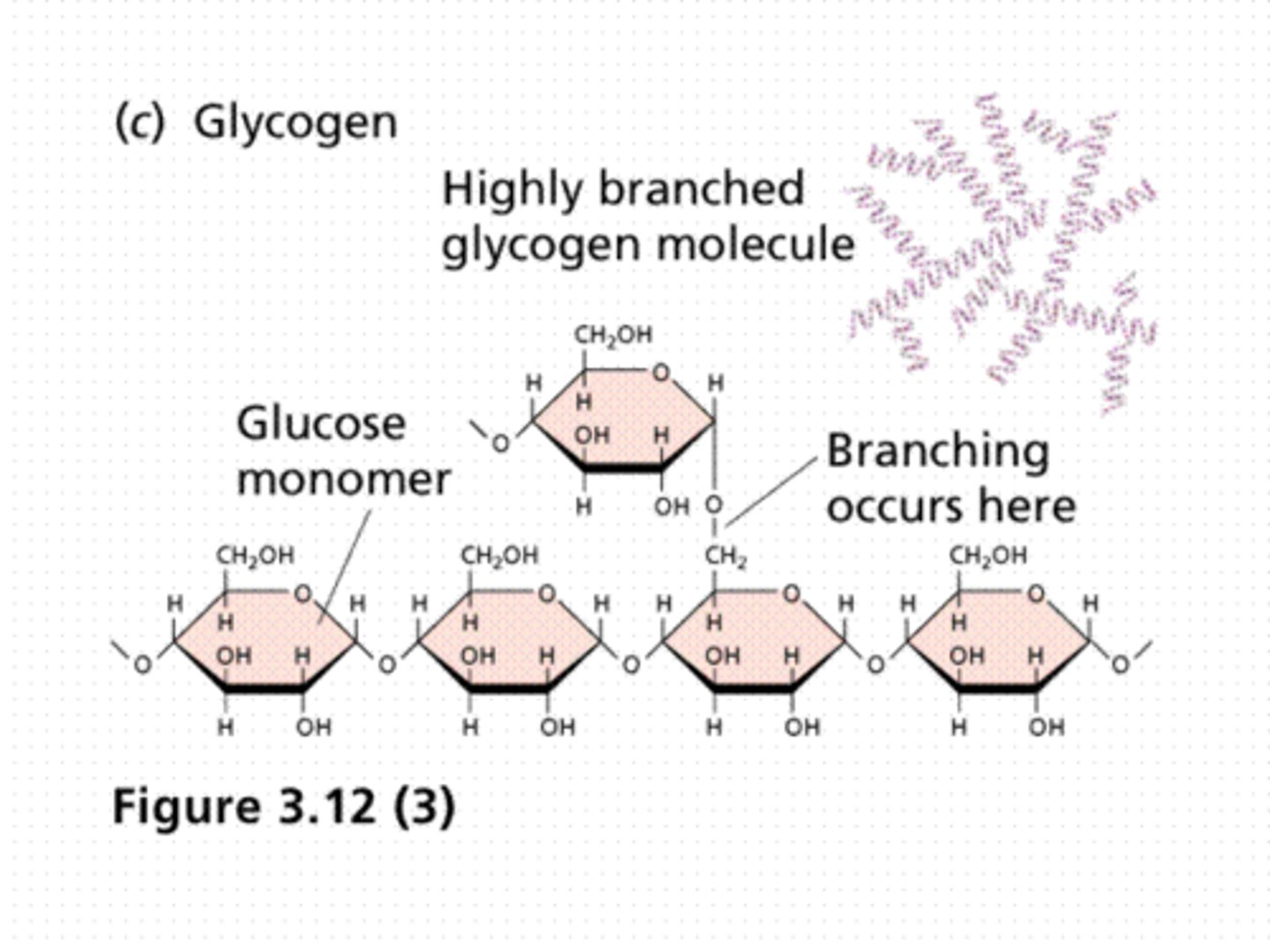
Describe and explain the properties and functions of starch, glycogen and cellulose
Starch: Coils into helix, amylase unbranched and amylopectin branched. Compact and insoluble so ideal for storage - food store in plants
Glycogen: More branched than amylopectin, coils into helix. Compact and insoluble so ideal for storage - animals and fungi
Cellulose - Unbranched, does not form helix - forms layers of fibres to give great strength to cell wall
