ERP Display, Maps and Components
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
What are guidelines for plotting ERPs? (6)
1. sufficiently long epoch
2. include the pre-stimulus baseline
3. include voltage scale
4. include polarity
5. include time on x axis
6. indicate the electrode location (either with a map for those unfamiliar with EEG, or just state electrode)
How many waveforms can reasonably be superimposed on one another when plotting ERPs? Why?
no more than 4, unless you want to show that they are all the same. If there are too many, the waveform differences cannot be easily seen
difference waveform
a waveform created by the subtraction of other waveforms, can allow for information that would otherwise be missed to be seen
spherical splines
method of interpolation in which extrapolation is used, creating a continuous curve and voltages between and beyond the recording electrodes to be estimated
Why is the spherical spline method used now instead of the traditional method without extrapolation for creating scalp distributions of ERPs?
it creates a smoother curve where voltages beyond the recorded points can be predicted and where the electrode doesn't record the maximum, which makes more sense
How do EEG and MEG contour lines differ?
In EEG, the dipole points from the "cold" to the "hot" area, while in MEG, the source is between the 2 points of the dipole.
tangential dipole
dipole oriented roughly parallel to cortical surface, potentials on scalp are of equal strength and CSD doesn't result in sharpening
oblique dipole
dipole is oriented at an angle to cortical surface, see a potential more on one side, sharpens with CSD for the radial portion
Radial dipole
perpendicular to cortex, see one polarity for potential, greatly sharpened with CSD
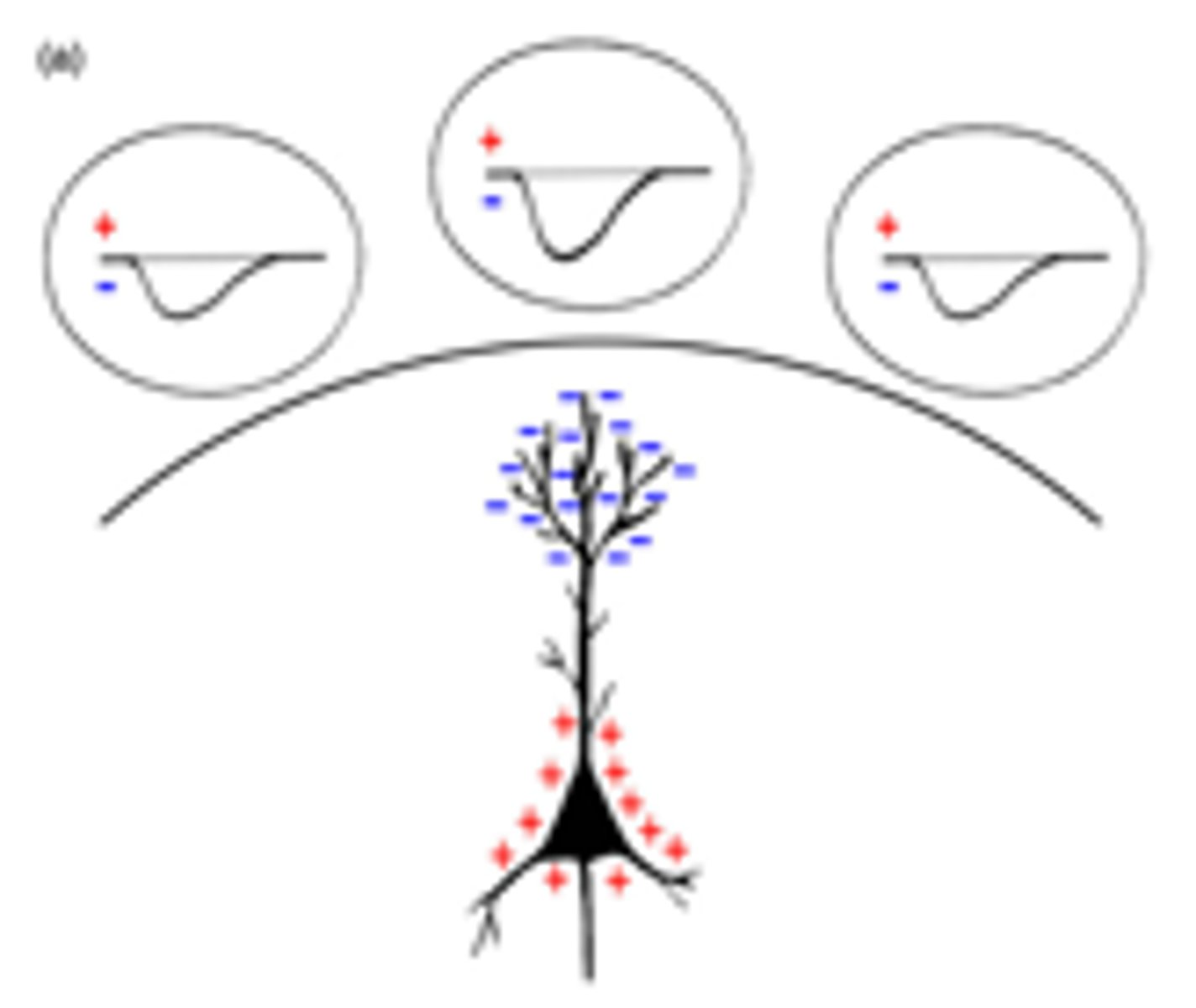
deep dipole
dipole is located perhaps subcortically, may be at various orientations, results in weak and broad potential and no sharpening with CSD
How does reference choice impact topographic and voltage maps of scalp voltage?
