Luke Anatomy Lecture Exam 2
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
Skeletal System Functions
Support, Protect, Movement, Electrolyte Balance, Acid-Base Balance, Blood Formation
4 Principle Types of Bone Cells
Osteogenic Cells, Osteoblasts, Osteocytes, Osteoclasts
Osteogenic Cells
Stem cells, form and regenerate bone tissue
Osteoblasts
Build bone
Osteocytes
Maintain bone health and structure
Osteoclasts
Dissolves bone (bone remodeling) - maintains calcium balance in body
The Bone Matrix is made up of
Osseous tissue, 1/3 organic and 2/3 inorganic
Calcium salts make bones rigid and collagen gives bones some degree of flexibility
Rickets
Soft bones due to deficiency of calcium salts
Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Brittle bone disease; lack of protein and collagen
Spongy Bone Provides:
Strength with minimal weight
Bone Marrow
Soft tissue that occupies the marrow cavity; red and yellow bone marrow
Red Marrow
Hemopoietic tissue - within spongy bone
Yellow Marrow
In adults; replaces much red marrow
Types of Forces on a Bone
Compression, Tension, Shear, Torsion, Bending
Compression
⇅
Tension
↕
Shear
→←
Torsion
Twisting
Bending
↕⇅
Ossification or Osteogenesis
Bone formation
2 Methods of Bone Development
Intramembranous ossification
Endochondral ossification
Intramembranous ossification
Bone develops from a fibrous membrane
Endochondral ossification
Process in which bone develops from pre-existing cartilage
Primary Ossification Center
Diaphysis; starts to develop blood supply
Secondary Ossification Center
Epiphysis
Ossification Continues...
Throughout your entire life (bone remodeling)
Interstitial Growth
Bones increase in length; stops when growth plate closes
Appositional Growth
Bones increase in thickness; exercising
Bone Remodeling does...
Repairs microfractures, releases minerals into blood
Wolff's Law of Bone
Architecture of bone determined by mechanical stresses placed on it and bones adapt to withstand those stresses
(Exercise thickens bones)
Mineral Resorption
The process of dissolving bone and releasing minerals into the blood (performed by osteoclasts)
Calcium Homeostasis
Regulation of calcium levels in the body.
Hypocalcemia
Blood calcium deficiency
Causes muscle tremors, spasms
Hypercalcemia
Blood calcium excess
Causes sluggish reflexes, depression
Calcitrial
Synthesized from Vitamin D
Required for calcium absorption
Calcitonin
Secreted by thyroid gland when calcium concentration rises too high
Inhibits osteoclasts
Lowers blood calcium concentration
Reduces bone loss in women during pregnancy and lactation
Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)
Raises blood calcium levels
Secreted by parathyroid glands
Stress Fracture
Break caused by abnormal trauma to the bone
Pathological Fracture
Break in a bone that is weakened by some other disease
Ex. Break a bone when you have osteoporosis
Types of Bone Fractures
Closed/Simple
Open/Compound
Greenstick
Comminuted
Impacted
Closed/Simple
Break, but bones stay together
Open/Compound
Break where bones come apart
Usually go through skin, but don't have to
Greenstick
Cracks along one side, but doesn't break all the way through the bone
Happens to infants and children with softer bones
Comminuted
Breaks into 3 or more pieces
Impacted
Break, but stay together, caused by ⇅
Steps to Healing of Fractures
1. Bleeds, blood clots and creates hematoma
2. Soft callus formation - collagen and hyaline cartilage
3. Hard callus formation - deposits a temporary bony collar; mineralizes
4. Bone remodeling - converts to compact bone
Axial Skeleton
Skull, Vertebrae, Ribcage
Appendicular Skeleton
Pectoral and pelvic gIrdle, arms, and legs
Types of Bones
Long bone, short bone, flat bone, irregular bone, sesamoid bone
How Many Bones in the Skull?
22
8 Cranial
14 Facial
Auditory Ossicles
Malleus, Incus, Stapes
Fontanels
Soft spots of connective tissue within the skull during infancy when skull is growing
When Does Skull Reach Adult Size?
8 or 9 years old
Vertebral Column Functions
Support skull and trunk
Protect spinal cord
Allow movement
Provide attachment points
How many vertebrae? In each section?
