CFI - Corporate Finance Fundamentals | Quizlet
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Corporate Finance objective:
...A...of a business while...B...
A) Maximizing the value
B) balancing risk and profitability
Capital Investment:
Deciding what...A...while the...B...
A) projects/businesses to invest in
B) highest possible risk-adjusted return
Capital financing:
Determining how to...A...while optimizing the firm's...B...
A) fund capital investments
B) capital structure
Dividends & Return of Capital:
Deciding how and when to...
return capital to investors
Corporate finance is mainly about: (3)
1.Capital Investments
2.Capital financing
3.Dividends & Return of Capital
Players in corporate finance – primary market (4)
1. Corporations ( need capital )
2. Institutions ( investors )
3. Investment Banks (broker)
4. Public accounting firms (over all financial info)
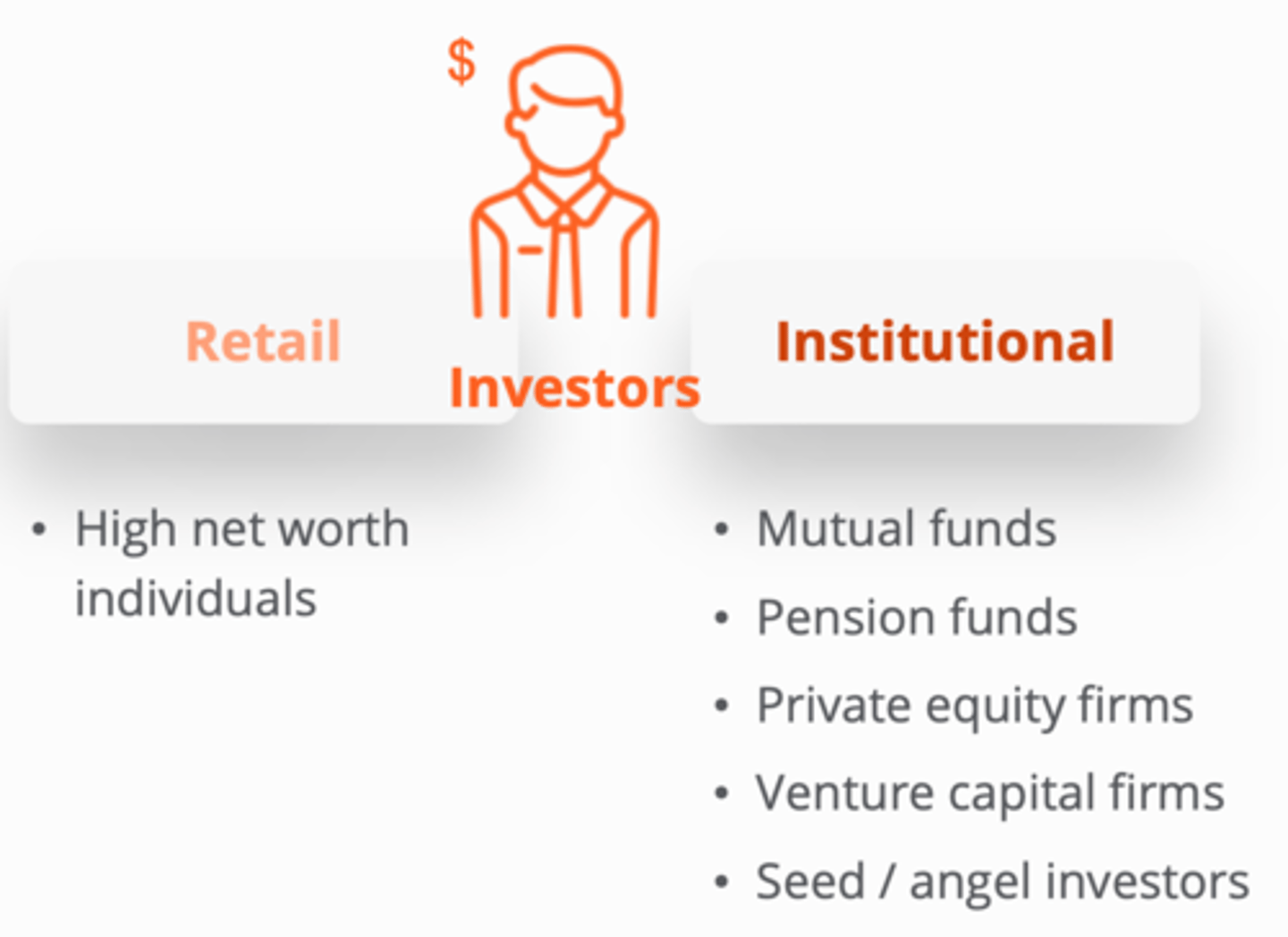
Investors
1. Retail:(1)
2. Institutional:(5)
1. a) HNWI
2.
a) mutual funds
b) pension funds
c) private equity firms
d) VC firms
e) seed / angel investors
Corporations:
1. ...
