Economic Activity
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Unit 2 AOS 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Living Standards
refers to one’s quality of life
Material Living Standards
refers to access to consume goods and services
Non-Material Living Standards
refers to one’s quality of life
Economic Activity
refers to the process where resources are transformed into goods and services
Non Economic Activity
refers to those which are not sold for money, such as volunteering
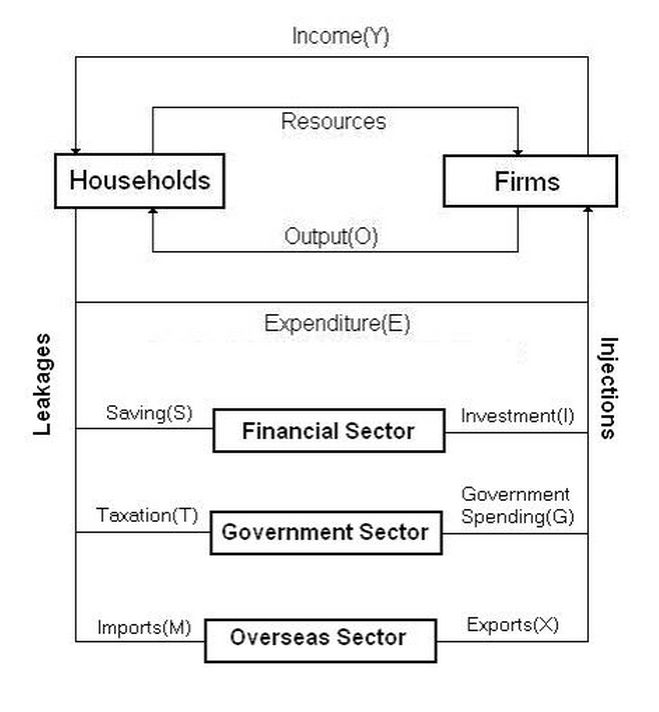
5 Sector Circular Flow Model
Flow 1: Resources
Flow 2: Income
Flow 3: Spending on Australian Production
Flow 4: Finished Goods and Services
Business Cycle - Expansion
Rising GDP, falling unemployment, rising inflation
Business Cycle - Peak
GDP at a maximum, unemployment at a minimum, inflation at a maximum
Business Cycle - Contraction
falling GDP, rising unemployment, falling inflation
Business Cycle - Trough
GDP at a minimum, unemployment at a maximum, inflation at a minimum
Economic Indicators
Lagging Indicators
Coincident Indicators
Leading Indicators
Lagging Indicators
are measure of the economy that only tell the level of activity that occured some time ago
Unemployment Rate
Inflation Rate
Coincident Indicators
are measures of the economy that move very closely with actual changes in the level of economic activity
Share Prices
Monthly retail sales
New Car registrations
Leading Indicators
are measures that can help to predict where the economy may be heading soon
Consumer Confidence
Business Confidence
Gross Domestic Product
the total production of goods and services in the economy
How GDP is measured
The average of Production, Income and Expenditure approaches
Real GDP
is a measure of the total value of all goods and services produced in an economy adjusted for inflation
Labour Force
people who are working or actively seeking work
Not in the labour force
people who are not in a paid job and who are not looking for work. eg. students, retired or volunteers
Employed
includes people who are in a paid job
Unemployed
occurs when a person 15+ does not have a paid job
The Unemployment Rate (%)
= Number of people unemployed x 100/ Total number of people in the labour force
The Participation Rate (%)
= Total number of people in the labour x 100/ Total number of people 15 or over in the population
Underemployment Rate
= Number of Unemployed + Underemployed/ Number of people in the labour force x 100
Under-utilisation Rate (%)
Unemployement Rate (%) + Underemployment Rate (%)
Potential Benefits of Economic Growth
New employment opportunities
Increase incomes and material standards
Reduces government tax
Potential Costs of Economic Growth
Possible rise in inflation rate
Environment Costs: CO2 Emissions, climate change
Reduced leisure time, increased stress
Aggregate Demand
refers to the total level of spending in the economy
Aggregate Demand Equation
AD = C + I + G + (X-M)
C - Consumption
I - Investment
G - Government
X - Exports
M - Imports
Aggregate Supply
represents the total volume of goods and services that all suppliers have produced and supplied over a period of time
Macroeconomic supply factors
influence the willingness and/or ability of producers to offer goods and services for sale and in turn the level of aggregate supply
Factors increasing economic growth (Demand)
Higher disposable income
Higher discretionary income
lower interest rates
stronger consumer confidence
Factors increasing economic growth (Supply)
More factors of production
Better quality production
Lower costs of production
Macroeconomic Demand Factors
Disposable Income, Discretioanry Income, Interest Rates, Consumer Confidence, Business Confidence, Exchange Rates, Rates of economic growth overseas
Disposable Income
the money u received from working after tax
Discretionary Income
a measure of how much money households have left over after buying essentials
Interest Rates
the cost of credit or reward of saving
Consumer Confidence
the degree of optimism of households about the future incomes and employment prospects
Business Confidence
the degree of optimism of firms about future profits
Exchange Rates
the value of one currency in terms of another curency
Rates of economic growth overseas
the percentage change in the volume of goods and services produced in a nation from one measurable time period to another