HBS test
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
smooth muscle
A type of involuntary muscle, Non-striated, controls movements such as digestion and blood flow. A tissue specialized for contraction, composed of smooth muscle fibers (cells), located in the walls of hollow internal organs, and innervated by the autonomic moto
skeletal mucle
A type of striated muscle tissue that is under voluntary control. It is responsible for the movement of bones, attached to the skeleton via tendons. Skeletal muscles are composed of long, cylindrical fibers and are involved in various functions, including locomotion, posture, and heat production. They are characterized by their ability to contract quickly and with great force.
Cardiac muscle
A type of involuntary striated muscle found only in the heart. It is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body and is characterized by intercalated discs that facilitate synchronized contractions. Cardiac muscle cells are branched and have a single nucleus, allowing for efficient heart function.
striated
A muscle tissue that has a banded appearance due to the arrangement of actin and myosin filaments. It includes skeletal muscle, which is under voluntary control, and cardiac muscle, which is involuntary. The striations are visible under a microscope and are a result of the repeating sarcomere structure.
voluntary control
A muscle under voluntary control means that its contraction is consciously regulated by the nervous system, allows for intentional movements, such as walking or lifting objects, as opposed to involuntary muscles, which operate automatically without conscious thought.
involuntary muscle contraction
movements that occur without conscious control. These contractions are primarily associated with smooth and cardiac muscles. An example is Your brain doesn't tell your heart to beat it happens without you thinking about it. These contractions are essential for functions like digestion, circulation, and respiration.
tropin
hormones that stimulate the activity of other glands. Examples include adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH).
ATP
A compound composed of adenosine and three phosphate groups, which supplies energy for many biochemical cellular processes.
ADP
A nucleotide that plays a crucial role in cellular energy transfer. It consists of adenine, ribose, and two phosphate groups. When it gains a phosphate group, it converts to ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate), the primary energy carrier in cells.
sarcomere
the basic unit of striated muscle tissue, located between two Z lines. It contains actin (thin) and myosin (thick) filaments that enable muscle contraction. Sarcomeres are arranged end-to-end in myofibrils, aiding in the contraction of muscle fibers.
actin
a globular protein that forms microfilaments in the cytoskeleton of eukaryotic cells. It is essential for muscle contraction, cell motility, and maintaining cell shape. Actin has two forms: G-actin (globular) and F-actin (filamentous).
myosin
a motor protein that interacts with actin filaments to enable muscle contraction and cellular movements. It converts ATP hydrolysis into mechanical work, essential for muscle function and processes like cytokinesis and vesicle transport.
neuromuscular juntion
A synaptic connection between the terminal end of a motor nerve and a muscle (skeletal/ smooth/ cardiac). It is the site for the transmission of action potential from nerve to the muscle.
sarcoplasmic reticulum
a network of tubules and sacs in skeletal muscle fibers that plays an important role in muscle contraction and relaxation by releasing and storing calcium ions.
tropmyosin
actin-binding proteins that are central to the control of calcium-regulated contraction in striated muscle.
sliding filament theory
explains the molecular mechanisms behind muscle contraction. Within the sarcomere, myosin slides along actin to contract the muscle fiber in a process that requires ATP.
insertion
The movable attachment of the distal end of a muscle, which produces changes in shape or skeletal movement when the muscle contracts.
Action
movement of a muscle, can be described relative to the joint or the body part moved
endomysium
The delicate connective tissue surrounding the individual muscular fibers within the smallest bundles.
Epimysium
The external connective-tissue sheath of a muscle.
Perimysium
The connective-tissue sheath that surrounds a muscle and forms sheaths for the bundles of muscle fibers.
Fascicle
A small bundle or cluster, especially of nerve or muscle fibers
Tendon
A flexible but inelastic cord of strong fibrous collagen tissue attaching a muscle to a bone.
myofibril
A threadlike structure, extending longitudinally through a muscle fiber (cell) consisting mainly of thick filaments (myosin) and thin filaments (actin, troponin, and tropomyosin).
