Patterns of inheritance
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What’re pedigrees?
Graphic representation of a family’s health history and genetic relationships
Uses standardized symbols
For, fast, accurate communication of medical and family history
What’re the instructions of a pedigree?

Understand these symbols
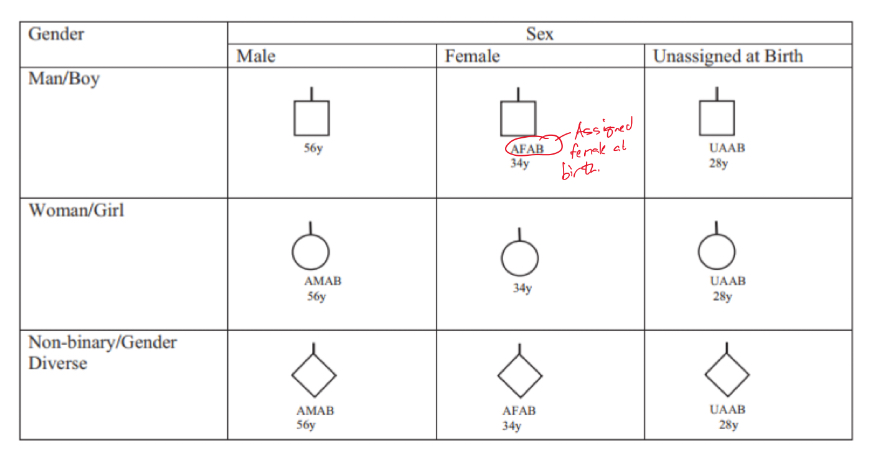
Understand all these common symbols
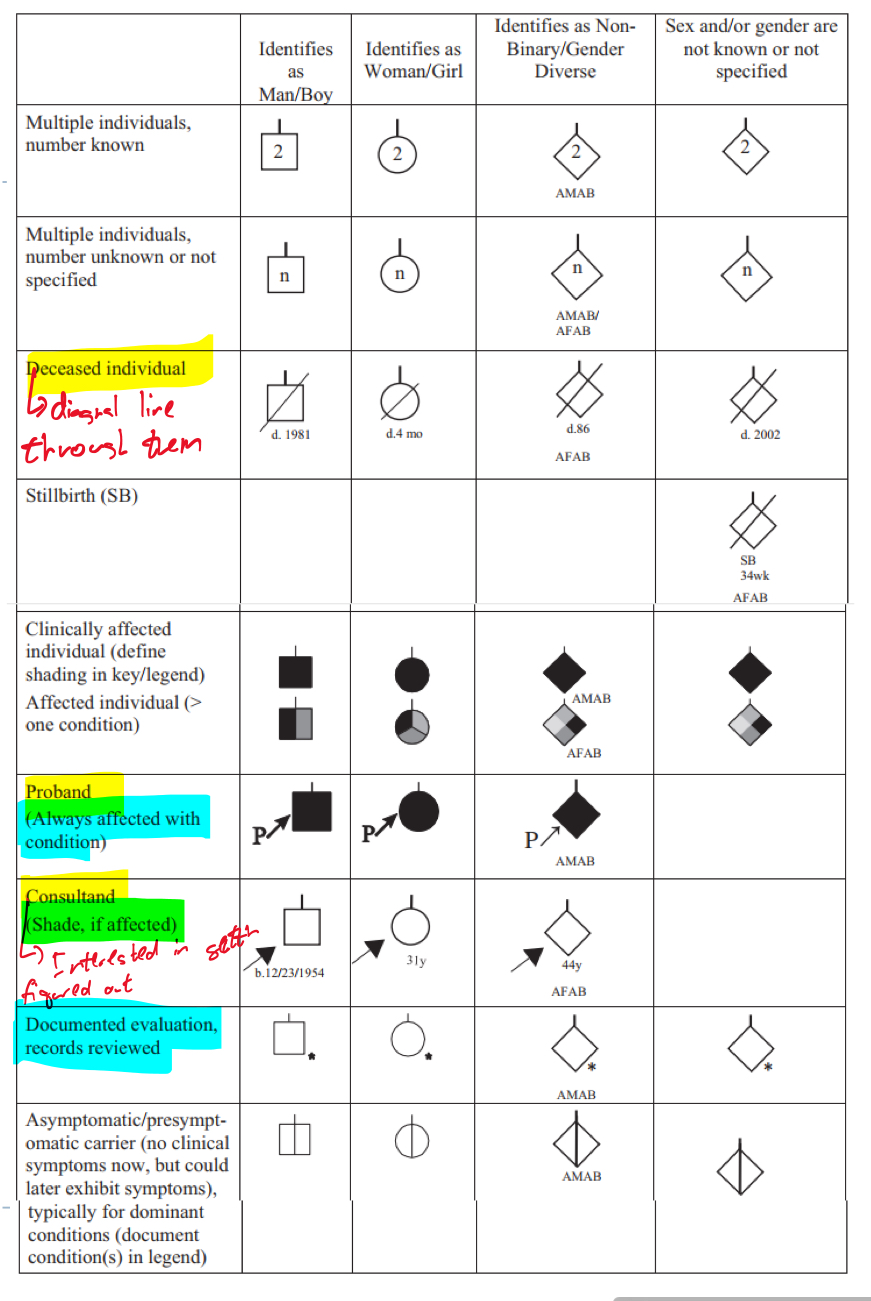