State the elements present in lipids (and the additional element needed to make phospholipids)
Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen
Phophorus
State the 3 categories of lipids (or lipid derived molecules)
Triglycerides, Steroids and Phosopholipids
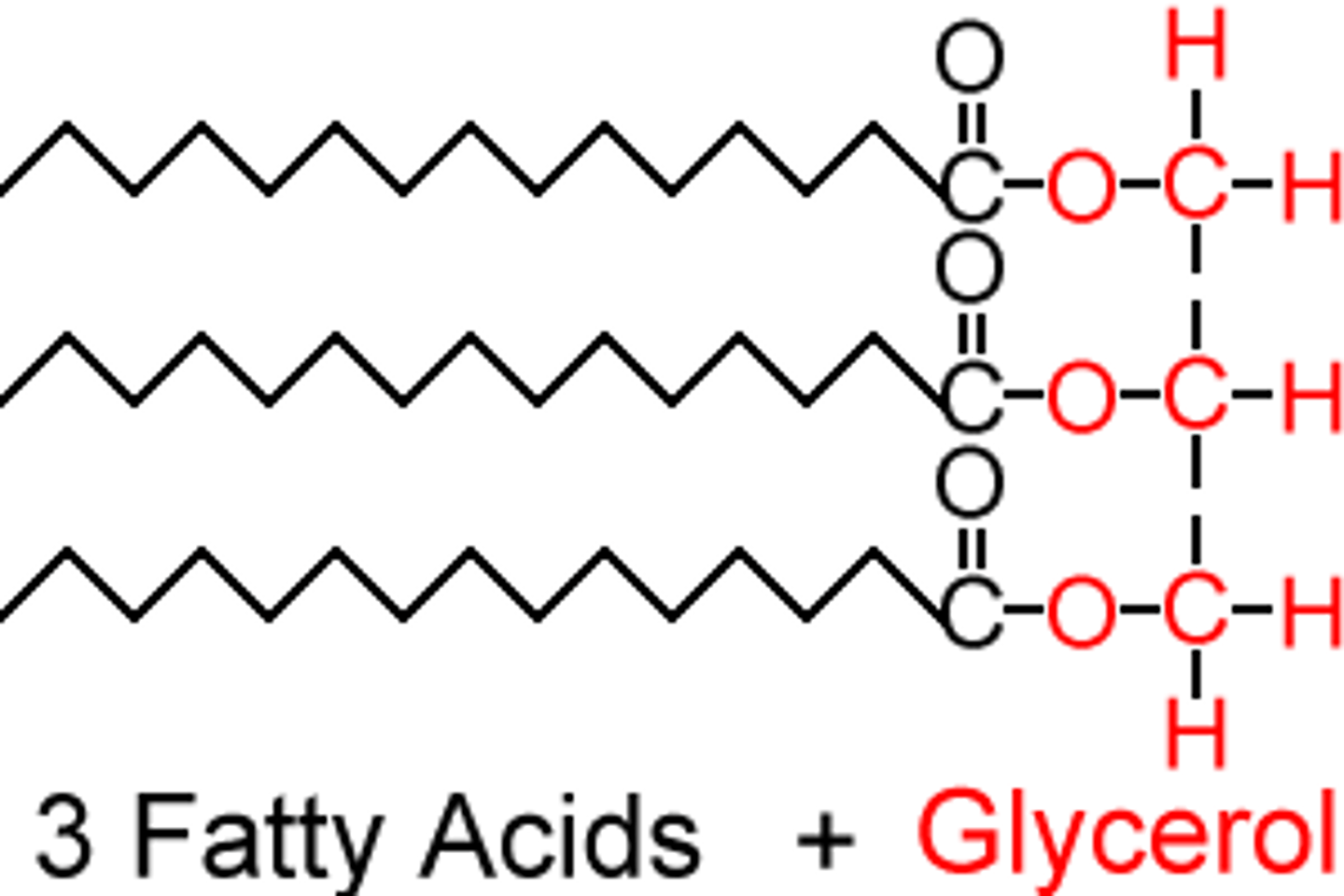
Draw a labelled diagram showing the basic structure of a triglyceride.
3 fatty acids joined to a glycerol
Draw diagrams to show the difference between saturated, monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids/triglycerides.