It does not change topographic maps, but it does change where the 0V is on voltage maps. Average reference is generally best because it does not place 0 voltage in the center of the field
scalp current density
reflect the current flowing in (sink) and out (source) of head, created by computing second derivative of scalp electric field. Especially sharpen RADIAL source and removes other orientations and sink current flow for a deblurred, reference free picture
Why does MEG have better spatial resolution than EEG?
magnetic fields go in fewer directions and are thus more spatially precise. However, they don't show radial sources usually
What is the simple definition of a component?
it is a feature (peak or trough) in an individual ERP waveform
What are the problems with the simple definition of a component?
waves may reflect the activity of multiple simultaneously active brain regions (they add together, so experimental design must try to isolate) and features on different waveforms may be from related activity
What is the physiological definition of component?
a component is measurable brain activity from a specific neuroanatomical locus in the brain (common location)
What is the psychological or functional definition of a component?
a component is electrical activity that arises from brain processes involved in performing a specific information processing function (common function)
Describe the classification of components as exogenous or endogenous and the issues with this
exogenous are early/sensory, endogenous are late/cognitive. The issue is that there is grey area in between and sometimes components may be both, like the impact of attention on a sensory response
Which components are only visible on difference waves?
mismatch negativity, N2pc
What are the naming conventions for ERPs?
1. polarity/timing names (P1, N1, N170, P300)
2. descriptive (best option), MMN, Nd, distractor positivity
3. presumed function (bad idea to do this), ERN, PN, LDAP
4. scalp location (N2pc, ABRs, C1)
C1 ERP
