ANSC 325 - Midterm 2 - Lecture 4
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Head and mental status
Gait and posture
Neck and forelimbs
Trunk
Tail and anus
Neuro exam should assess these 5 categories
Sensory
Integration
Motor systems (upper vs lower motor neurons)
Divisions of neuro examination should include (3)
Upper Motor Neuron
Brain to spinal cord in CNS
Weakness or paralysis
Spasticity
Increased muscle tone (hypertonia)
Over-response reflexes (hyperflexia)
Lower Motor Neuron
Spinal cord to structure (muscle, organ, etc.)
Decreased of absent muscle tone (hypotonia or atonia)
Decreased or absent or areflexia)
Muscle atrophy
Mentation and alertness
Cranial nerve function
Neurological exam - Head and Mental Status assesses (2)
Alert
Depression
Stupor
Coma
Four consciousness levels
Alert
Level of Consciousness
Aware of environment-normal
Aware and awake
Depression
Level of Consciousness
Awake but unresponsive to the environment
Stupor
Level of Consciousness
Asleep except when aroused: needs to be aroused by strong (i.e. noxious) stimulus: pain, loud noise, bright light
Asleep, but will wake up
Coma
Level of Consciousness
Deep state of unconsciousness and animal can not be aroused with noxious stimuli
CN II
Cranial Nerve - Optic
Related to pupillary reflex
Function: vision
Assessment: menace response and pupillary light reflex, lesions cause blindness and loss of pupillary light reflex

CN III
Cranial Nerve - Oculomotor
Related to pupillary reflex
Function: pupillary constriction, extra ocular muscles
Assessment: pupillary light reflex, pupil size, eye position, lesions cause ventral strabismus, loss of PLR

CN VIII
Cranial Nerve - Vestibulocochlear
Related to head dropping, vestibular disease
Function: posture, balance, hearing
Assessment: head and eye position (strabismus) and nystagmus, lesions cause nystagmus, head tilt, balance loss, deafness
CN VII
Cranial Nerve - Facial
Related to facial nerve tone and lip dropping
Function: motor to muscles of facial expression
Assessment: facial symmetry, palpebral blink, ear and muzzle/lip movement, lesion causes facial paralysis, loss of palpebral reflex, blink, dry eye

CN XII
Cranial Nerve - Hypoglossal
Related to difficulty eating and drinking and not pulling tongue back when pulled
Function: motor to tongue
Assessment: tongue stretch and symmetry, lesions cause atrophy and paralysis
CN IX
Cranial Nerve - Glossopharyngeal
Related to difficulty swallowing, saliva/mucous coming out
Function: Sensory and motor to pharynx
Assessment: Ability to swallow, lesions cause dysphagia and displaced soft palate
CN X
Cranial Nerve - Vagus
Related to difficulty swallowing, saliva/mucous coming out
Function: sensory and motor to pharynx and larynx
Assessment: ability to swallow, laryngeal movement, lesion causes dysphagia, laryngeal paralysis, displaced palate
Standing Sway Test
Test of posture during neurological exam
apply pressure of the shoulder: Horse should always maintain balance initially leaning into the examiner, then the horse should step away
Should be resistant and come back to original position
Thoracic limb test
Test of posture during neurological exam
lift thoracic limb and force horse to hop on the down leg: some examiners consider this a test dangerous to both owner and the horse
Take front limb and lift, unstable
Not very safe

Tail pull test
Test of posture during neurological exam
pelvic limb weakness
Should be able to readjust back