Unsaturated fatty acids have kinks in the chain due to the double bonds (1 for mono, several for poly)
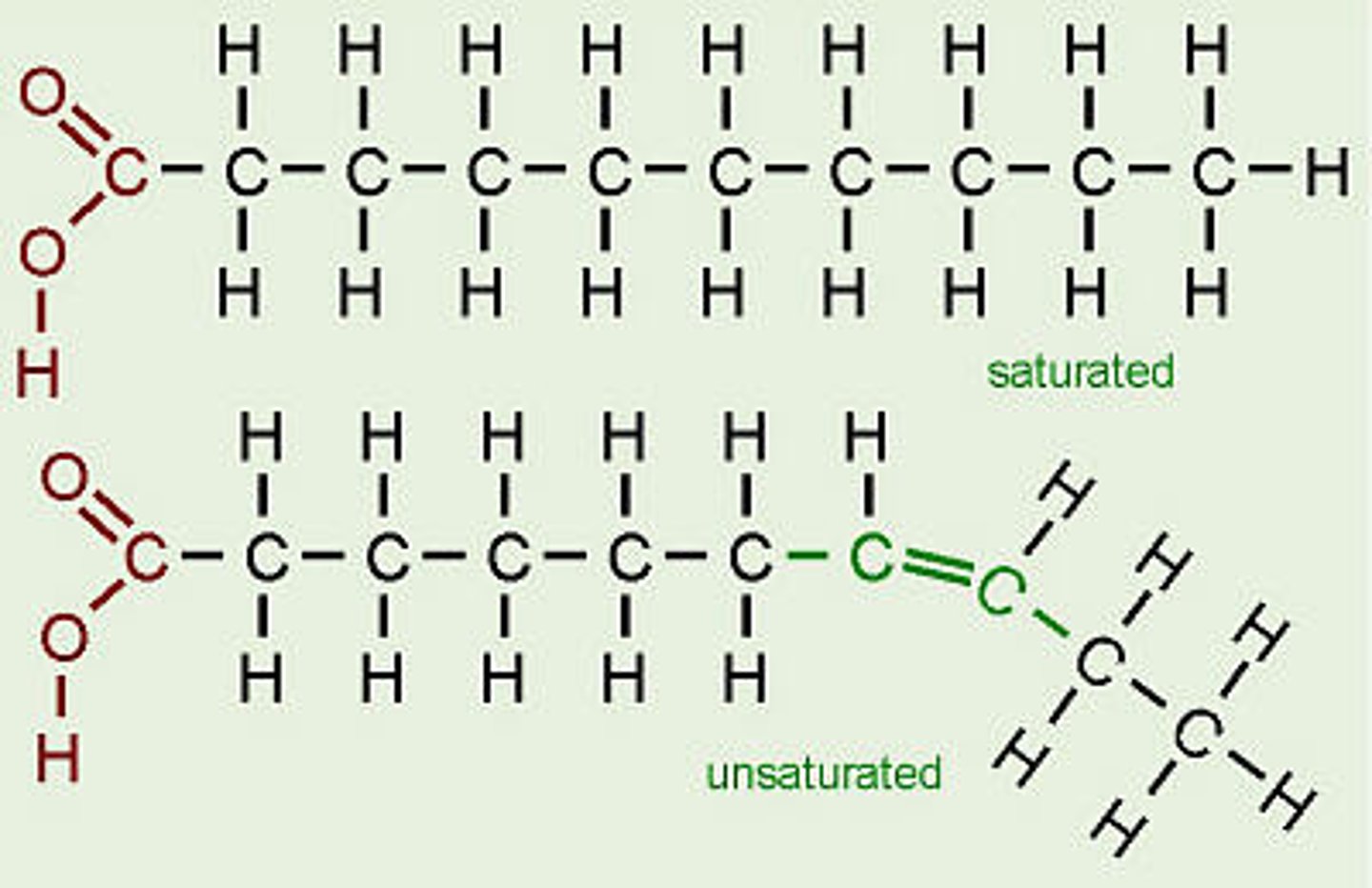
Explain why saturated triglycerides tend to be solid (fats) at room temperature whereas unsaturated triglycerides tend to be liquid (oils).
Saturated fatty acids can pack more tightly as do not have kinks and therefore have higher melting points than unsaturated which are more spread out so melt at lower temperatures.
State the difference between the triglycerides found in non-fish animals and those in plants and fish.
Plant and fish triglycerides tend to be unsaturated whereas other animal fats tend to be saturated
Draw a labelled diagram showing the basic structure of a phospholipid.
