Taste - Chemoreception
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Gustation
taste
olfaction
smell
5 basic taste qualities
salty, sour, sweet, bitter, and umami (meaty)
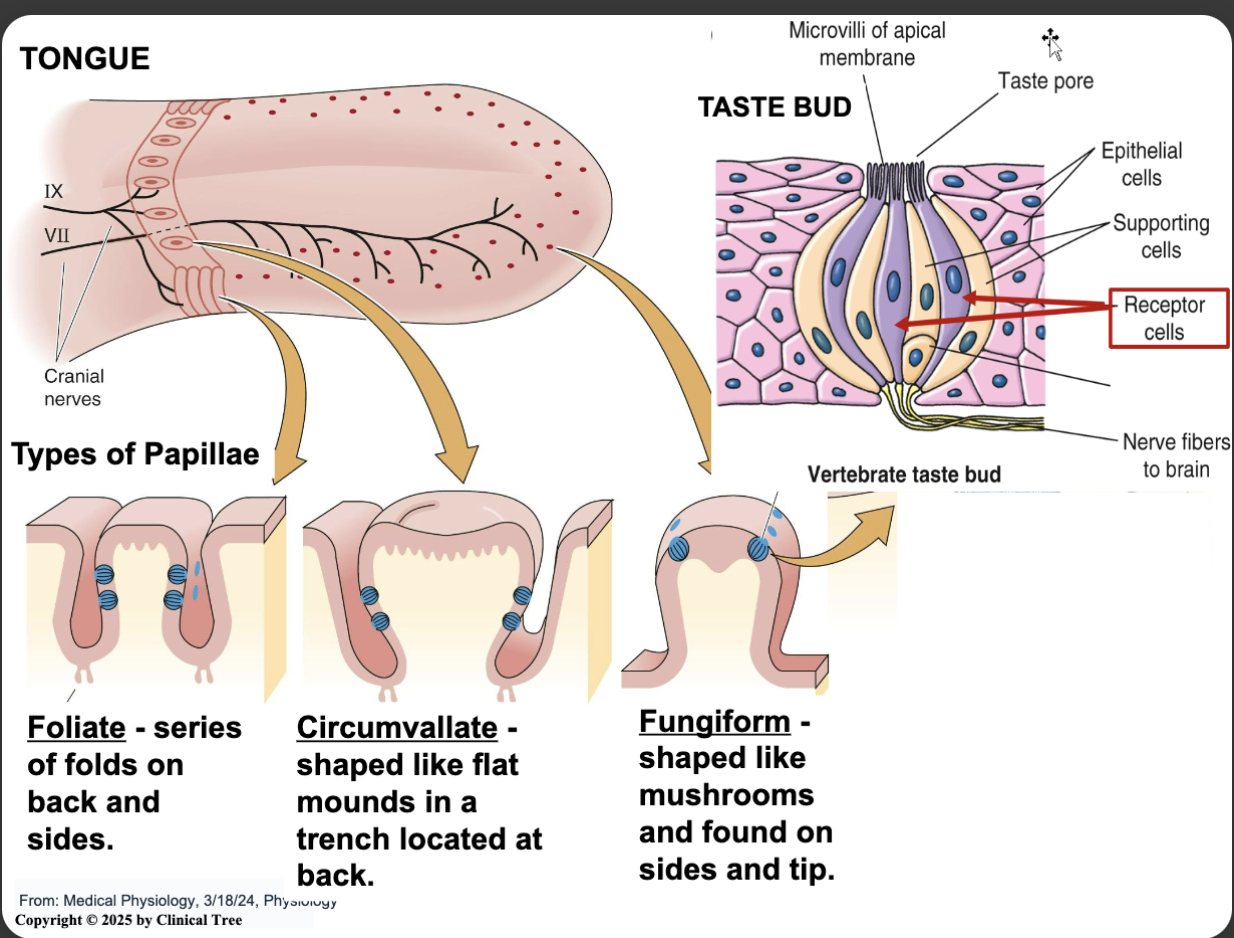
tongue structure
papillae
foliate: senses of bolds on back and sides of tongue
circumvallate: shaped like fat mounds in a trench located on the back of tongue
