Geography - Rivers
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
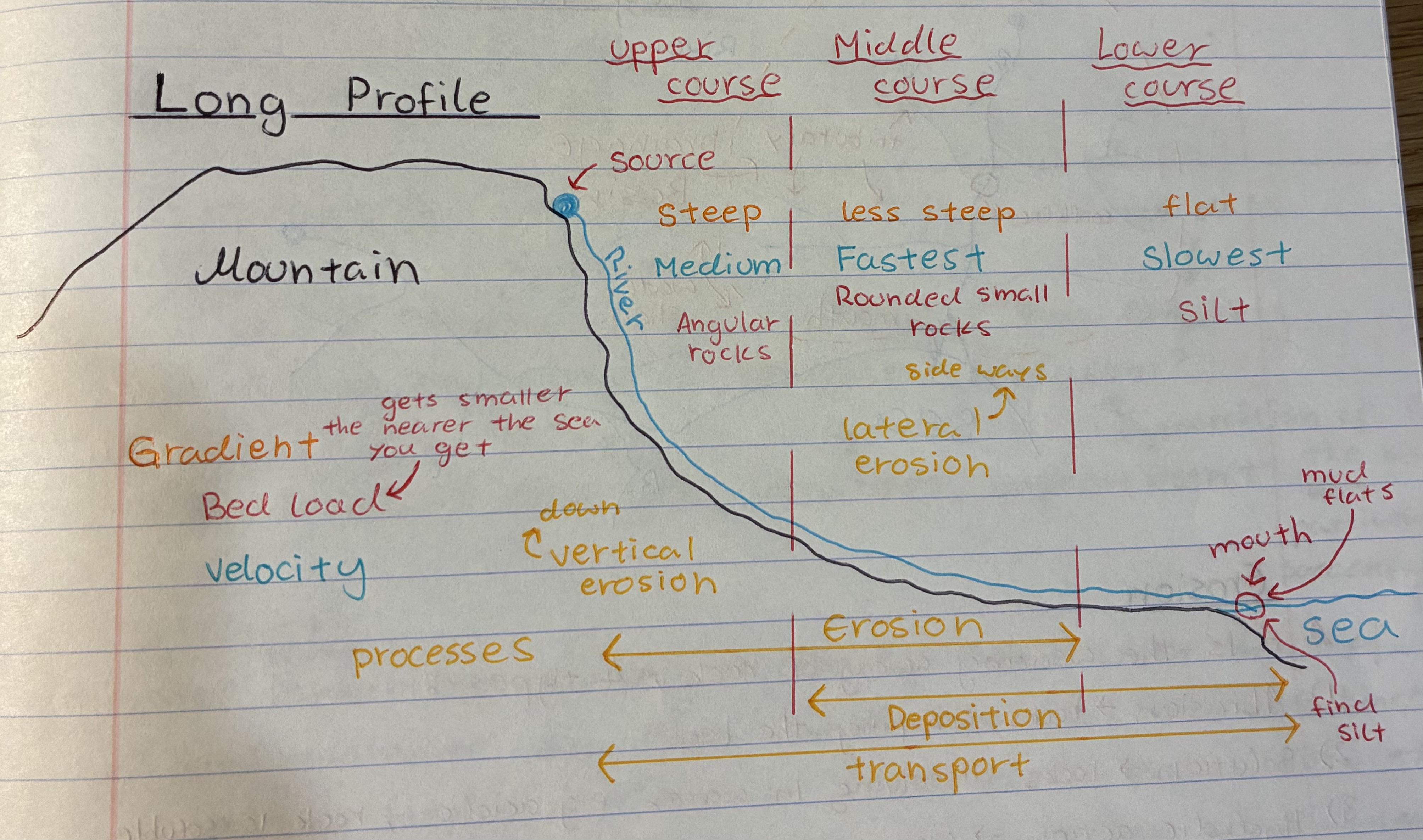
Describe the long profile of a river
what are some landforms you can find in the upper course
V shaped valleys
waterfalls + gorges
interlocking spurs

what are some landforms you can find in the middle course
meanders + oxbow lakes
what are some landforms you can find in the lower course
flood plains and levees
Estuary + salt marshes + mud flats
what is a river’s discharge
The amount of water flowing past a point in 1sec