Phosphate head with fatty acid tails
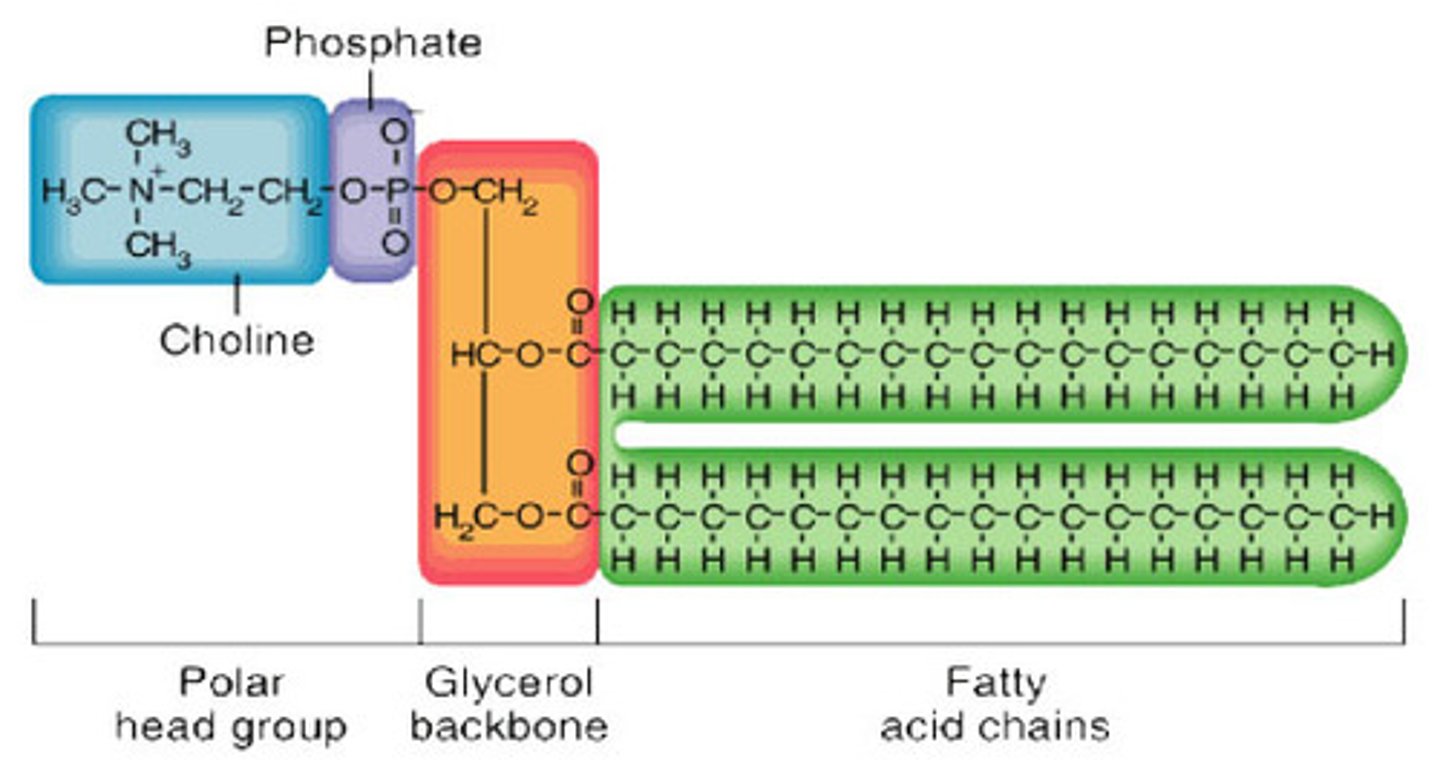
State the property that each end of the phospholipid has.
Head is hydrophilic and fatty acid tails are hydrophobic
Describe the difference between a triglyceride and a phospholipid.
Phospholipids have a phosphate group in place of one of the fatty acids
Draw a diagram to show how a triglyceride is formed and broken down.
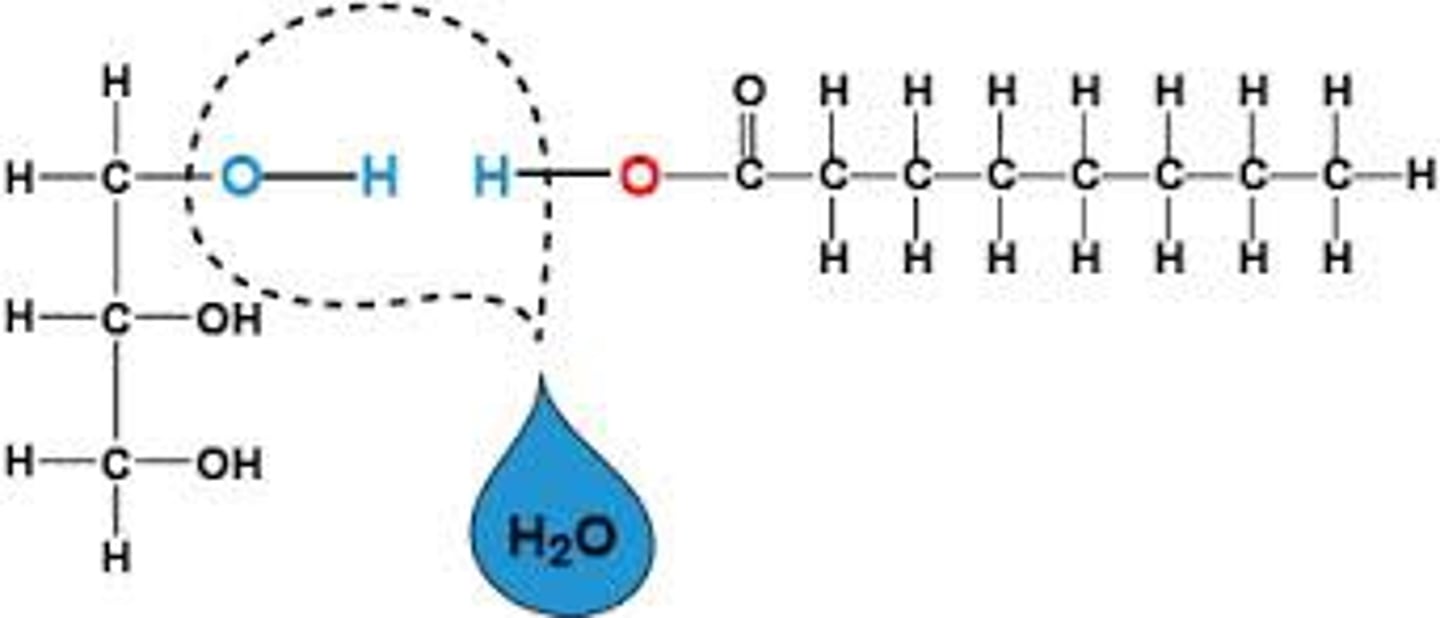
Name the bond that holds the building blocks of a triglyceride together
Ester bond
State the names of the reaction that forms triglycerides and the reaction that breaks them apart
Form by condensation
Broken down by hydrolysis
Explain how an ester bond is formed between glycerol and a fatty acid
Called esterification
Reaction between hydroxyl of glycerol and carboxyl of fatty acid, expelling water
State the number of water molecules produced in the production of one triglyceride
3
State the products of digestion of a triglyceride (include partial digestion) and state what would happen to the pH of the solution (and why)
Produces fatty acids and glycerol or partially only removes some of the fatty acids to produce a monoglyceride etc.
Due to fatty acids, pH would decrease (more acidic)
Describe the structure of sterols/cholesterol
Base nucleus of 4 connected organic rings
They differ from each other due to different side groups
List the functions of triglycerides (5 functions), phospholipids (2 functions) and cholesterol (2 functions) and relate these functions to the properties of the molecules
Triglycerides - Energy store, thermal insulation, cushioning for internal organs, buoyancy, waterproofing
Phospholipids - Membranes, myelin sheaths
Cholesterol - Membranes, hormones (made by adding different side groups)
