Lipids
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
what are lipids?
lipids are macromolecules, they contain all the chemical elements: carbon, hydrogen and oxygen
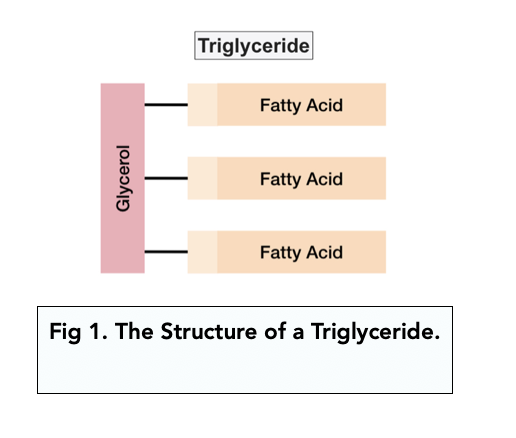
what are triglycerides and their structure?
triglycerides have one molecule of glycerol with three fatty acids attached to it.
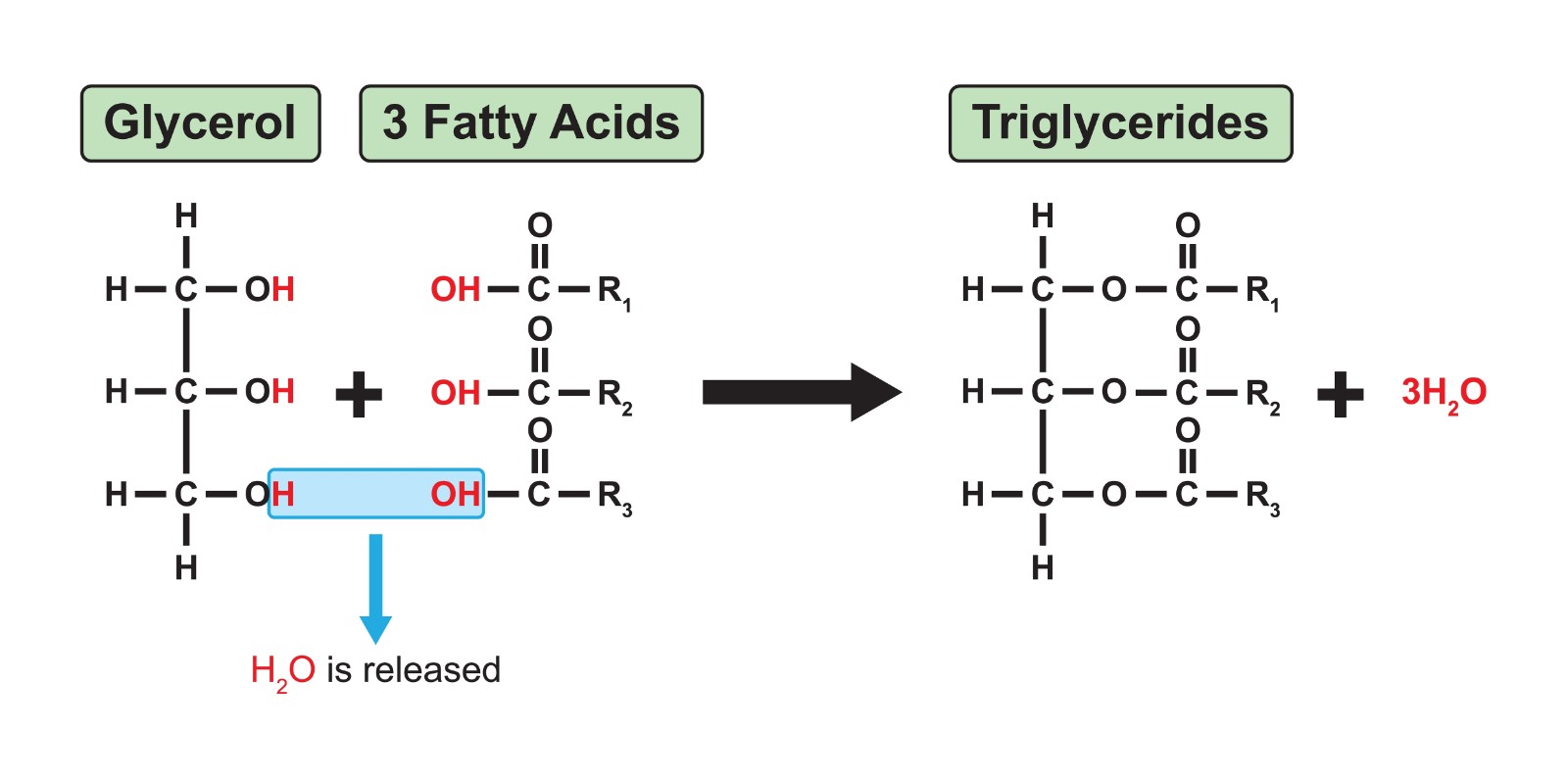
they’re synthesised by the formation of an ester bond between each fatty acid and the glycerol molecule
information on the ester bonds in triglycerides and how they’re formed
one triglyceride molecule has three ester bonds, each ester bond is formed in a condensation reaction in which a water molecule is released
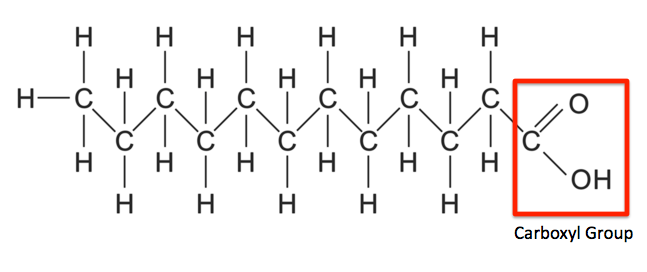
information on fatty acids and their structure
fatty acids have long tails made of hydrocarbons, the tails are hydrophobic ( they repel water molecules)
these tails make lipids insoluble in water
all fatty acids have the same basic structure but the hydrocarbon tail varies
