Biology - Topic 1: molecules
1/211
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
212 Terms
Most abundant elements in living organisms?
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur
Where do almost all chemical reactions of life take place?
Aqueous solutions
Four main groups of organic molecules?
> carbohydrates
> Proteins
> Lipids
> Nucleic acids
What percentage of cells are water?
80%
Main role of water in living things?
Solvent
Properties of water as a biological molecule?(4)
> one oxygen, one hydrogen
> covalent bonds between O and H
> Polar
> Oxygen slightly negative and hydrogen slightly positive
What is it meant by water being 'polar'?
Water is 'charged' because electrons are not shared equally - oxygen slightly negative and hydrogen slightly positive
Diagram of a water molecule?
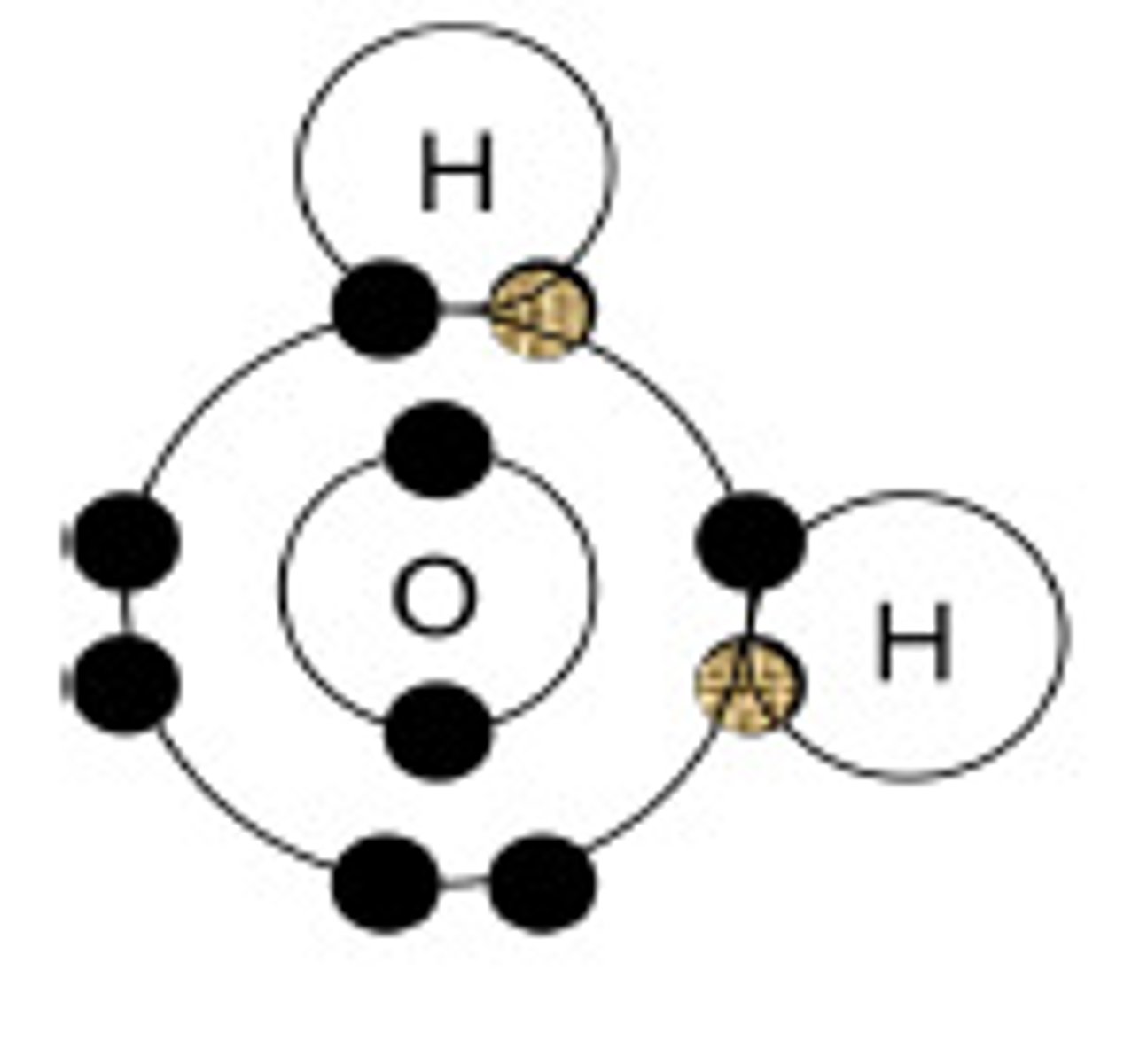
What does the polar nature of the water molecule allow it to do?
for weak chemical bonds with other water molecules
How do water molecules stick together?
