Diagnostic approach to equine cardiology
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Why is it hard to assess cardiac function at rest
Low resting heart rate (30-40)
Horses hide CV dx at rest
Large heart, big change in heart rate (HR) (highest 240) and stroke volume (SV) with exercise and training
Massive cardiac reserve
High vagal tone → related arrhythmias & cardiac abnormalities common in horses
Often mild or no signs of cardiac disease in early stages or at rest/low level exercise
How does cardiac disease present in horses?
History of poor performance (depends on use)
Clinical signs of cardiac failure (rare)
Systemic illness → secondary heart disease
Often incidental finding in pre-purchase examination and vaccination
What do you need to do if you find a cardiac murmur/arhythmia in a vetting?
Interpret findings according to use of the horse (more significant in athletes)
Many have no effect on performance on life expectancy
What can cardiac condition affect?
Athletic performance
Risk of collapse (→ human injury)
Resale value
Risk of developing CHF (death)
What is being shown in this ECG of a horse?
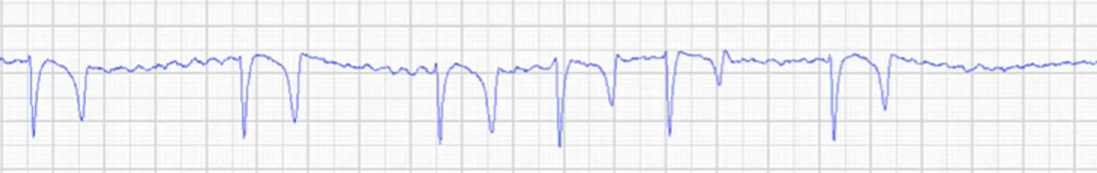
Atrial fibrillation (bigger horses more likely to have)
Irregularly irregular pattern
No p wave —> fibrillating baseline
Low HR at rest, but cannot be ridden (don’t exercise)
What can be used to investigate the CV system?
History / signalment
Clinical Examination / Auscultation (be aware of gut sounds caused by colon, resp sounds, background noise etc.)
+/- Ancillary techniques
ECG +/- exercise and 24-hour
Echocardiography (Ultrasound)
Clinical pathology
Exercise testing
How would you determine the effect of a heart condition when exercising?
Strava trace and ECG attached then exercise the horse
What useful things can we find out when taking a history?
Include performance history
Current fitness level
History of any concurrent disease especially respiratory noise, EIPH etc.
What disease in other bodily systems can cause a cardiac abnormality?

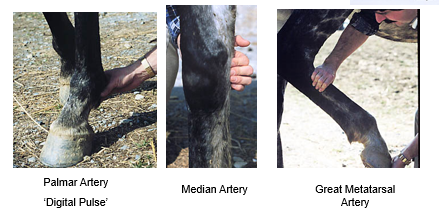
What do we assess about the pulse?
Peripheral arterial pulses —> facial
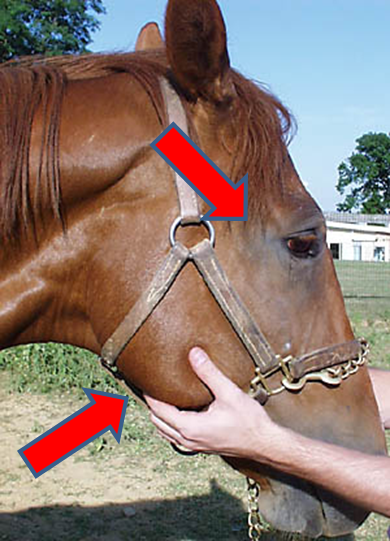
Regular —> timing and strength
Strength —> diff between diastolic and systolic
Easy to occlude
How turgid the artery is
Palpate while auscultating
What can severe backflow from the aortic valve (severe aortic valve regurg) cause?
Bounding 'hyperdynamic' pulse
What does a high jugular pulse tell us about systemic pressure?
Jugular pulse should not be observed more than one third of the jugular
Increased pressure in the right side of the heart
What do we assess in the cv system?
Heart Rate
Peripheral oedema
Ventral oedema - inc hydrostatic pressure
Mucous membranes
Colour
CRT
Hydration status
Peripheral perfusion
What is being shown here?
