Knee/Ankle joint conditions
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
differential diagnosis of pathologies at the knee and ankle
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Patellofemoral syndrome (Runner’s knee)
- Age -20-50
- MOI- trauma, tight ITB, gmax, & TFL
- Worsen symptoms after
prolonged sitting
(Moviegoer’s sign), stairs,
kneeling
- End-range knee flexion is
painful
- Tenderness on anterior
knee especially with
patella compression
- Swelling may occur on
anterior knee
-Positive clarkes test
Patellar tendinopathy (jumper’s knee)
- Age 15-30
- Inflammation of patellar
tendon
- Onset- gradual
- MOI- gradual (repeated
eccentric overloading during
deceleration activities)
- Pain increases with
squatting and jumping
- End range knee flexion
painful
- Tenderness over patellar
tendon (inferior or
superior to patellar)
Positive Special tests:
- Patellar grind test
- Single leg hop test
- High step-up test
Prepatellar bursitis
- Age 15-50
- Inflammation of bursa due to
recurrent minor trauma of
anterior knee
- MOI- direct trauma to the
anterior aspect of the knee
- Pain increases with
kneeling
- Local swelling, fluctuation
Quadriceps muscle tear
- Age 20-40
- MOI- sudden eccentric overload
- Squatting increases
symptoms
- Bruising and/or swelling
can occur over the anterior
thigh/knee
- Knee flexion is limited
- Combined hip extension
and knee flexion is painful
- Resisted hip flexion and
knee extension is painful
- Tenderness over anterior
thigh
Osgood Schlatter disease
- Age 8-13 yrs in female, 10-15yrs in male
- Onset – sudden
- Traction apophysitis of tibial tubercle
- Visible lump over the site
- Pain with activities
(running, jumping,
squatting, kneeling, acute
knee impact, and
ascending or descending
stairs)
- Knee extension against
resistance or stressing
quads increased symptoms
- Anterior knee pain
Sinding-Larsen-Johansson syndrome
- Traction epophysitis at inferior pole of patella
- Traction epophysitis at inferior pole of patella-Pain with activities like cycling, athletics, resisted Knee extension
X-ray-fragmentation of tibial tubercle or irregular calcification
Anterior Cruciate ligament injury
- Age- 15-45
- Contact & non-contact MOI
- Contact-> Blow to the lateral
side of knee- valgus force to
knee results in ACL, MCL,
medial meniscus injury(terrible triad) or (unhappy
triad)
- Non-contact- Tibia ER on
planted foot
- Forceful hyperextension
-pain with resisted knee rotatio
- Immediate swelling of
knee and popping sound
- Feeling of instability
- Symptoms increase with
weight-bearing
- Pain at end ranges
Positive: - Lachman’s test
- Pivot Shift test
- Anterior drawer test
Medial collateral ligament injury
- Valgus forces across
medial joint line of knee
- Symptoms increases with Valgus stress (MCL)
Positive: collateral ligament instability test
Lateral collateral ligament injury
- Lateral collateral ligament- traumatic varus force across knee
- Symptoms increases with Varus stress (LCL)
Positive: collateral ligament instability test
Posterior cruciate ligament injury
- Forceful blow to anterior tibia
in knee flexed, Dashboard or
falling onto the flexed knee
- Hyperflexion
- Popping sound
- Pain in the posterior
aspect of the knee joint
which aggravates with kneeling
Positive: - Posterior Sag test
- Posterior drawer test
- Reverse Lachman test
Iliotibial band friction syndrome
- Age 25-55
- MOI- overuse
- Pain with repetitive movements, climbing or descending stairs
- Lateral knee pain diffuse & hard to localize
- Localized tenderness at lateral femoral condyle
- Ober’s test (ITB tightness)
- Noble compression test
- Renne test
Plantar fasciitis
- Age- 20-60
- MOI- gradual with no known cause
- Painful sole of foot under heel when weight bearing especially first thing in the morning
- Pronated foot or flattened arches observed
