Hemolytic Anemias (Chapter 9)
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Defects of the RBC leads to:
Premature destruction & hemolysis
Hemolytic anemias
Disorders associated with both: intrinsic (intracorpuscular) defects of the RBC and extrensic (extracorpuscular) abnormality
Intracorpuscular
Caused by defect inside the RBC
Extracorpuscular
Caused by factors outside the RBC
The most frequent tests used to reflect increased red cell destruction are:
Unconjugated (indirect) bilirubin
Serum haptoglobin (binds free Hgb in blood)
Coombs’ test
Establish cause of hemolysis
Coombs’ test - positive means:
The hemolysis is caused by the immune system (antibodies)
Coombs’ test - negative means:
Hemolysis is not caused by antibodies. Further divided into:
Smear positive
Smear negative/nonspecific
Smear-positive
Abnormal RBC morphology visible; hemolysis due to RBC membrane damage/fragmentation
Smear-negative/nonspecific
No clear smear findings, other causes like enzyme defects
Hereditary spherocytosis (HS)
Decreases amounts of spectrin, ankyrin, AE1, or protein 4.2
Patients with HS who test for osmotic fragility should show
Increased
Patients with HS who test for Glycerol lysis should show
Increased
Patients with HS who test for Eosin 5’Maleimide Flow Cytometry should show:
Lower fluorescence
Hereditary Elliptocytosis is characterized by:
The presence of elliptical RBCs
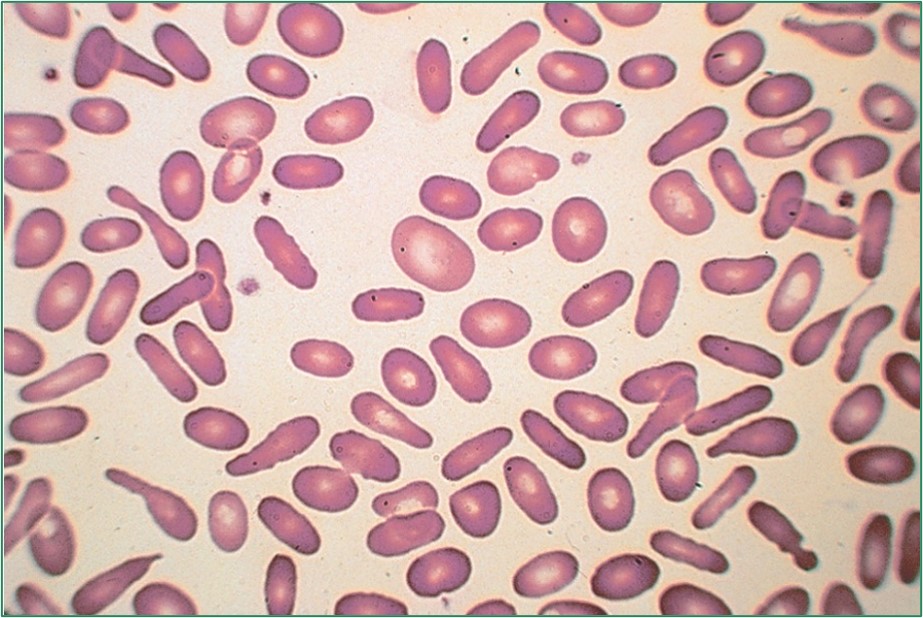
What disease could cause this?
Hereditary elliptocytosis
Southeast Asian Ovalocytosis (SAO)
Very common in Melanesian & other Southeast Asian population groups due to the protective effect toward malarial parasites
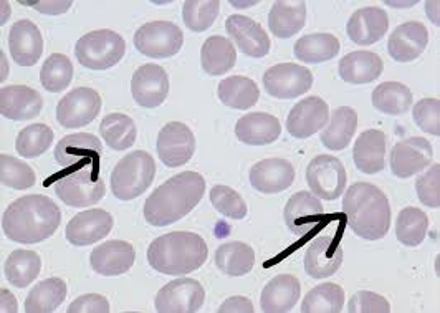
What condition could cause this?