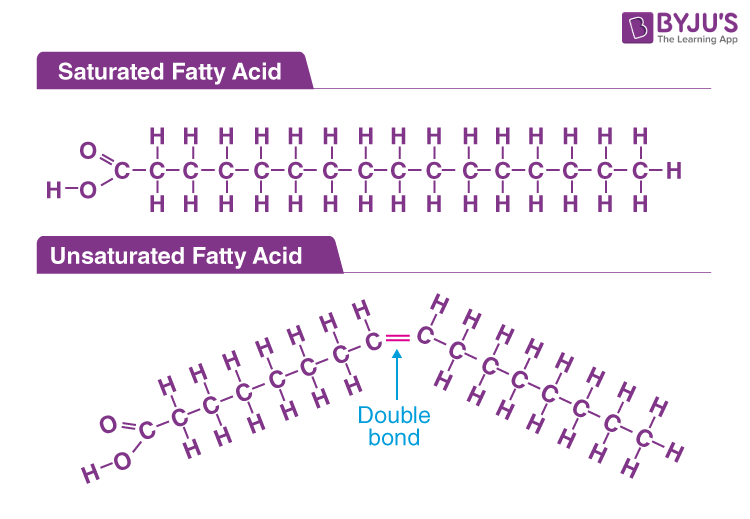
there are two kinds of fatty acids unsaturated and saturated the difference is in their hydrocarbon tails
saturated vs unsaturated fatty acids
saturated don’t have any double bonds between their carbon atoms in their hydrocarbon tails, the fatty acid is saturated with hydrogen
unsaturated have at least one double bond between carbon atoms which causes the chain to kink
what are phospholipids
similar to triglycerides except one of the fatty acid molecules is replaced by a phosphate group
the phosphate group is hydrophillic ( it attracts water) and the fatty acid tails are hydrophobic
the phosphate head is polar whereas the fatty acid tails are non polar
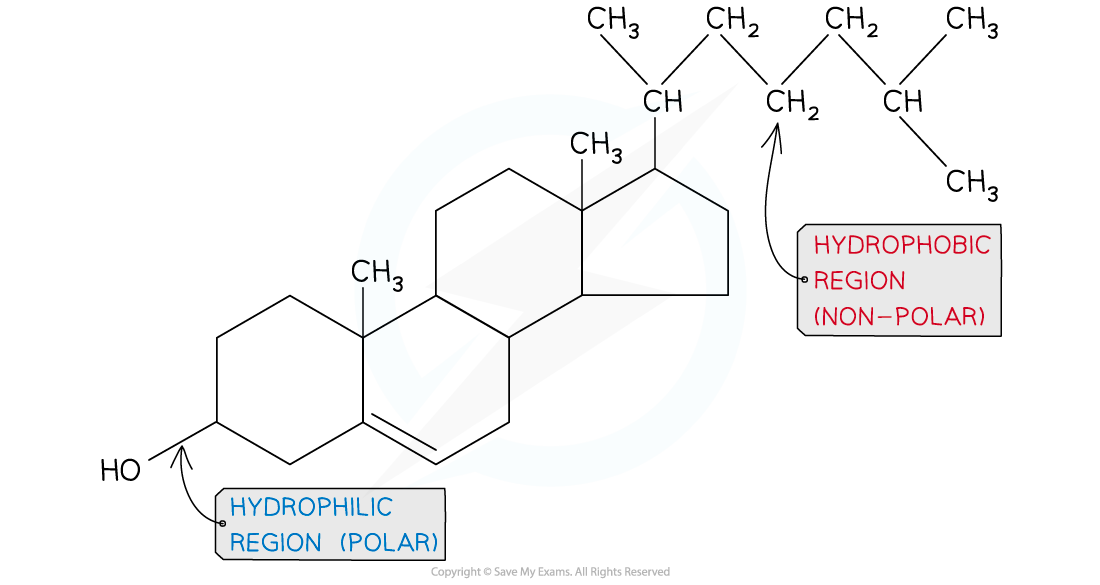
what is cholesterol
another type of lipid
has a hydrocarbon ring structure attached to a hydrocarbon tail
the ring structure has a polar hydroxl OH group attached to it
Why are triglycerides good for energy storage?