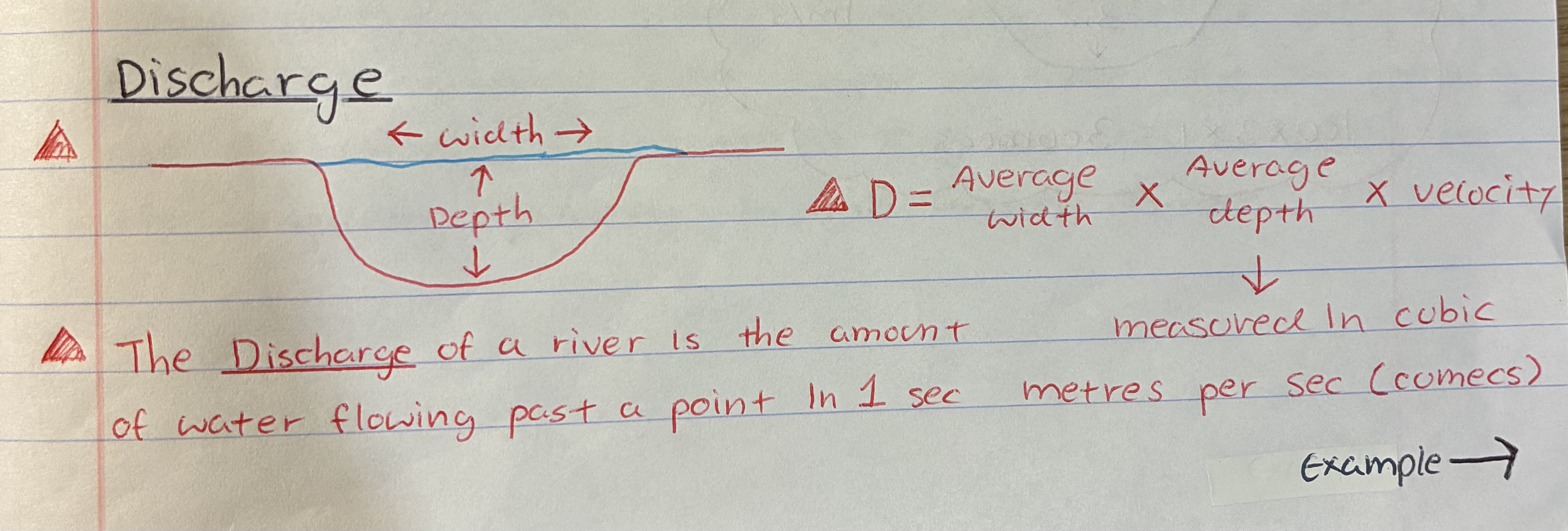
what are the cross profile like in the 3 courses of a river

what is a drainage basin
a geographical area where all surface water, such as rain and snowmelt, collects and drains into a single point, like a river, lake, or ocean
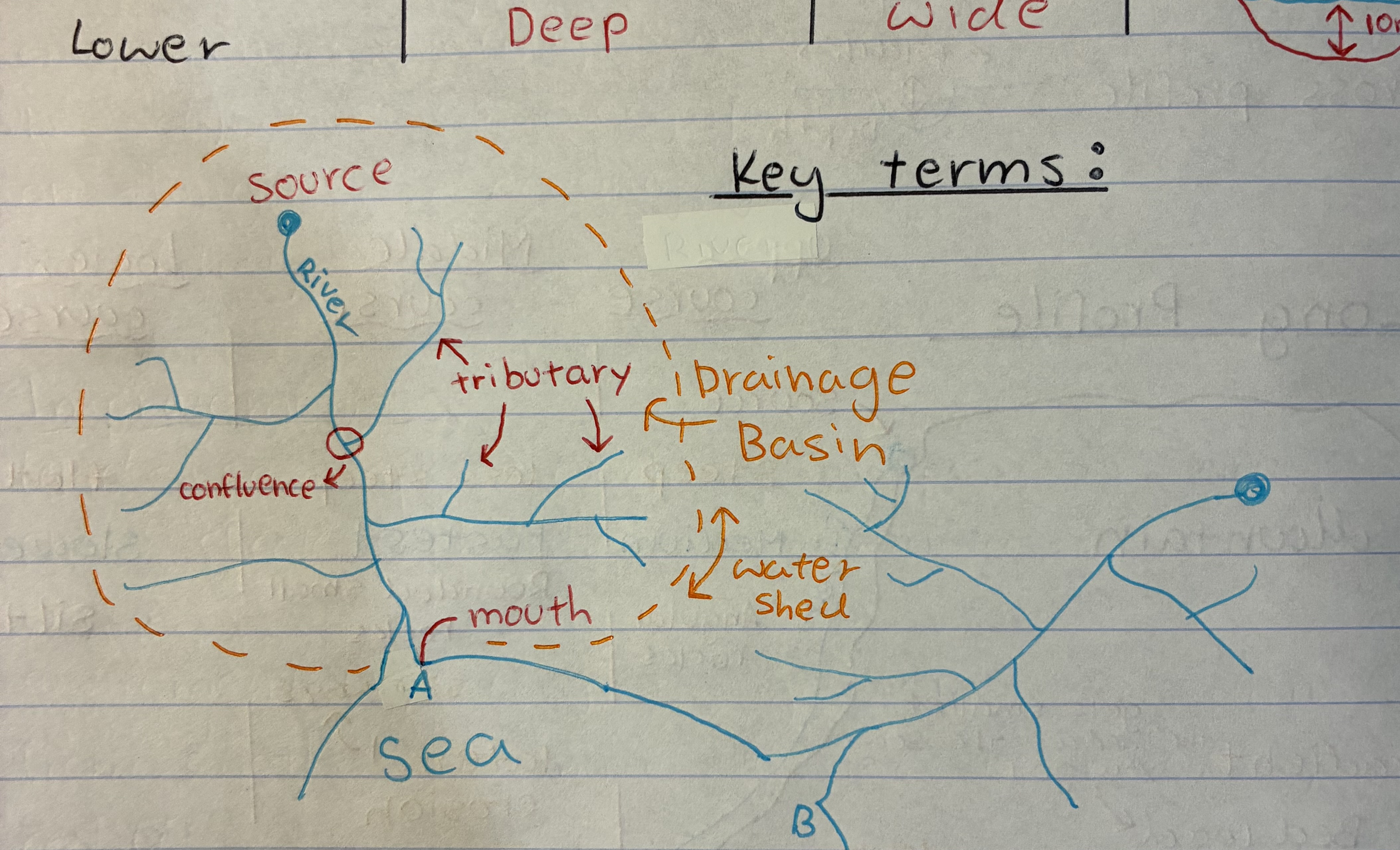
what is a tributary
a river or stream flowing into a larger river or lake
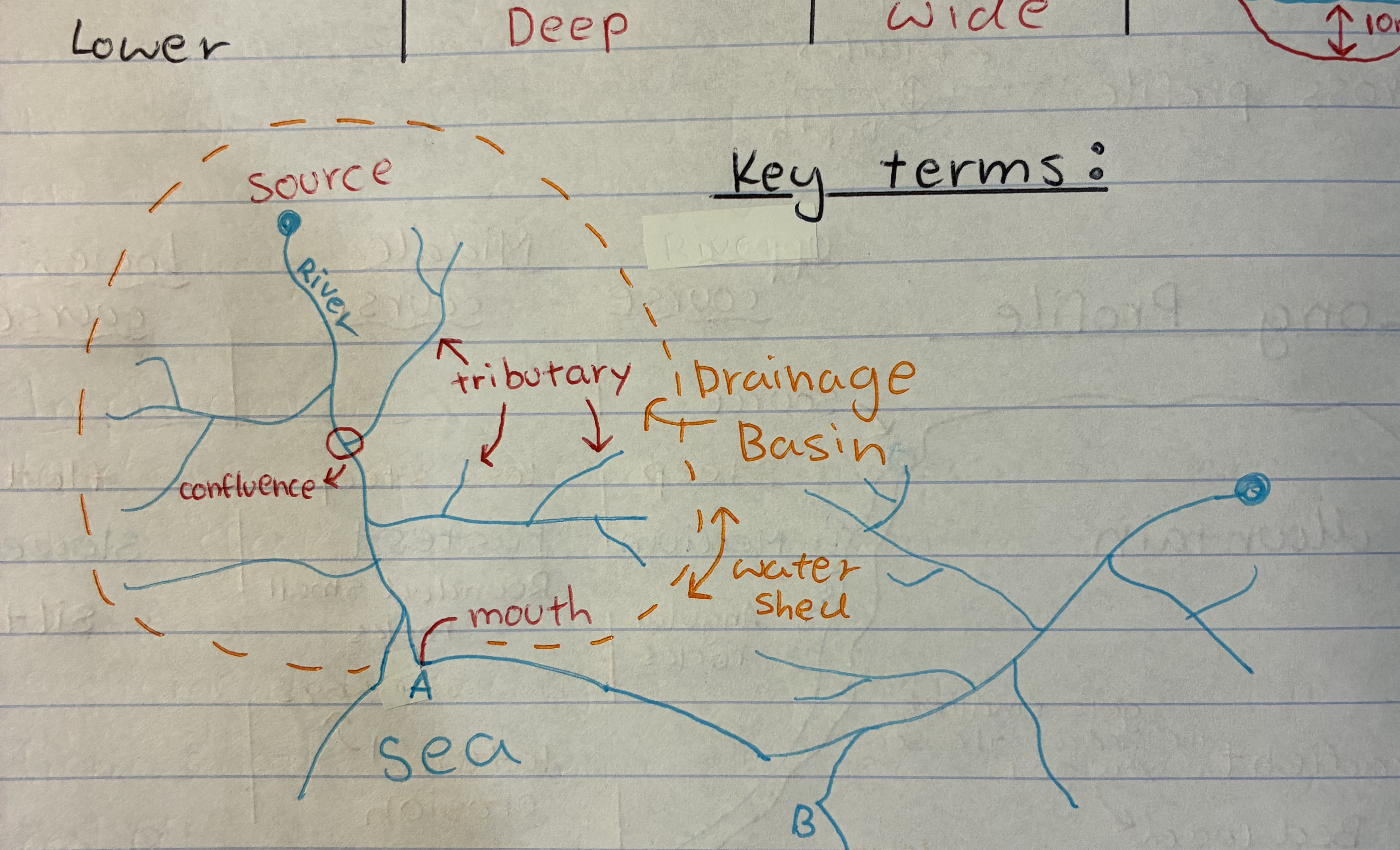
what is a water shed
an area or ridge of land that separates waters flowing to different rivers, basins, or seas.
