Intro to Diagnostic Imaging
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
Procedures that are guided by medical imaging
Fluoroscopy, angiography/angioplasty, stent placement, biopsies, etc
interventional radiology
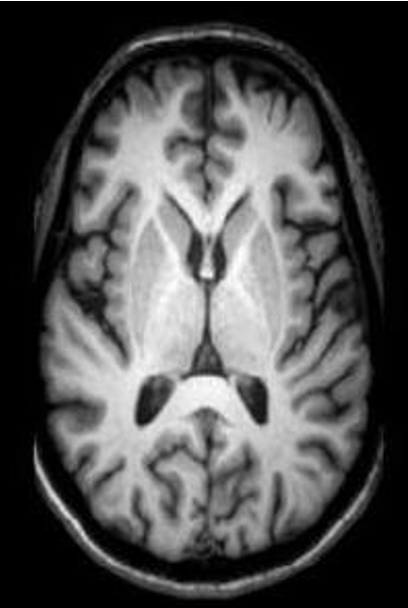
what type of view?
axial
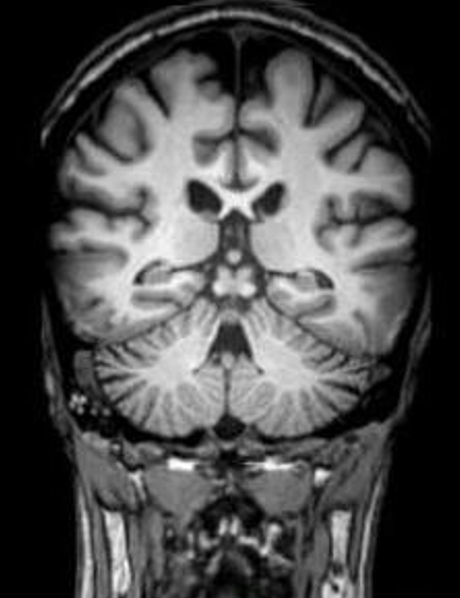
what type of view?
coronal
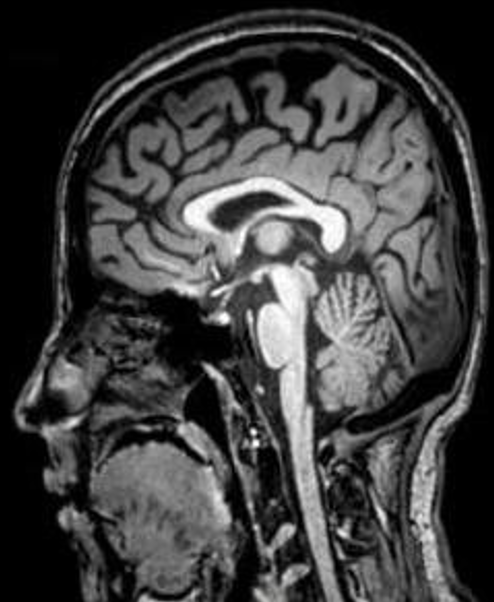
what type of view?
sagittal
Using targeted doses of high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells
radiology oncology
radiographs (x-ray/plain films) use what type of radiation?
ionizing
what is remnant radiation?
beam passes through the patient, leftover beam that makes it through the patient
What determines X-ray attenuation?
Tissue density
What captures remnant radiation?
Image receptor
What happens after the image receptor captures radiation?
Information is processed into a viewable image
what is ionizing radiation?
A type of high-energy radiation that has enough energy to remove an electron (negative particle) from an atom or molecule, causing it to become ionized
What is radiodensity?
Combination of physical qualities of an object that determine how much radiation it absorbs from the x-ray beam
in an x-ray, if there is more absorption (high radiodensity), how will the image look?
whiter
what primarily determines radiodensity?
Density and thickness
what is radiographic density?
Amount of radiation that passes through an object (blackening on radiograph)
Relationship between radiodensity and radiographic density?
Inverse
if there is greater radiodensity, there is more/less radiographic density, resulting in whiter/blacker image
less radiographic density; whiter image
Radiodensity categories from black to white?
Air (black)
Fat (gray-black)
Water (gray)
Bone (white)
X-ray color = air
black
X-ray color = fat
grey-black
X-ray color = water
grey
X-ray color = bone
white
if there is high radiographic density, and low radiodensity, how will the image look? (lighter/darker)
darker
Indication for radiographs after trauma?
