ANA300 - Brainstem and cranial nerves
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
In both the brainstem and spinal cord, grey matter is ___ and white matter is ___
deep, superficial
In both the brainstem and spinal cord, white matter consists of axons carrying sensory information _____, and motor information ________
rostrally, caudally
While grey matter in the spinal cord is a ________, grey matter in the brainstem is ______
continuous column, broken up into a discontinuous series of functionally specialized nuclei
Both brainstem and spinal cord subserve ___ and ___ functions
somatic, autonomic
Unlike the spinal cord, the brain stem subserves ____ and contains a ______ responsible for the maintenance of ____ and ____
special senses, reticular formation, vital functions, arousal
Descending fibre tracts in the brainstem carry _____ from the cerebral cortex to the spinal cord controlling ______: _______
voluntary output, contralateral body, corticospinal tract
Descending fibre tracts carry voluntary output from _____ to _____ controlling (contralateral, ipsilateral, bilateral) ____: _______
cerebral cortex, brainstem, face, corticobulbar tract
Descending fibre tracts also made of involuntary tracts that modulate
Posture, muscle tone, balance (vestibulospinal tract)
Autonomic functions (hypothalamus)
Ascending fibre tracts from the spinal cord to the ____ transmit somatosensory info destined for ______
thalamus, conscious appreciation in the cerebral cortex
Ascending fibre tracts from the spinal cord to the _____ transmit _______ input from muscles and joints
cerebellum, subconscious proprioceptive input
Peduncles:
white matter bundles
Paired superior cerebral peduncles join the ____ and _____
midbrain, cerebral hemispheres
3 paired cerebellar peduncles join the ____ and _____
brainstem, cerebellar hemispheres
A & B
A: Diencephalon
B: Optic nerve
C-F
C: Midbrain
D: Cerebral peduncles
E: Occulomotor nerves
F: Trochlear nerves
G-K
G: Pons
H: Trigeminal nerves
I: Abducens nerves
J: Facial nerves
K: Vestibulocochlear nerves
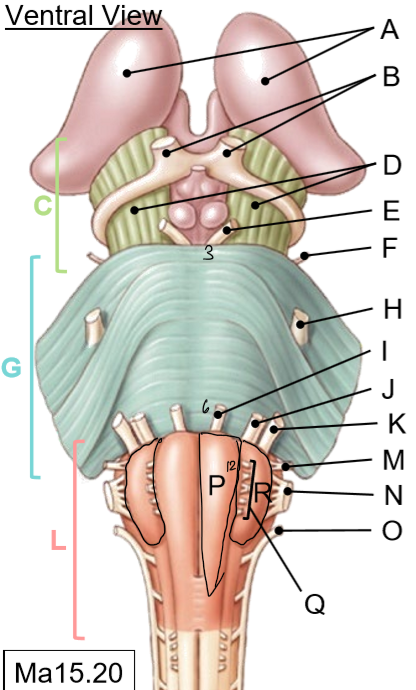
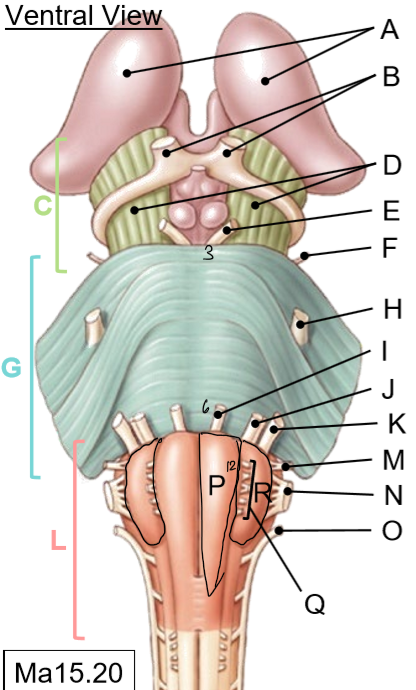
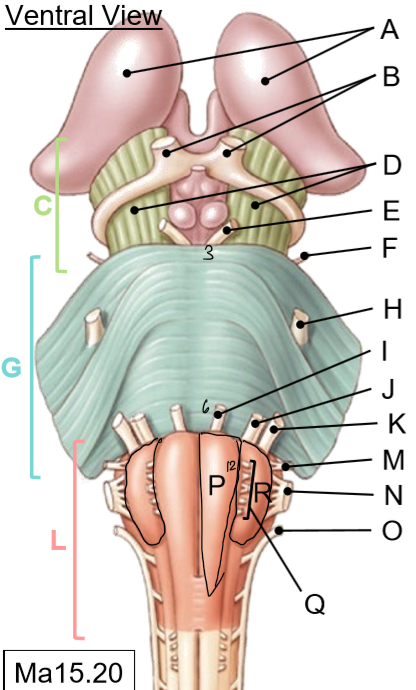
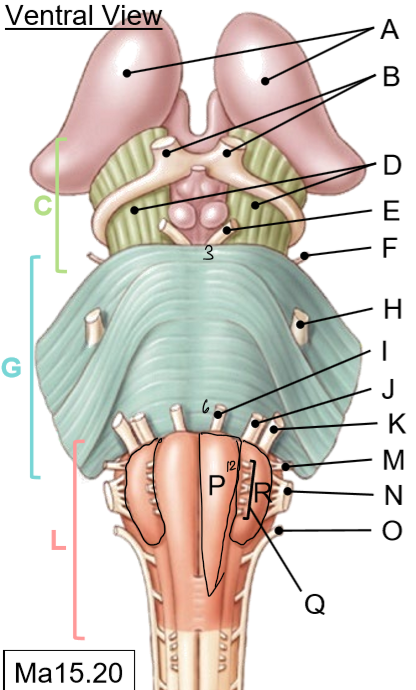
L-R
L: Medulla
M: Glossopharyngeal nerves
N: Vagus nerves
O: Accessory nerves
P: Pyramids
Q: Hypoglossal nerves
R: Olives
Cerebral peduncles are mostly _______-