33
7 Cervical
12 Thoracic
5 Lumbar
5 Fused Sacral
3-5 Fused Coccyx
Spinal curvatures
Cervical - C
Thoracic - Ↄ
Lumbar - C
Pelvic - Ↄ
Intervertebral Discs Are Made Up of...
Fibrocartilage
Ring of the Intervertebral Disc is Called...
Annulus Fibrosus
Inside of Intervertebral Disc is Called...
Nucleus Pulposus
How Many True, False, Floating Ribs?
1-7 True
8-12 False
11,12 Floating
Pectoral Girdle is Made Up Of...
Clavicle and Scapula
Brachium
Upper arm - humerus
Antebrachium
Forearm - radius and ulna
Carpus
Wrist - Carpals, 8 small bones arranged in 2 rows
Manus
19 bones in 2 groups, 5 metacarpals and 14 phalanges
Male Pelvis Has What Shape and Female Pelvis Has What Shape?
Male: V
Female: U
Femoral Region
Thigh - femur and patella
Crural Region
Lower leg - tibia and fibula
Tarsal Region
Ankle
Pedal Region
Foot - 7 tarsal bones, 5 metatarsals, 14 phalanges
Patella is What Type of Bone?
Sesmoid
2 Foot Arches
Longitudinal Arch - the normal foot arch you think about
Transverse Arch - sideways/horizontal
Joint Types
Fibrous, Cartilaginous, Synovial
Fibrous Joints
Non-moveable
Bound by collagen fibers
Ex. Sutures in skull
Cartilagenous Joints