Due to hydrophobic qualities useful for waterproofing
Explain why triglycerides store more energy per gram than carbohydrates
They require more oxidation to be broken down into CO2 and O2 so release more energy although it takes longer.
Explain how phospholipids form a membrane
Phopholipid bilayer
Two layers with the hydrophobic fatty acid tails sandwiched on the inside and the hydrophilic heads on the outside
Describe how the presence of cholesterol affects the properties of cell membranes
Regulates membrane fluidity
Draw and label a diagram of an amino acid
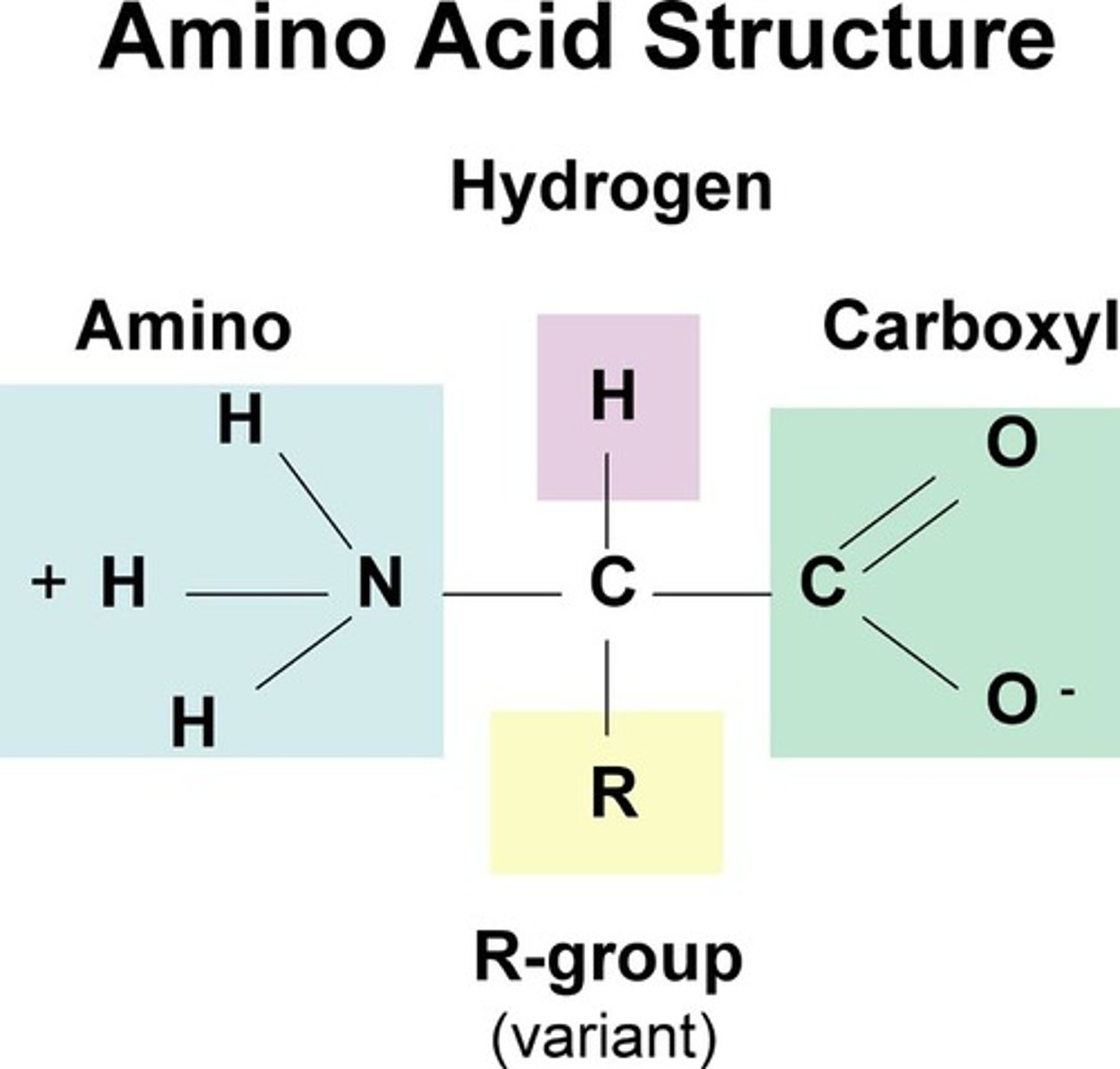
State how many amino acids occur in life
20
Describe the different types of amino acid in life
Nonpolar hydrophobic
Polar hydrophilic
Polar hydrophilic basic (positively charged)
Polar hydrophilic acidic (negatively charged)
Draw a labelled diagram demonstrating the condensation and hydrolysis of peptide bonds. Draw a dipeptide and label the peptide bond.
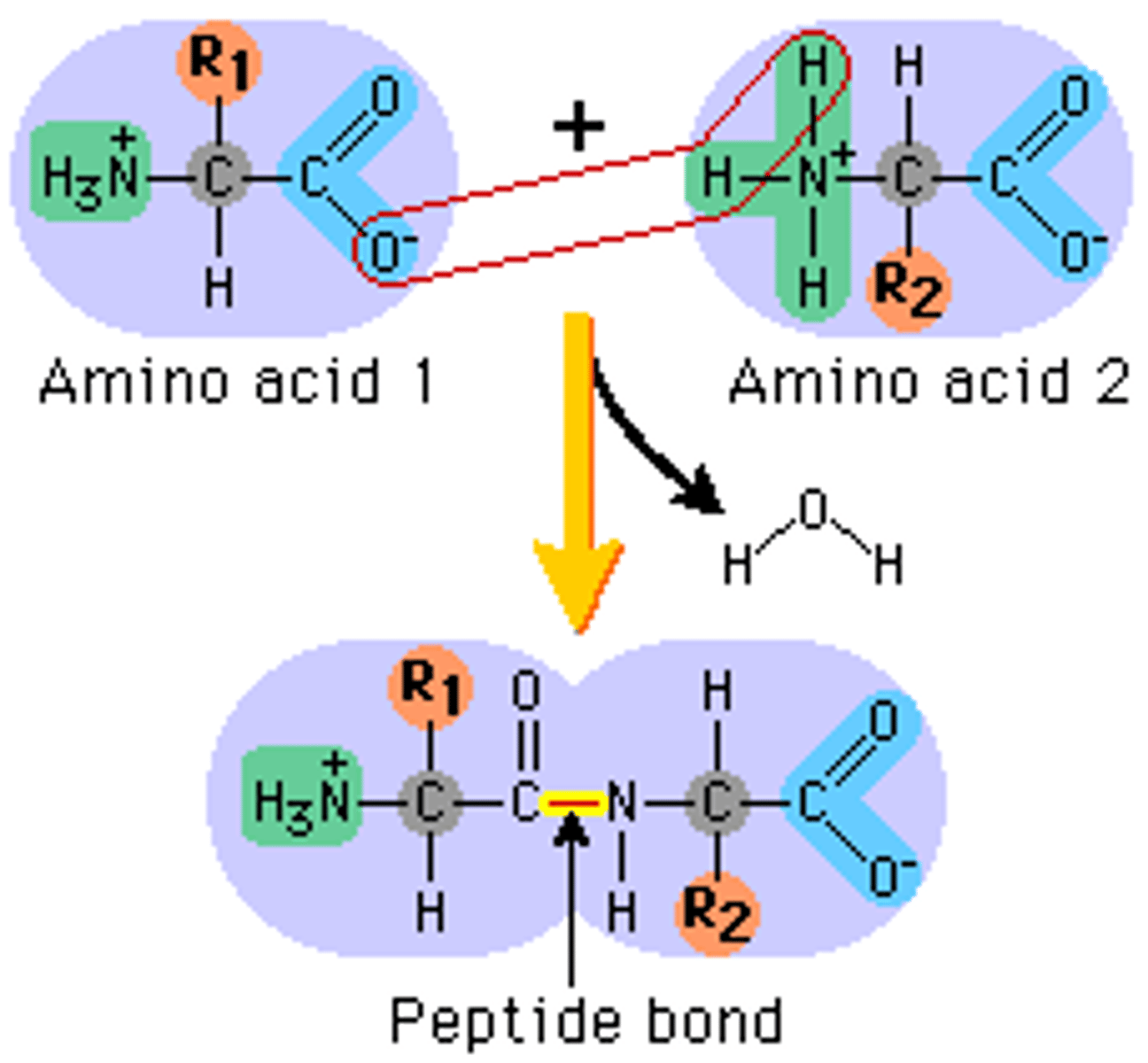
Explain how the variety of amino acids leads to a wide range of dipeptides and very quickly to an incredible variety of polypeptide chains
20 amino acids therefore 400 dipeptides as the order does change the molecule
There are 20^3 tripeptides and so on giving rise to incredible variation in polypeptides
Define the terms "polypeptide chain" and "protein"
polypeptide chain - chains of three or more amino acids
protein - one or more polypeptides arranged as a macromolecule
Describe how one end of a polypeptide chain differs from the other end
One end is the C terminal which is the carboxyl end and the other is the N terminal, the amine group.
Define the term "primary structure" of a protein and describe how it is held together