axons of the corticospinal tract
Trochlear nerves are the only CNs arising from the ______
dorsal aspect
Trigeminal nerves mostly carry
sensory information from the face
Facial nerves
Motor neurons
Vestibulocochlear neres
Special senses
Vagus nerves
PNS outflow to thorax and abdominal viscera
Accessory nerves arise from the _______, enters the cranium through the _______, exits through the _______-
upper cervical segment, foramen magnum, jugular foramen
The superior cerebellar peduncles connect the ______ and _________
midbrain, cerebellum
The middle cerebellar peduncles connect the ____ and _____
pons, cerebellum
Inferior cerebellar peduncles connect the ____ and ____
medulla, cerebellum
The cerebellum overlies the ______
fourth ventricle
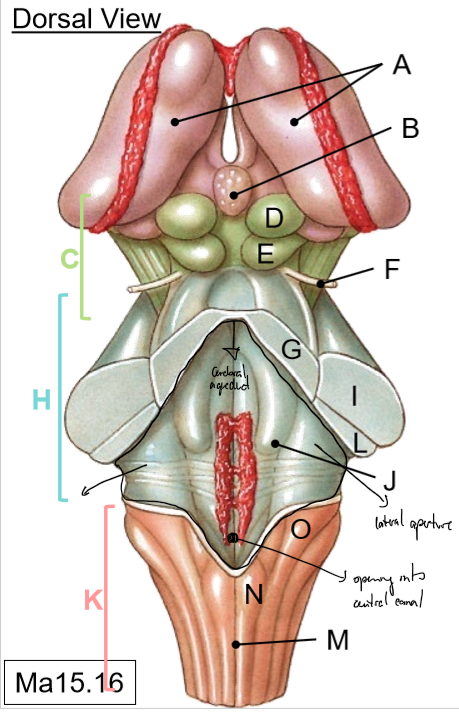
A-B
A: Thalami
B: Pineal gland
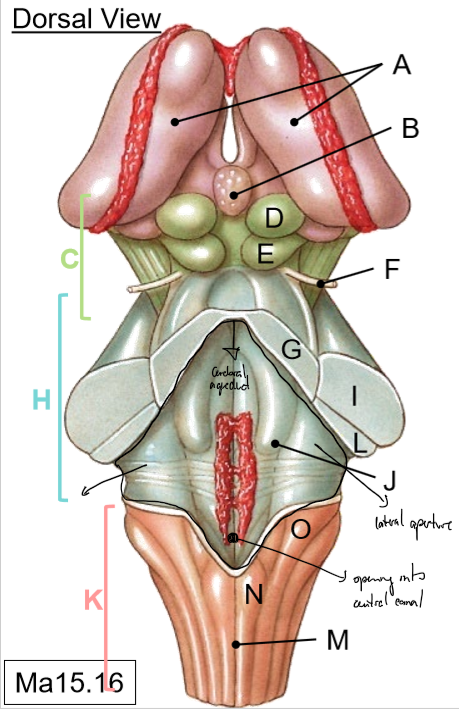
C-G
C: Midbrain
D: Superior colliculus (vision)
E: Inferior colliculus (hearing)
F: Trochlear nerve
G: Superior cerebellar peduncle
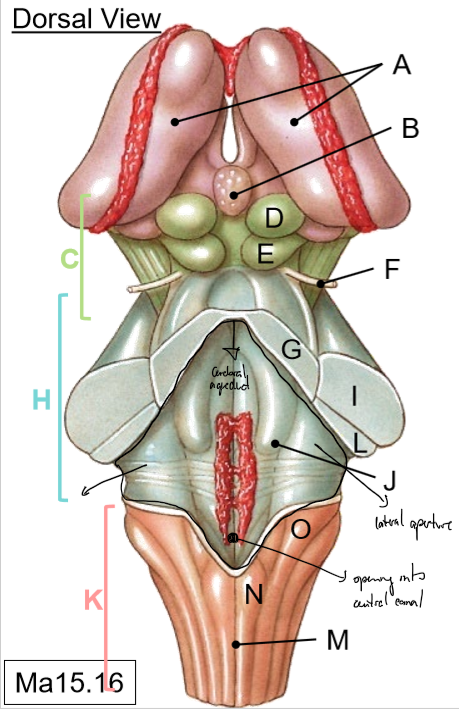
H-J
H: Pons
I: Middle of cerebellar peduncle
J: Floor of 4th ventricle
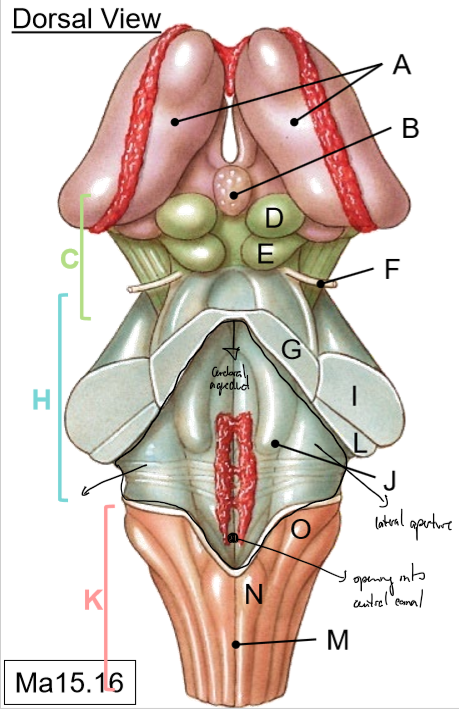
K-O
K: Medulla
L: Inferior cerebellar peduncles
M: Posterior median sulcus
N: Gracile tubercle
O: Cuneate tubercle
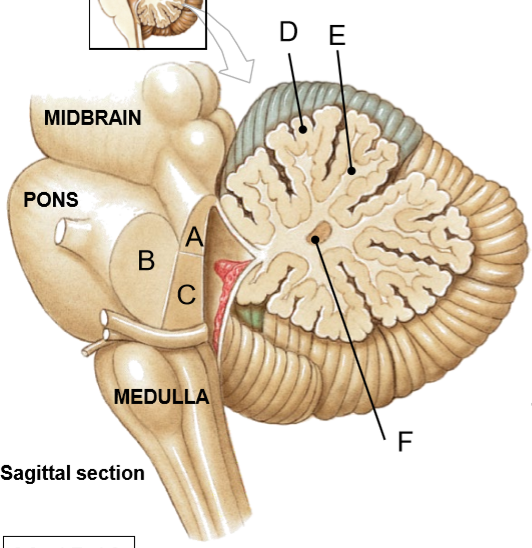
A-F
A-C: Superior, middle, inferior cerebellar peduncles
D: Cortical grey matter
E: Subcortical white matter
F: Cerebellar nuclei
Cerebellum made of two _____
bilaterally paired hemispheres
Cerebellum controls ___, ____ and coordination of _______
posture, balance, motor function
Spinocerebellar proprioceptive info into cerebellum reports ___________ and _____
ipsilateral body position, muscle tone
Vestibulo-cerebellar input into cerebellum reports _____ and ______-
position, acceleration of the head in space
Contralateral corticopontocerebellar afferents into the cerebellum report
movement planning
Motor and premotor cortex output from the cerebellum via _____
thalamus
Motor cortex controls movement of ______
contralateral body
Like the body, the head has both
sensory and motor components, voluntary and involuntary components
Unlike the spinal cord, functional columns disperse into a series of ______
longitudinally arranged, distinct nuclei
Unlike spinal nerves, CNs may carry a _________
single modality