Understand the following slides of lines and pregnancy
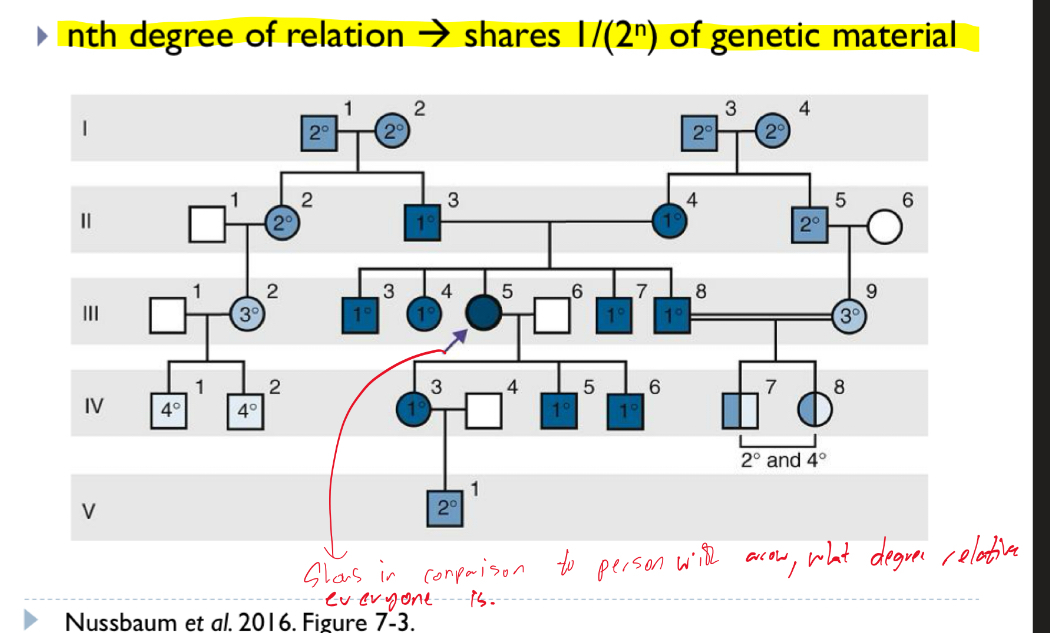
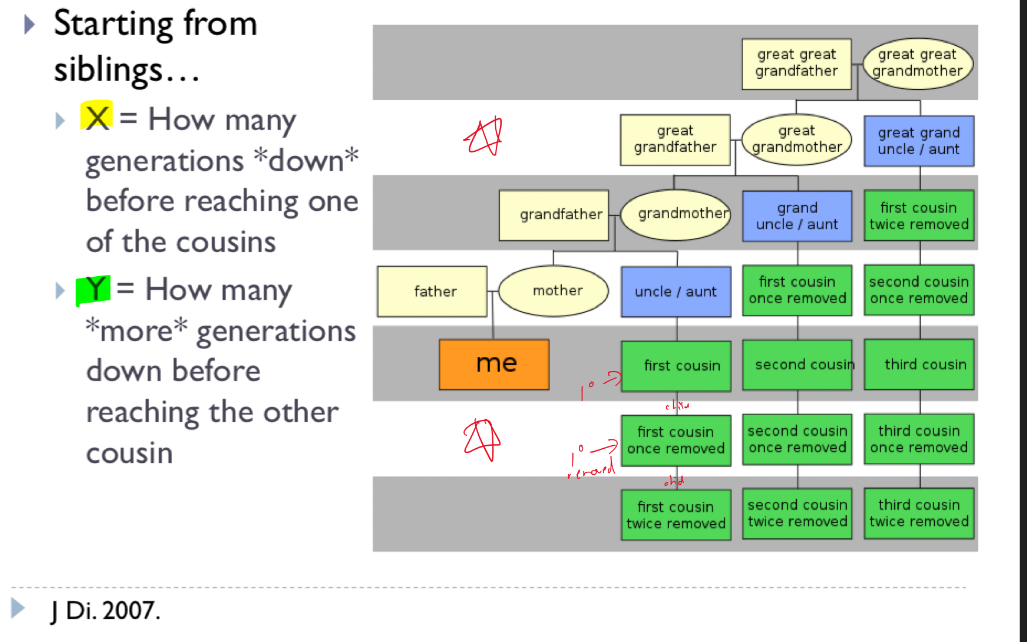
Explain degree of relation
Explain the concept of cousins removed
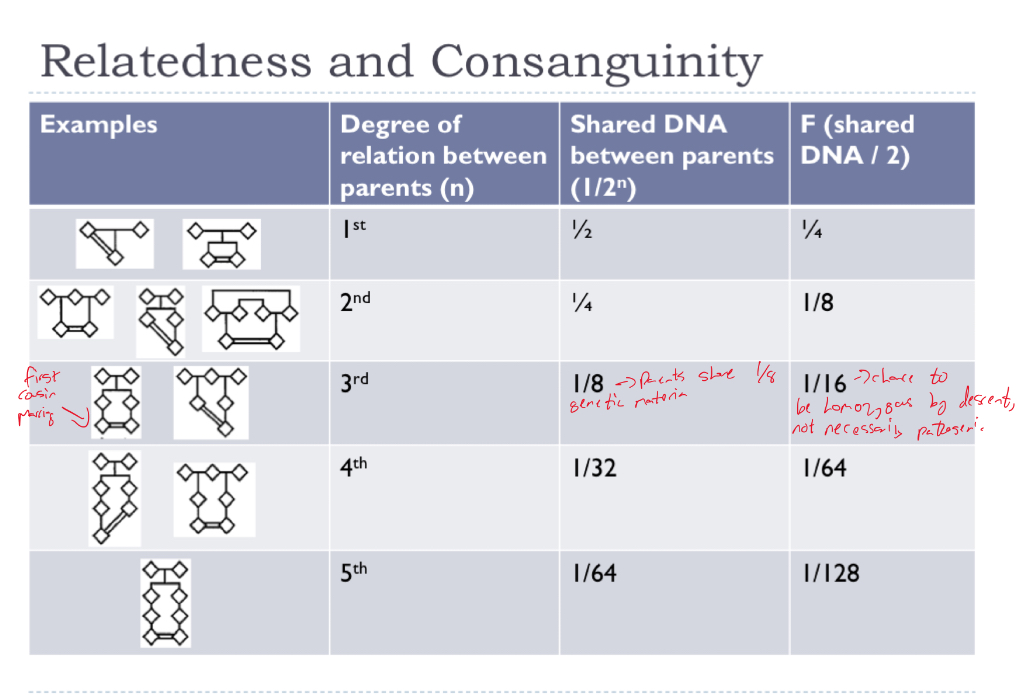
Explain relatedness and consanguinity
Ex: Lady Mary (Downtown Abbey)
What’re the 3 things used to evaluate a pedigree?
Transmission: Vertical (multiple generations), Horizontal (siblings in single generations)
Sex difference: Affected males to females, Difference in severity between sexes
Segregation: Male-male transmission, transmitted through parents of which sex, transmitted to children of which sex and in what proportion
What are the 2 general modes of inheritance?
Mendelian (i.e, monogenic, single-gene)
Non-Mendelia
What’re the different types of Mendelian inheritance?
Autosomal dominant
Autosomal recessive
X-linked dominant
X-linked recessive
Y-linked
What’re the different types of non-Mendelian inheritance?