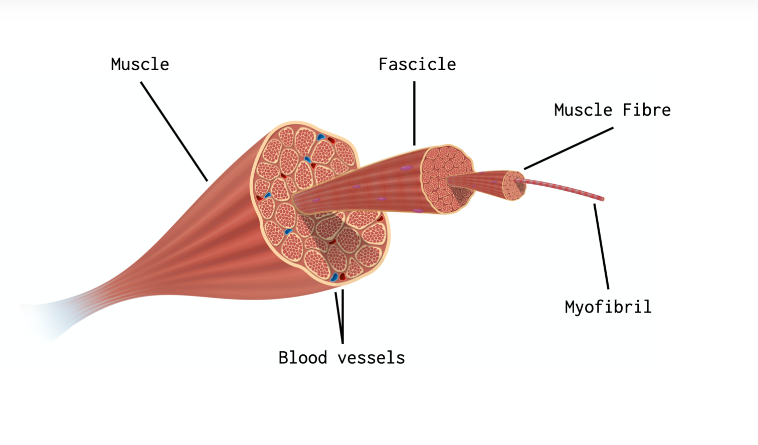
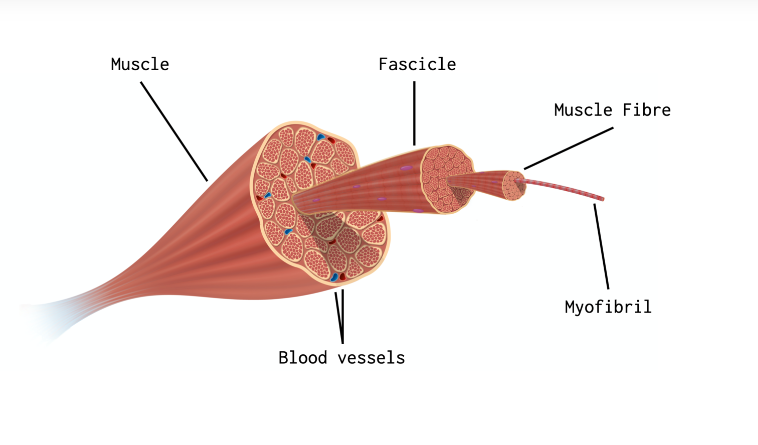
make up of a skeletal muscle
groups of muscle fibers called fascicles surrounded by a connective tissue layer called perimysium. Multiple units of individual muscle fibers within each fascicle are surrounded by endomysium, a connective tissue sheath.
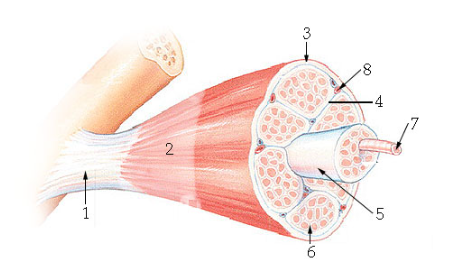
what is #1?
Tendon
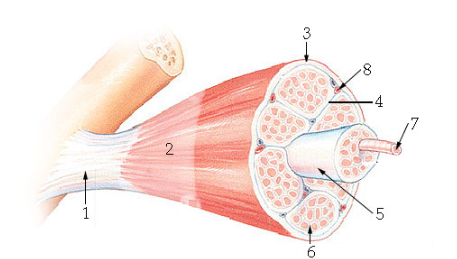
what is #2?
Epimysium
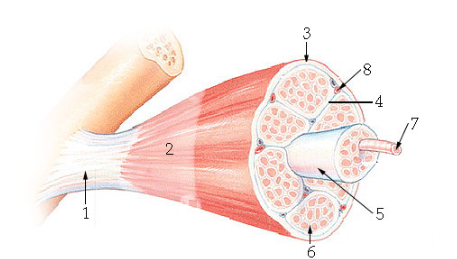
what is #3?
Perimysium
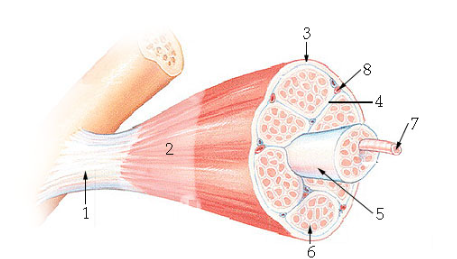
what is #5?
Fascicle
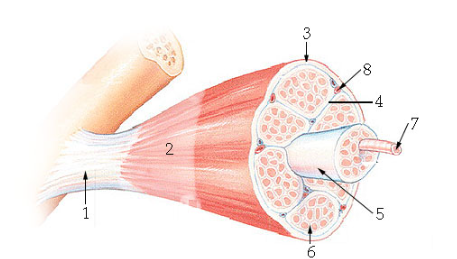
what is #6?
Endomysium
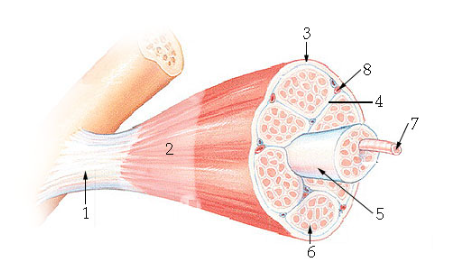
what is #7?
Muscle fiber
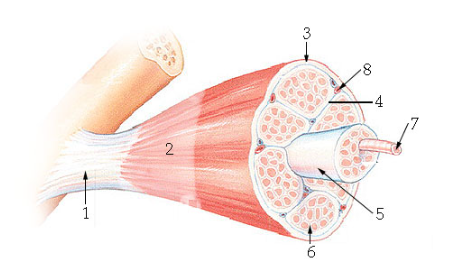
what is #8?
blood vessel