Fluoroscopic Clinical Applications
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Which of the follwoing fluoroscopy types is primarily used for diagnostic purposes?
a. conventional fluoroscopy
b. interventional fluoroscopy
c. digital subtraction angiography (DSA)
d. vascular fluoroscopy
a. conventional fluoroscopy
What term is used for a continuous or pulsed x-ray beam that produces real-time, moving images of the body’s internal structures?
a. Computed tomography (CT) scan
b. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
c. Fluoroscopy
d. Ultrasound
c. Fluoroscopy
Which of the following is a sub-category of conventional fluoroscopy?
a. Gastrointestinal fluoroscopy
b. Pediatric fluoroscopy
c. Vascular fluoroscopy
d. Magnification fluoroscopy
b. Pediatric fluoroscopy
Interventional fluoroscopy provides physicians with which of the following?
a. Imaging without the use of radiation
b. Real-time visualization for precise procedures
c. Retrospective images for post-analysis
d. Macroscopic overview of a specific body part
b. Real-time visualization for precise procedures
Which of the following is a mobile fluoroscopic system?
a. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machine
b. Radiography-Fluoroscopy (R-F) room
c. Computed tomography (CT) scanner
d. C-arm
d. C-arm
Which of the following procedures might use fluoroscopy to guide the placement of screws, rods, and other implants?
a. Gastroenterology
b. Cardiology
c. Orthopedics
d. Urology
c. Orthopedics
Which type of fluoroscopy can potentially have the highest patient dose due to its duration during a procedure?
a. Conventional fluoroscopy
b. Pediatric fluoroscopy
c. Interventional fluoroscopy
d. Pulsed fluoroscopy
c. Interventional fluoroscopy
Which of the following explains why Radiography-Fluoroscopy (R-F) rooms are distinct from other fluoroscopic settings?
a. R-F rooms are mobile fluoroscopic systems
b. R-F rooms produce both radiographic and fluoroscopic images
c. R-F rooms are primarily used for pediatric patients
d. R-F rooms are cheaper than other fluoroscopic systems
b. R-F rooms produce both radiographic and fluoroscopic images
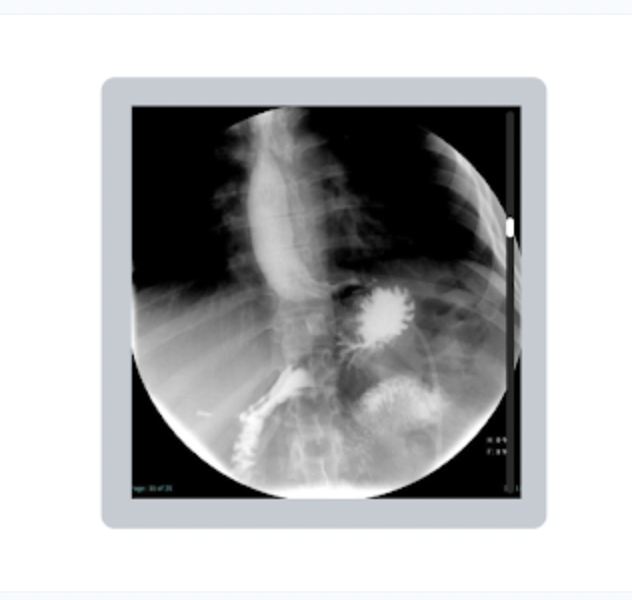
Which fluoroscopic procedure is demonstrated in the following image?
a. urology study
b. gastroenterology study
c. cardiology study
d. orthopedic study
b. gastroenterology study
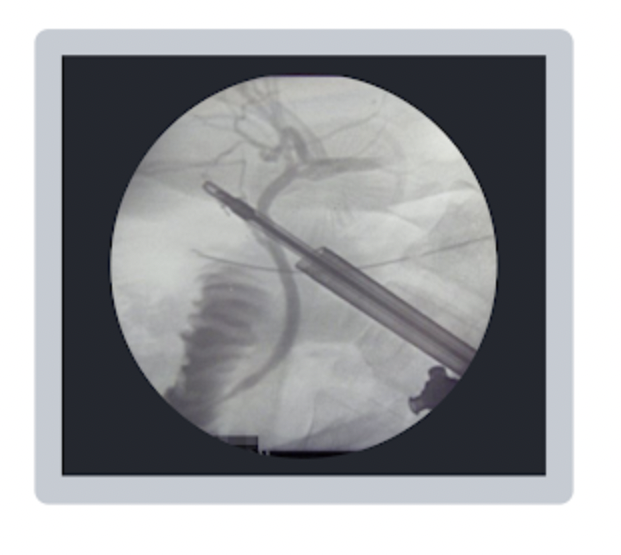
Which mobile fluoroscopy procedure was taking place when the following image was taken?
a. retrograde urethrogram
b. upper gastrointestinal (GI) study
c. intraoperative cholangiogram
d. barium enema
c. intraoperative cholangiogram