fungiform: shaped like mushroom and found on sides and tip of tongue
these contain your taste buds
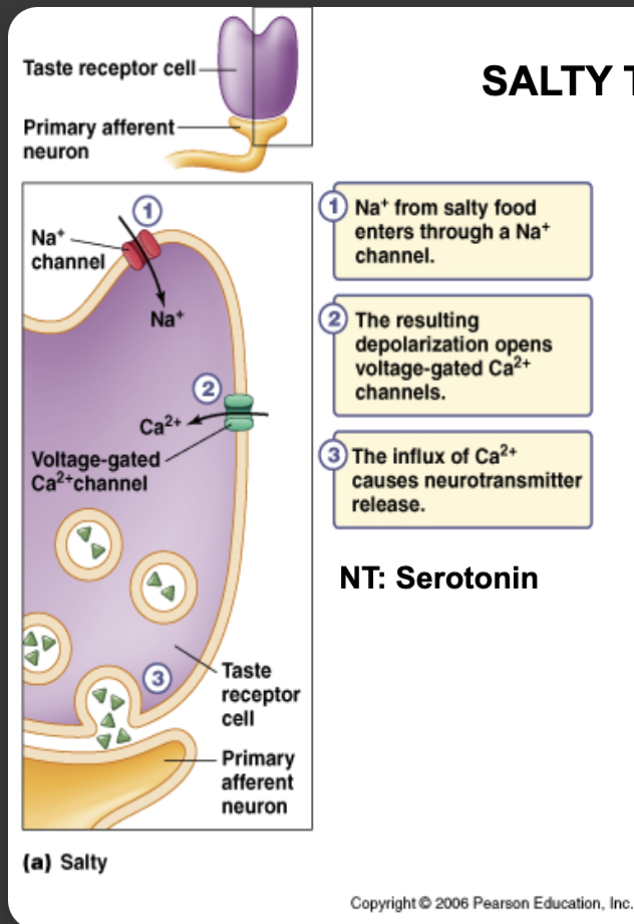
Salty taste transduction
Na+ through ion channel, depolarization, opens Ca2+ channels
NT: serotonin
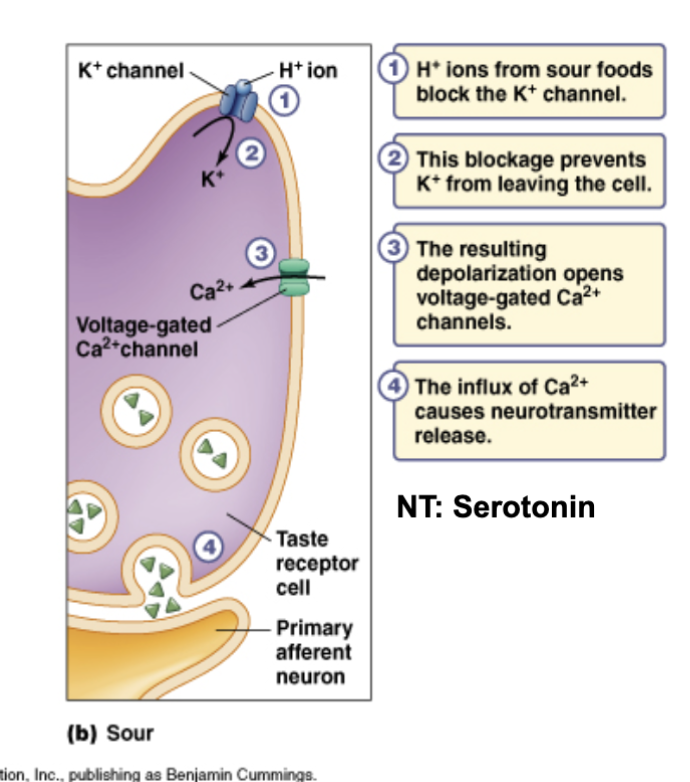
sour taste transduction
Sour: H+ through ion channel, depolarization, opens Ca2+ channels
Nt serotonin