Unlike the spinal cord, the brainstem and cranial nerves subserve ______
“special” visceral sensation, taste and the “special senses” of hearing balance
Somatic components of spinal cord and cranial nerve
Somatic voluntary motor
Somatic sensory
Autonomic components of spinal cord and cranial nerves
Visceral motor
Visceral sensory
Visceral sensory including taste
Hearing and balance
Cranial nerves that convey special senses
I (Olfactory N)
II (Optic N)
VIII (vestibulocochlear N)
Cranial nerves that control skeletal muscle
III (Oculomotor N)
IV (trochlear N)
VI (abducens N)
XI (accessory N)
XII (hypoglossal N)
Mixed cranial nerves
V (trigeminal N)
VII (facial N)
IX (glossopharyngeal N)
X (vagus N)
Olfactory nerve conveys _____ from the ______ in the roof of the nasal cavity
smell, olfactory epithelium
Olfactory nerves enter cranium by passing through the _________-
Cribiform plate of the ethmoid
Optic nerve conveys ______ from the ______
visual input, retina
Optic nerve enters the cranium through the _______
Optic foramen
Vestibulocochlear nerve conveys _______ from the ____ via the cochlear division and ______ from the _______ via the vestibular division
auditory sensations, cochlea, balance info, vestibular apparatus
Vestibulocochlear nerve enters cranium through the __________
internal auditory (acoustic) foramen
Cranial nerves III, IV, VI exit the cranium through the _______ to enter ___
superior orbital fissure, orbit
Cranial nerves III, IV, and VI control _______ that position the eye in orbit
extraocular eye muscles
Nerve damage to cranial nerves III, IV, and VI can cause ____ () and _____ ()
strabismus (misaligned eye), diplopia (double vision)
Cranial nerves III, IV, and VI also control the _______ (paralysis causes _____) and _______ (nerve damage causes ______)
levator palpebrae superioris, ptosis (droopy eyelid), parasympathetic preganglionic fibres, mydriasis (enlarged pupil)
The accessory nerve (__) emerges as a series of rootlets from the _________
XI, lateral aspect of upper cervical cord
The accessory nerve enters cranium through ______ and exits via _____ with CN and_
foramen magnum, jugular foramen, IX, X
The accessory nerve controls the ______ and _____
sternocleidomastoid, trapezius muscles
SCM ___________ and the trapezius _____
opposite side, elevates the shoulder
The hypoglossal nerve (__) exits the cranium via _____ and controls the shape and position of tongue via _____