The number and sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide is its primary structure. Each amino acid is bonded to the next by peptide bonds.
Define the term "secondary structure" of a protein, describe the two different types and describe how the secondary structure is held in place
All or part may fold into a secondary structure most commonly and alpha-helix or a beta-pleated sheet. To produce one of these there needs to be a regular repeating pattern of amino acids. The structures are held together by hydrogen bonds between N-H groups and C=Os.
Define the term "tertiary structure" of a protein, and describe how it is held in place (include all the different possible bonds)
The compact 3-D shape adopted by most polypeptides. These molecules are called globular. The R groups form the bonds that hold the structure in place.
Hydrogen bonds form between slightly charged R groups
Ionic bonds form between R groups carrying opposite charges
Disulphide bonds or bridges form between the sulfur containing R groups of two cysteine amino acids - strong covalent bond
Hydrophobic interactions - protein folds so that hydrophobic R groups lie in centre of the molecule away from the aqueous environment.
Explain how the primary structure of a protein determines its tertiary structure
As tertiary structure depends on the R groups and therefore which amino acids are present and in which order it is highly dependent on primary structure.
Define the term "quaternary structure" of a protein, and describe how it is held in place (include all the different possible bonds)
A protein with quaternary structure contains two or more polypeptide chains bonded together which have no function on there own and only form a functional molecule when bonded. Bonds that hold tertiary structure also hold quaternary; hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds, disulfide bridges and hydrophobic interactions