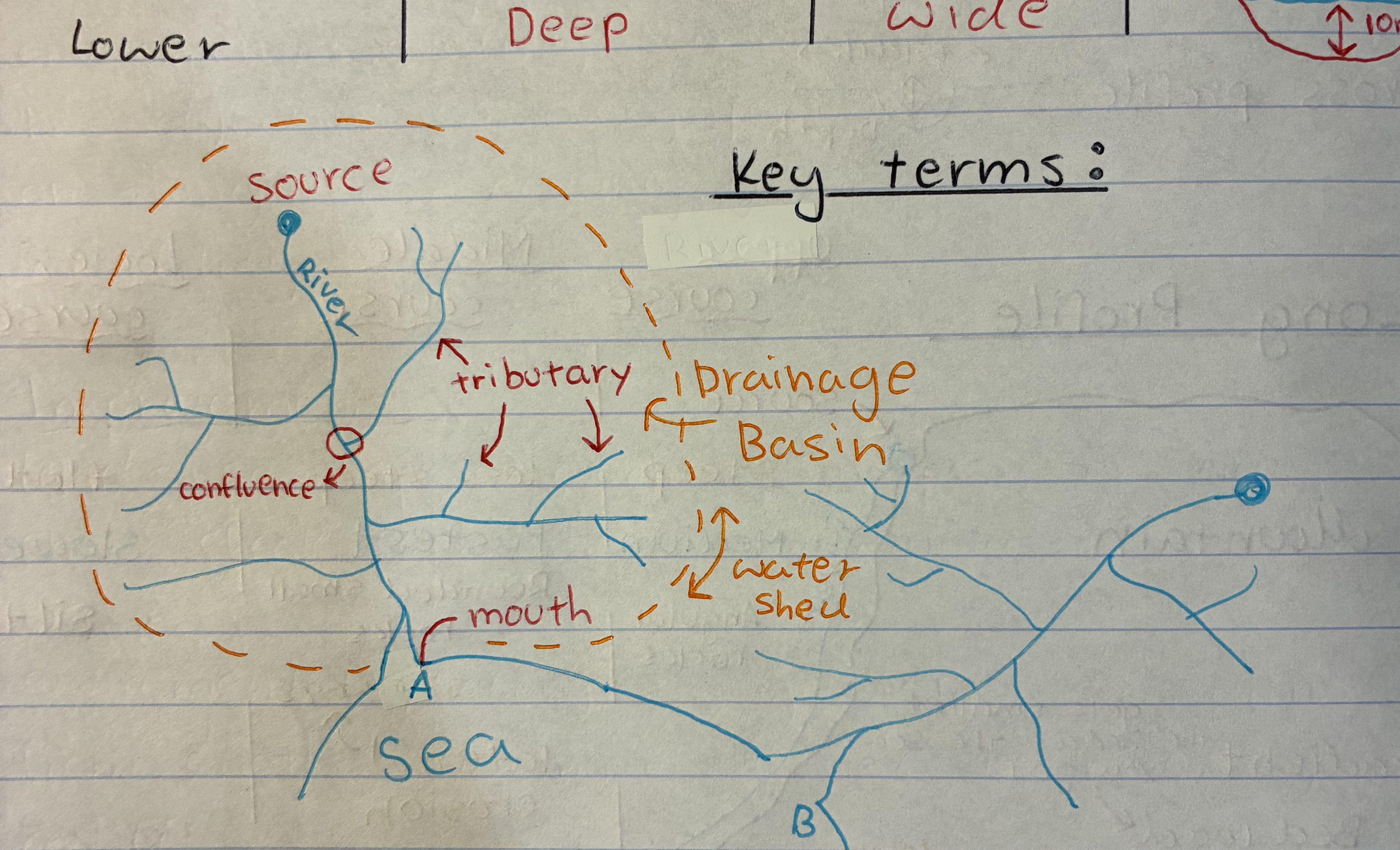
what is a confluence
where the tributaries meet the main river
what are the 4 types of erosion
1) Abrasion → rocks scraping land
2) solution → rocks dissolving in water e.g water is acidic/ rock is soluble
3) Hydrolic action → water smash against bed/bank
4) Attrition → rocks banging together
what’s one of our case study about rivers called
The River Tees
what’s the gradient like in a river
UC → steep
MC → less steep
LC → flat
what’s the bed load like in a river
UC → Angular rocks
MC → rounded small rocks (due to erosion)
LC → silt
what’s the velocity like in a river and state why
UC → medium bc the channel is shallow and small + friction from big rocks slows down flow
MC → fastest bc the channel becomes wider and deeper + less friction from rocks in river beds + more discharge from tributaries
LC → slowest bc flatter gradient + inc of friction on river bed
when does vertical (downwards) and lateral (side ways) erosion happen in a river
vertical → upper course, why it forms V-shaped valleys
Lateral → middle course, why it forms river cliffs
what’s the largest river in the UK
River severn
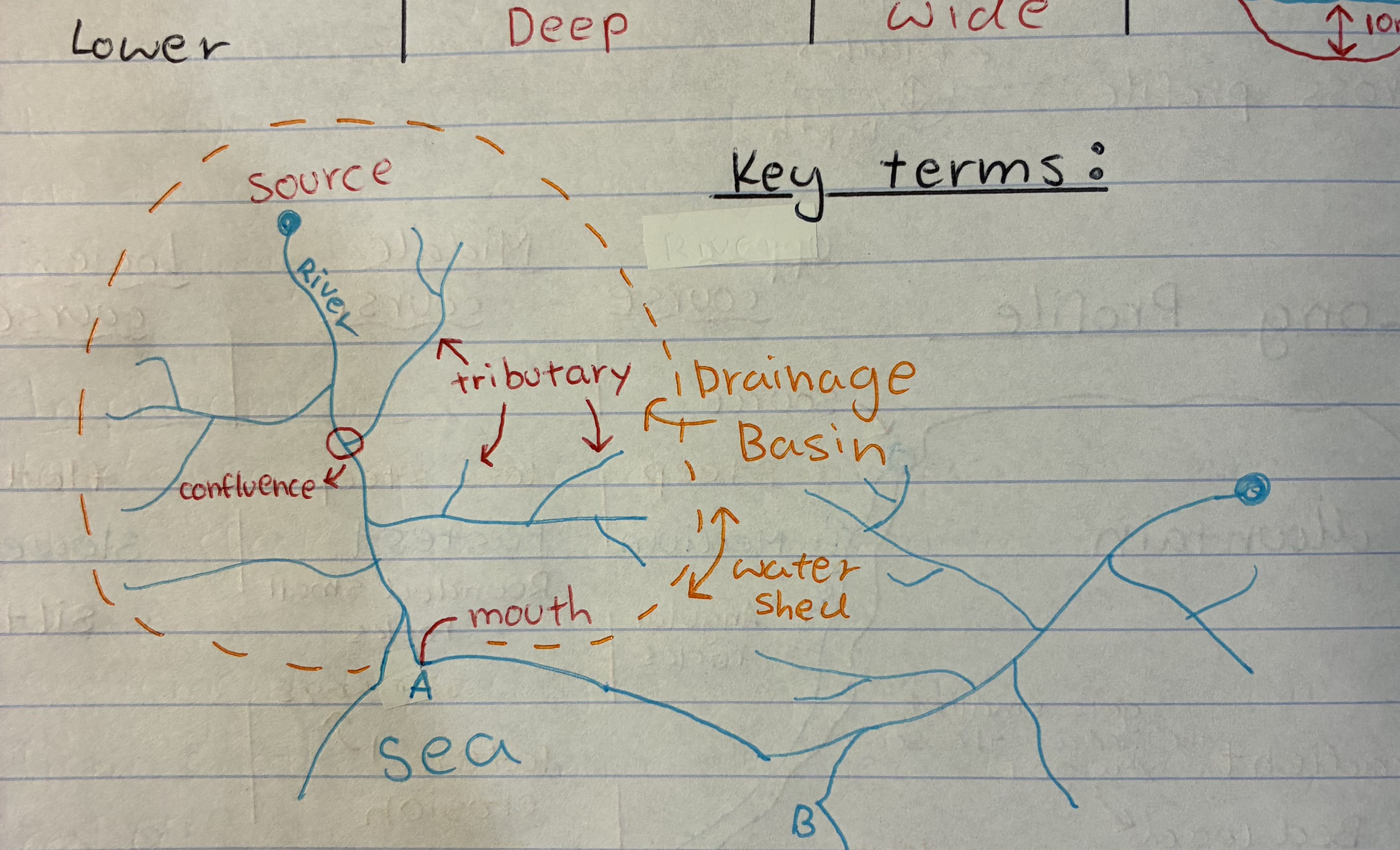
what are the 4 types of transportation in rivers
1) Traction → rolling
2) saltation → bouncing
3) suspension → carried e.g salt
4) solution → dissolved
What are info abt case study - River Tees that i do not know how to put in question so like just remember it + watch video

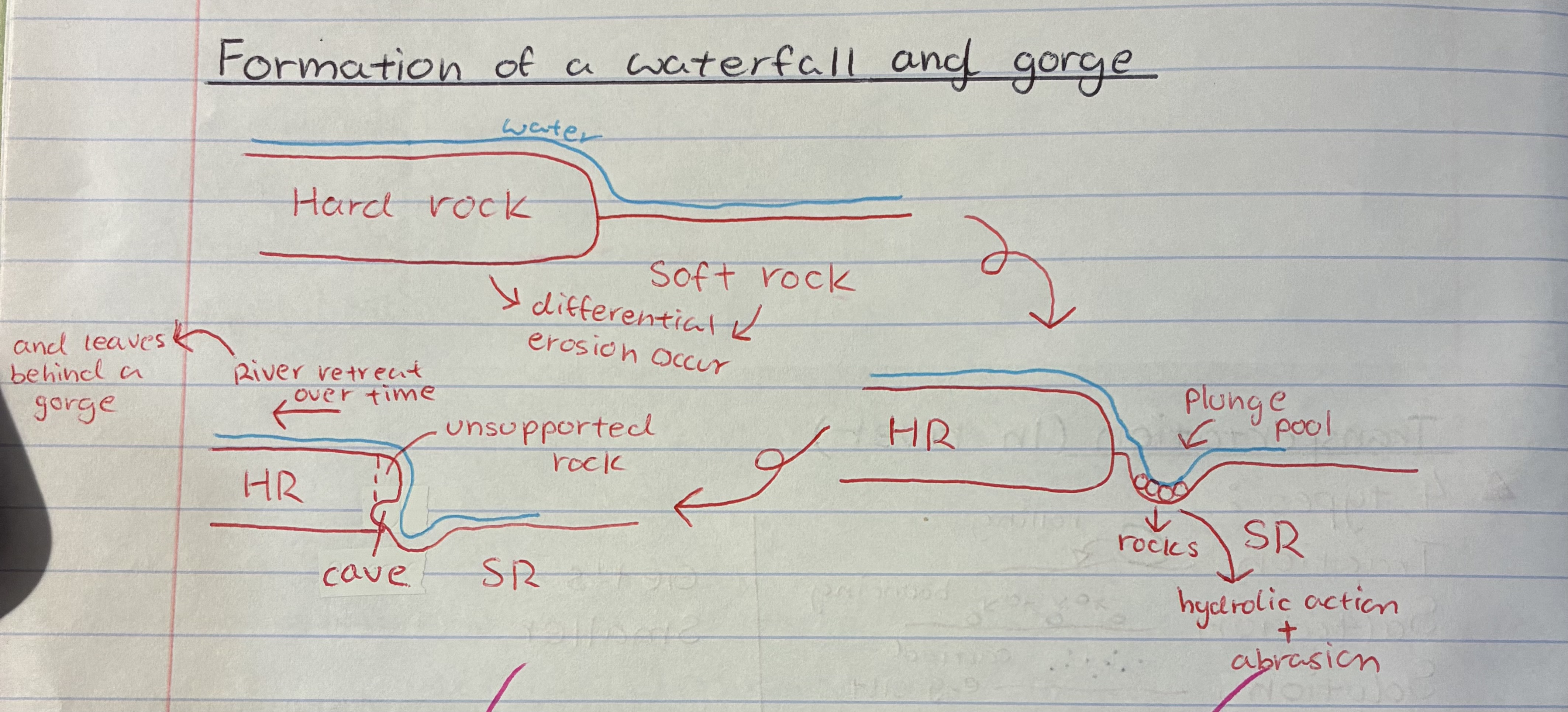
explain the formation of a waterfall + gorge