2 bones linked together by fibrocartilage
Have limited movement
Ex. Pubic symphysis, intervertebral discs
Synovial Joint
Freely moveable
2 bones separated by a joint cavity and surrounded by a synovial fluid filled sac
Ex. Glenohumeral Joint
Articular Cartilage
A layer of hyaline cartilage that covers the surfaces of 2 bones that face each other on the joint
Joint (Articular) Cavity
Separates the articular surfaces
Synovial Fluid
Fluid that lubricates joints; in the joint cavity
Joint (Articular) Capsule
Connective tissue that encloses the cavity and retains the fluid
Tendons Connect...
Bone to muscle
Ligaments Connect
Bone to bone
Bursa
Fibrous sac filled with synovial fluid, located between adjacent muscles, where tendon passes over bone, or between bone and skin
Levers Enhance Either...
Distance or power
Mechanical Advantage of a Lever
The ratio of its resistance force to its effort force
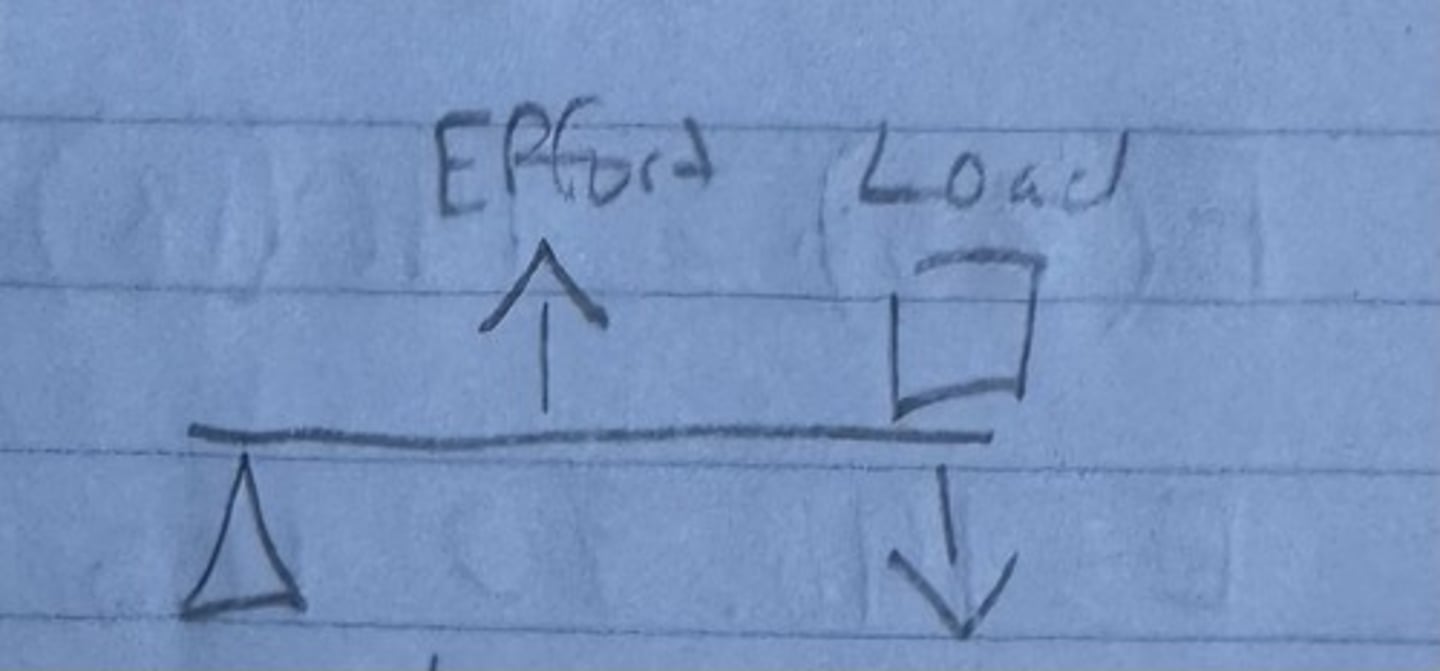
First Class Lever
The fulcrum is between the effort and resistance
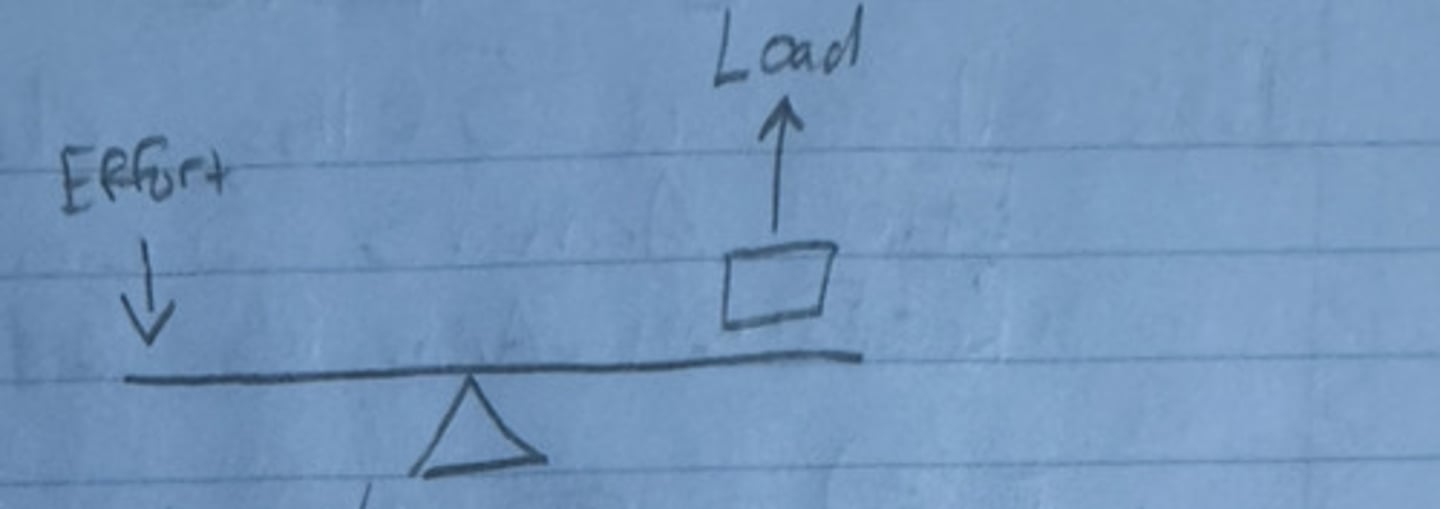
Second Class Lever
The load is between the fulcrum and the effort
(Amplifies Power), ex. standing on your toes, calf muscle lifting body weight up