Define the terms "globular protein" and "fibrous protein"
globular protein - spherical, water soluble proteins
fibrous protein - long, insoluble, structural proteins
Define the terms "prosthetic group" and "conjugated protein"
prosthetic group - non-protein component of a conjugated protein
conjugated protein - A protein that is joined to a non-protein group (prosthetic group). Both parts are needed to function.
Describe an example of a conjugated protein, an enzyme and a peptide hormone and for each identify key structural components, properties and functions.
Haemoglobin - each of the four polypeptide chains is bonded to a haem group. It carries oxygen.
Catalase - quaternary protein with four heam groups. The presence of iron II ions allows it to calayse break down of hydrogen peroxide which is a harmful waste product of metabolism
Antidiuretic hormone - Regulates the body's retention of water by increasing water absorption of kidney's collection duct
Give 3 examples of fibrous proteins
Keratin, Elastin, Collagen
Compare the structure, properties, location and functions of collagen, keratin and elastin
Collagen - Connective tissue found in skin, tendons, ligaments and the nervous system. £ polypeptides wound round each other to form a rope like structure
Keratin - Hair, skin and nails. Many sulphur containing amino acids means many disulphide bridges which make it very strong. Nails more disulphide bridges - less flexible
Elastin - Found in elastic fibres in blood vessels and alveoli allowing them to expand and return to normal as needed. Made by linking many soluble tropoelastin protein molecules which act as little springs together to form an isoluble macromolecule.