2. ... - ...
1. public
2. private - traded and owned by a few investors
Types of transactions: (6)
1. IPO
2. Follow-on offering
3. Private placement
4. M&A
5. LBO
6. Divestiture

IPO (initial public offering):
The first time a company...
sells shares of its stock to the public.
Follow-on offering:
Issuance of stock shares following a company's...
Initial public offering (IPO)
private placement:
...A...in which shares are sold directly to a...B...
A) primary offerings
B) small group of institutional or wealthy investors
Mergers and acquisitions:
A merger is the combination of two firms, which subsequently form a new legal entity under the banner of one corporate name. An acquisitions when, one company purchases another outright
Leveraged Buyout (LBO):
...A...is completed almost entirely with...B...
A) the acquisition of another company
B) borrowed funds
Divestiture:
Disposing all or some of its...A... by...B...,...C...,...D...them down, or through...E...
A) assets
B) selling, exchanging, closing them down, or through bankruptcy.
What is a capital investment ?
Any investment for which...A.. is ...B...
A) the economic benefit
B) greater than one year
capital investment examples
1.
2.
3.
4. ...A... and ...B... of ...C...
Opening a new factory
Entering a new market
Acquiring another business
4. A) Research B) development C) new products
Before any capital investment the company assesses
Investment payoff
Techniques for valuing an investment
1.Net Present Value (NPV)
2.Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
terminal value (Vt)
company's value into perpetuity beyond a set forecast period
Terminale value calculation methods
1.Growing perpetuity formula
2.Exit multiple formula
Growing Perpetuity Formula
Free cash flow*( 1+growth ) / ( Cost of capital - growth )

Exit Multiple Formula
assume that the business is sold at the end of the forecast period

Free Cash Flow refers to
Business strategy
Revenue
Cost structure
Asset utilization
Growth refers to
Organic growth
What's sustainable
Cost of capital refers to
Risk
Current capital structure
Macrofactors
Organic growth
growth achieved through the expansion of current business activities