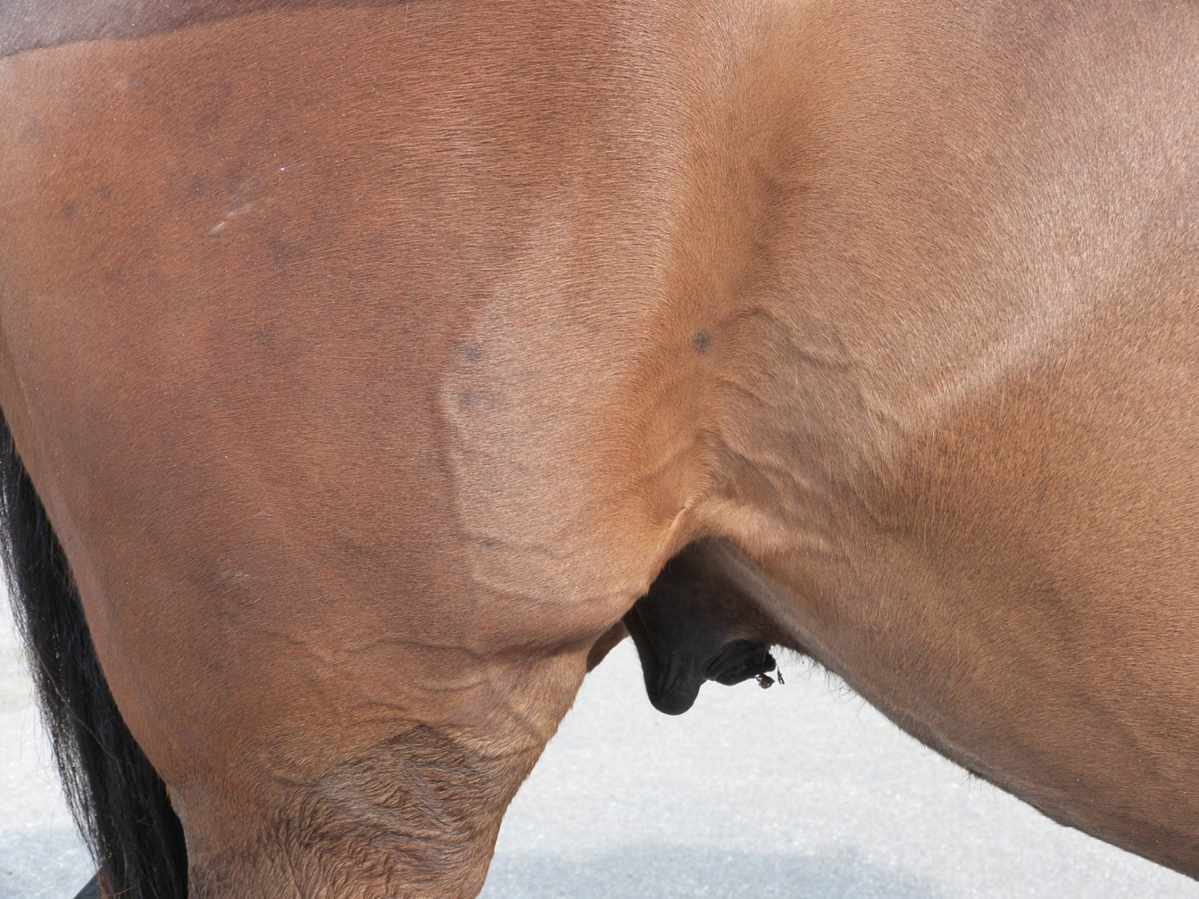

Build up of blood in veins (increased BP) due to right sided CHF
What do we listen for in cardiac auscultation?
Heart Rate:
Physiological tachycardia:
Exercise, temperature, stress
Pathological tachycardia
Metabolic, compensation for reduced stroke volume, reduced ABP (arterial blood pressure)
Rhythm
Regular
Regularly irregular
Irregularly irregular
Pulse
Quality
Deficits
Murmurs
What is the process of auscultating the heart?
Quiet environment
Take time
Let horse settle
Get into the rhythm
Pull leg forward —> opens up cardiac window
Feel for the apex beat (i.e. most prominent beat = @ mitral valve) then move dorsally or cranially
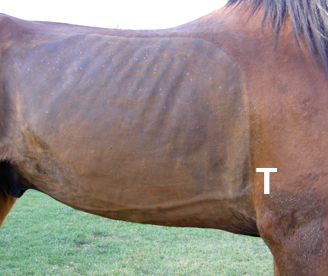
Where do you put your stethoscope on the left and right side?
Pull leg forward, stick stethoscope bell right under triceps just dorsal to point of elbow (harder on right)
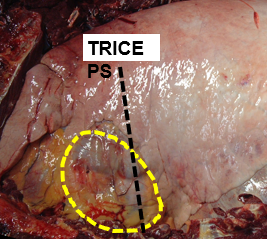
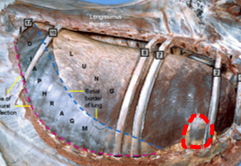
What valves are you listening to on the right and left side?
