Cell Cycle & Mitosis
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/31
Last updated 6:36 PM on 3/5/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
1
New cards
cell cycle
the life of a cell from its formation to its own division
2
New cards
reasons a cell divides
reproduction, growth, repair damage
3
New cards
genome
all the DNA in a cell
4
New cards
histones
proteins that help to organize, support, and package DNA
5
New cards
chromosomes
organized, condensed structures of DNA that are seen when the cell is dividing (during mitosis)
6
New cards
chromatin
uncondensed DNA that is seen when the cell is not dividing (interphase)
7
New cards
sister chromatids
identical sides of a chromosome
8
New cards
centromere
structure that connects two sister chromatids together
9
New cards
mitosis
division of the nucleus
10
New cards
cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm
11
New cards
G1 Phase
The first gap, or growth phase, of the cell cycle, consisting of the portion of interphase before DNA synthesis begins.
12
New cards
S Phase
The synthesis phase of the cell cycle; the portion of interphase during which DNA is replicated.
13
New cards
G2 Phase
The second growth phase of the cell cycle, consisting of the portion of interphase after DNA synthesis occurs. Cell is preparing to divide.
14
New cards
centrioles
pair of structures that help to organize the spindles during cell division
15
New cards
spindle
long, thin structure composed of microtubules that help to move chromosomes during cell division
16
New cards
interphase
period of growth and DNA replication, contains 3 subphases G1, S, G2
17
New cards
prophase
phase of mitosis in which the chromatin condenses into chromosomes, the nucleus begins to breakdown, spindles form, and the centrioles begin to migrate to opposite ends of the cell
18
New cards
metaphase
spindles attach to the centromeres and move chromosomes to the middle of the cell
19
New cards
anaphase
sister chromatids are separated and pulled to opposite poles
20
New cards
telophase
chromosomes uncondense back to chromatin, 2 nuclei begin to reform, spindles break down, cytokinesis begins
21
New cards
cleavage furrow
The area of the cell membrane in animal cells that pinches in and eventually separates the dividing cell
22
New cards
cell plate
structure seen forming between two dividing plant cells that will become the cell wall
23
New cards
G1 checkpoint
checkpoint in which the cell checks for cell size, nutrients, growth factors and DNA damage
24
New cards
Apoptosis
programmed cell death
25
New cards
G2 checkpoint
checkpoint in which the cell checks to make sure DNA replication occurred and DNA is not damaged
26
New cards
M checkpoint
checkpoint in which the cell determines if the chromosomes are attached to spindles and lined up in the middle of the cell
27
New cards
cell cycle regulatory proteins
growth factors, cyclins, CDKs
28
New cards
picture of interphase
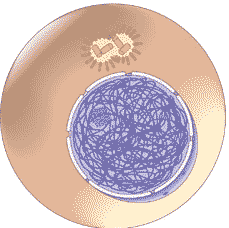
29
New cards
picture of prophase
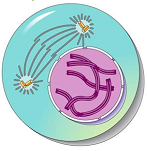
30
New cards
picture of metaphase
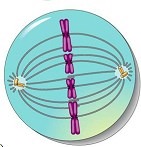
31
New cards
picture of anaphase
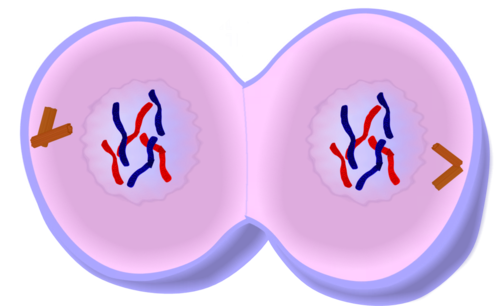
32
New cards
picture of telophase