Exclude or diagnose fractures
Radiographs are used to assess joint or spinal disease such as?
DJD, spondylosis, scoliosis
Radiographs are used to assess cardiopulmonary disease such as?
Pneumonia (chest X-ray)
Radiographs are used to assess surgical equipment placement such as?
Screws or pins
Radiographs are used to monitor what?
Healing of fractures or surgical procedures
Radiographs are used to screen for what conditions?
Bone tumors, breast cancer, kidney stones, foreign bodies, osteoporosis, enlarged heart
x-rays indicated for assessment of…
joint or spinal disease
cardiopulmonary disease
surgical equipment placement
heeling progress
How many radiographs are needed for proper evaluation?
At least two images, made as close to 90˚ to each other as possible, are required to view all three dimensions
# and orientation of images taken typically depends on?
body part
Common radiographic projections?
AP, lateral, oblique
Advantages of radiographs?
Fast, inexpensive, low radiation
excellent bone detail
screens many pathologies
helps guide next imaging study
Main limitation of radiographs?
show only significant bone density changes → some may not be observable until later stages (osteoporosis, avascular necrosis, stress fractures)
Why might some fractures still be missed even with 2 views?
bone thickness can obscure areas (e.g., tibial plateau fx)
what are not well-defined on an x-ray?
soft tissues
What does CT merge?
X-ray with computer processing
How does CT work?
x-ray beam and detector system rotate in an arc around patient → computer reconstructs data into an image
What does each CT image represent? how thick?
Axial cross-sectional slice 0.2-1.5 cm thick
Why are multiple CT slices viewed together?
To evaluate dimensions of a structure
What do newer CT technologies allow?
Multiplanar (sagittal, coronal) and 3D images
what are the 3D images from a CT scan called?
reformations
Modality of choice for neuroimaging in acute/trauma settings?
CT scan
CT primarily for the evaluation of…
Loose bodies within a joint
Degenerative changes within the spine
Spinal stenosis, exp if combined with myelogram
Soft tissue processes like cellulitis or abscesses
indications for CT scan
High-risk trauma patients (initial examination) at thorax, abdomen, and pelvis (TAP) → assess for life threatening injuries
Identification of subtle and/or complex fractures
what types of fractures are best for CT scan?
Subtle or complex
Advantages of CT?
Detailed anatomy/pathologic processes
faster than MRI/US
cheaper than MRI
better for claustrophobic patients
Main disadvantage of CT?
Higher radiation dose
less soft tissue contrast than MRI
Patient movement or metal implants can produce artifacts
What happens to radiation that passes through the patient?
It is collected to make an image
What is effective radiation dose? measured in?
Amount of radiation absorbed by patient
millisieverts (mSv)
What principle guides radiation safety in imaging? its purpose?
ALARA (As Low As Reasonably Achievable)
Every effort is made to decrease radiation risk
how can you tell T1 and T2 weighted images apart?
T2 = find a structure that has a lot of water in it, see if its the lightest/whites thing in the picture
what imaging technique is used in MRI?
cross-sectional
What does MRI use to generate signals?
magnet orients protons in a specific direction, radio frequency shifts them away from magnet
realignment of protons releases energy, which the MRI measures
what does MRI stand for
magnetic resonance imaging
how does MRI work?
magnetic field is used to align hydrogen protons
radio frequency waves are absorbed by protons and then emitted as a signal
a radio frequenting coil picks up the signal and transmits it to the computer
computer processes the data and an image is generated
Why do tissues appear different on MRI?
resonate at different radiofrequencies
MRI signal intensities of tissues differ based on ____
composition
What does MRI sequence mean?
timing of the radiofrequency pulse and the capturing of the energy signal
Why are multiple MRI sequences used?
compare how the tissue appears in different sequences to help with diagnosis
Most common MRI sequences?
T1 and T2 weighted
What does MRI T1 sequence show best?
resolution of anatomy
What does MRI T2 sequence show best?
Signal from water is brightest
what MRI weighted sequence is most valuable for identifying pathology that has a component of inflammation/edema?
T2
what is hypo-intensity on an MRI?
less bright than surrounding structures
What contrast medium is commonly used in MRI?
Gadolinium
why would a contrast medium be needed in an MRI?