Left

Right
What is the dorsal view of the valves?
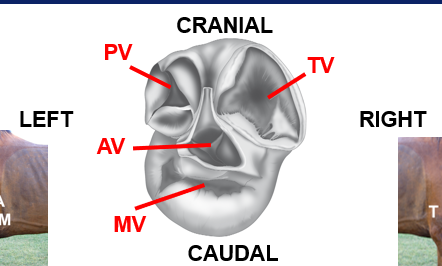
Can hear the aortic on the right also
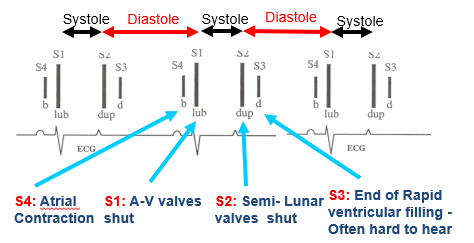
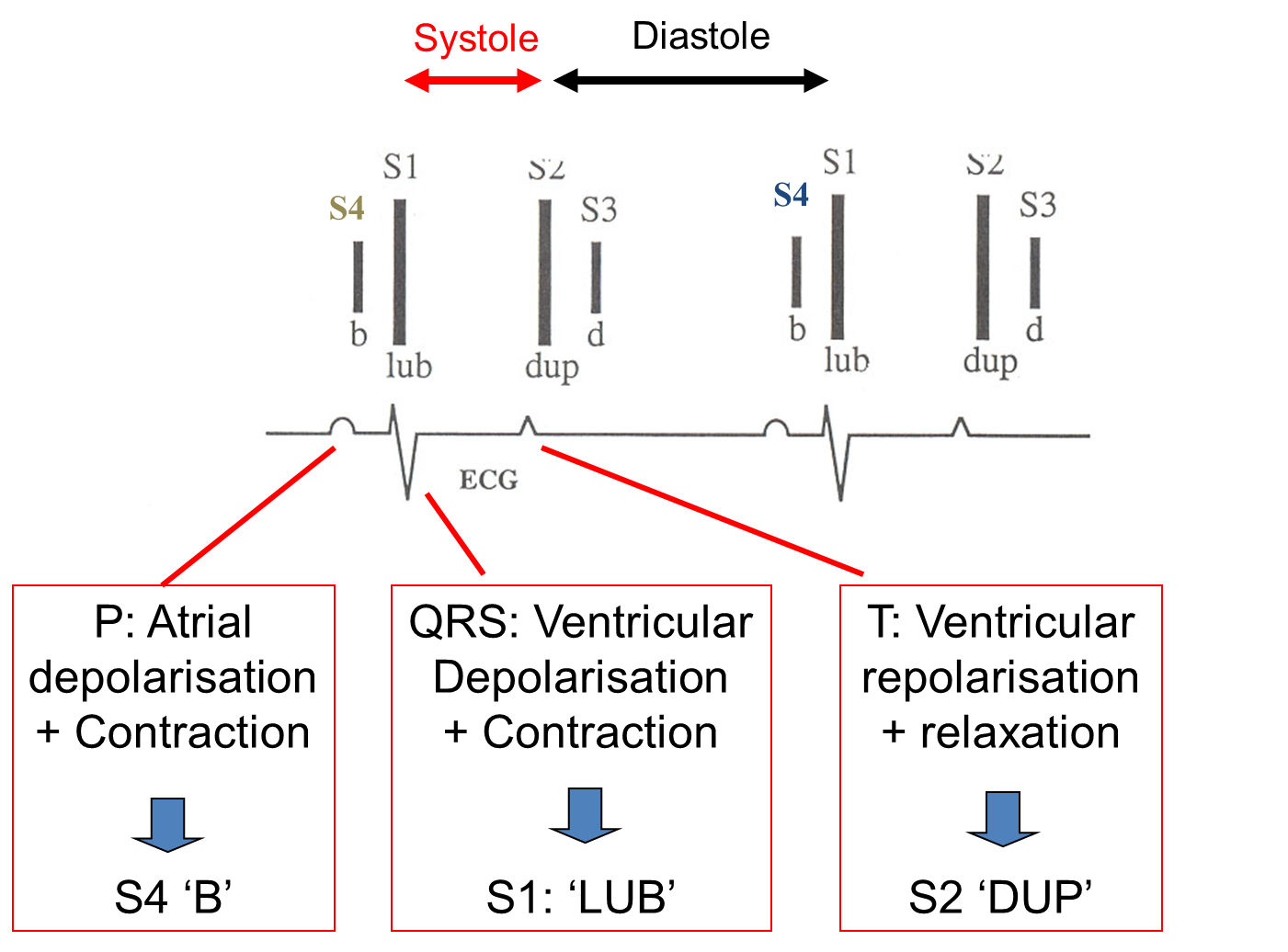
Describe the basic heart sounds
Depolarisation, systole (contraction) —> AV valves shut, semi-lunar valves open
Repolarisation, diastole (relaxation) —> AV valves open, semi-lunar valves shut
What are the features of the S1 heart sound?