1) Where you find hard rock over soft rock, differential erosion occurs causing soft rock to erode faster
2) making a plunge pool where hydraulic action and abrasion happen
3) causing a cave to form behind the waterfall, this then causes the rock above to become unsupported
4) which will then eventually collapse and the waterfall will retreat as this process repeats
5) Eventually leaving behind a gorge
explain how V-shaped valleys are formed
through vertical erosion where due to the potential difference, the river erodes downwards

explain how interlocking spurs are formed
differential erosion occurs as the river meets both hard and soft rock so the river erodes the soft rock faster, causing the river to bend
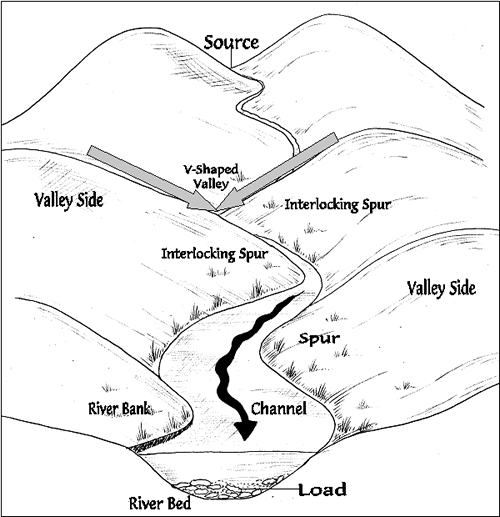
explain how meanders and oxbow lakes are formed ( EXAMINERS FAV Q)
1) River flows faster on the outside than inside of a river bend
2) Therefore river cliffs form outside of bend through hydrolic action + abrasion
3) On the inside bend you get deposition which forms a river beach
4) as the bends grow, the neck of the meander slowly joins leaving behind an oxbow lake
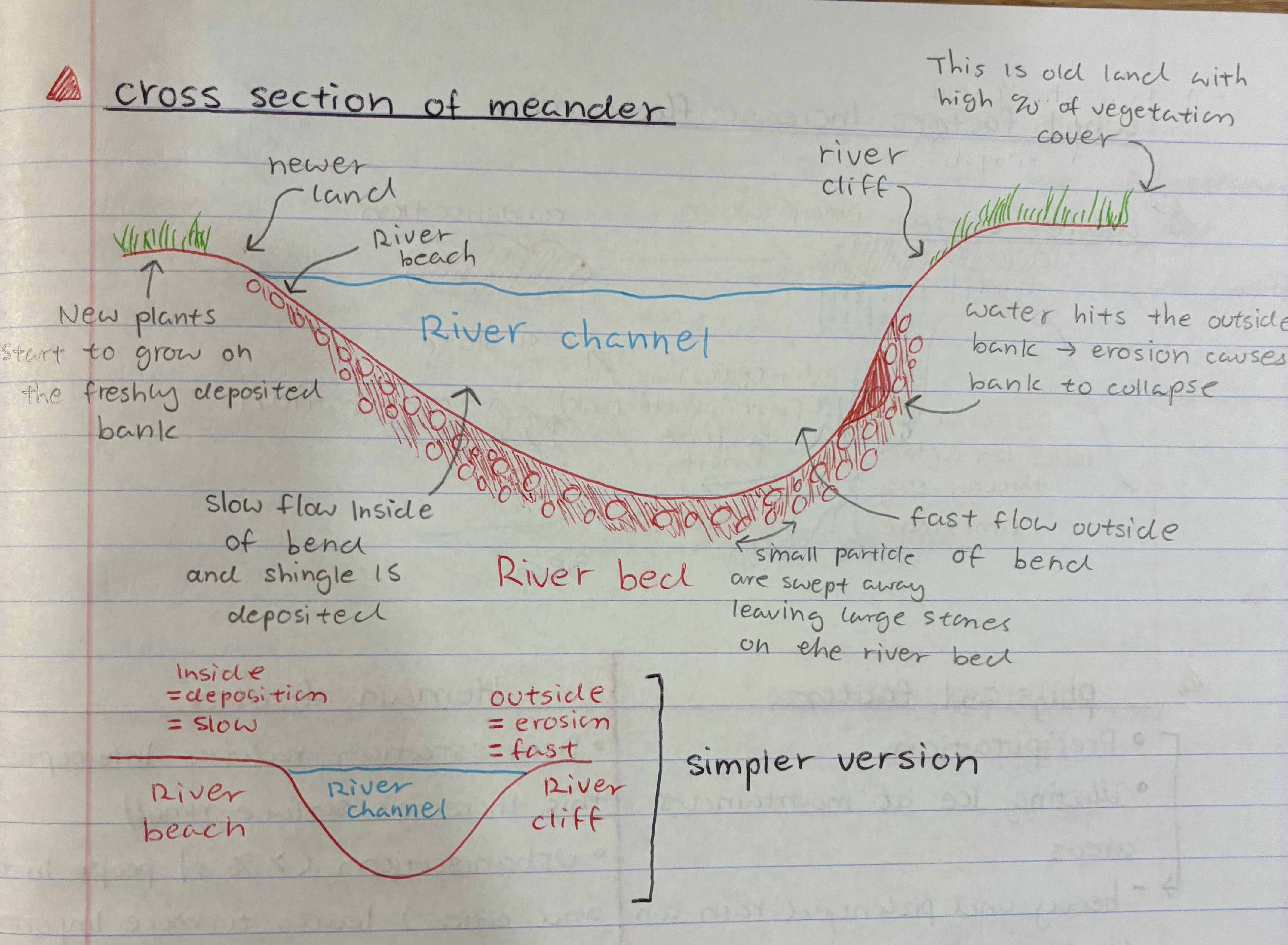
describe the cross section of a meander
1) the channel is asymmetrical meaning one side is steep and the other gentle
2) steep side is outside bend = river flows fast + lateral erosion + deeper = river cliff
3) gentle side is inside bend = river flows slower + deposition = river beach
what are flood plains and how are levees formed
Floodplains is the area of flat land on both sides of a river that regularly floods