calcarine sourced ERP seen in the posterior areas of the scalp. First peak, on side contralateral to stimulus. Polarity depends on whether the stimulus is in the upper visual field (negative, upward peak) or lower visual field (positive, downward peak)
P1
extrastriate positive response to visual stimuli
N1
first negative peak of a visual or auditory stimulus response, amplitude and skewedness depends on attention
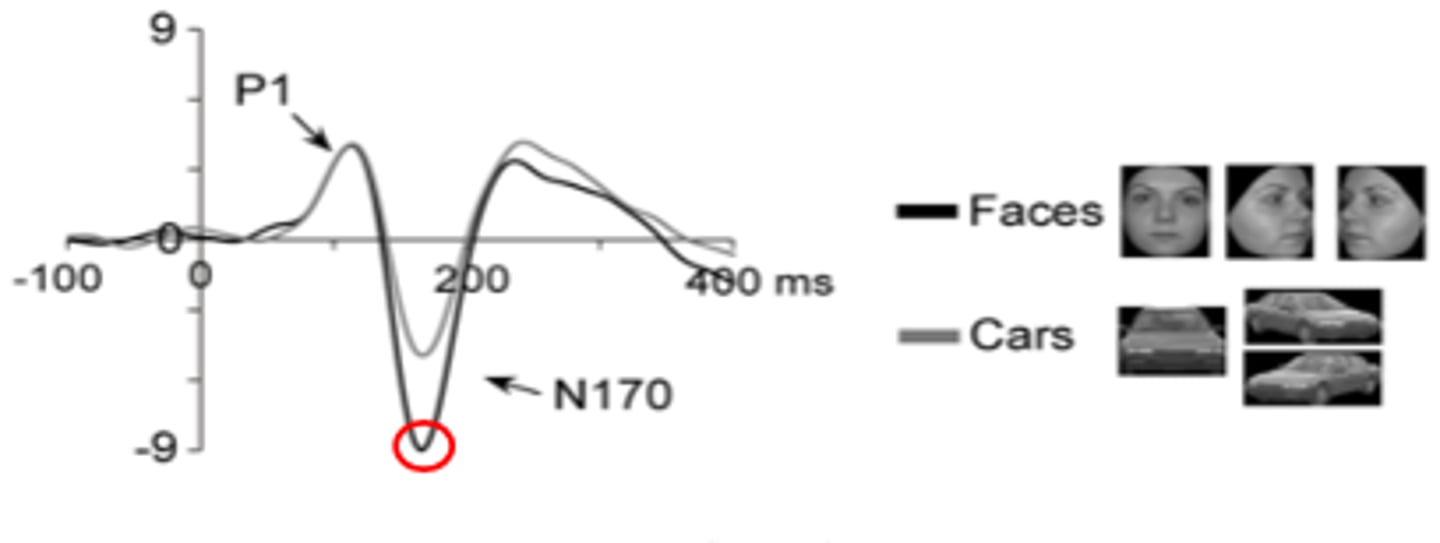
N170
an ERP component (negative potential at 170 ms) linked to perceiving facial structure
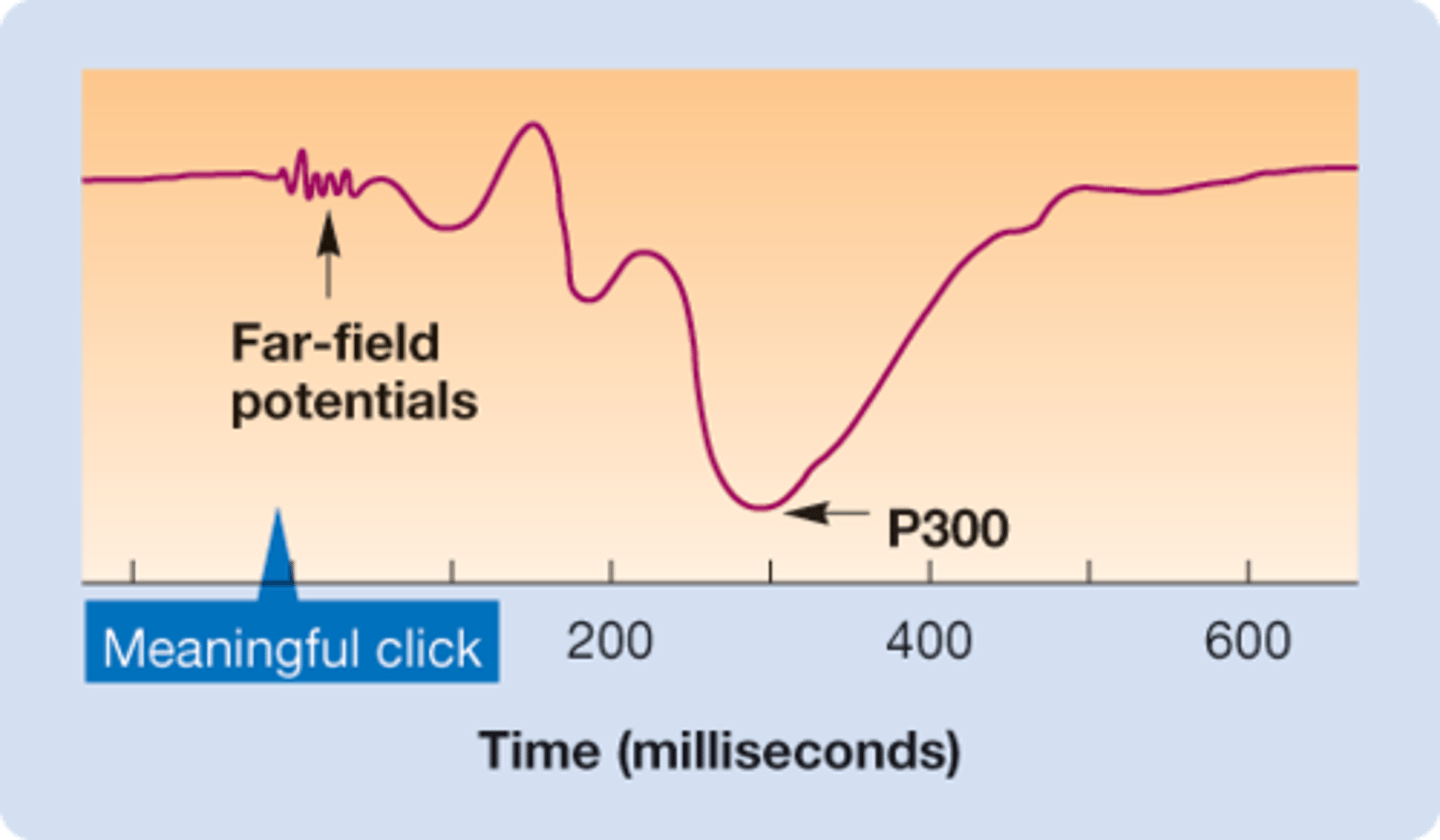
P300
is an EEG wave that often occurs after the presentation of a momentary stimulus meaningful to the volunteer
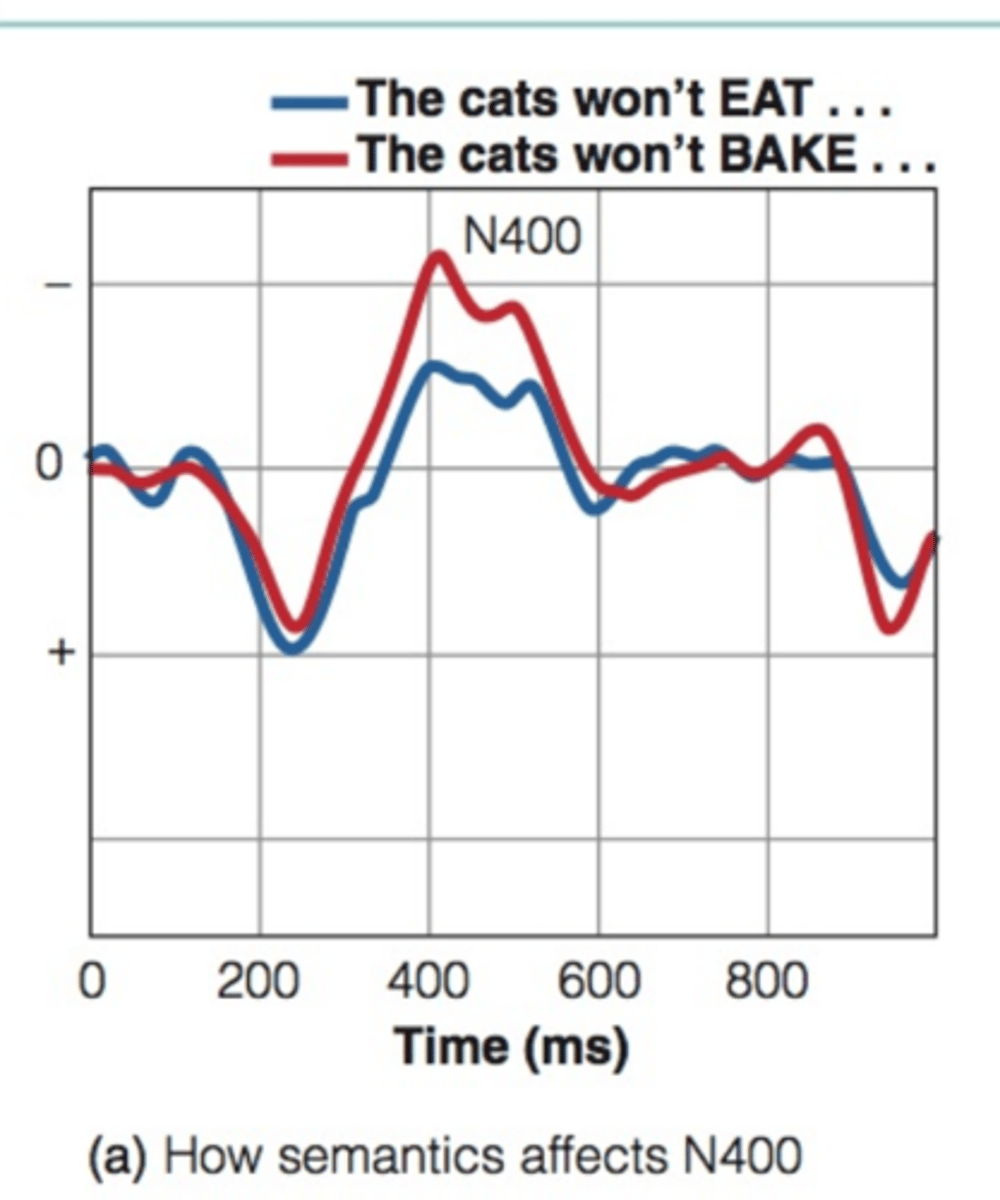
N400
an event-related component in EEG found when a word meaning appears out of context or unexpectedly
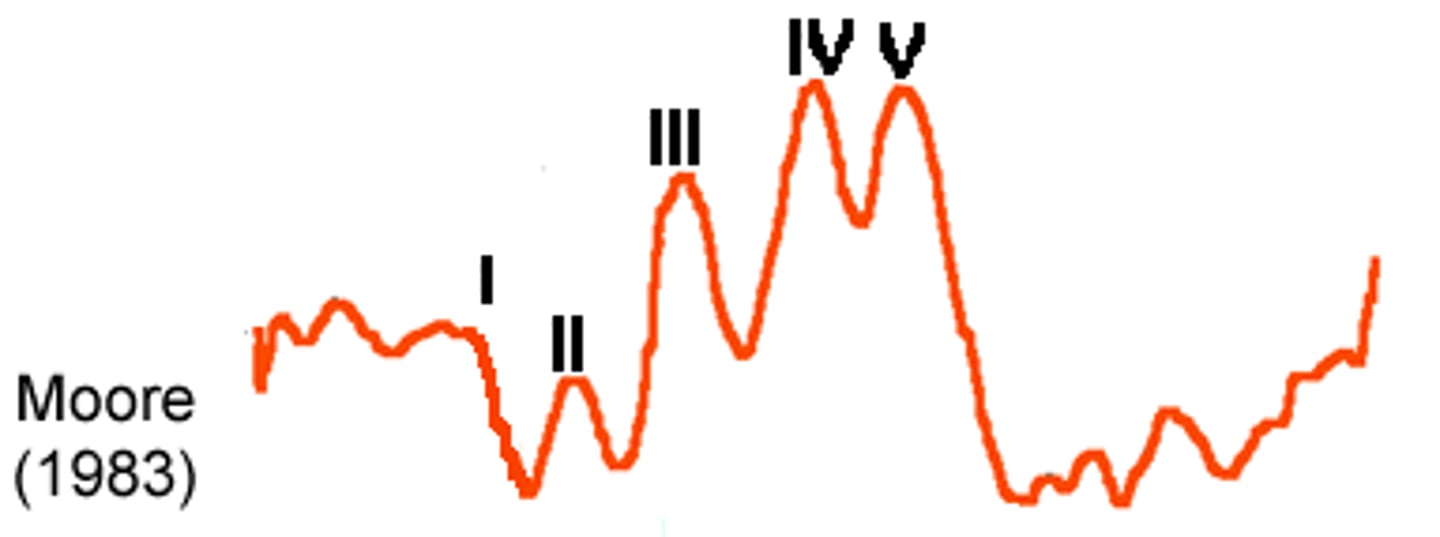
Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR)
measurable responses in the brainstem to a series of acoustic stimuli, occur at high frequencies very early (within 10ms)
