Biology Unit Test
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/72
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
1
New cards
Why do cells divide?
**Growth** → To increase the number of cells in the body.
**Repair** → To replace dead, damaged or old cells.
**Reproduction** → Can make exact copies (clones).
**Repair** → To replace dead, damaged or old cells.
**Reproduction** → Can make exact copies (clones).
2
New cards
G1 Phase
\
* Cell grows
* New proteins and organelles made
* Cell grows
* New proteins and organelles made
3
New cards
S Phase:
\
* Synthesis
* DNA is replicated (copied)
* Synthesis
* DNA is replicated (copied)
4
New cards
**G2 Phase:**
* Cell grows again and prepares for mitosis (division)
\
\
5
New cards
Chromosome
**the condensed form of genetic material; composed of DNA and proteins (hereditary material)**
6
New cards
Chromatin
**the non-condensed form of genetic material; composed mostly of DNA and proteins**
7
New cards
Necrosis
Cells may die due to external factors (ex: toxins, infections, trauma).
8
New cards
Apoptosis
The controlled death of old cells. (ex: White blood cells divide to fight viral infections. When they’re no longer required, they undergo apoptosis).
9
New cards
Normal Cells vs Cancer Cells
Normal Cells -
Make exact copies of themselves through mitosis
Reproduce for about 50-60 cell divisions
Stick together to form masses of cells as appropriate
Self-destruct when too old or too damaged
\
Cancer Cells -
Make exact copies of themselves through mitosis
Do not stop reproducing
Do not stick to other cells, behave independently
May move to another location in the body
Make exact copies of themselves through mitosis
Reproduce for about 50-60 cell divisions
Stick together to form masses of cells as appropriate
Self-destruct when too old or too damaged
\
Cancer Cells -
Make exact copies of themselves through mitosis
Do not stop reproducing
Do not stick to other cells, behave independently
May move to another location in the body
10
New cards
Cell Differentiation
the process of creating a specialized cell
11
New cards
zygote
the cell where a sperm fertilizes the egg
12
New cards
embryo
unborn offspring, more cells than a zygote
13
New cards
**What Causes Cell Specialization?**
\
1. **Cytoplasm differences**
* **Asymmetric distribution (different on each side of cell) of organelles and other factors (ie. Proteins)**
* **Produces different daughter cells**
2. **Environmental conditions**
* Differences in temperature, nutrients, stress, etc
3. **Neighboring cells**
* **Substances made by nearby cells can diffuse into the developing cell through the cell membrane (remember, the cell membrane is selectively permeable)**
* These substances then accumulate and affect change in cell development
1. **Cytoplasm differences**
* **Asymmetric distribution (different on each side of cell) of organelles and other factors (ie. Proteins)**
* **Produces different daughter cells**
2. **Environmental conditions**
* Differences in temperature, nutrients, stress, etc
3. **Neighboring cells**
* **Substances made by nearby cells can diffuse into the developing cell through the cell membrane (remember, the cell membrane is selectively permeable)**
* These substances then accumulate and affect change in cell development
14
New cards
Stem cells
**cells able to differentiate into many different types of cells**
15
New cards
Cell Potency
**ability for stem cells to differentiate into different cell types. The more potent the stem cell, the more types of cells it can give rise to.**
16
New cards
Totipotent/Omnipotent
**gives rise to all cell types, cells found only in the early stages of the embryo and placenta**
17
New cards
**Pluripotent**
**gives rise to all types, except placenta**
18
New cards
Multipotent
**limited number of cell types**
19
New cards
Three levels of cell potency
Totipotent/Omnipotent, **Pluripotent** and Multipotent
20
New cards
**Embryonic stem cells**
\
* **Pluripotent**
* Divides into any cell type
* **Research often banned due to ethical reasons**
* **Pluripotent**
* Divides into any cell type
* **Research often banned due to ethical reasons**
21
New cards
**Umbilical stem cells**
\
* **Multipotent (limited differentiation)**
* Used to **treat blood disorders, cancer,** some **immune disorders** and **bone marrow failure**
* Retrieved at birth of a child