1) when river flood they carry sediments
2) larger sediments are deposited closer to river
3) as water flows away from river they lose energy = becomes slower
4) smaller sediments deposites further away from river
5) so sediments left behind are called levees
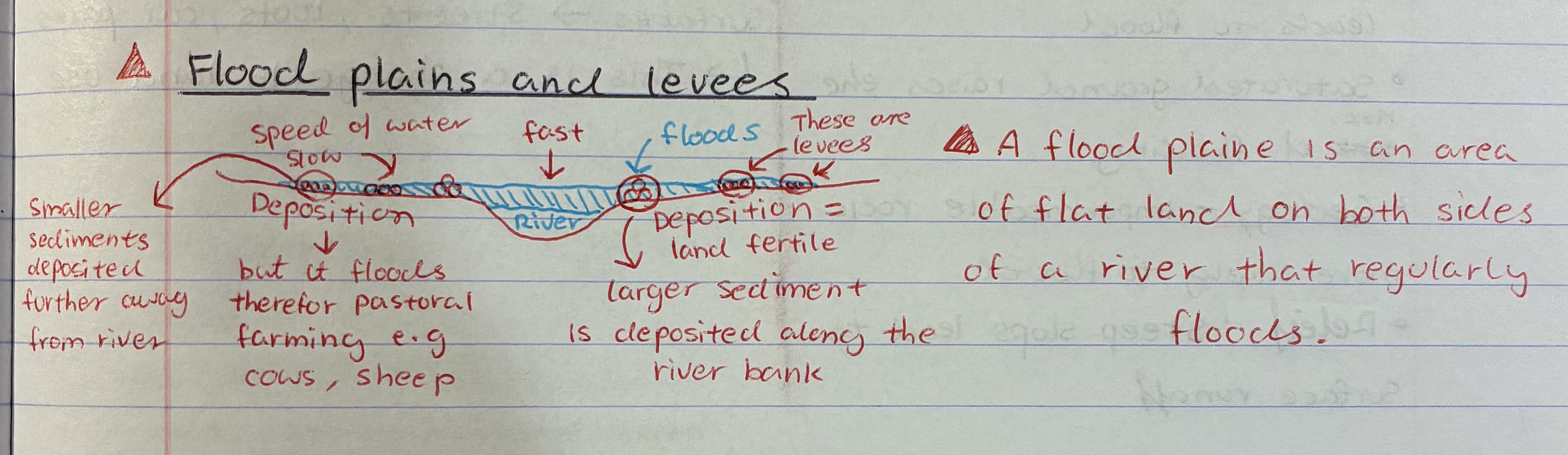
what is a method to make use of floodplains
do pastoral farming e.g cows + sheeps
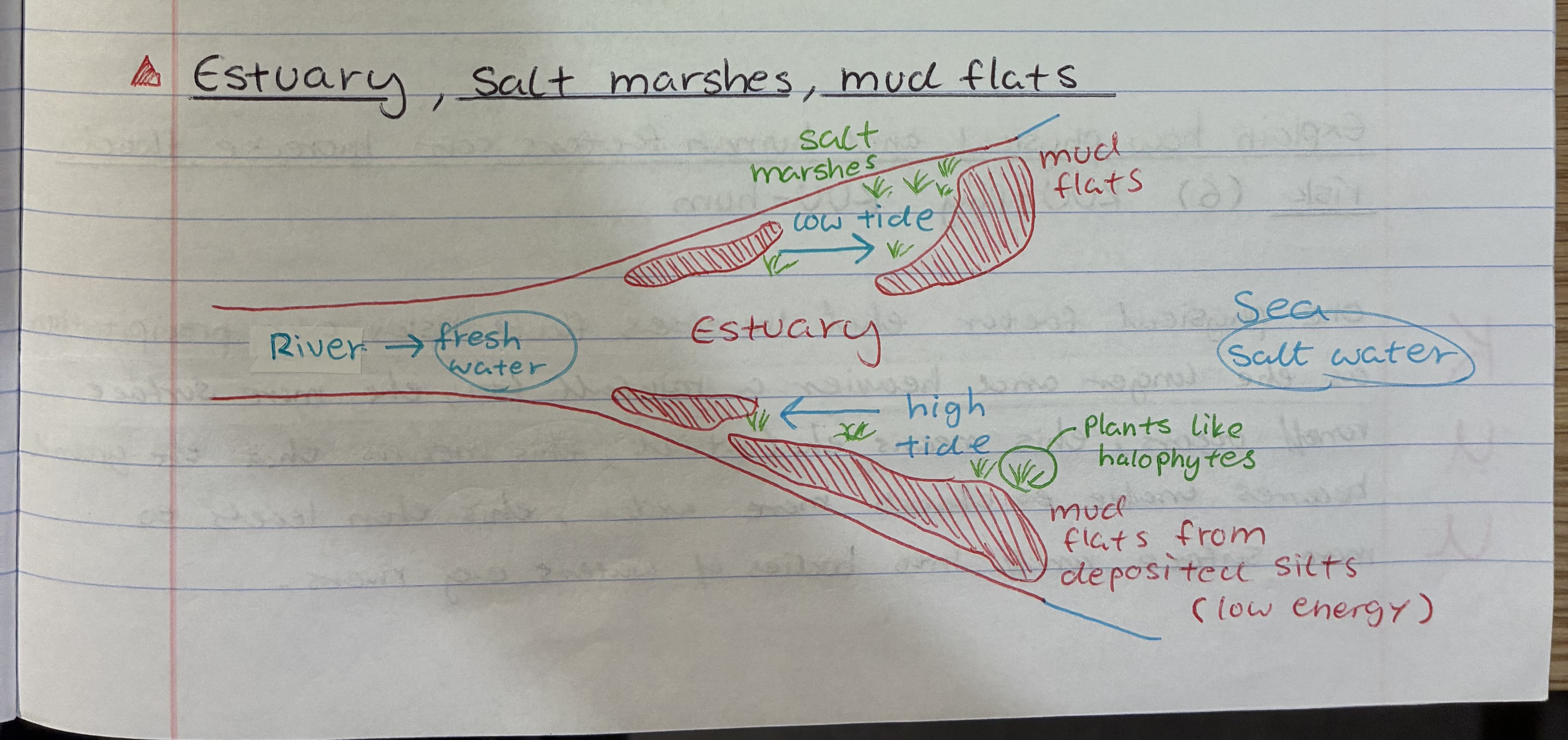
what is an estuary and how are salt marshes and mud flats formed
Estuary is the mouth of the river where fresh river water meets salt water from the sea
1) As water constantly moves from high to low tide, sediments like silt is deposited by the banks or bed → bc water flows at low energy = mud flats
2) overtime salt resistant vegetation will grow on the mud flats e.g halophytes = salt marshes
describe the water cycle
1) Water evaporates from the sea
2) condenses to form clouds, which are carried by wind
3) When clouds become heavy, water falls back to Earth as rain, snow, sleet, or hail
4) water flows overland into rivers and streams
5) Some water infiltrates into the ground bc of permeable rocks, e.g lime limestone → eventually back to rivers, lakes, or sea
6) Some are intercepted by trees, reducing surface runoff into rivers/streams
7) Eventually, the water collects in oceans, lakes, and rivers — and the cycle repeats.
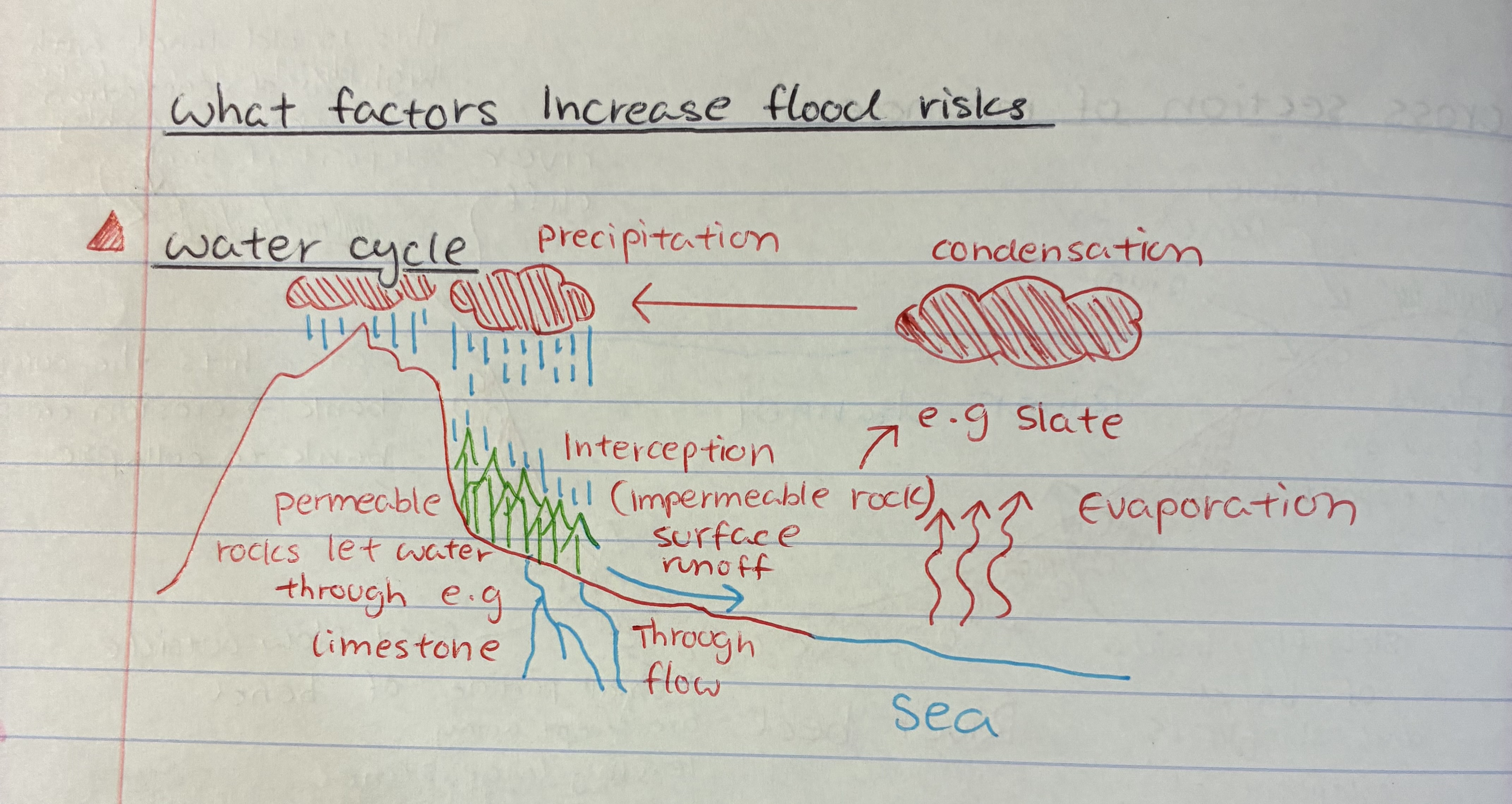
what are the physical factors effecting flood risks
precipitation → heavy + prolonged rain can lead to floods