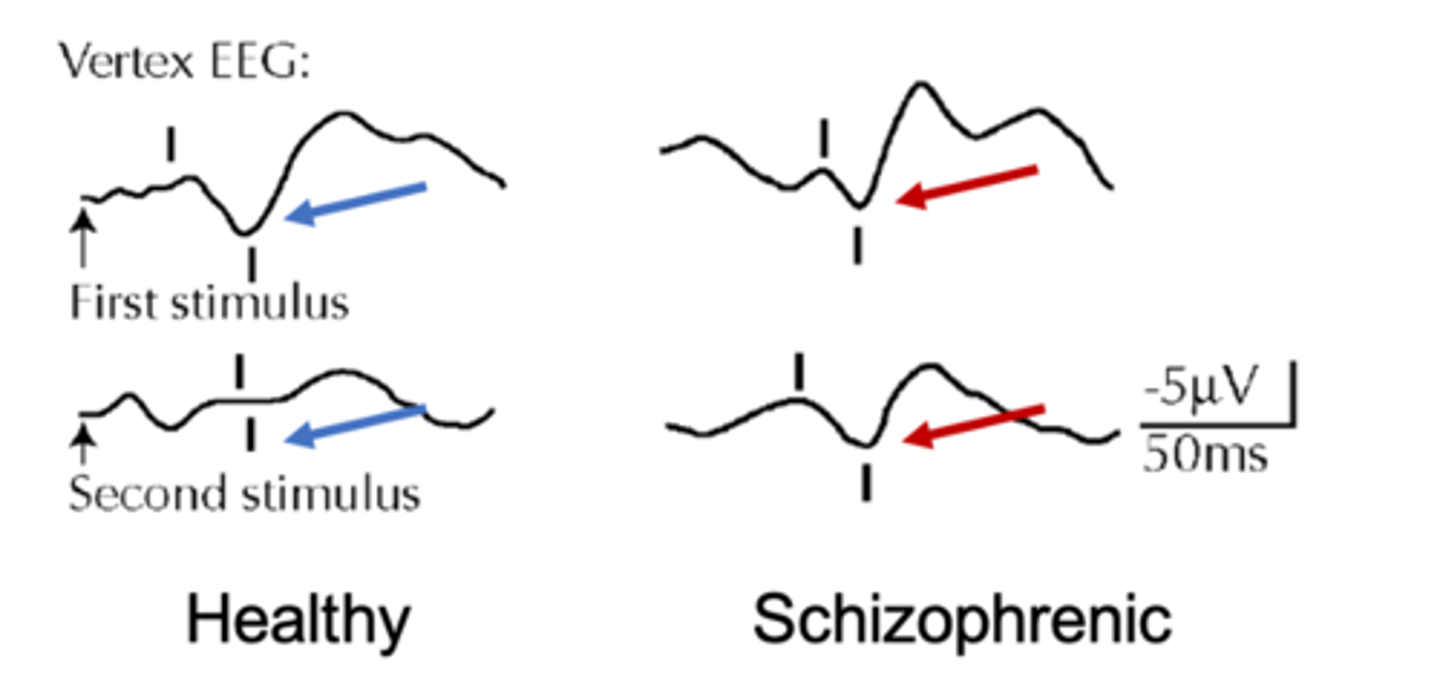
P50 gating
response to startling stimuli (eye air puff, fast beeps), initially large and then decreases each time the stimulus is presented. Decrease not seen in schizophrenia
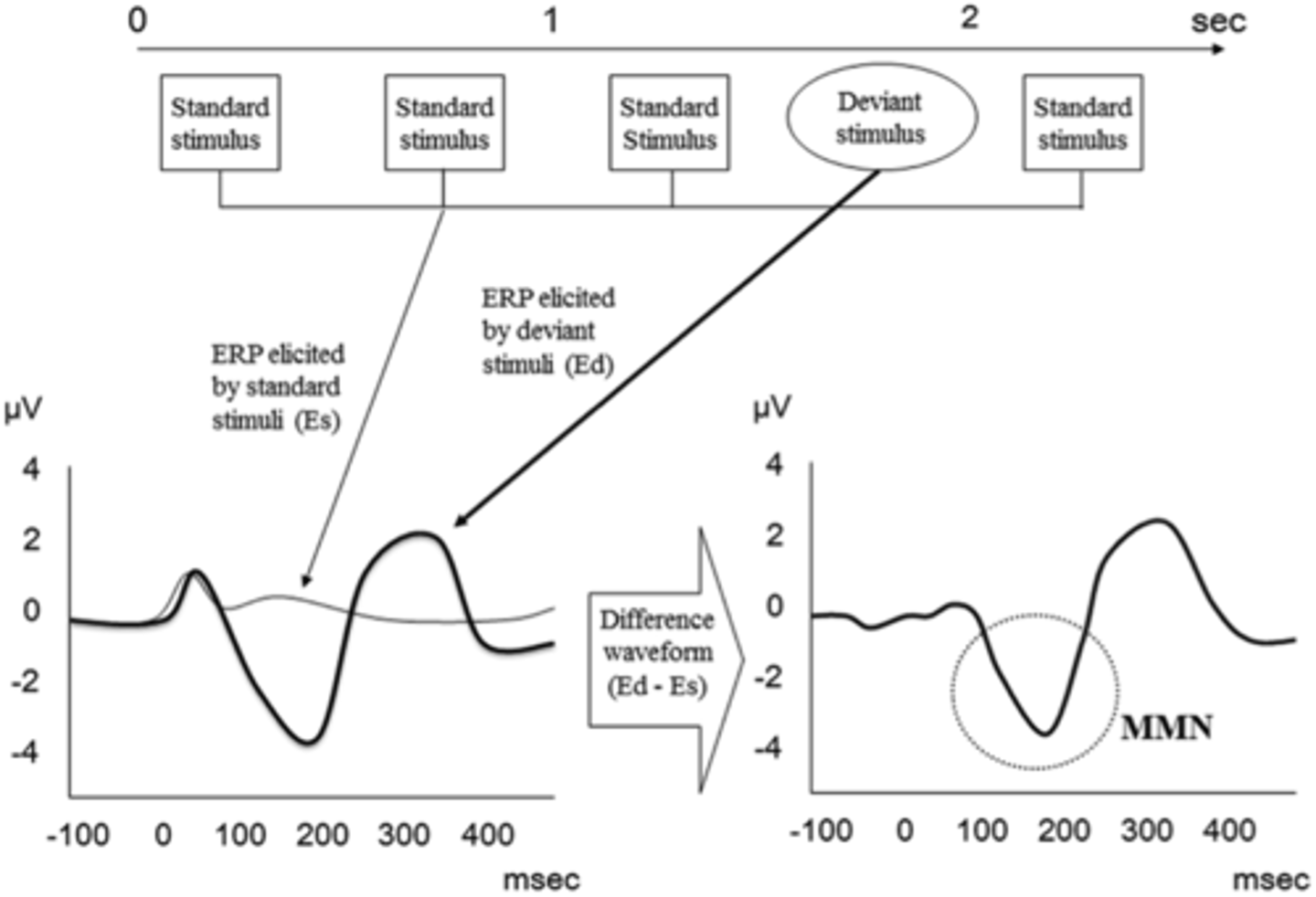
mismatch negativity (MMN)
what: An ERP component that occurs when an auditory stimulus deviates from previously presented auditory stimuli by any detectable amount
where: Seen near N1 source, auditory cortex and secondary frontal cortex
why: change detector, attentional shift to deviant stimulus
processing negativity
A slow, long-lasting negative-polarity ERP wave that is elicited during auditory selective attention, the amplitude of which reflects how well each stimulus matches an attentional "template."
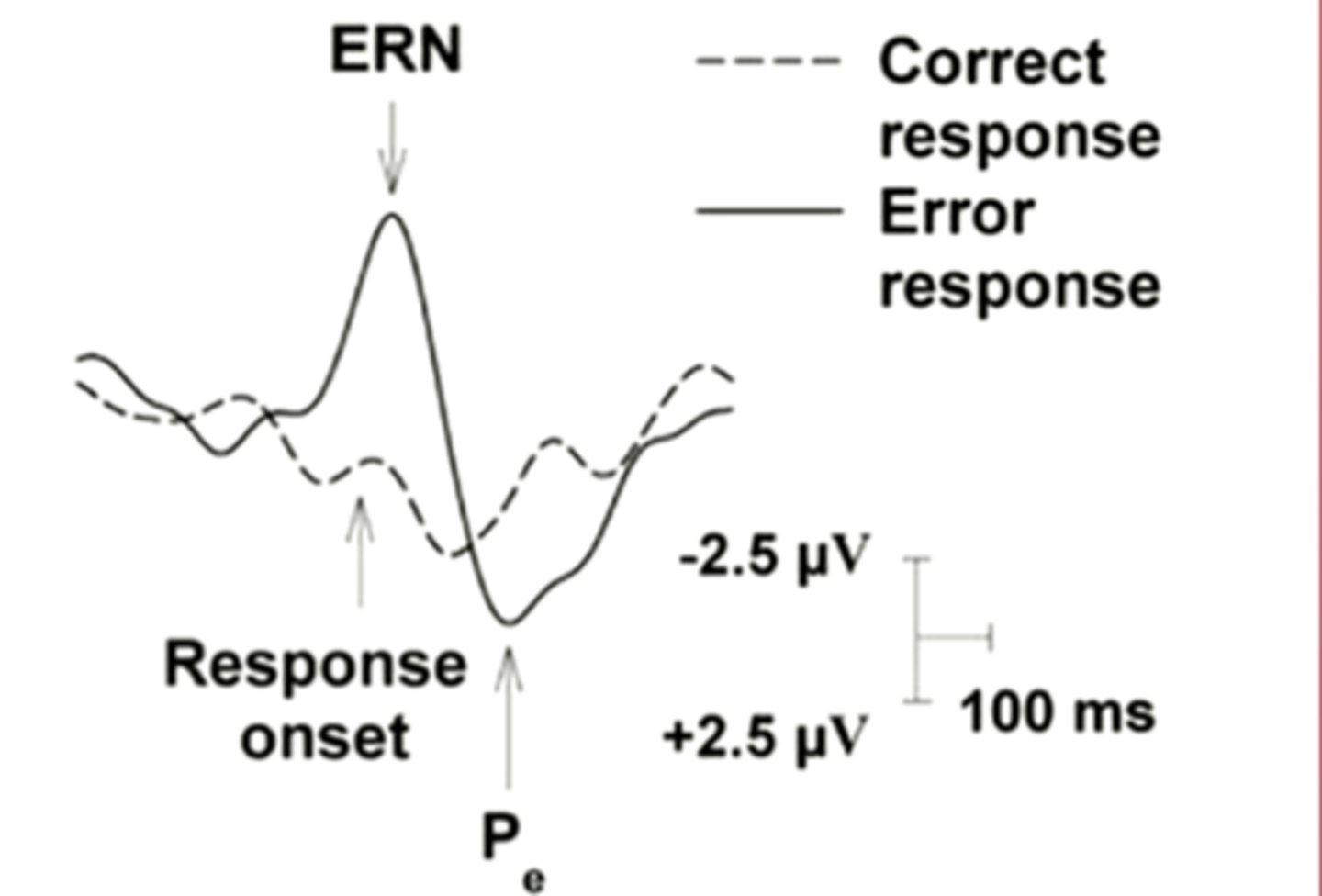
error-related negativity (ERN)
An electrophysiological marker that occurs when participants make errors in cognitive tasks, but occurs whenever someone makes an action in some regard