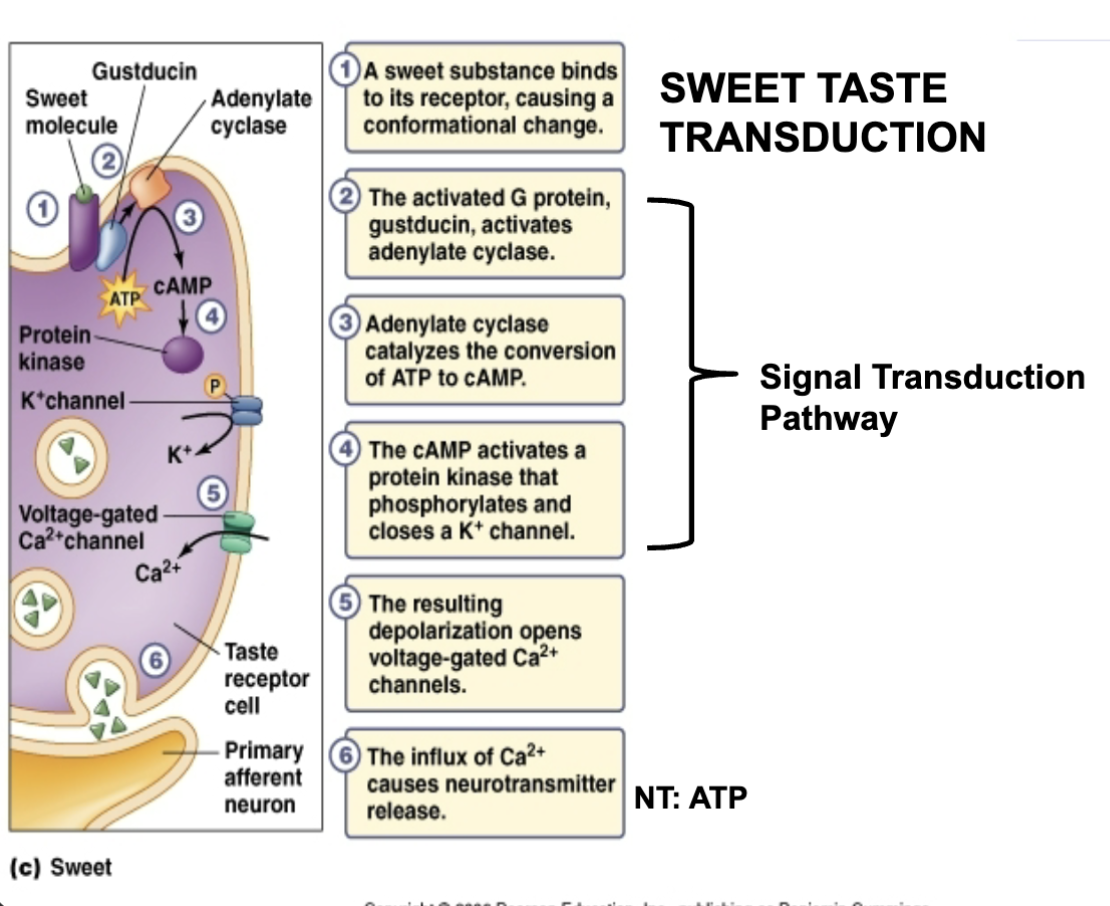
Sweet taste transduction
Sweet: binds to membrane receptors, G proteins activated, close K+ channels
NT: ATP
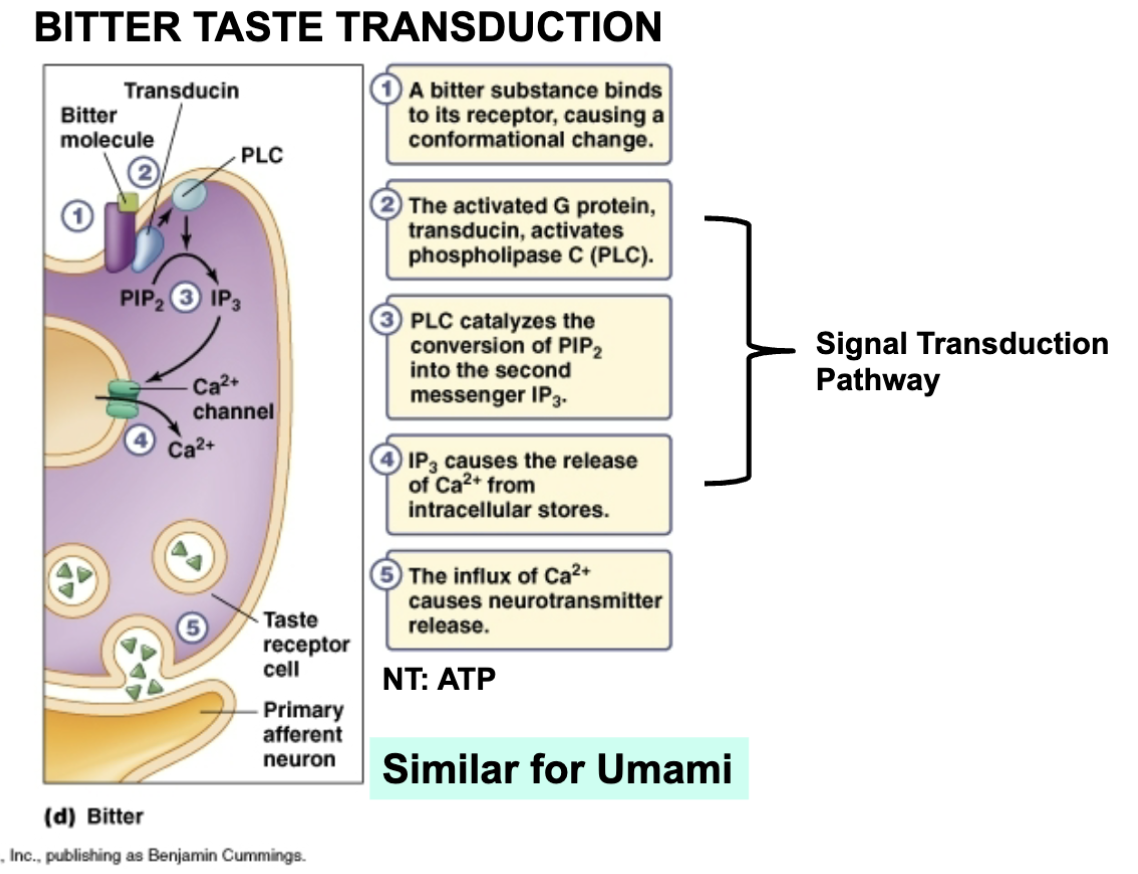
Bitter taste transduction
Bitter: binds to membrane receptors, G proteins activated, Ca2+ entry
NT: ATP
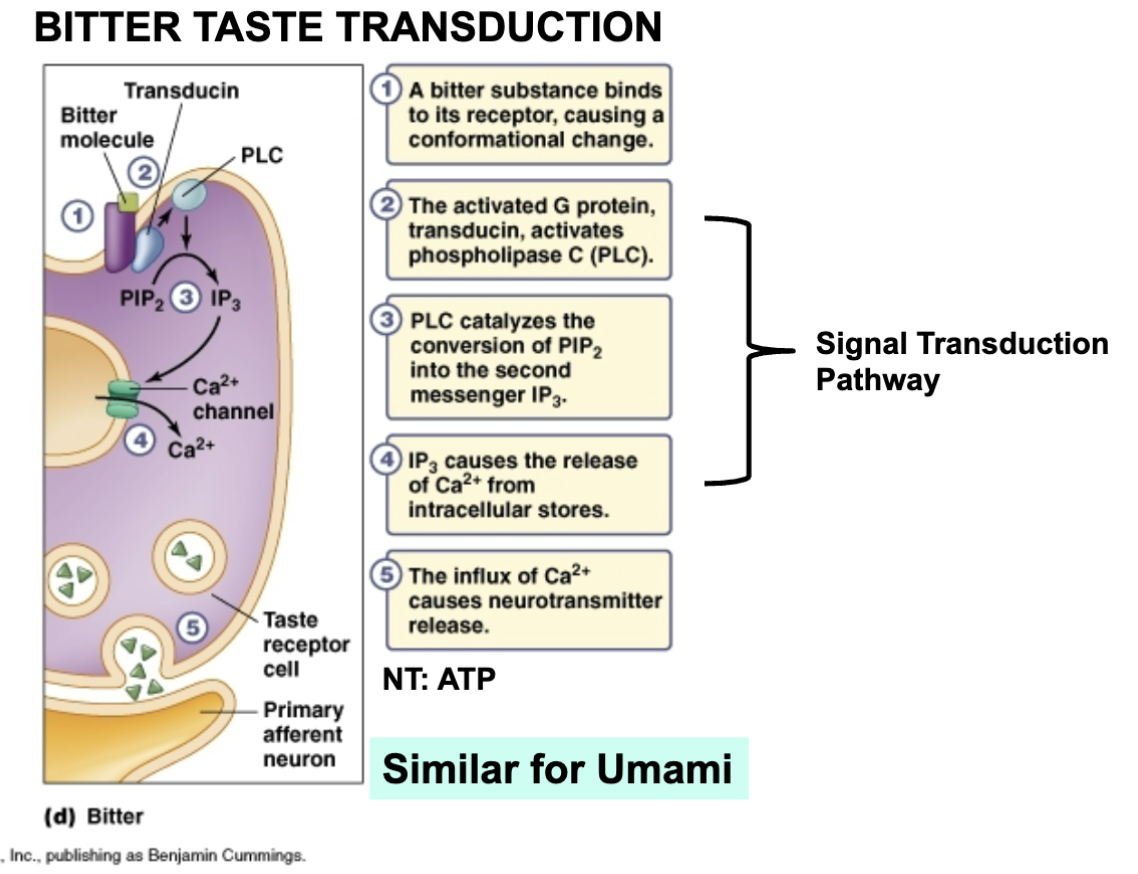
umami taste transduction
Umami: meaty, brothy, savory assoc. w/ MSG – same mechanisms as sweet