Compare the structure, properties and functions of globular and fibrous proteins
Globular - Spherical and water soluble due to folding so that hydrophobic regions are inside ut hydrophilic regions are on the outside.
Fibrous - Long, strong, insoluble molecules. Tend to contain a limited range of amino acids with small R groups and arranged in a pretty regular pattern containing many hydrophobic amino acids.
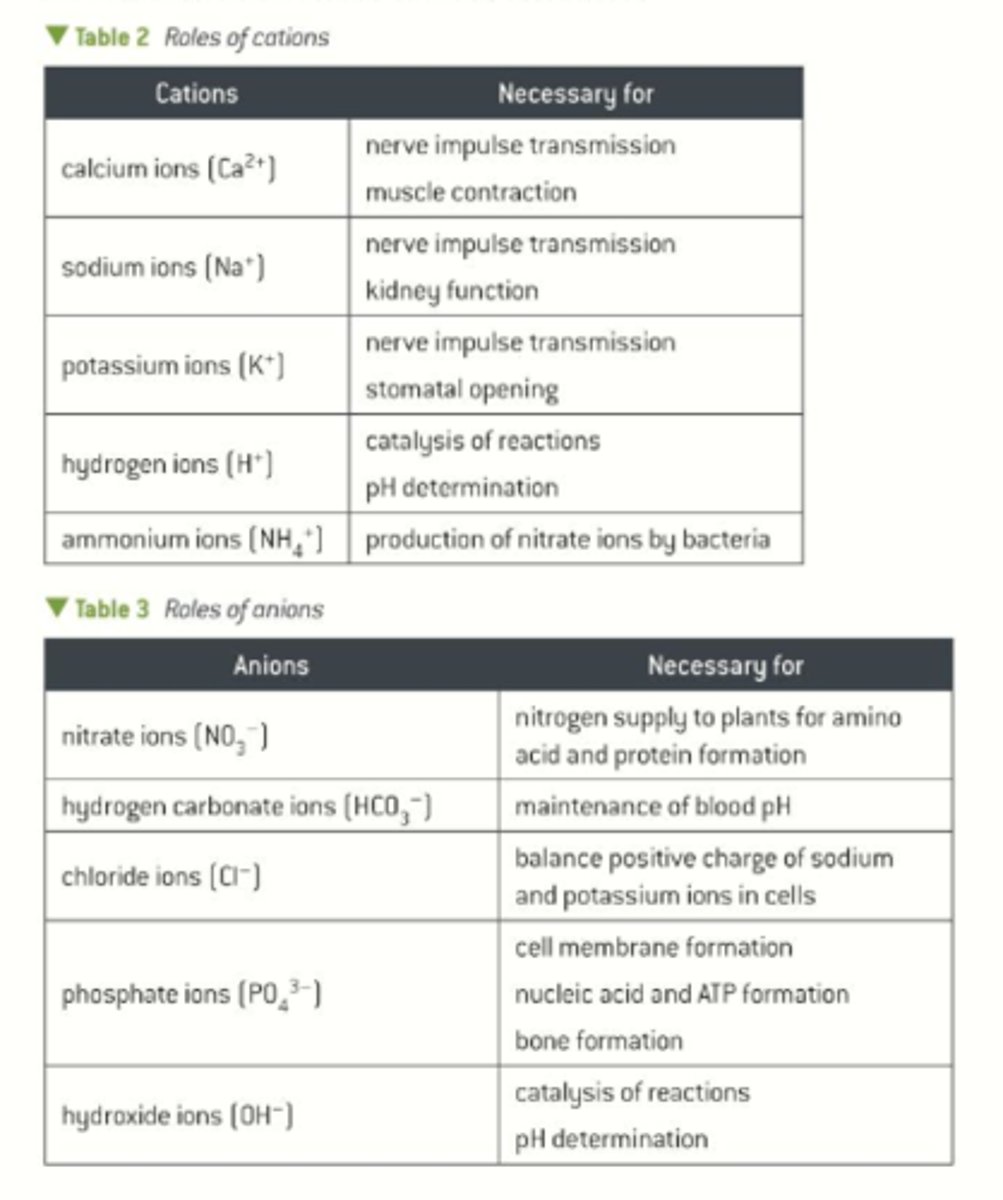
Define the term "inorganic", "cation" and "anion"
Inorganic - relating to or denoting compounds which are not organic (broadly, compounds not containing carbon)
cation - positive ion
anion - negative ion
Draw a table showing the chemical symbol and at least one example of a biological process they are involved in for: calcium ions, sodium ions, potassium ions, hydrogen ions, ammonium ions, nitrate ions, hydrogen carbonate ions, chloride ions, phosphate ions and hydroxide ions.