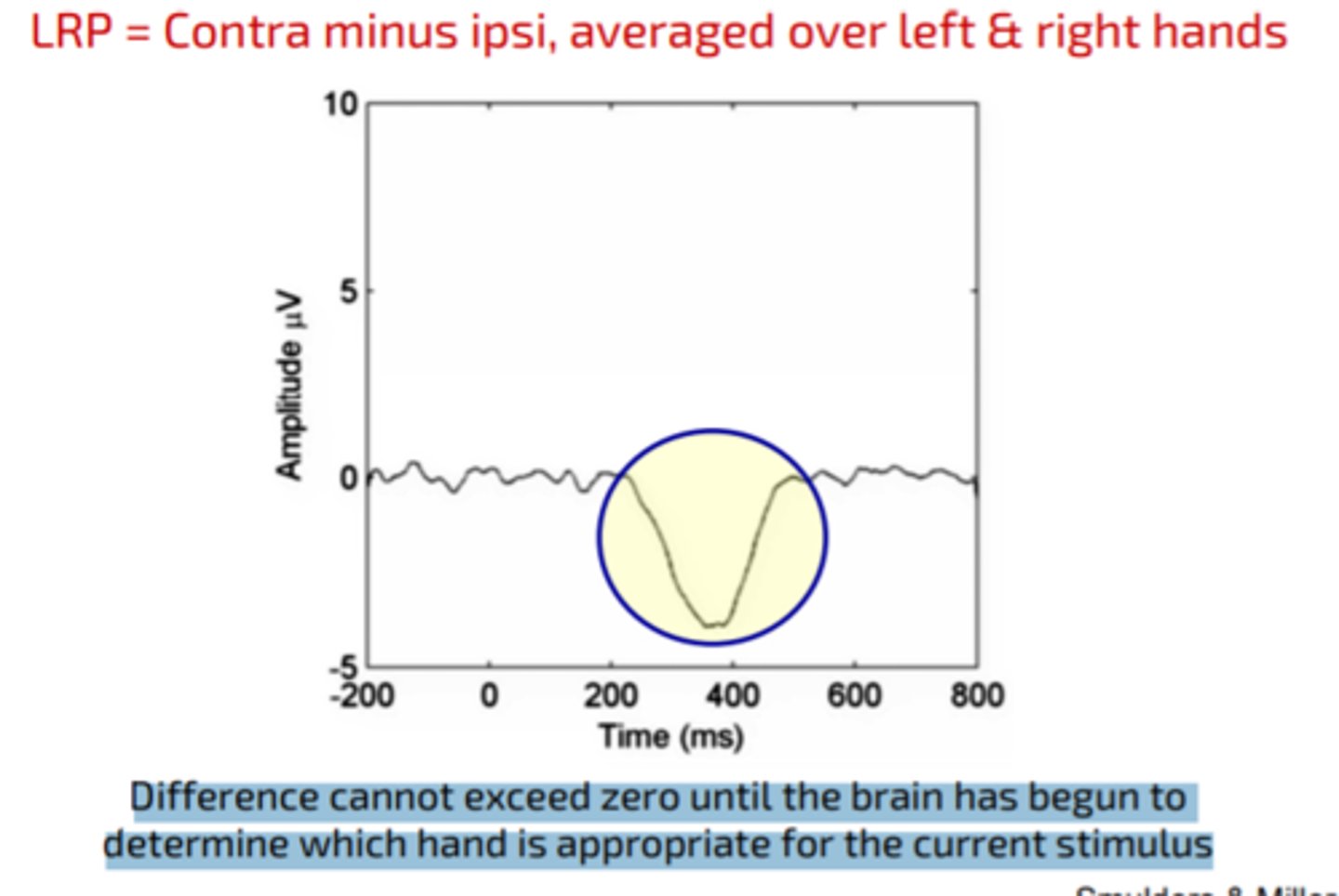
Lateralized Readiness Potential (LRP)
an event-related brain potential that is thought to reflect the preparation of motor activity on a certain side of the body; in other words, it is a spike in the electrical activity of the brain that happens when a person gets ready to move one arm, leg, or foot
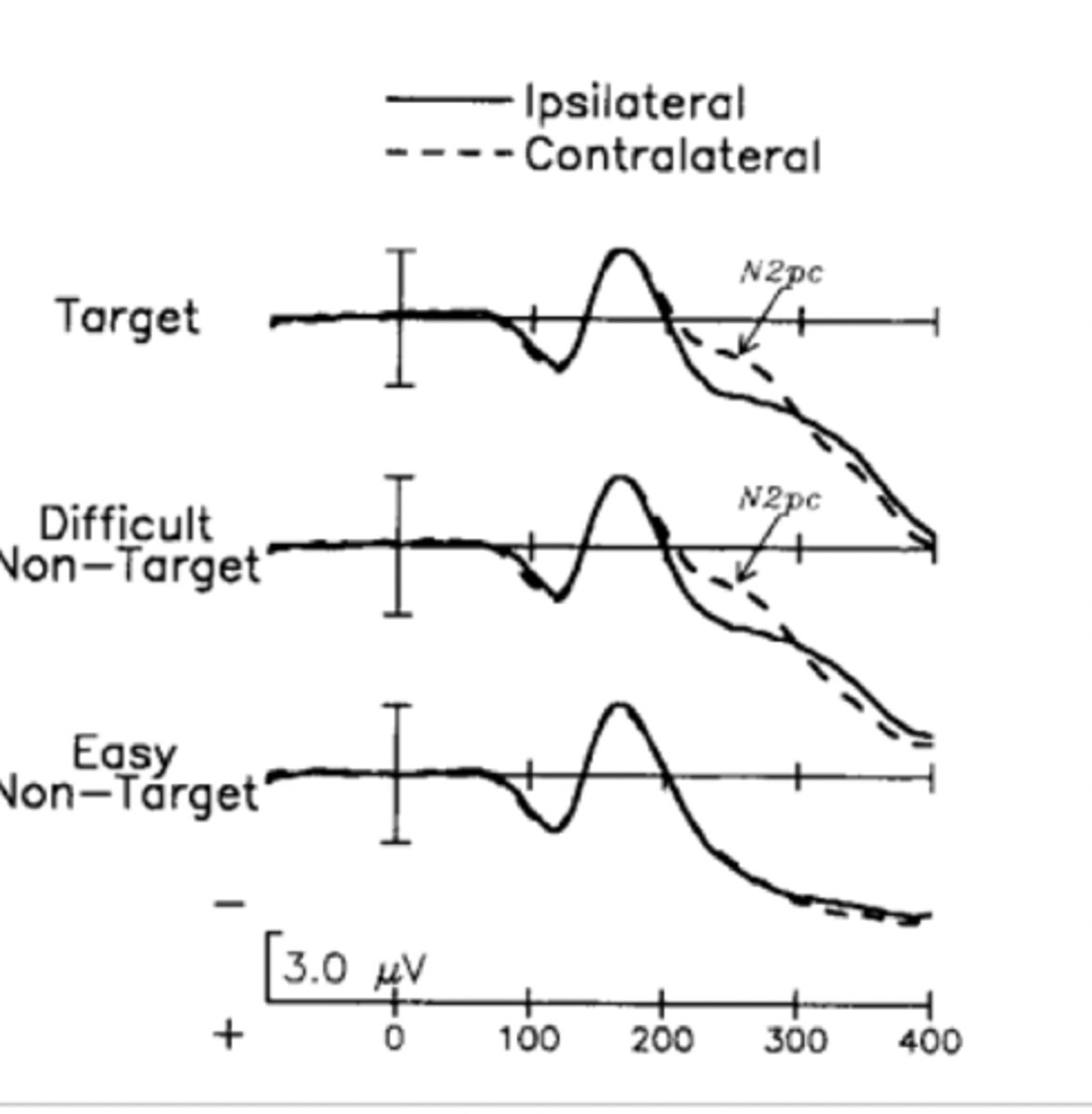
N2pc
What: ERP component seen after the presentation and response to a visual stimulus
Where: PO7/PO8 of contralateral side to stimulus (from difference wave)
Why: focusing of visuospatial attention (either distractor suppression or target processing)
distractor positivity
positive component seen when a distractor is present in a task. Thought to represent attentional dampening of the distractor. Occurs in contralateral cortex
What are advantages of a three stimulus oddball paradigm? (3)
1. deviants have same STR (same frequency/number of trials)
2. attention and motor responses are controlled for
3. deviants can be novel or not