* **Clinical trials of umbilical tissues**
* **Multipotent (limited differentiation)**
* Used to **treat blood disorders, cancer,** some **immune disorders** and **bone marrow failure**
* Retrieved at birth of a child
* **Clinical trials of umbilical tissues**
22
New cards
Adult stem cells
\
* Multipotent
* **Example – bone marrow: produces white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets**
* **Still being researched through clinical trials**
* Multipotent
* **Example – bone marrow: produces white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets**
* **Still being researched through clinical trials**
23
New cards
Tissue
**a collection of similar cells that perform a specific function**
24
New cards
Animals have **4 types of tissues**
\
1. **Epithelial**
2. **Muscular**
3. **Connective**
4. **Nervous**
1. **Epithelial**
2. **Muscular**
3. **Connective**
4. **Nervous**
25
New cards
Tissues - Epithelial
\
* **Lines the internal and external surfaces of the body**
* **Forms barriers by connecting adjoining cell membranes**
* **Lines the internal and external surfaces of the body**
* **Forms barriers by connecting adjoining cell membranes**
26
New cards
**Tissues - Muscular**
**Moves the body or organ by contracting and relaxing**
27
New cards
**Tissues - Connective**
\
* **Many different functions**
* **Strengthens, supports, insulates, protects, fuel source, transportation**
* These **cells** are **surrounded by an extracellular matrix** (substances between cells, substance depends on the tissue but could include proteins, minerals, support molecules, etc)
* **Many different functions**
* **Strengthens, supports, insulates, protects, fuel source, transportation**
* These **cells** are **surrounded by an extracellular matrix** (substances between cells, substance depends on the tissue but could include proteins, minerals, support molecules, etc)
28
New cards
**Tissues - Nervous**
\
* Made of **neurons**
* Have **long projections** to **send and receive signals**
* Coordinates bodily actions
* Made of **neurons**
* Have **long projections** to **send and receive signals**
* Coordinates bodily actions
29
New cards
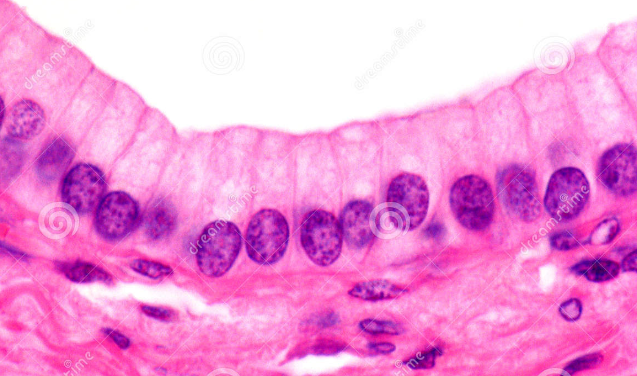
What is this? What is its general tissue type? Its Function?
columnar epithelial, epithelial tissue.
30
New cards
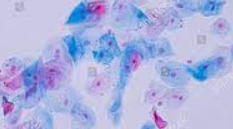
What is this? What is its general tissue type? Its Function?
Squamous epithelial, epithelial tissue
31
New cards
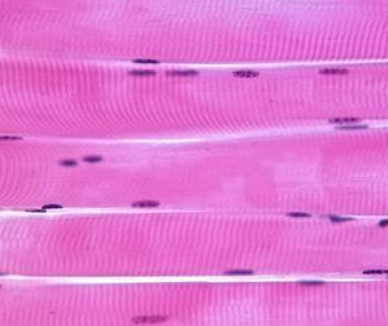
What is this? What is its general tissue type? Its Function?
Muscular tissue, Skeletal Muscle
32
New cards
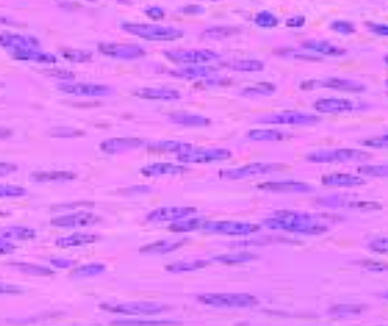
What is this? What is its general tissue type? Its Function?
Muscular tissue, smooth muscle.
33
New cards
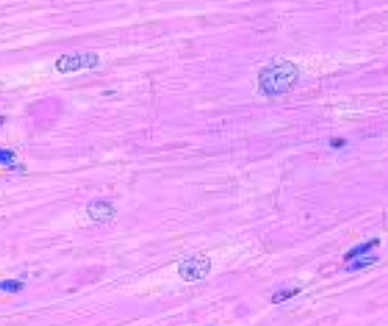
What is this? What is its general tissue type? Its Function?
muscular tissue, cardiac muscle.
34
New cards
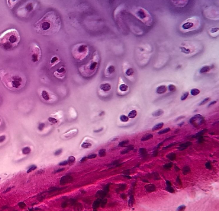
What is this? What is its general tissue type? Its Function?
connective tissue, cartalige
35
New cards
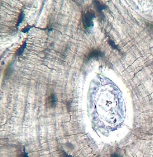
What is this? What is its general tissue type? Its Function?
Connective tissue, bone
36
New cards
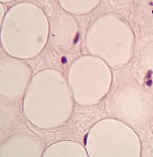
What is this? What is its general tissue type? Its Function?
connective tissue, adipose (fat)
37
New cards
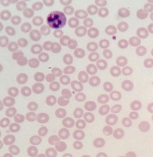
What is this? What is its general tissue type? Its Function?
Connective tissue, Blood
38
New cards
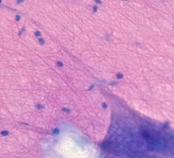
What is this? What is its general tissue type? Its Function?
Nervous tissue, Neurons
39
New cards
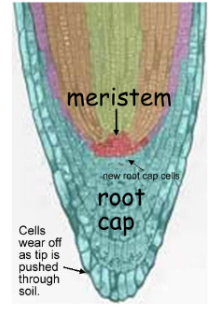
Meristematic cells
**unspecialized stem cells in plants, divides and differentiates into different plant tissues**
40
New cards
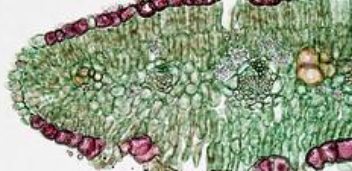
Plant Tissues – Dermal (or Epidermal)
* **Outermost layer of a plant**
* **Think of dermal tissues like the skin of the plant**
* Can be specialized further
* **Epidermal root cells – form root hairs to absorb water, minerals**
**Epidermal leaf cells** – produce a **waxy waterproof cuticle** around the leaf
* **Think of dermal tissues like the skin of the plant**
* Can be specialized further
* **Epidermal root cells – form root hairs to absorb water, minerals**
**Epidermal leaf cells** – produce a **waxy waterproof cuticle** around the leaf
41
New cards