Imprinting
Mitochondrial
Multifactorial
Sporadic
Contiguous gene syndromes
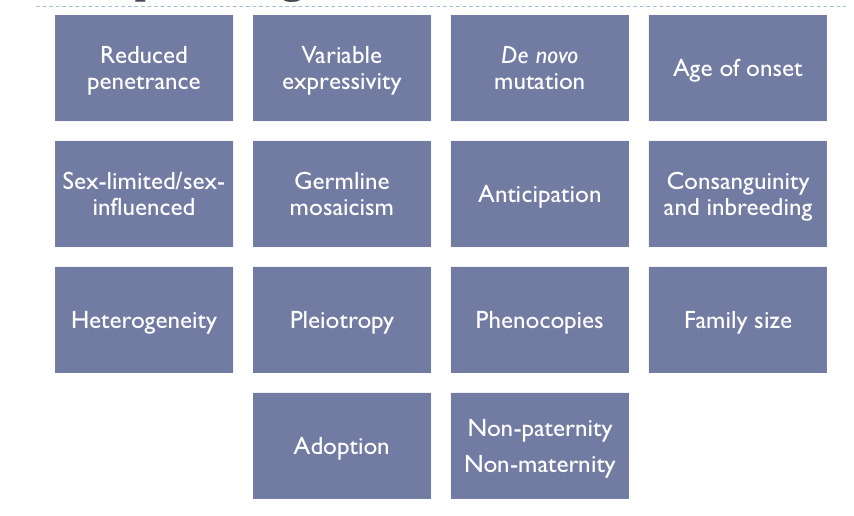
What’re some complicating factors in inheritance?
What kind of transmission is in autosomal dominant?
Vertical: Multiple generations affected
What’re the sex differences in autosomal dominant?
Usually none
Whats the segregation in autosomal dominant?
No specific segregation, could be inherited by male to male transmission
Parent of any sex could transmit to children of any sex
