f) Translocation
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
5 Terms
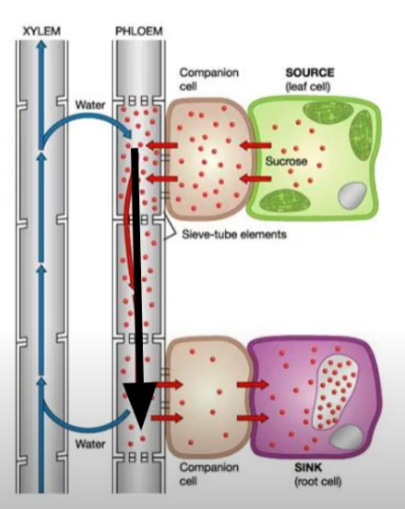
Source
Where sugars are made or released from a carbohydrate source (starch)
Sink
Anywhere in the plant where the sugars are used in respiration or converted for storage (starch in roots) and are therefore in a low concentration
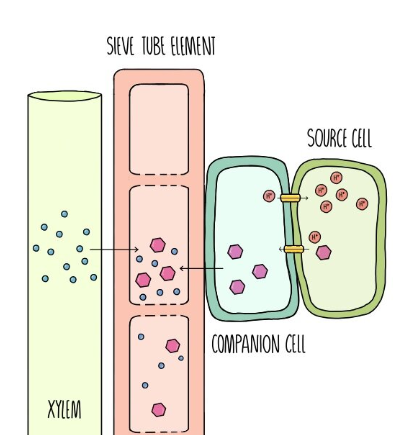
Translocation Process - Active Loading at the Source
H+ ions in the companion cells are actively transported out into surrounding tissue
H+ ions move back into the companion cell with a sucrose (or an amino acid), using a cotransporter protein.
This process is facilitated diffusion
Sucrose diffuses through the plasmodesmata into the sieve tube elements
Mass flow hypothesis. Sucrose lowers the water potential of sieve tube elements and therefore water moves into the sieve tube elements from the xylem via osmosis
This causes an increase in hydrostatic pressure inside the sieve tube elements at the source
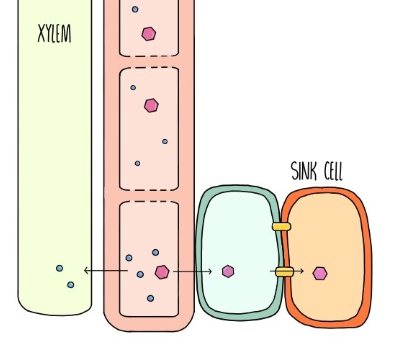
Translocation Process - Removal at the Sink
At the sink, sucrose leaves the sieve tube elements by diffusion and therefore the water potential of the sieve tube elements increases
Therefore water leaves the sieve tube elements via osmosis
This causes a decrease in hydrostatic pressure inside the sieve tube elements at the sink
Because there is a high hydrostatic pressure at the source and low hydrostatic pressure at the sink, what happens?
Assimilates move from source to sink down the hydrostatic pressure gradient by mass flow