**Plant Tissues – Vascular**
\
* For **water and nutrient delivery**, think of blood vessels
* **Xylem**
* **transports water and dissolved minerals**
* **from the roots to the leaves (transport goes one way only)**
* **Phloem**
* **transports a sugar solution (plant food)**
* **from the leaves to the roots and vice versa (transport goes both ways)**
* For **water and nutrient delivery**, think of blood vessels
* **Xylem**
* **transports water and dissolved minerals**
* **from the roots to the leaves (transport goes one way only)**
* **Phloem**
* **transports a sugar solution (plant food)**
* **from the leaves to the roots and vice versa (transport goes both ways)**
42
New cards
Xylem
* **transports water and dissolved minerals**
* **from the roots to the leaves (transport goes one way only)**
* **from the roots to the leaves (transport goes one way only)**
43
New cards
**Phloem**
* **transports a sugar solution (plant food)**
* **from the leaves to the roots and vice versa (transport goes both ways)**
* **from the leaves to the roots and vice versa (transport goes both ways)**
44
New cards
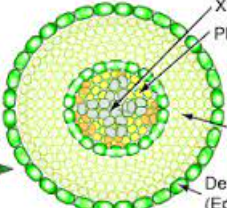
Plant Tissues – Ground Tissue
\
* Many functions
* **Photosynthesis**
* **Food and water storage**
* **Structural support**
* Many functions
* **Photosynthesis**
* **Food and water storage**
* **Structural support**
45
New cards
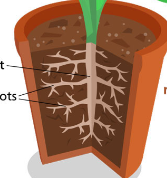
Root system
* Organs
* **Roots**
* **Roots**
46
New cards
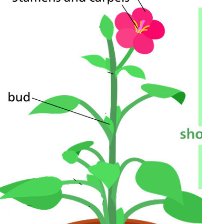
Shoot system
\
* Organs
* **Stem**
* **Leaves**
* **Flowers**
* Organs
* **Stem**
* **Leaves**
* **Flowers**
47
New cards
Root System - Functions
\
* **Absorption – water, minerals, nutrients**
* **Anchorage – hold the plant firmly in the soil**
* **Storage – food, water**
* Produces a slimy later at the tip of the root to reduce friction
* **Absorption – water, minerals, nutrients**
* **Anchorage – hold the plant firmly in the soil**
* **Storage – food, water**
* Produces a slimy later at the tip of the root to reduce friction
48
New cards
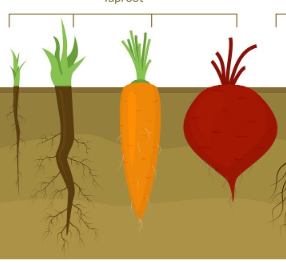
Tap roots
**one main root growing downward**
49
New cards
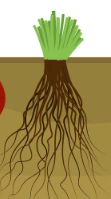
Fibrous roots
**many thin, branched out roots coming from the stem**
50
New cards
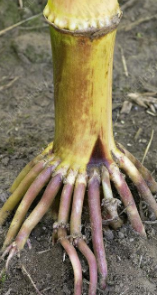
Adventitious roots
**comes from non-root tissue**
51
New cards
Shoot System - Stem
\
* Function
* **Supports the branches, leaves and flowers**
* **Transport substances between roots and leaves**
* Grows towards the light
* Function
* **Supports the branches, leaves and flowers**
* **Transport substances between roots and leaves**
* Grows towards the light
52
New cards
Shoot System - Leaves
\
* Function
* **Photosynthesis**
* Its **shape maximizes light capture and minimizes water loss (surface area)**
* Function
* **Photosynthesis**
* Its **shape maximizes light capture and minimizes water loss (surface area)**
53
New cards