Enterprise Value (EV)
the value of the entire business
Equity Value/Market Capitalization
the value shareholders would receive if the company is sold
Equity Value Formula
=Share Price x Outstanding Shares
=NPV of the business - Debt + Cash
Enterprise Value Formula
=Equity Value + Debt - Cash
=NPV of the business
Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
the annual rate of growth that an investment is expected to generate
the higher the IRR
the more valuable is the project is
IRR goal is to
identify the rate of discount, which makes the present value of the sum of annual nominal cash inflows equal to the initial net cash outlay for the investment.
Mergers and acquisitions
the process of companies buying, selling, or combining businesses.
Mergers and acquisitions benefits
• Cost savings
• Revenue enhancements
• Increase market share
• Enhance financial resources
Mergers and acquisitions potential drawbacks
• Overpaying
• Large expenses associated with the investment
• Negative reaction to the merger or acquisition
10 steps acquisition process
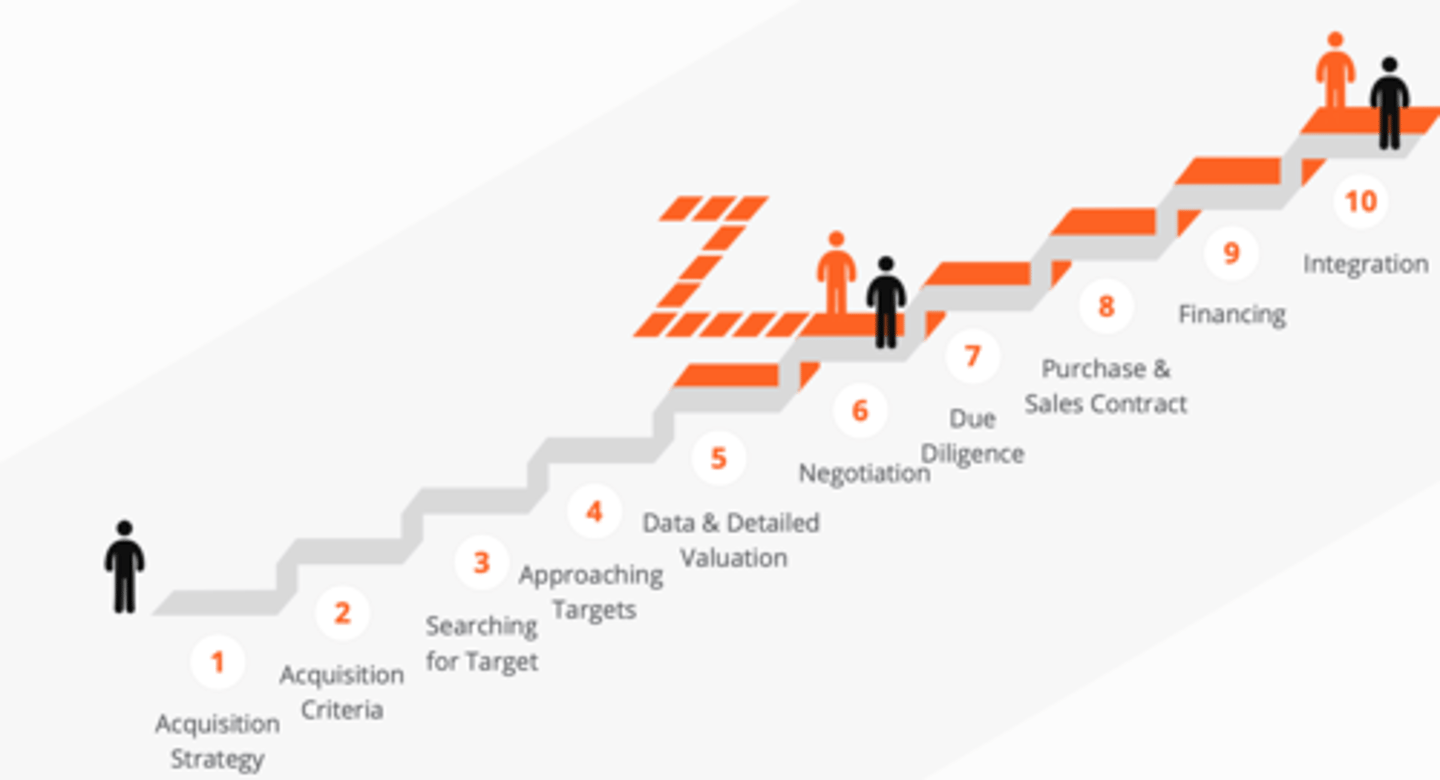
M&A process step 1
Acquisition Strategy tying with company overall strategic plan
M&A process step 2
Defining acquisition criteria (size, location, type of business)
M&A process step 5
Business Evaluation & Detailed Evaluation based on public information
M&A process step 10
Integration of the business when the transaction is closed
Two types of buyers in M&A
1.Strategic Buyers
2.Financial Buyers
Strategic Buyers are
Operating businesses looking for expansion (vertical or horizontal) and achieve operating synergies ( cost savings or revenue enhancement)
Financial Buyers are
Private equity or Professional investor looking for maximizing their ROE
rival bidder
another party offering to buy the asset from the seller at a specific price
Companies pay more than rival bidders because

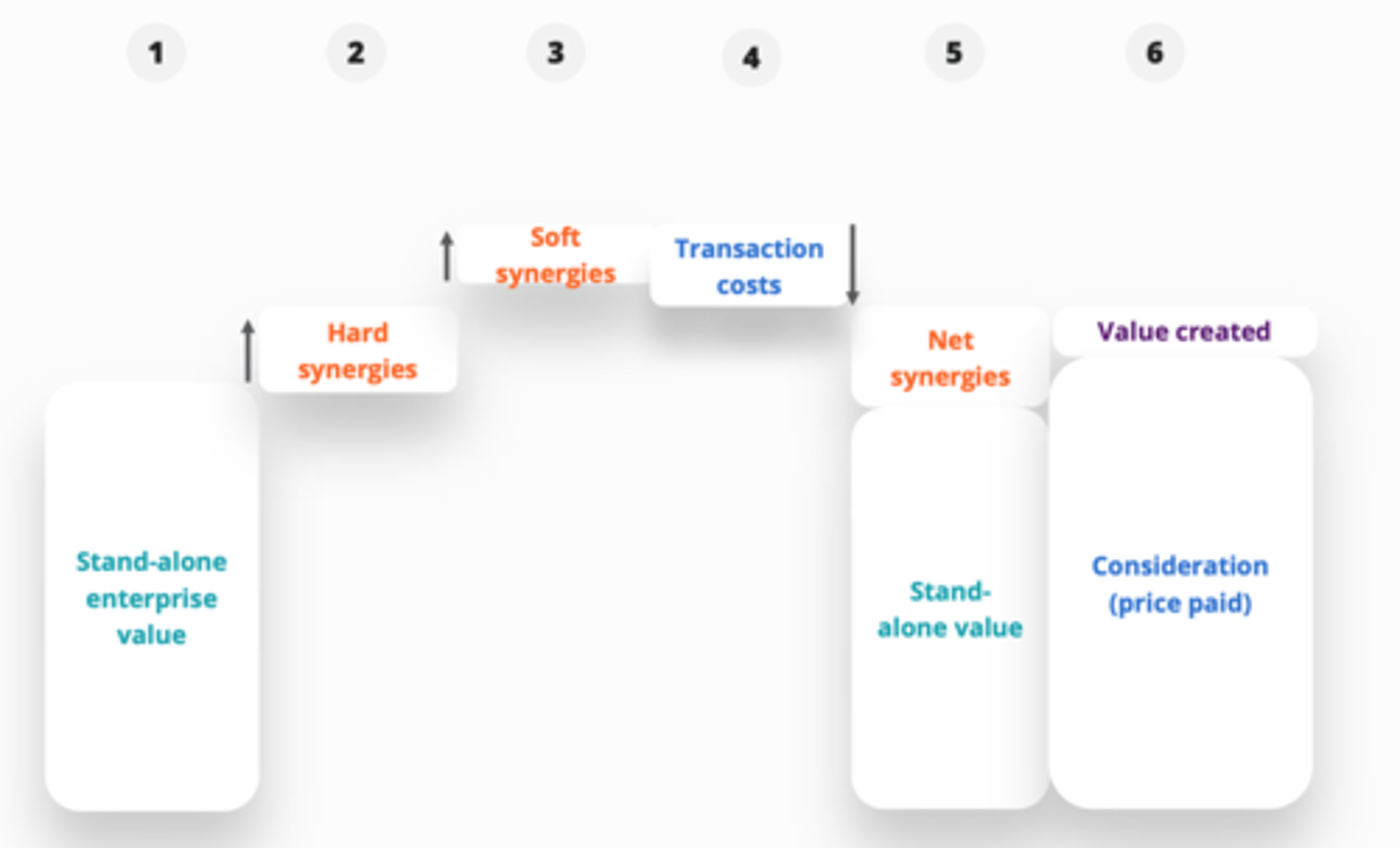
Acquisition valuation process
1. Value the target as stand-alone (Enterprise value)
2. Value synergies (Hard (cost savings) and soft (revenue enhancements))
Best practice acquisition analysis