Positive hydrogen ends of a water molecule attract the negative ends of an oxygen molecule
What bonds form between water molecules?
Hydrogen bonds
Diagram of water molecules and bonds between them?
page 7
Purpose of water as a solvent?
> most cell's reactions take place in aqueous solution
> it can act as a transport medium in living organisms
> its different effects of hydrophilic and hydrophobic molecules like lipids
Why are ions soluble in water?
They are charged
List of inorganic ions?
> calcium
> iron
> magnesium
> potassium
> nitrate
> phosphate
> hydrogen carbonate
Role of calcium?
> Calcium pectate of the middle lamella of plant cell walls
> essential in bones, teeth, blood clotting and muscle contraction
Role of iron?
> Part of Haem group in haemoglobin
>important electron carrier in respiration
Role of magnesium?
Gives chlorophyll its light absorbing properties
Potassium role?
maintains electrical gradient across membrane of neurone
Role of nitrate?
important in amino acids, nucleic acids and chlorophyll
Role of phosphate?
> phospholipids in cell membrane
> part of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and nucleic acids
Role of hydrogen carbonate?
natural buffer
What is a buffer?
chemicals which resist changes to pH and ensure the environment remains at a particular pH
What are organic molecules?
all carbon containing molecules?
How are organic molecules made?
Polymers made of monomers through polymerisation
What are carbohydrates?