They have long hydrocarbon chains with many C–H bonds and little oxygen (highly reduced).
So their oxidation during respiration releases large amounts of ATP.
They store more energy per gram due to the hydrocarbon tails (≈37 kJ/g) more than carbohydrates and proteins (≈17 kJ/g).
They are hydrophobic, so they do not affect osmotic balance, allowing more storage of triglycerides in cells.
the fatty acid tails face inwards shielding themselves from water with their glycerol heads
How are triglycerides stored in plants and animals?
Plants: stored as oils in seeds/fruits. Liquids at room temperature due to unsaturated fatty acid chains (double bonds add kinks).
Animals: stored in adipose tissue as oil droplets. Important for energy during food scarcity (e.g. hibernation).
What roles do triglycerides play beyond energy storage?
Metabolic water: oxidation of C–H bonds releases water (important for desert animals & developing embryos).
Insulation: part of myelin sheath (faster nerve impulse conduction) + blubber/adipose tissue prevents heat loss.
Buoyancy: low density aids floating (e.g. aquatic animals).
Protection: adipose tissue cushions and protects organs.
How are phospholipids different from triglycerides?
Made of glycerol + 2 fatty acids + phosphate group.
Phosphate group is polar (hydrophilic).
Fatty acid tails are non-polar (hydrophobic).
They are amphipathic (both hydrophobic & hydrophilic regions).
How do phospholipids contribute to cell membranes?
Form bilayers: hydrophobic tails inwards, hydrophilic heads outwards.
Create a hydrophobic core by forming small areas where the inside and the outside of the cell do not touch that prevents passage of water-soluble molecules.
The hydrophilic phosphate heads form H-bonds with water allowing the cell membrane to be used to compartmentalise
Compartmentalisation enables cells to organise specific roles into organelles, helping with efficiency
Allow selective permeability of membranes, as the phospholipid heads are hydrophillic and the fatty acid tails are hydrophobic so they form a double layer with their heads facing out to the water on either side. This forms the phospholipid bilayer, allowing the cell to separate the inside of the cell from the outside.
How does fatty acid composition affect membrane fluidity?
If they’re mainly saturated fatty acids → less fluid (tighter packing).
If they’re mainly unsaturated fatty acids → more fluid (kinks prevent close packing).
How do phospholipids influence membrane proteins?
Weak hydrophobic interactions between phospholipids and proteins hold proteins in place, while allowing lateral movement within the bilayer.
Where is cholesterol found and how is it structured?
Cholesterol is a lipid with both hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions.
Found in eukaryotic cell membranes (not prokaryotes).
Synthesised in the liver and transported in the blood.
has a small flattened shape allowing it to fit between phospholipid molecules in the cell membrane
What are the roles of cholesterol in membranes?
Regulates membrane fluidity: in high temps it causes phospholipids to pack closely together by binding to the hydrophobic tails, helps to make membrane less fluid and more rigid whereas in low temperatures, cholesterol prevents phospholipids from packing too close together and so increases membrane fluidity
Reduces permeability to small water-soluble molecules by acting as a barrier fitting in the spaces between phospolipids
used to produce steroid hormones (oestrogen, testosterone, progesterone).