1. stand-alone...
2. hard...
3. soft...
4. transaction...
5. net...A... and...B...
6. ...A...created and...B...
1. enterprise value
2. synergies
3. synergies
4. costs
5. A) synergies B) stand-alone value
6. A) value B) consideration (price paid)
Value the target as stand-alone (Enterprise value)
• Sales growth
• EBIT margin
• Operating tax
• Working capital requirements
• Capital expenditures
Value synergies (Hard (cost savings) and soft (revenue enhancements))
• Sales : volume & price
• EBIT margin : Product mix & Overhead reductions
• Operating tax :Tax efficiency & Tax losses
• Working capital : Vendor relationships
• Capital expenditures : Efficiencies
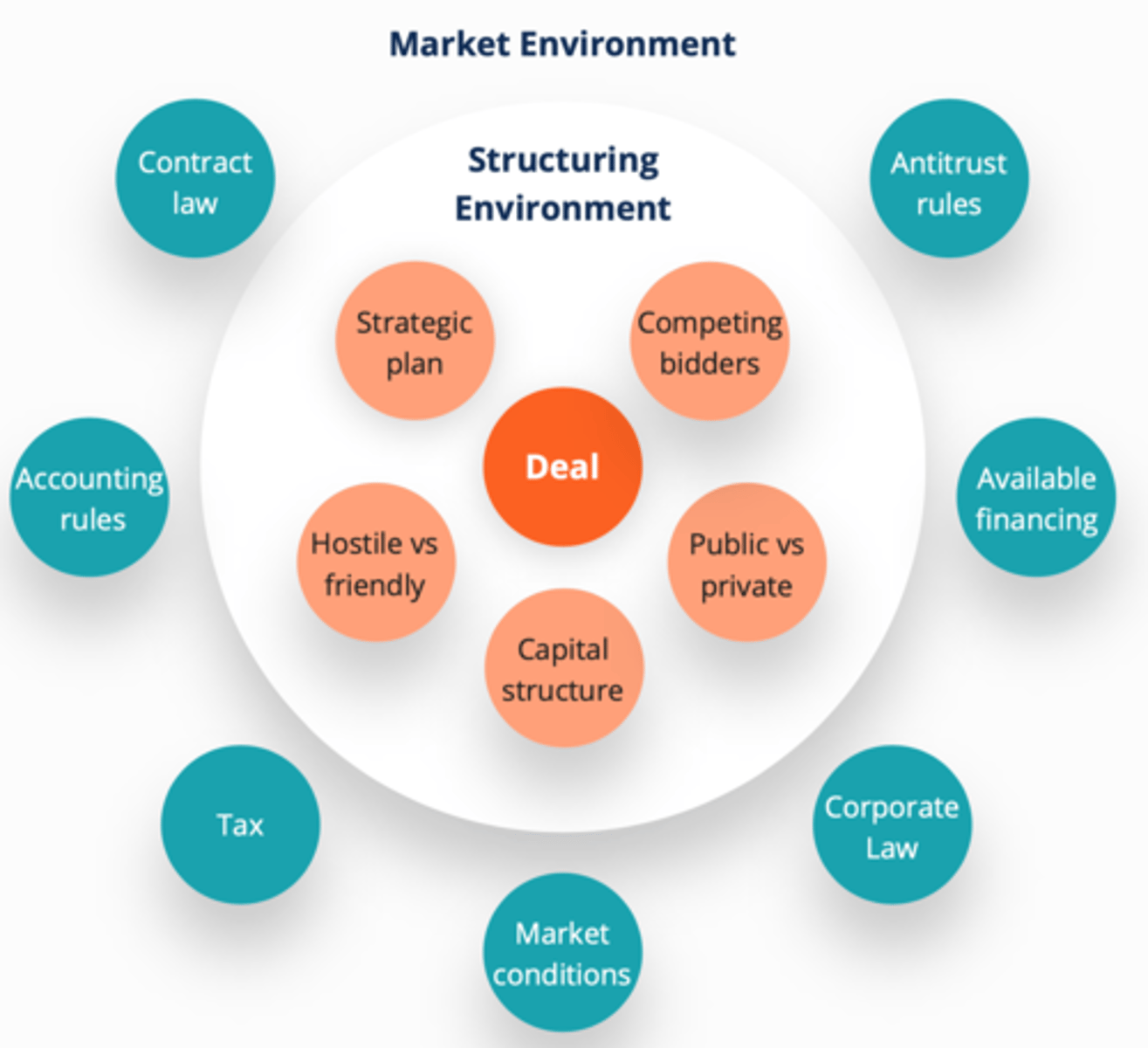
Issues to consider when structuring a deal
Structuring Environment
Market Environment
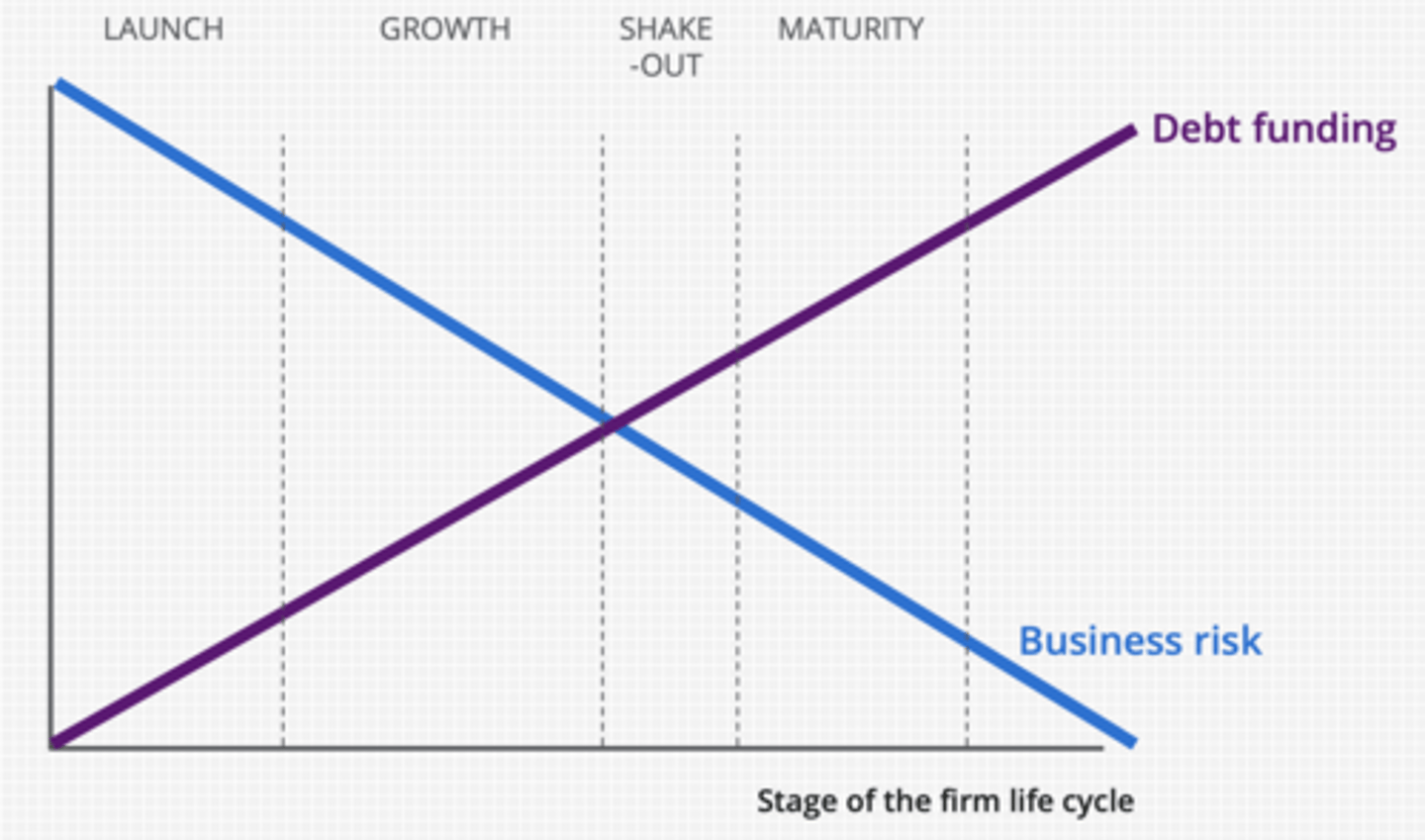
The corporate funding life-cycle - with time:
1. ...decreases
2. ...increases
1. business risk
2. debt financing
capital structure refers to:
the amount of debt and/or equity employed by a firm to fund its operations and finance its assets.