A group of organic compounds whose molecules contain C, H, and O only
3 groups of carbohydrates?
> monosaccharides
> disaccharides
> polysaccharides
Sugars that are monosaccharides?
> glucose
> fructose
> ribose
Sugars that are disaccharides?
> maltose
> sucrose
> lactose
Sugars that are polysaccharides?
> starch
> cellulose
> glycogen
Features of monosaccharides? (3)
> same number of carbon and oxygen atoms
> white crystalline solids which dissolve in water to give a sweet taste
> reducing sugars
General formula for monosaccharides?
C(H2O)n
What is a reducing sugar?
it takes oxygen or electrons from other chemicals pr donates hydrogen to it, in doing so the sugar becomes oxidised
Name for sugars that contains 6 carbon atoms?
Hexose sugars
Diagram for alpha glucose?
see page 13
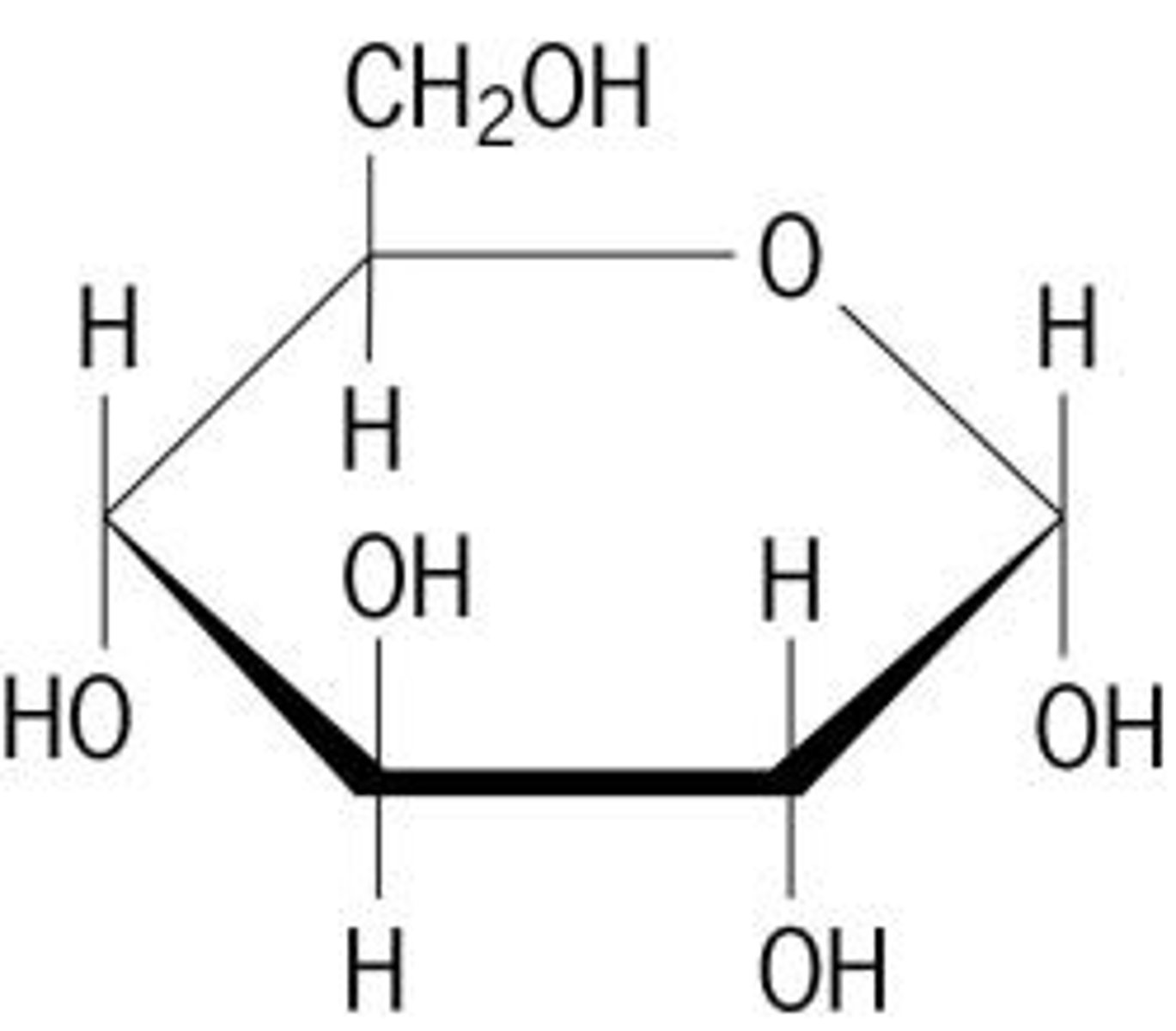
Diagram for beta-glucose?
page 13
Fructose diagram?
see page 13
How are alpha-glucose, beta-glucose, and fructose all related?
They are isomers
Iosmer?
same molecular formula but different structural formula
How is a disaccharide formed?
formed when 2 monosaccharides chemically bond together
What reaction creates a disaccharide?
Condensation - water is produced
Reaction when a disaccharide is reversed?
Hydrolysis
Name of bond between the two monosaccharides?
Glycosidic bond
General formula for disaccharides?
C12H22O11
Diagram for formation of disaccharide?
see page 15
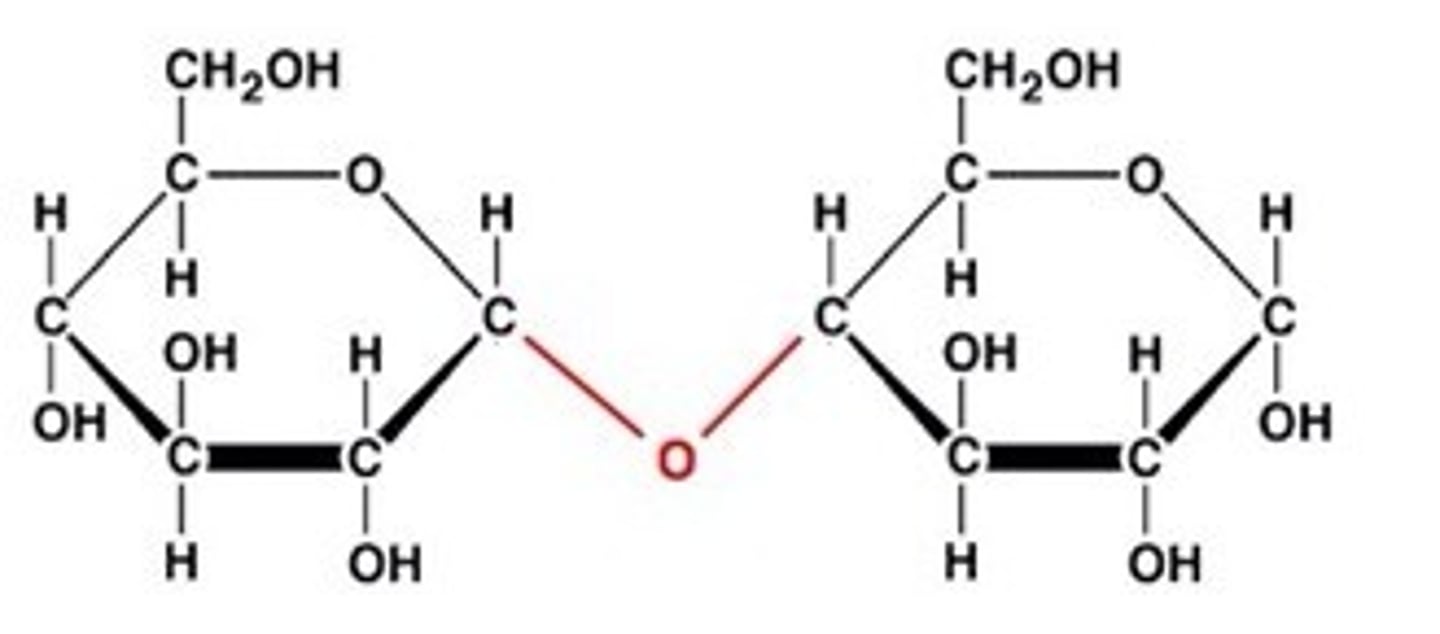
Hydrolysis?