Cuticle
**outer layer of protection, waxy**
54
New cards

Epidermis
produces the waxy layer
55
New cards
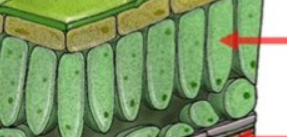
**Palisade mesophyll**
**where most photosynthesis happens**
56
New cards
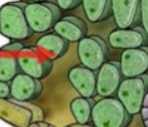
**Spongy** **mesophyll**
where O2 exits and CO2 enters the cells
57
New cards

**Vein**
**(xylem, phloem inside)**
58
New cards
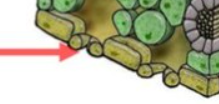
Stoma
**a pore to let water, O2, CO2 in and out of the leaf**
59
New cards

**Guard** **cells**
**open and close the stoma**
60
New cards

Chloroplast
61
New cards

Air pocket
**where gases circulate**
62
New cards
**Shoot System - Flower**
\
* Function
* **Sexual reproduction**
* Function
* **Sexual reproduction**
63
New cards
**Petal**:
**attract pollinators to flower**
64
New cards

Stamen:
the male sexual organs
65
New cards

**Anthers**:
produces pollen
66
New cards

**Filament**:
holds anther, attaches it to flower
67
New cards
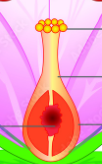
Pistil:
**the female sexual organs**
68
New cards

Stigma:
**where pollen enters**
69
New cards

Style:
pollen travels through here to fertilize the ovule
70
New cards

Ovary
houses the egg (ovule) for pollination (fertilization), eventually becomes a seed
71
New cards

**Sepal**:
modified leaves, protect developing flowers
72
New cards

**Pedicel**:
connects stem to flower
73
New cards
\-cot” = cotyledon
\
* An **embryonic leaf** in plant development, the **first to emerge from the seed**
* Plants with one cotyledon (**monocots**) and plants with two (**dicots**)
* An **embryonic leaf** in plant development, the **first to emerge from the seed**
* Plants with one cotyledon (**monocots**) and plants with two (**dicots**)