Why would an oddball paradigm with novel deviants be used?
they prevent boredom and the ERP changing due to the stimulus being familiar
What ERP components are seen in auditory oddball experiments?
1. MMN
2. N2 family (N2b, N2c)
3. P300
What kinds of factors affect MMN latency and size?
similarity to the standard tone, when it is more different the MMN is larger and earlier
What is often used as a reference for MMN experiments and why?
the nose, since due to the dipole being in auditory cortex the dipole may result in a reading of positive or negative
Sensory Memory Model
- explanation theory of MMN
- memory based model, where standard tone at first shows an N1 due to just hearing something, then this stays in echoic memory and you seen MMN when there is a mismatch between memory and the tone
Sensory adaptation model
- explanation theory of MMN
- N1 stops due to boredom (adaptation of neurons)
- MMN represents different neurons becoming active
Prediction Error Model
- explanation theory of MMN
- N1 is prediction error at first, then model updates and it lessens
- MMN is a new prediction error
What evidence supports that MMN is a result of prediction error?
When a series of descending tones is played but one breaks the sequence, even if it is the same pitch as the previous tone, an MMN can be seen
No-go P3
ERP component seen on Cz due to motor inhibition, looks similar to P3a. Appears when told to not respond
Singleton
an element with a popout feature. Different from surroundings in one or more basic features
What basic feature of a singleton tends to be most salient?
colour (above shape, orientation)
What is a key important control for object arrays used in visual search tasks?
lateral balance of items on the left and right visual fields
Why is a circle configuration often used in visual search tasks?
it makes sure that all the items are equidistant from the fixation point
What does a larger distractor positivity tend to correlate with?
better working memory (able to not commit unneeded things to memory)