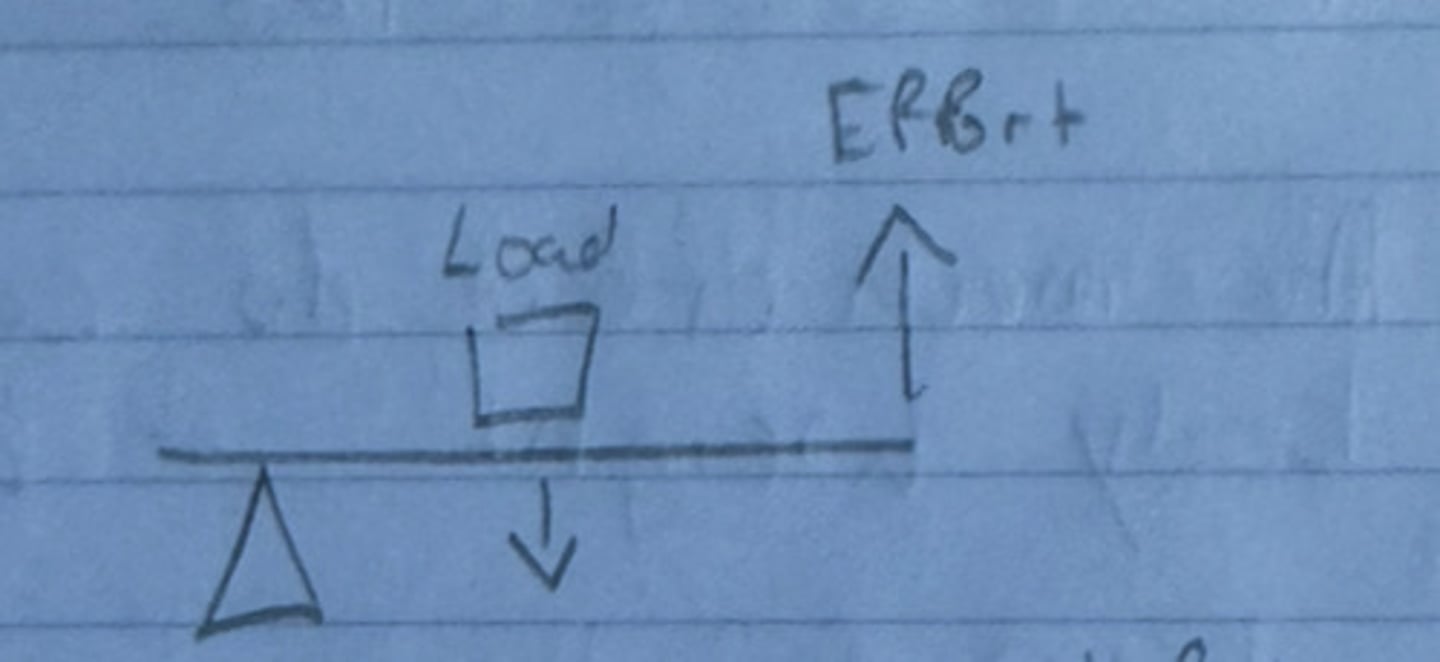
Third Class Lever
The effort is between the fulcrum and load
(Amplifies Distance), ex. bicep contracting and lifting a dumbell (load) in you hand
Forces Equation
E(Ea) = R(Ra)
Range of Motion is Determined By:
Structure of articular surfaces
Strength and tautness of ligaments and joint capsules
Muscle tone
Monaxial Joint
Only moves on one axis
Ex. Knee
Biaxial Joint
Has 2 axis of movement
Ex. Wrist
Multiaxial Joint
Has 3 or more axis of movement
Ex. Shoulder
Ball and Socket Joints are...
Multiaxial joints. Ex. Femur and acetabulum
Plane (Gliding) Joints
Flat articular surfaces in which bones slide over each other
Usually biaxial joints
Ex. Carpal bones of wrist, tarsal bones of ankle
Hinge Joints
One bone with convex surface fits into a concave depression of another bone
Monoaxial joints
Ex. Knee, elbow (humeroulnar)
Pivot Joints
One bone has a projection that is held in place by a ring-like ligament; bone spins on longitudinal axis
Monaxial Joints
Ex. Radioulnar Joint
Meniscus Are Made Up Of...
Fibrocartilage
Grade 1 Sprain
Ligament stays intact
Grade 2 Sprain
Ligament partially tears