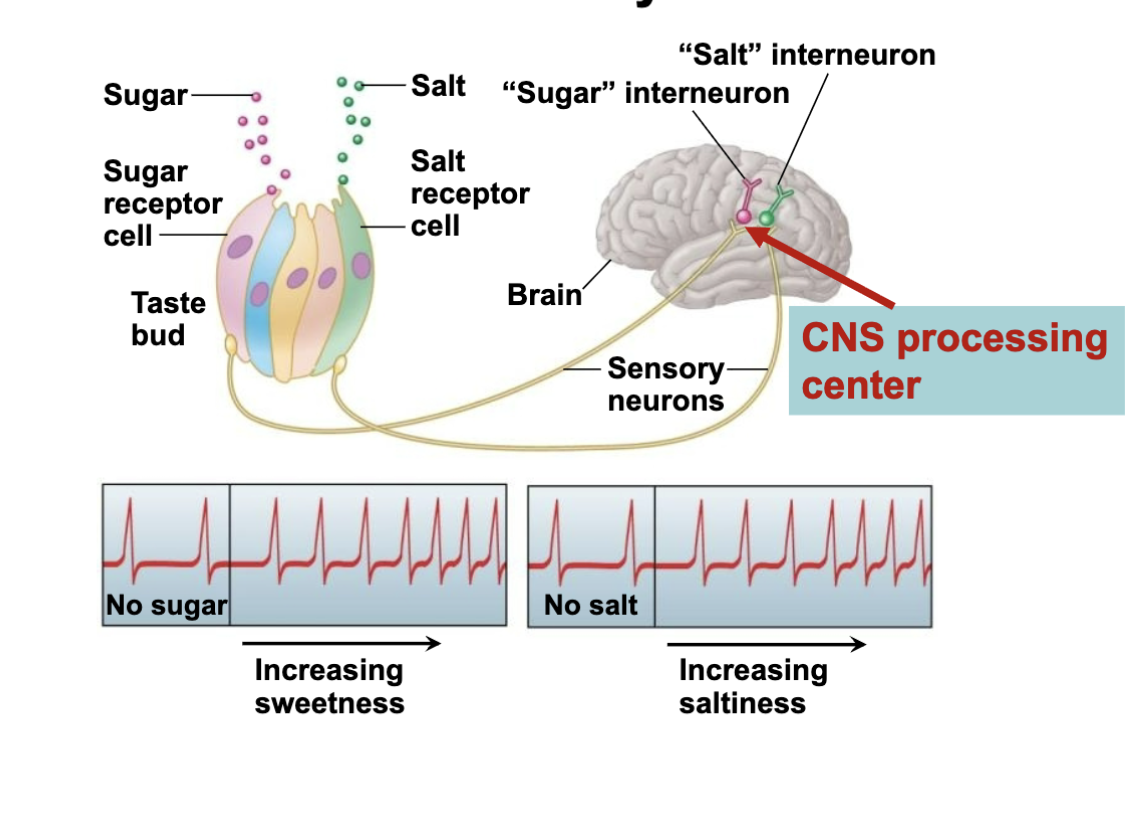
neural pathways
sugar/salt is eaten, the taste bud goes through the process we just talked abt, the NT is sent through sensory neurons to the sugar/salt interneurons in the CNS
more sugar/salt, the more APs there are sent to the brain
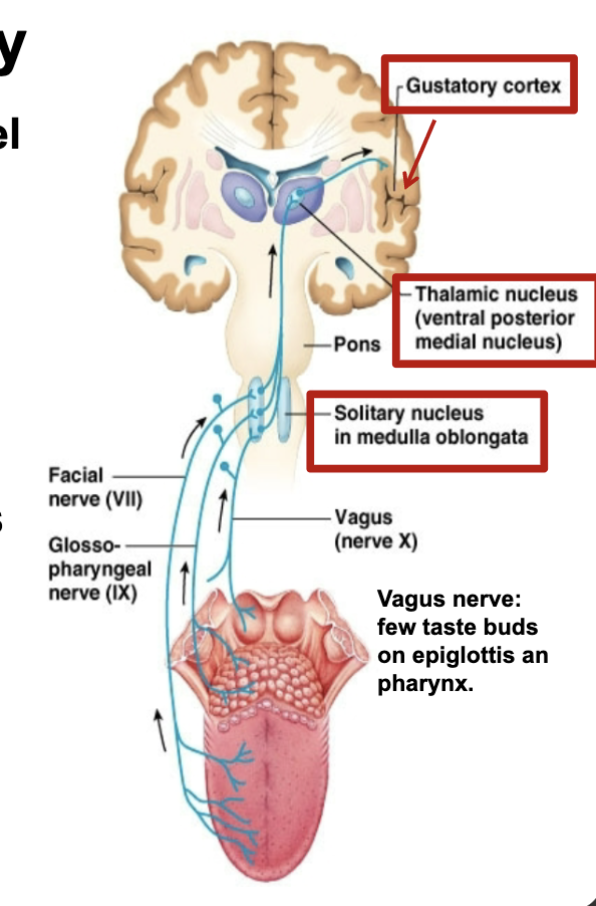
Gustatory pathway
signals from taste cells trave along a set of pathways