Any child of an affected parent has a 50% chance of being affected
Whats an important note about autosomal dominant?
Unless otherwise specified, assume these are rare diseases: Spouses unlikely to have the same rare condition
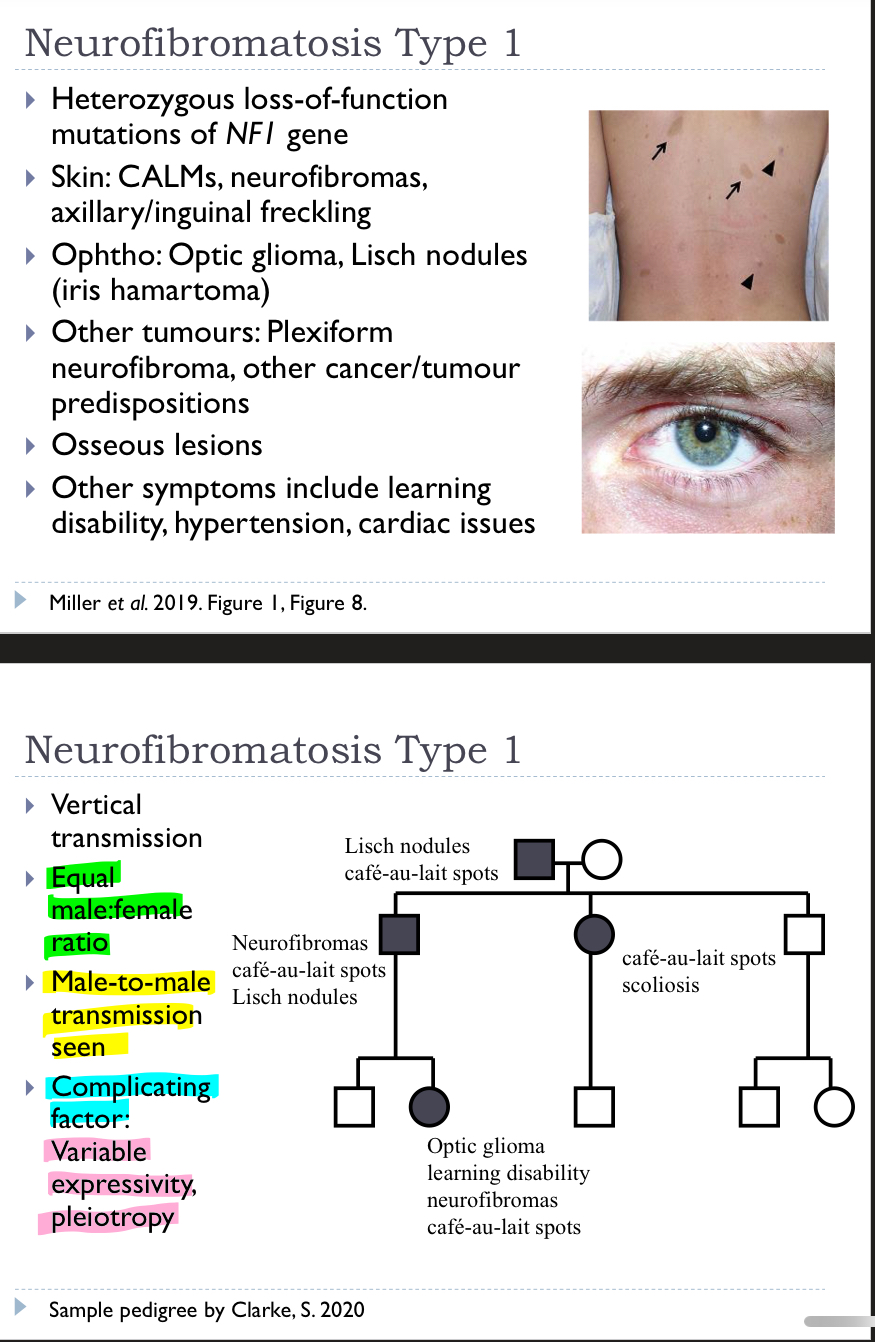
Explain Neurofibromatosis Type 1
Understand the slides of COL1A1/2 Osteogenesis imperfecta
Whats mosaicism
2 or more cell lines with different genetic makeup due to post-zygotic event
Explain mosaicism in placental, somatic, and germline?