a reaction in which a larger molecule reacts with water and, in doing so, split into smaller ones
Condensation reaction?
when two smaller molecules join together to form a larger one an release a water molecule
Monomers of maltose?
alpha-glucose molecules
Monomers of sucrose?
alpha-glucose and fructose
Properties of maltose and sucrose?
> dissolve in water to give sweet taste
How is maltose formed?
formed when starch is digested but further digestion is needed to form glucose monomer
Where is maltose found?
Small intestine
Role of sucrose?
sucrose is the form in which carbohydrate is transported through the phloem
Where is sucrose found?
Phloem
Is maltose a reducing sugar?
Yes
Is sucrose a reducing sugar?
No
Examples of polysaccharides?
> starch
> glycogen
> cellulose
General formula of polysaccharides?
(C6H10O5)n
Are polysaccharides sweet?
No
Where is starch found?
Chloroplasts
Properties of starch? (4)
> Compact
> No osmatic effect
> Easily hydrolysed
> Large molecule
Why is starch readily broken down?
branching in amylopectin creates terminal ends which are easily hydrolysed
What does starch being a large molecule prevent it from doing?
Passing through a cell membrane
What compounds are starch composed from?
> amylose
> amylopectin
What monomers is starch made from?
Alpha glucose
Why does starch have a different shape?
Amylose and amylopectin have different bonds between the molecules
What is amylose made up of?
alpha glucose
Bonds in amylose?
1-4 glycosidic bonds
Shape of amylose?
Spiral
How are amylose spirals held in place?
Hydrogen bonds
How much of starch is made up of amylose?
20%
amylose diagram?
page 21
What is amylopectin made up of?
alpha glucose
Bonds in amylopectin?
1-4 glycosidic bonds and 1-6 glycosidic bonds
Shape of amylopectin?
Branched
Why is amylopectin more easily hydrolysed?
Large number of terminal ends due to branching
amylopectin diagram?
page 22
How much of starch is made up of amylopectin?
80%
Where is glycogen found?
fungal and animal cells
Where in mammals is glycogen found?
Liver and muscle cells since a lot of respiration occurs there
form in which glycogen is found in liver and muscle?
Small granules
Structure of glycogen?
Similar to amylopectin but more highly branched
What monomer is glycogen made up of?
alpha glucose
Bonds in glycogen?
1-4 and 1-6 glycosidic bonds
Why is it important for glycogen to be easily hydrolysed?
It is more important for animals to be able to gain access to glucose quickly than for plants
Main difference between cellulose and starch/glycogen?
Cellulose is not for storage but is a structural polysaccharide
glycogen diagram?
page 23
Role of cellulose?
providing strength and rigidity to plant cell walls
What monomer is cellulose made up of?
beta-glucose
Bonds in cellulose?
1-4 glycosidic bonds
Shape of cellulose chains?
Straight chains
How is cellulose formed/structure?
> every other beta-glucose has to rotate 180°
> this allows hydrogen bonds between chains for cross linkage
> chains group together to form microfibrils
> microfibrils arrange into lattice for more tensile strength
diagram of cellulose structure?
page 24
What are lipids called instead of polymers?
Macromolecules
Why aren't lipids molecules?
it is not made up of monomers - it has two different sub units
How to lipids react with water?
They are insoluble
Why are lipids insoluble?
They are non-polar and so are hydrophobic
What are lipids soluble in?
organic solvents
Examples of lipids?(4)
> triglycerides
> phospholipids
> steroids
> waxes
Most common type of lipids?
Fats and oils