Optimal capital structure relies on a large number of factors
The current economic climate
The business' existing capital structure
The business' life cycle stage
capital structure is important because
1.Having too much debt may increase the risk of default in repayment.
2.Depending too heavily on equity may dilute earnings and value for original investors.
Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC) is
the proportion of debt and equity a firm has, multiplied by their respective costs.

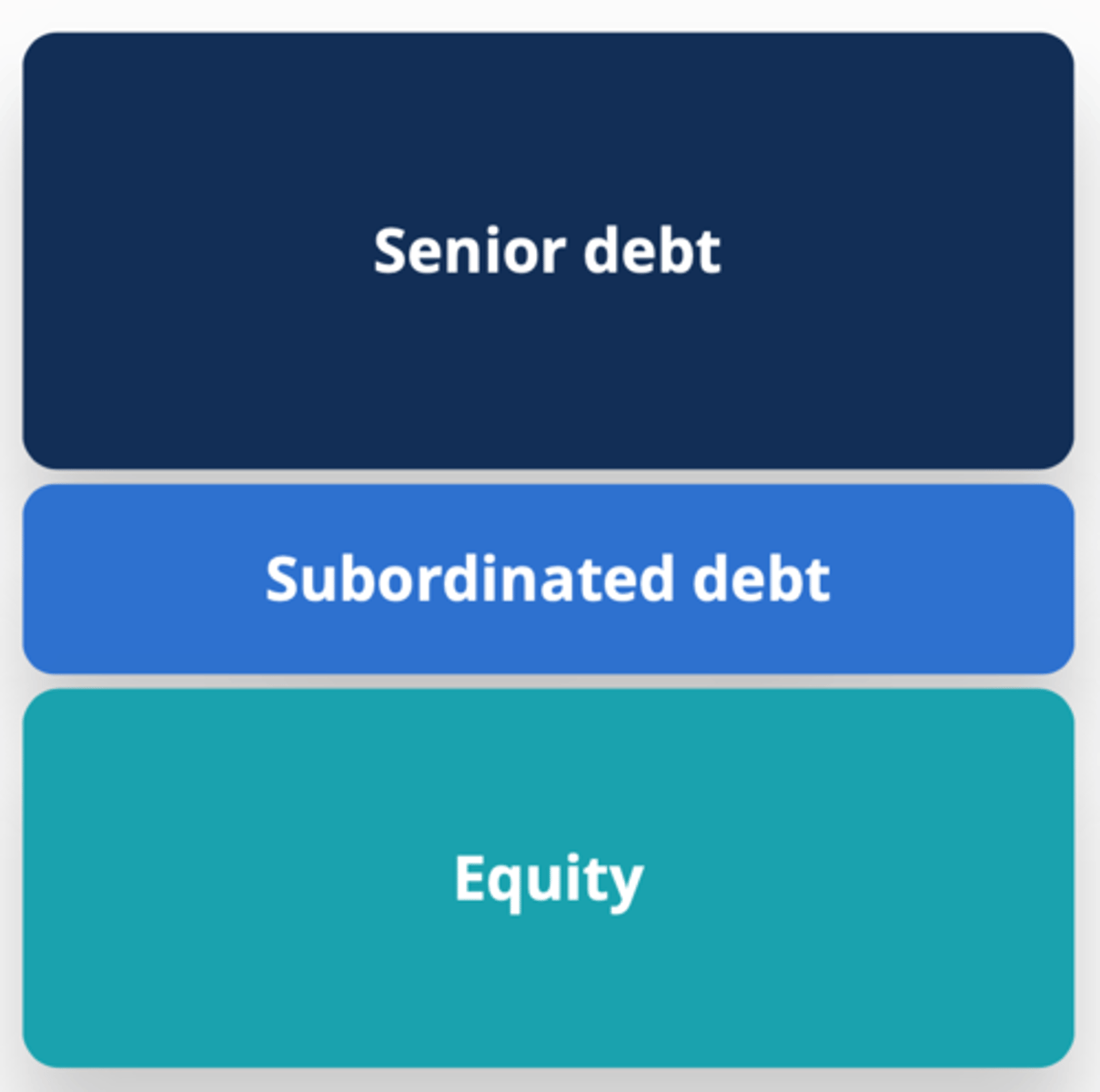
Capital Stack (Structure)
1. Senior debt
2. Subordinated debt
3. Equity
Types of Equity
1. ... - higher...A...;...B... but...C...
2. ...shares - higher...A...and higher...B...
3. ...shares - last...A... and last...B...
1. S/holder loans - A) liquidation position B) no dividend C) pays interest
2. pref. shares - A) liquidation B) dividend priority (vs common)
3. common shares - A) liquidation position B) dividend position

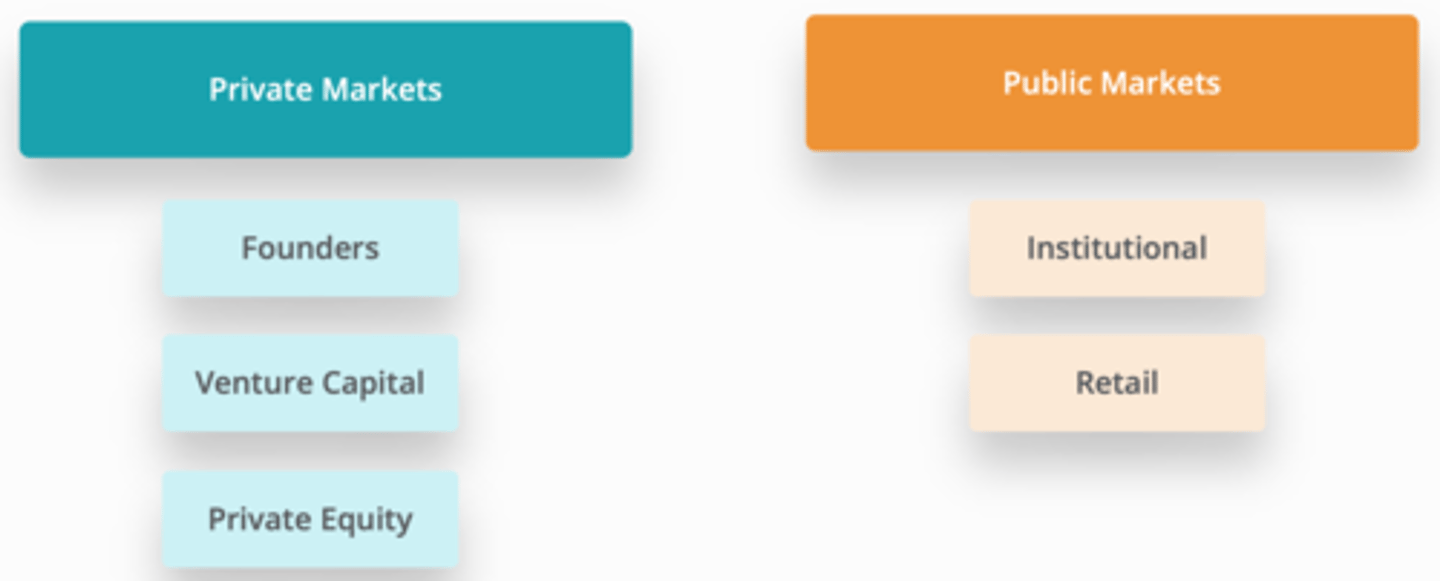
Sources of equity
1. private markets: (3)
2. public marets: (2)
1.
