CAPE Chemistry Module 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
1
New cards
Explain how a mass spectrometer works to obtain a mass spectrum of a molecule (2022) \[4mks\]
* sample inserted into ***sample inlet***
* sample transformed into gas by collision with high-velocity e- from Tungsten filament
* mass analyzer separates ion based on mass to charge ratio
* detector counts ion
* data system records and process the output to produce a spectrum, a graph of abundance versus M/z ratio
* sample transformed into gas by collision with high-velocity e- from Tungsten filament
* mass analyzer separates ion based on mass to charge ratio
* detector counts ion
* data system records and process the output to produce a spectrum, a graph of abundance versus M/z ratio
2
New cards
Name the process by which TLC separates Alpha-amino acids (2022)
Adsorption chromatography
3
New cards
Explain how to analyze TLC to identify components (2022)
* calculate Rf
* Compare calculated Rf to known values
* Compare calculated Rf to known values
4
New cards
Several alpha-amino acids have similar structure. Why would this be problematic for analyzing alpha-amino acids using TLC? (2022)
* poor separation and identification of the individual amino acids
* If two or more amino acids have similar polarity and functional groups, they will have similar interactions with the stationary phase, leading to poor separation and co-elution of the analytes
* difficult/ incorrect/ similar Rf values
* If two or more amino acids have similar polarity and functional groups, they will have similar interactions with the stationary phase, leading to poor separation and co-elution of the analytes
* difficult/ incorrect/ similar Rf values
5
New cards
State formula for partition coefficient, K (2022)
K = conc of solute in organic / con of solute in aqueous
6
New cards
define partition coefficient (2022)
ratio of the concentration of a solute in two immiscible phases at a particular temperature
7
New cards
define accuracy vs precision (2022)
Accuracy: closeness to accepted value
Precision: closeness to set of results
Precision: closeness to set of results
8
New cards
State the criteria for primary standards (2022)
* stable in air
* high purity
* soluble in titration medium
* high formula weight
* inexpensive
* fast, complete reaction with primary and compound
* high purity
* soluble in titration medium
* high formula weight
* inexpensive
* fast, complete reaction with primary and compound
9
New cards
Why is NaOH sometimes NOT a suitable primary standard? (2021)
* reacts with water vapour in air
* reacts with CO2 in air
* reacts with CO2 in air
10
New cards
define standard deviation (2021)
measure of how spread out a set of values are from the mean
11
New cards
Outline steps to determine ethanoic acid content of vinegar by titration (2021)
* vinegar in conical flask
* phenolphtalein added
* NaOH in burette
* titrate until colourless to pink
* Repeat
* phenolphtalein added
* NaOH in burette
* titrate until colourless to pink
* Repeat
12
New cards
define EM radiation (2019)
propagation of energy in the form of waves through space, without the need for a medium.
13
New cards
define wavelength (2019)
distance between two successive peaks
14
New cards
define frequency (2019)
number of waves passing a reference point per unit time.
15
New cards
State the formula relating c, wavelength and frequency
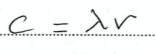
16
New cards
List the transitions that result in UV-Vis region
𝒏 → 𝝅∗
𝒏 → 𝝈∗
𝝅 → 𝝅∗ \n
𝒏 → 𝝈∗
𝝅 → 𝝅∗ \n
17
New cards
Describe steps to prepare solid sample for IR spectroscopy. (2019)
*KBr pellet*
* mix finely grounded sample with KBr
* press mixture under high pressure; seal into matrix
* KBr pellet placed into in instrument
\
*Nujol mull*
* compound grounded with Nujol (mineral oil) to create suspension
* suspension placed between KBr or NaCl plates
* mix finely grounded sample with KBr
* press mixture under high pressure; seal into matrix
* KBr pellet placed into in instrument
\
*Nujol mull*
* compound grounded with Nujol (mineral oil) to create suspension
* suspension placed between KBr or NaCl plates
18
New cards
Why use NaCl for IR spectroscopy? (2019)
NaCl does not absorb IR
19
New cards
Describe the function of each following in gravimetric analysis: suction flask, suction funnel, silica crucible, sintered glass crucible, oven/furnaces (2018)
* Suction Flask: to filter the sample solution. It is fitted with a glass filter flask and a side arm with a stopcock. The stopcock allows for the suction to be applied, which draws the sample solution through the filter paper into the flask. The filtered residue is retained on the filter paper and used for subsequent gravimetric analysis.
* Suction Funnel: to aid in the filtration of a sample solution. It consists of a conical glass funnel with a stem that fits into a flask. The stem of the funnel is fitted with a glass stopcock that allows for the suction to be applied, which draws the sample solution through the filter paper into the flask.
* Silica Crucible: to hold the sample for the gravimetric analysis. The sample is heated in the crucible to evaporate any water or volatile solvents, leaving behind the residue for weighing.
* Sintered Glass Crucible: similar to a silica crucible but has a porous structure that allows for the sample to be filtered and washed in the same container. The pores of the crucible act as a filter, retaining the residue while allowing the filtrate to pass through.
* Oven/Furnace: to heat the sample in the crucible to drive off any volatile components.
* Suction Funnel: to aid in the filtration of a sample solution. It consists of a conical glass funnel with a stem that fits into a flask. The stem of the funnel is fitted with a glass stopcock that allows for the suction to be applied, which draws the sample solution through the filter paper into the flask.
* Silica Crucible: to hold the sample for the gravimetric analysis. The sample is heated in the crucible to evaporate any water or volatile solvents, leaving behind the residue for weighing.
* Sintered Glass Crucible: similar to a silica crucible but has a porous structure that allows for the sample to be filtered and washed in the same container. The pores of the crucible act as a filter, retaining the residue while allowing the filtrate to pass through.
* Oven/Furnace: to heat the sample in the crucible to drive off any volatile components.
20
New cards
State ONE example of the use of gravimetric analysis in quality control (2018)
* determine moisture in drugs/soil
* presence of particles in air/food
* determine solid in water sample
* presence of particles in air/food
* determine solid in water sample
21
New cards
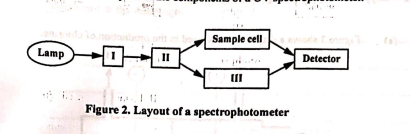
Identify I, II, III.
I → monochromator
II → beam splitter
III → reference cell
II → beam splitter
III → reference cell
22
New cards
State Raoult’s law
* The vapor pressure of a component in a mixture is equal to the vapor pressure of the pure component at that temperature, multiplied by its mole fraction in the mixture.
* PA = xA \* P0A where PA is the partial pressure of component A in the mixture, xA is the mole fraction of A in the mixture and P0A is the vapor pressure of pure A.
* PA = xA \* P0A where PA is the partial pressure of component A in the mixture, xA is the mole fraction of A in the mixture and P0A is the vapor pressure of pure A.
23
New cards
Explain ideal mixture
An ideal mixture is one where the interactions between molecules of the different components are the same as those between molecules of the pure substances. \n
24
New cards
Explain positive deviation from Rault’s Law
* The vapour pressure of the mixture is higher than would be expected
* boiling point is lower than expected
* Interactions between the unlike molecules are weaker than those between like molecules, usually from differences in polarity
* Enthalpy of mixing is positive
\
* boiling point is lower than expected
* Interactions between the unlike molecules are weaker than those between like molecules, usually from differences in polarity
* Enthalpy of mixing is positive
\