facial nerve and glossopharyngeal nerve
medulla oblongata: initiate PNS refflexes to trigger saliva and gastric secretion
project this info to thalamus and gustatory cortex
fibers also project to hypothalamus and limbic system (enjoyment)
chemosensory coding
coding in the sensory system could theoretically follow
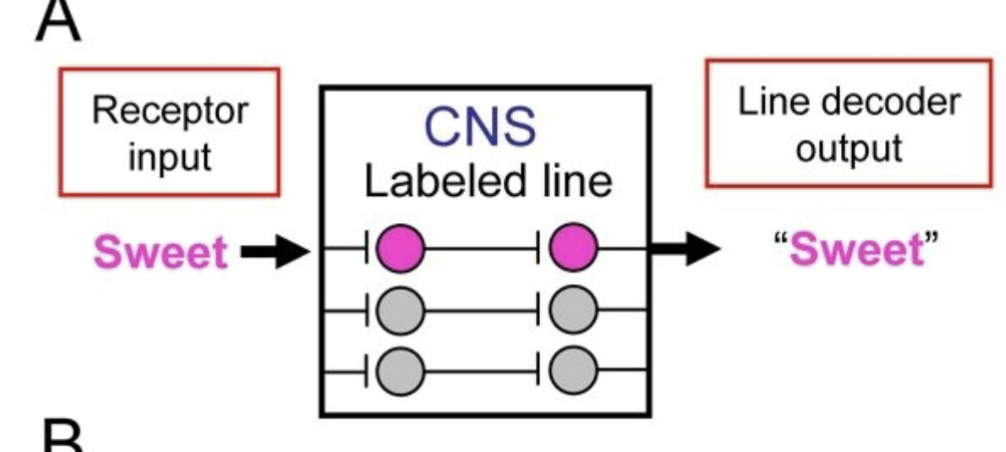
labeled line coding