Improved resolution in tissues when evaluating blood vessels, possible tumor, infection, or inflammation
MRI indications
Soft tissue injuries, especially to ligaments and tendons
Diagnosis of bone tumors, stress fractures, osteomyelitis, and avascular necrosis
Evaluation of intervertebral disc pathology
why is MRI indicated for looking at bone?
Can be revealed in the early stages due to sensitivity of MRI to detect bone marrow changes
MRI contraindications
Cardiac pacemakers
Ferromagnetic aneurysm clips
Metal foreign bodies in eyes/orbit
Cochlear implants
1st trimester pregnancy
main advantages of MRI
Excellent resolutions of all soft tissues
No ionizing radiation
main disadvantages of MRI
Poor for imaging bone (due to limited water content)
Is expensive, time consuming
Claustrophobia is an issue
Nuclear medicine procedure using radioactive tracer to diagnose the severity of a variety of bone diseases and conditions
Skeletal Scintigraphy (Bone Scan)
bone scan primarily looks at what bones diseases and conditions?
fractures, infection, and cancer (esp. metastasis)
how does bone scan work?
radioactive tracer adheres to metabolically active bone (hot spots)
Bone scans being replaced by _____ as they may be more sensitive and specific
PET scans
Enhanced form of a radiograph that is used to measure bone loss and bone mineral density
Gold standard for diagnosing osteoporosis
Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DEXA or DXA)
how does DXA machine work?
sends x-rays with two distinct energy peaks through the bones being examined
soft tissue amount can be subtracted from the total and what remains is a patient's bone mineral density
in DXA machine, what are the energy peaks absorbed by?
one by soft tissue, other by bone
Cross sectional imaging technique based on the reflection of sound waves off tissue interfaces
diagnostic MSK ultrasound
diagnosis MSK US indications
Soft tissue pathology, particularly in sports injuries including tendon and muscle tears
Evaluation of fluid collection, including cysts, bursas, synovitis, infections, inflammation
Assessment of articular cartilage
Evaluation of nerves for inflammation or entrapment
advantages of MSK US
Low cost, portable
image soft tissue in the presence of hardware
Easy to compare to opposite side of body
Able to include dynamic movements and/or stress tissues
disadvantages of MSK US
Operator dependent → need STRONG anatomy knowledge
US does not penetrate bone, cannot see some intra-articular ligaments
Time consuming
Can be difficult to image patients who are obese
ABCs of radiologic analysis
A: Alignment
B: Bone Density
C: Cartilage Spaces
S: Soft Tissues
what is the purpose of search patterns in radiography?
methodology for looking at an image in an organized fashion
Helps to ensure that everything possible to observe has been visually accounted for
ABCS: alignment evaluates?
skeletal architecture
contour of bone
bones to adjacent bones
ABCS: bone density evaluates?
textural abnormalities
local bone density changes
ABCS: cartilage spaces evaluates?
joint space width
subchondral
epiphyseal plates
ABCS: soft tissues evaluates?
muscles
fat pads, fat lines
joint capsules
periosteum
misc. findings
open mouth films look at?
C1/C2 instability
flexion/extension films look at?
Atlantodental interface >3mm indicates instability (C1/C2 subluxation)
search pattern for MRI (ABCDS)
A = alignment of anatomy
B = bone signal
C = cartilage
D = edema
S = soft tissues and synovial tissue
MRI ABCDS: bone signal looks at?
altered signal in bone MARROW. Can also assess for tumors, cysts, or avascular bone
MRI ABCDS: alignment of anatomy looks at?
Assess the alignment and continuity of ligaments, nerve, and muscles
MRI ABCDS: cartilage looks at?
Assess for osteochondral or articular cartilage abnormalities or tears (e.g. labral, meniscus, TFC)
MRI ABCDS: edema looks at?
”footprint” of injury.
On T2 images, look for edema due to inflammation
what are the 4 validated clinical decision rules?
Ottawa Ankle Rules
Ottawa Knee Rules
Pittsburgh Rules for Knee Trauma
Canadian C-spine Rule
purpose of clinical decision rules in radiology
Standardize care among first-contact providers
Reduce unnecessary radiologic imaging
Identify injuries that should be evaluated by radiograph
Pittsburgh Rules for Knee Trauma
blunt trauma or fall mechanism of injury AND
age under 12 or over 50 AND/OR
inability to walk 4 WB steps in the ED