Ventricles contract
Shutting of AV valves (Mitral/tricuspid)
“ LUB “
What are the features of the S2 heart sound?
Ventricles relax
Shutting of Semilunar valves (Aortic/Pulmonic)
“ DUP “
What are the other common heart sounds in horses?
S4: ATRIAL CONTRACTION (Just before S1) = more common
S3: END OF RAPID VENTRICULAR FILLING (Just after S2) = usually seen in fit young horses i.e. only sometimes heard
How do the heart sounds fit with the ECG?
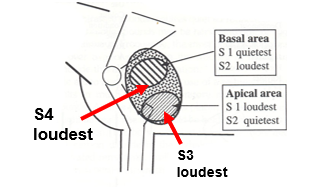
Where in the heart are the different heart sounds loudest?
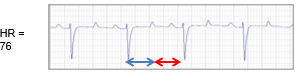
How does the duration of systole and diastole differ between different heart rates?
Resting heart rates —> Systole much shorter than diastole (long pause)
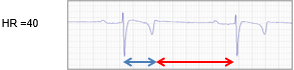
Higher heart rates —> more equal
What are examples of peripheral pulses you can take on the limbs?
What is the main cardiac biomarker we test for?
Cardiac Troponin (I or T —> I most commonly used)
marker of muscle damage in the heart (myocardial dx)
Mild increases in response to endurance/sprint racing
Minimal use of natriuretic peptides in horses
When would we use an ECG on horses?
Suspected non-physiological arrhythmia on auscultation
Chamber dilation on echocardiography
Poor performance
Monitoring of patients with CVS compromise e.g. systemically ill, under anesthesia
What do the different waves represent on an ECG and how does the normal complex differ in a horse?
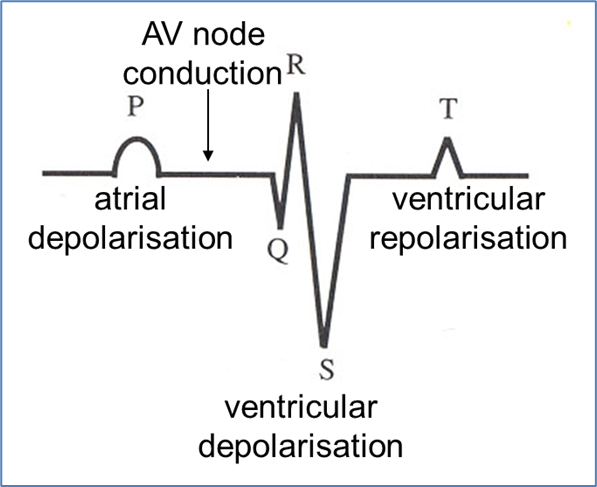
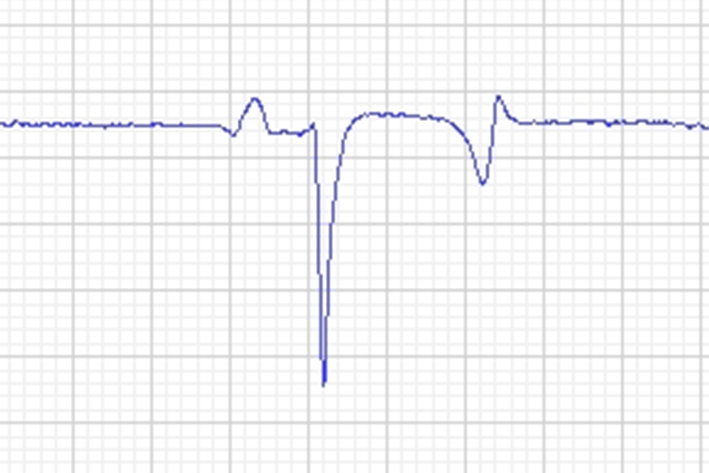
Downward QRS complex
Describe the match up of the P QRS T waves to horse heart sounds
Where do you place the ECG leads?