- Passive great toe extension is painful
- Plantar aspect of heel is tender on palpation
- Positive Windlass test
Achilles tendinitis
- Age 20-40
- MOI- overuse
- Jumping, and running increases symptoms on posterior ankle
- Slight swelling can be seen on posterior ankle
- Active and passive dorsiflexion is painful and limited
- Passive dorsiflexion is limited with knee in the extended position
- Resisted plantar flexion is painful
Gastrocnemius strain
- Age 20-40
- MOI- sudden overload
- Pain in the upper calf
- Heel raise increases symptoms
- Antalgic gait
- Active and passive
dorsiflexion painful and
limited with knee extended
position
- Pain on resisted plantar flexion
- Tender mid to upper calf area on palpation
Posterior tibialis tendinitis
- Age 20-40
- MOI- overuse with a flat pronated foot
- Pain on medial ankle throughout tendon
- Swelling may be present and tenderness over medial ankle
- Active and passive plantar flexion and eversion painful
- Resisted inversion with plantar flexed foot is painful
Anterior tibialis tendinitis
- Age 15-45
- MOI- overuse
- Symptoms increases with repetitive dorsiflexion on anterior lower leg
- Combined active Plantarflexion and inversion movements painful
- Passive plantar flexion painful
- Resisted dorsiflexion painful
- Tenderness over the anterolateral lower leg
Medial tibial stress syndrome (Shin splints)
- Age 15-30
- MOI- overuse
- Pain on anterior lower leg, posterior-medial lower leg
- Active combined plantarflexion and inversion painful
- Resisted plantar flexion and eversion painful
- Tenderness on posteromedial calf
Anterior Compartment syndrome
- Increased pressure in anterior compartment of leg causing an
ischemic condition of the leg
- MOI - direct trauma, muscle hypertrophy, fracture
- Severe cramping, diffuse
pain, and tightness
- Pain decreases with rest and
increases with activity
- Pain worsens with stretching
- Tender and tight
compartment on palpation
-Pain, pallor, paresis, paresthesia,
pulselessness, palpable tenderness
Acute – emergency surgery
Morton’s neuroma
- Weight-bearing increases symptoms on sole of foot
- Pronated foot or flattened arch can be observed
- Passive toe extension painful
- Tenderness with palpation on web space of toes
Tarsal tunnel syndrome
- Age 25-50
- MOI- posttraumatic, rapid weight gain, fluid retention, inflammatory, abnormal foot/ankle biomechanics or a valgus foot deformity
- Symptoms on medial malleolus, distribution of posterior tibial nerve up the leg, or down into the medial arch, plantar surface of the foot and toes
- Symptoms increases with excessive pronation in walking or running
- Pronated foot, pes planus can be observed
- Passive plantar flexion and eversion painful
- Resisted toe flexion painful
-Positive tinels sign
Metatarsal stress fracture
- Age 15-45
- MOI – overuse
- Symptoms increases with weight-bearing activities on the forefoot
- Tenderness over the fracture site
- Palpation, ultrasound, tuning fork, bone scan, MRI, CT scan
Midfoot sprain
- Age 15-40
- MOI – high impact landing, foot twisted when in fixed position
- Walking on toes increases symptoms on midfoot
- Generalized tenderness of midfoot
- pain during passive midfoot pronation and supination while the hindfoot is
stabilized.
- Weight Bearing lateral and anterior-posterior radiographs
Sever’s diseases (Calcaneal Apophysitis)
- Age 8-13 yrs
- traction apophysitis at the
insertion of Achilles tendon
- MOI- foot pronation, tight gastroc-soleus complex, jumping or landing from a height
- Limited dorsiflexion and stiffness
- Pain over the posterior-inferior heel which increases with weight-bearing
- Pain resolves with rest
- Squeeze test
- X-ray
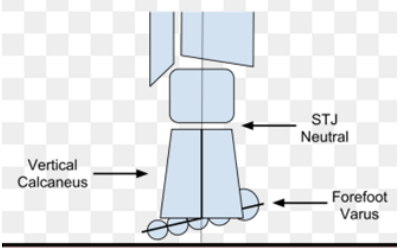
forefoot varus
- Inversion of forefoot
- subtalar joint in neutral
forefoot valgus
- Eversion of forefoot
- subtalar joint in neutral