Southeast Asian Ovalocytosis
Alterations in the permeability of the RBC membrane to cations affect:
RBC hydration
Hereditary hydrocytosis (stomatocytosis)
RBCs are swollen
Hereditary Xerocytosis
RBCs are markedly dehydrated
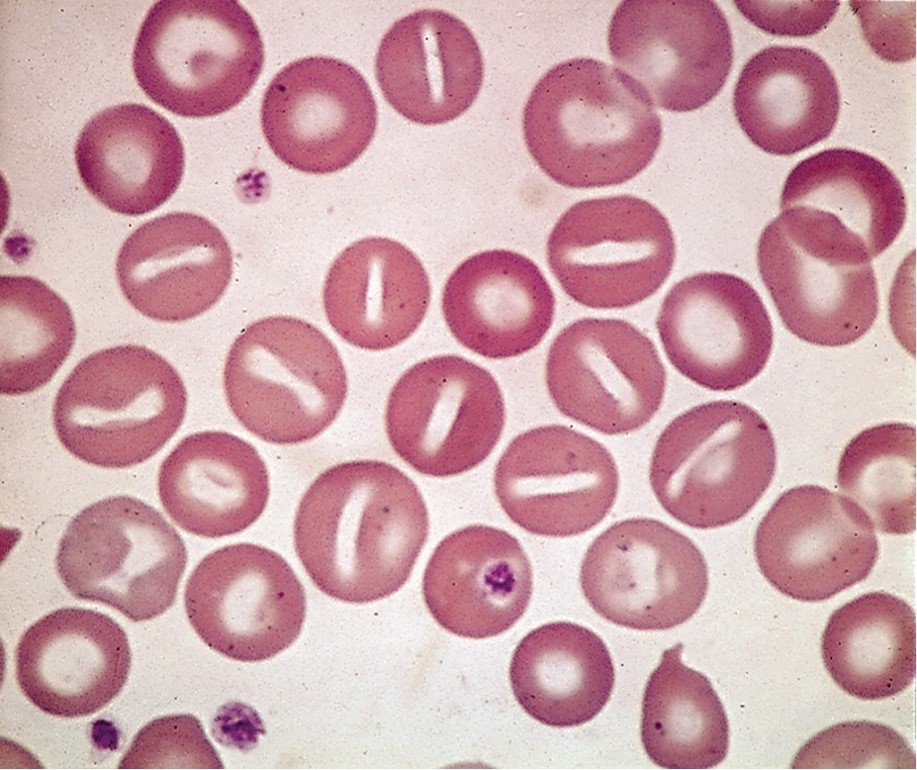
What condition could possibly cause this?
Hereditary hydrocytosis
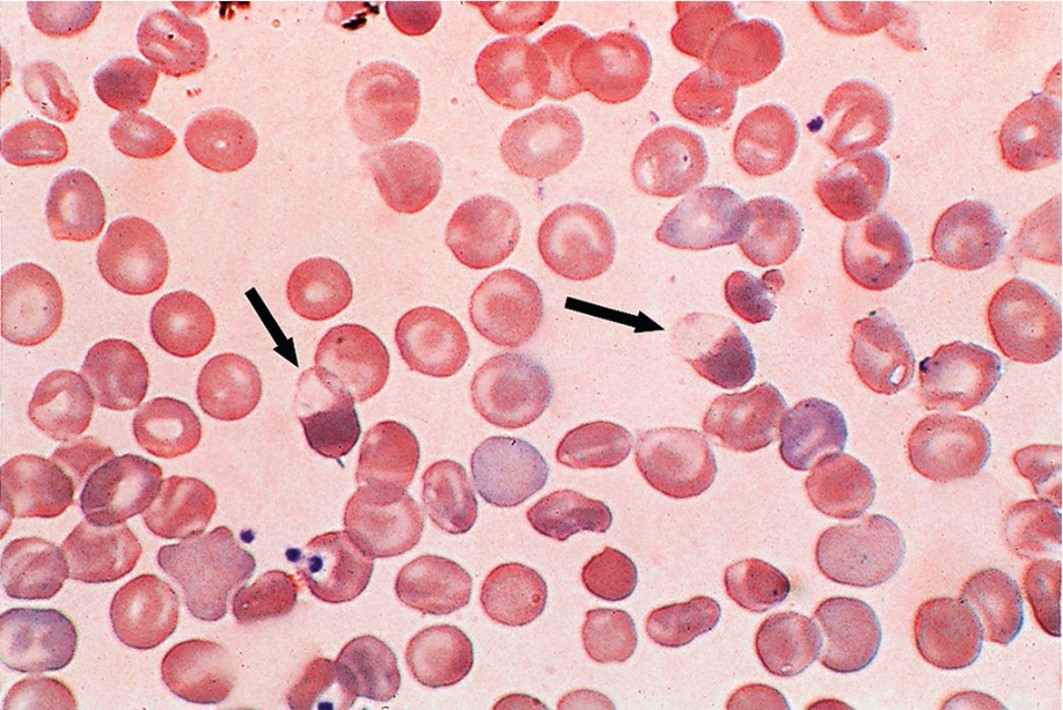
What condition could possibly cause this?
Hereditary xerocytosis
Passive sodium leak, increases the sodium & water content; causes macrocytosis is a characteristic of:
Hereditary hydrocytosis
The presence of stomatocytes can indicate:
Hereditary hydrocytosis
A smear with target cells present can possibly indicate:
Hereditary xerocytosis
Uneven Hgb distribution (caused by Hereditary Xerocytosis)
Cells with hemoglobin concentrated in one part of the cell (puddled)