melting ice at mountainous areas
saturated ground → raises risk
geology → impermeable rock = likely to flood
relief → steeps slopes lead to surface runoff

what are the human factors effecting flood risks
deforestation → reduces interception, inc. surface runoff
urbanisation → more impermeable surfaces e.g roofs, streets, car parks → this is a change in land use

what are hydrographs
A graph which shows how river discharge changes in response to rainfall
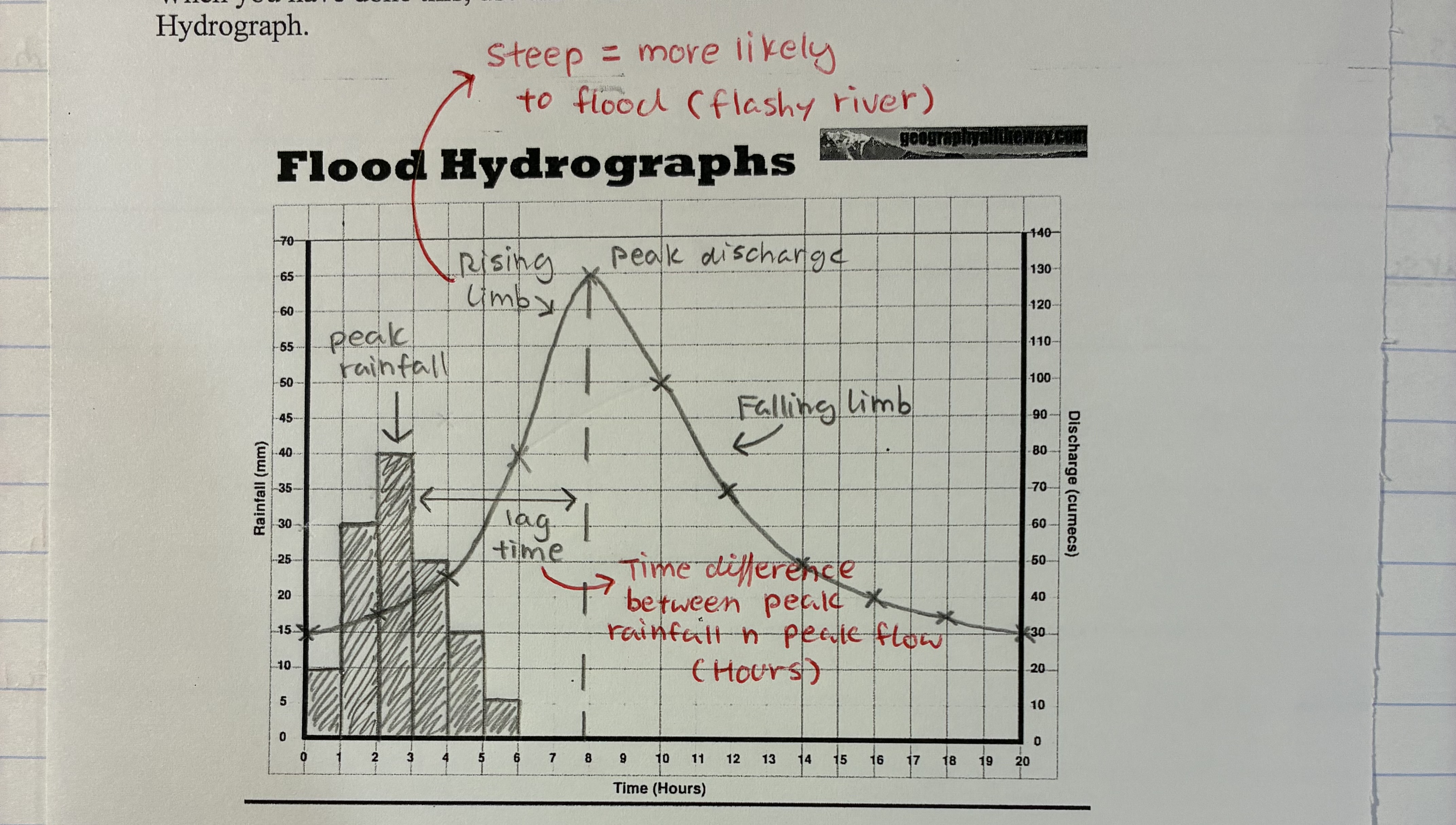
is the river cam a flashy river
NO bc:
1) permeable rock
2) land use - mainly farming
3) relief is flat - little surface runoff
4) small drainage basin
What are the different hard engineering flood defenses
dams + resevoirs
embankments
flood relief channel
channel straightening
what are the different soft engineering flood defences
flood warning and prep
afforestation
floodplain zoning
river restoration
what are the positive + negatives of dams and resevoirs
positive
hydroelectric power → green energy
can regulate flow of river → reduces flood risks
reliable water supply
negative
uses concrete which releases CO2 when produces
expensive → high maintenance + opportunity cost
can break if not maintained well and burst
what are the positive + negatives of embankments
positive
inc. rivers capacity → uses soil from bottom of river
cheap
negative
may disrupt aquatic life in river e.g newt
what are the positive + negatives of flood relief channel
positive
river discharge is reduced
negatives
There will be an increased risk of flooding where the flood relief channel re-joins the river. If bankfull capacity is reached in the flood relief channel, it will flood the surrounding area.
what are the positive + negatives of channel straightening
positive
inc. river capacity
less water flow in river
negative
moves problem downstream
made from concrete
what are the positive + negatives of flood warnings
positive
flood maps can be produced → allows ppl to plan for floods
local authority + emergency services can plan their responses to floods
negative
cannot be 100% certain of how an area will respond to flooding
areas at high risk of flooding can see house properties lose their value, insurance premiums can become very expensive
what are the positive + negatives of afforestation
positive
inc. interception/transpiration/root uptake → reduce surface runoff
it’s natural
negative
not possible to cover the whole drainage basin of a river with trees
most trees lose leaves during autumn + winter → reducing interception in those months
what are the positive + negatives of floodplain zoning
positive
Buildings are not constructed in areas at risk of flooding
Impermeable surfaces are not constructed on the floodplain → so the risk of flooding is not increased.
negative
might be too late to change location of the town e.g London
what are the positive + negatives of river restoration
positive
Discharge in the river reduces, meaning there is less risk of flooding downstream.
Little or no maintenance is required, which makes this a low-cost solution.
Biodiversity is maintained along the river.