0
Modified Mayhew Scale - Grade __
No neurological deficits
1
Modified Mayhew Scale - Grade __
Neurological deficits just detected at normal gait, but worsened by backing, turning, loin pressure, or neck extension
2
Modified Mayhew Scale - Grade __
Neurological deficits easily detected at the walk and exaggerated by backing, turning, loin pressure, or neck extension
3
Modified Mayhew Scale - Grade __
Neurological deficits prominent at the walk with a tendency to buckle or fall with backing, turning, loin pressure, or neck extension
4
Modified Mayhew Scale - Grade __
Stumbling, tripping, and falling spontaneously at a normal gait
5
Modified Mayhew Scale - Grade __
Horse recumbent
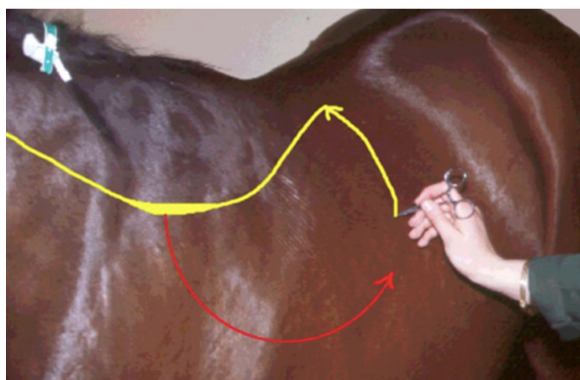
Cutaneous trunci reflex
Part of trunk part of neurological exam
Responses of spinal reflexes between thoracic nerve of the brachial plexuses and CN8-T1
Localize spinal cord injuries
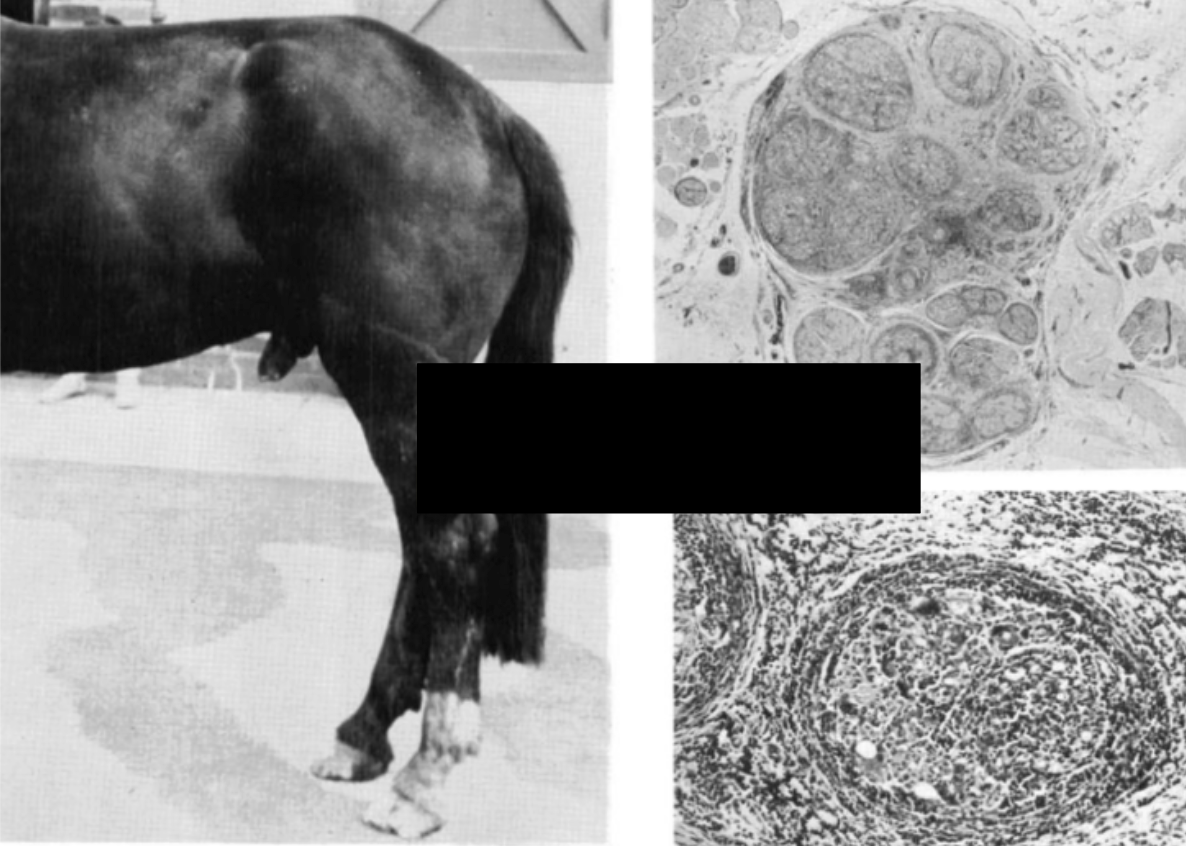
Cauda Equina Syndrome (Gegenerative Lumbosacral Stenosis)
Penis extending - not retracted in prepuce
Backend dropped (tail head dropped)
Dying and dead ganglion
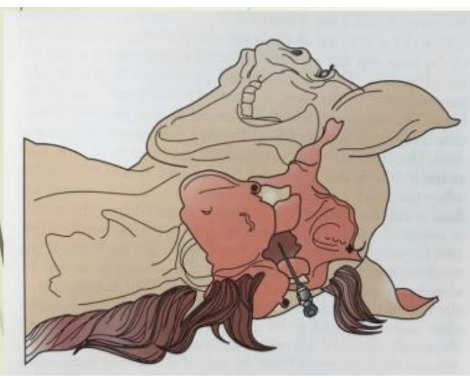
Cerebrospinal puncture
Collection fluid from subarachnoid space- indication of inflammation, infection, neoplasia, hemorrhage within the brain and spinal cord
2 sites:
Lumbosacral
Atlantooccipital
Lumbosacral
Site of Cerebrospinal Puncture
Sedate (standing) horse
Base of spine
Below foramen magnum
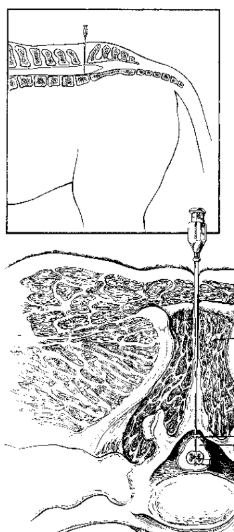
Atlantooccipital
Site of Cerebrospinal Puncture
Anesthetized horse
Higher up
Where spinal cord is leaving the skull
Above foramen magnum
Riskier