Placental: placental cell lines may not match genetic makeup of fetus
Somatic: 2 or more cell lines within an individual, which may or may not include germline
Germline/ gonadal: Confined to the germline - precursors to egg or sperm
Explain myotonic dystrophy type 1

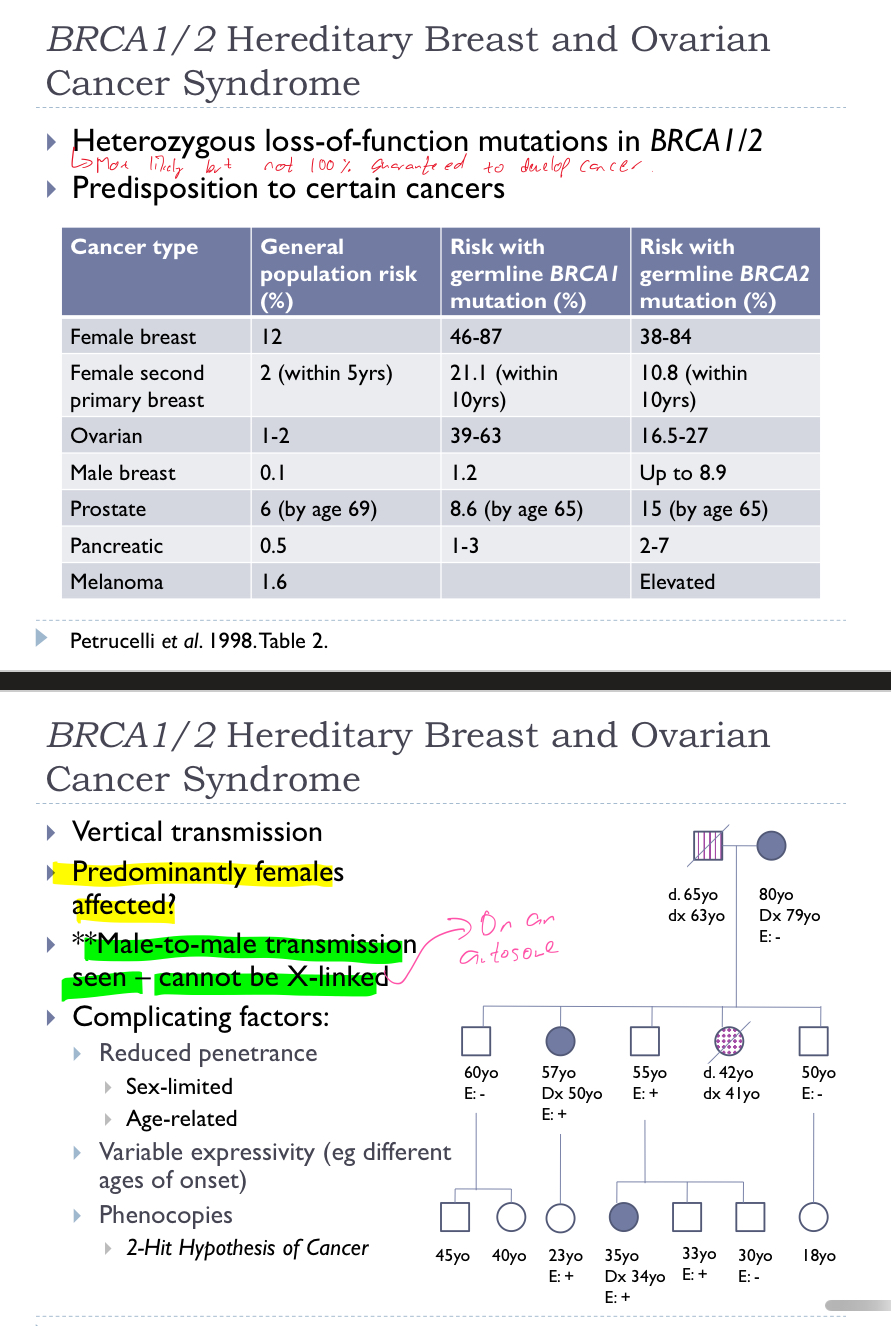
Explain BRCA1/2 Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer Syndrome
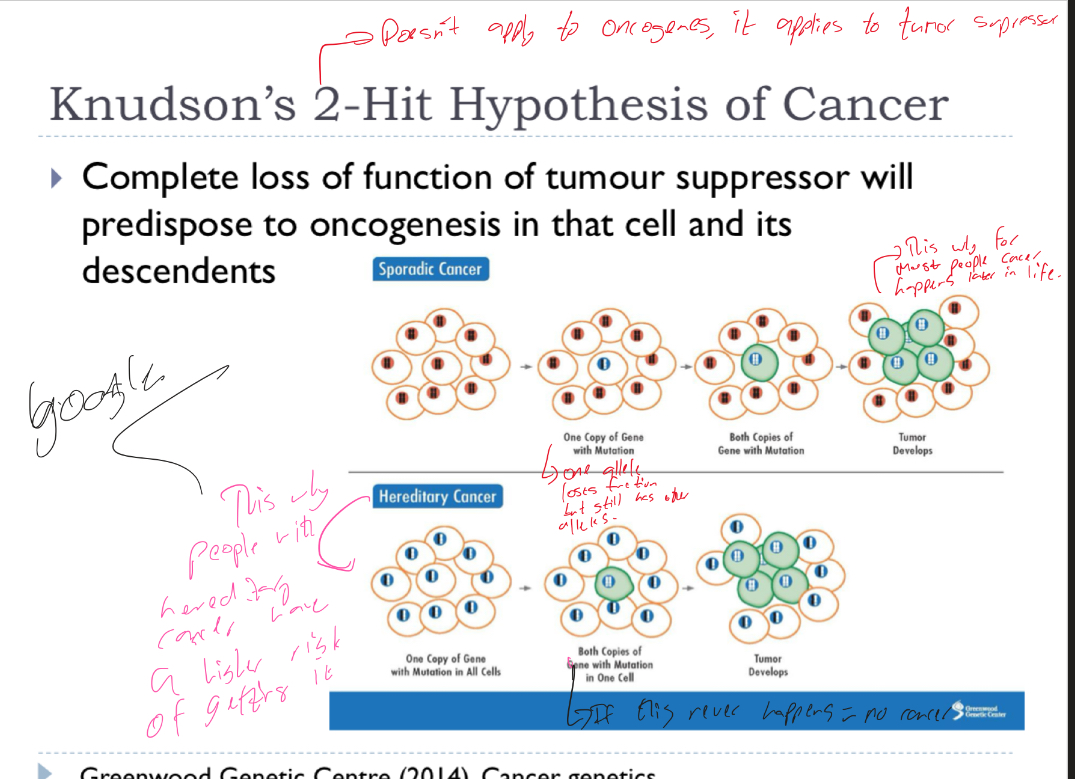
Explain knudsons 2 hit hypothesis of cancer