negative
flooding is reintroduced to the area. those with valuable land/housing/properties will now be significantly effected
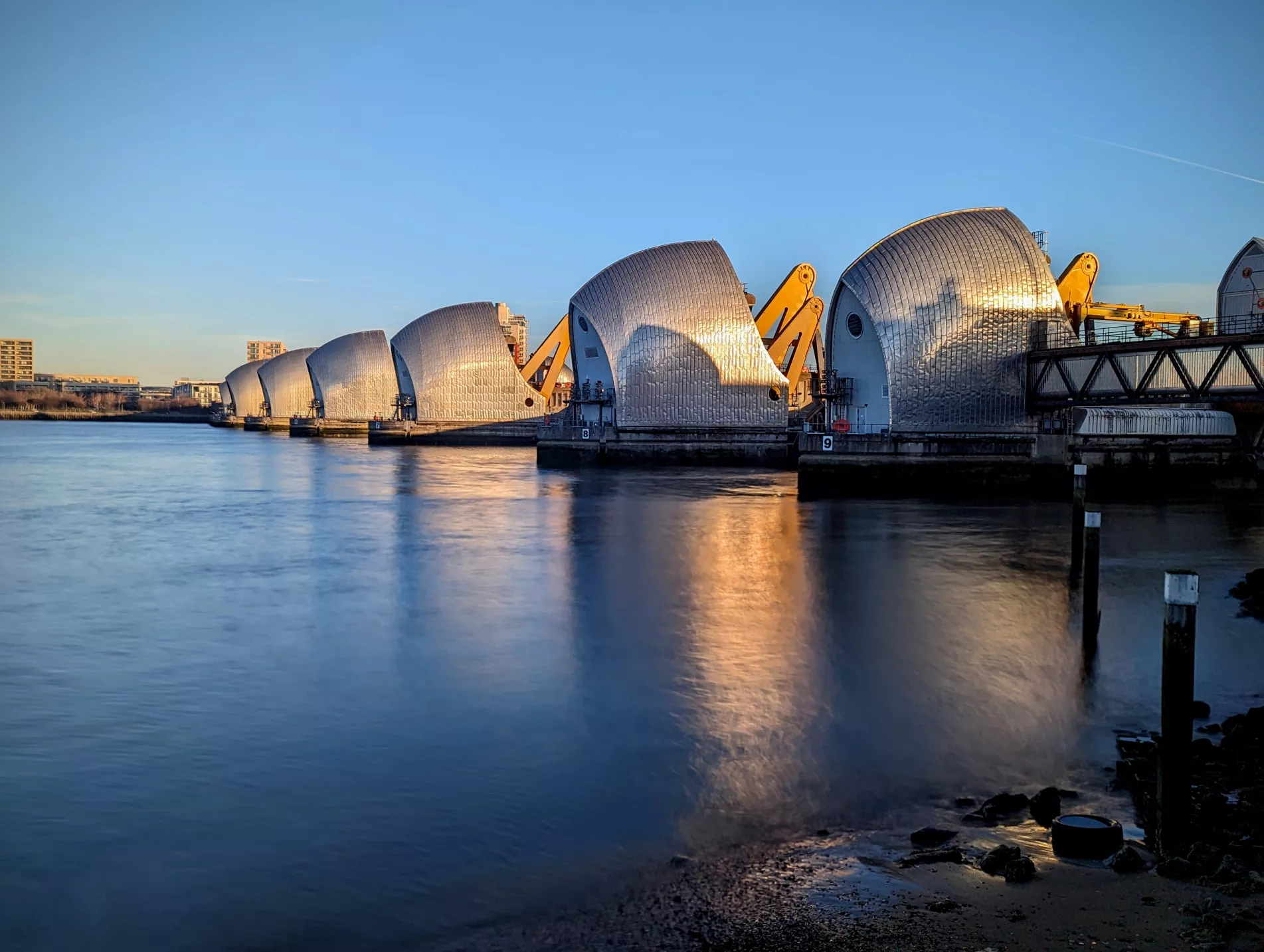
Give an example of a hard engineering in the UK
Thames Barrier (London)
big investment
going to rebuild in future → bc of rising sea lvl due to: melting ice at Antarctica + greenland and thermal expansion

Give an example of a river restoration
Using beavers
builds mini dams for free
reduce velocity of river
however they chop down trees and eats lots of fish
who manages flood risk in the UK
Environmental Agency
what’s another of our case study about rivers + coasts
the Sumerset levels (2014 flood)
what are some facts about the Sumerset Levels
located at the SW of England
they are an area of flat land in the centre of Sumerset
surrounded by high lands (Hills)
it’s very low lying + has been drained for farm land
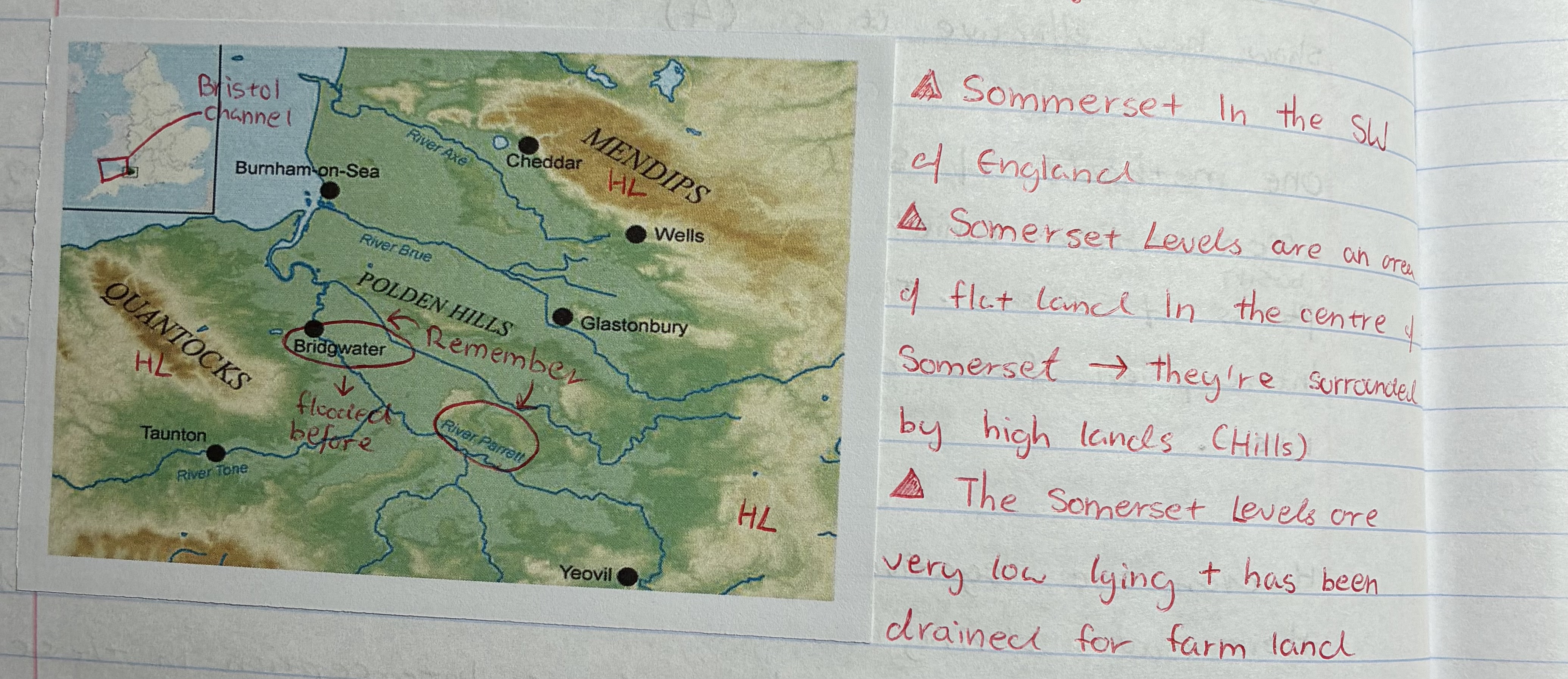
what are the causes of flooding in Sumerset Levels 2014
1) relief → steep slopes inc. surface run off, e.g Mendips average 240m above sea lvl
2) many rivers → inc. discharge, 7 major rivers w large flood plains
3) storm → low pressure causing sea lvl to rise, turns to flood + inc. in rainfall wettest Jan on record since 1910, 350mm of rain

what are the social impacts of floods in Sumerset Levels 2014
houses were flooded, properties + possessions dmg
needs to live in another area → job + schooling are disturbed → can last for weeks n months
mental health ⬇
what are the economic impacts of floods in Sumerset Levels 2014
houses were dmg £16m
house prices ⬇
insurance ⬆
farmers have to moce cattle → £ ⬆ (feed + rent)
what are the environmental impacts of floods in Sumerset Levels 2014
Barn owl → no food and died
snakes → can swim but ran out of energy n drowned
list 3 hard engineering flood management schemes in Sumerset Levels 2014
dredging → inc. capacity + velocity
Building river walls (proposed) + tidal barrage £100m! → contains water within river + prevent soil erosion at banks
Embankments

name the soft engineering method for flood management in Sumerset 2014
Sumerset city council + Environmental Agency + National Gov agreed that in return for £200m local organisation will be resposible next time
what are the advantages of the flood management schemes in Sumerset Levels
will reduce flood risk in the future, preventing ppl from leaving the area
gives Env Agency gave more power to local Gov in Sumerset

what are the disadvantages of the flood management scheme in Sumerset
hard engineering methods dmg wildlife habitats
not very sustainable → concrete = CO2
maintenance cost