Base —> apex trace (Only cross the heart in one direction)
The closer leads are to MEA, the larger amplitude deflection you get on your ECG trace

(lellow left, red right)
What is the usefulness of a Telemetric and 24 hour ECG?
No wires between horse and machine
Exercise, continuous assessment, or treatment monitoring
Detection of arrhythmias that may be missed on auscultation (can watch remotely)
How does the electrode placement differ in exercising ECGs?

Can get electrical interference due to muscular activitiy beneath electrodes during exercise
What is measured in exercising ECG?
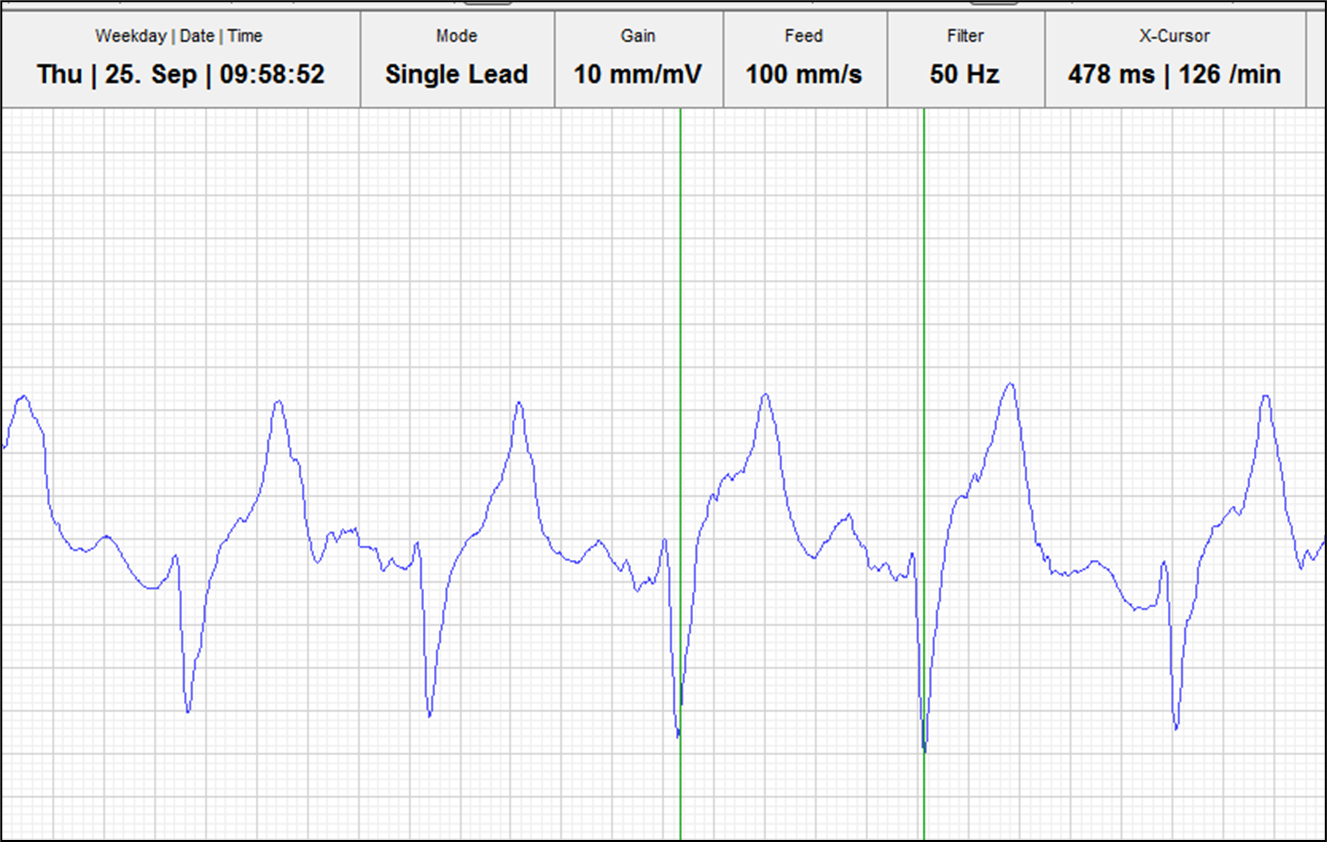
R-R interval —> normal? getting shorter / longer?
What are the features of echocardiography in horses?
Standard image planes
Use of Doppler
M mode technique
(similar to dogs/cats)