across fiber pattern/ensemble coding
labeled line coding
each receptor responds to limited range of stimuli and sends direct line to brain
receptors are narrowly tuned: specialist
ex: cell phone, you calling someone
receptor input: sweet to CNS: labled line to Line decoder output “sweet”
straight forward straight line
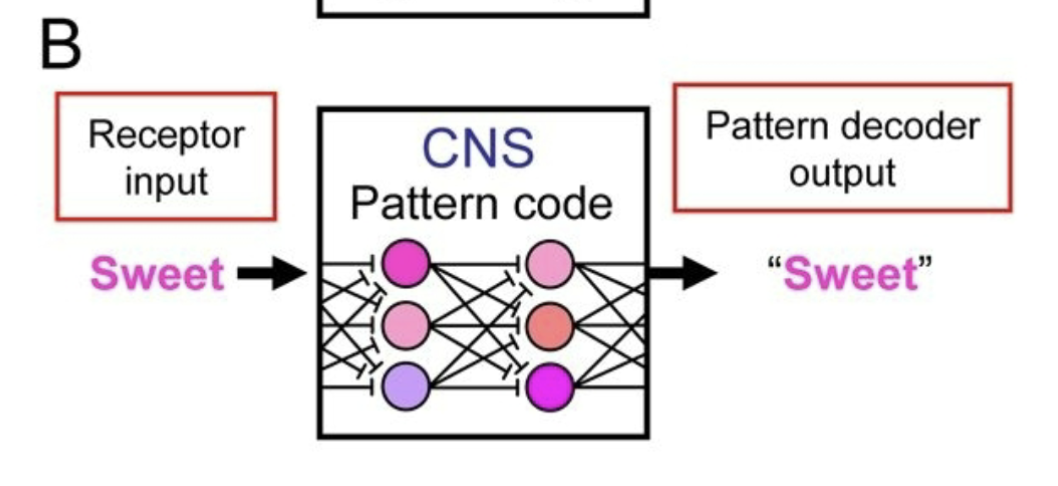
across fiber pattern/ensemble coding
each receptor respons to wider range of stimuli and contributes to perception of each of them
receptors are less narrowly tuned: generalists
receptor input: sweet to CNS: pattern code to pattern decoder output: “sweet”
not a straight line
neurons (type A-D) are sensitive to many diff stimulus, but show highest sensitivity to a few stimuli
in contrast: labeled line coding