XII, hypoglossal canal, intrinsic, extrinsic muscles
The trigeminal nerve is a ___ cranial nerves, conveying _______ from the face
mixed, somatic sensation
3 divisions of the trigeminal nerve
Opthalmic division
Maxillary division
Mandibular division
Opthalmic division exits the cranium via the _____
superior orbital fissure
Maxillary division exits via the ______
foramen rotundumM
Mandibular division exits via the ______
foramen ovale
Trigeminal ganglion contains the cell bodies of _______
pseudounipolar somatic sensory neurons
Mandibular division also ______ to the ________
voluntary motor, 4 muscles of mastication
Facial nerve (__) exits the cranium via the _______
CN VII internal auditory (acoustic) foramen
Voluntary motor fibres of facial nerve exit skull via ________ to innervate ______
stylomastoid foramen, muscles of facial expression
Facial nerve senses __________ from the _____ of the tongue through axons in ____ and cell bodies in _____
Special visceral sensory taste, anterior 2/3, chorda tympani, geniculate ganglion
Facial nerve is parasympathetic preganglionic via ______ to ______: postganglionic fibres distributed to the ______, ____, and ____, ___ the oral fissure
chorda tympani, submandibular ganglion; submandibular, sublingual glands, oral mucosa, below
Facial nerve is parasympathetic preganglionic via the _______ to the __________: postganglionic fibres distributed to the ____, _____ and ______, _____ the oral fissure
greater petrosal nerve, pterygopalatine ganglion, lacrimal gland, nasal mucosa, oral mucosa
Facial nerve damage causes ____
Bell Palsy
The glossopharyngeal nerve () exits the cranium via the ______
CN IX, jugular foramen
The glossopharyngeal nerve is responsible for ______ and from the _____ of the tongue, and ______
somatic sensory, special visceral,
The vagus nerve () exits the cranium via the _____
X, jugular foramen
The vagus nerve has ______ control to the pharynx and larynx, and ______from the _____ and ______
voluntary motor, general sensory. laryngopharynx, larynx
The vagus nerve has ______ nerves from _____ in the aortic body and ______ in the aortic arch, ____ and most _____-
chemoreceptors, baroreceptors. thoracic, abdominal viscera
The vagus nerve has _________ to the intramural ganglia of _____
parasympathetic preganglionic fibres, thoracic and abdominal viscera