a) founders
b) venture capital
c) private equity
2.
a) institutional
b) retail
Private equity firms manage...A...that invest in companies that represent an opportunity for a...B...for...C...
funds or pools of capital that invest in companies that represent an opportunity for a high rate of return for limited time periods
Why use debt financing?
Corporation: (1) to lower the cost of capital, and (2) avoid equity dilution
Investor : to increase their equity return
Assessing debt capacity: (3)
1. General measures
2. Balance sheet measures
3. Cash flow measures

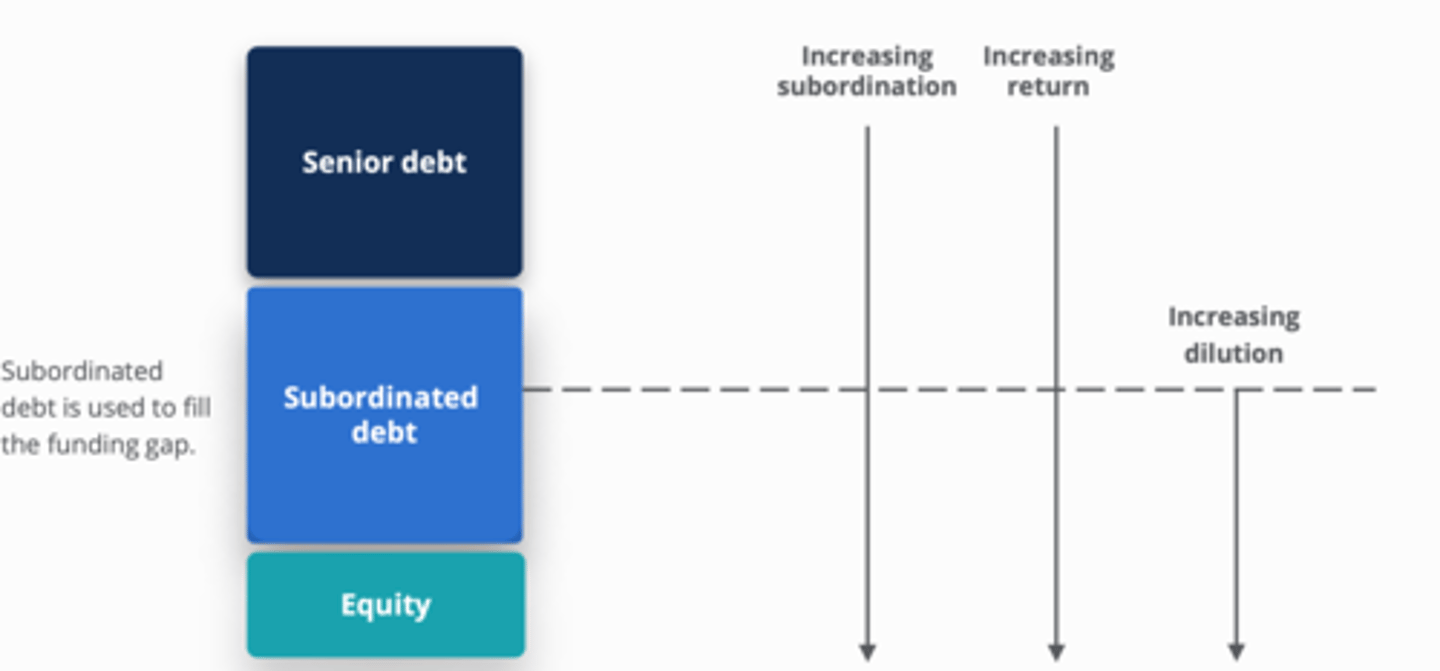
Capital stack order of increasing subordination & return + partially dilution)
1. senior debt
2. subordinated debt
3. equity
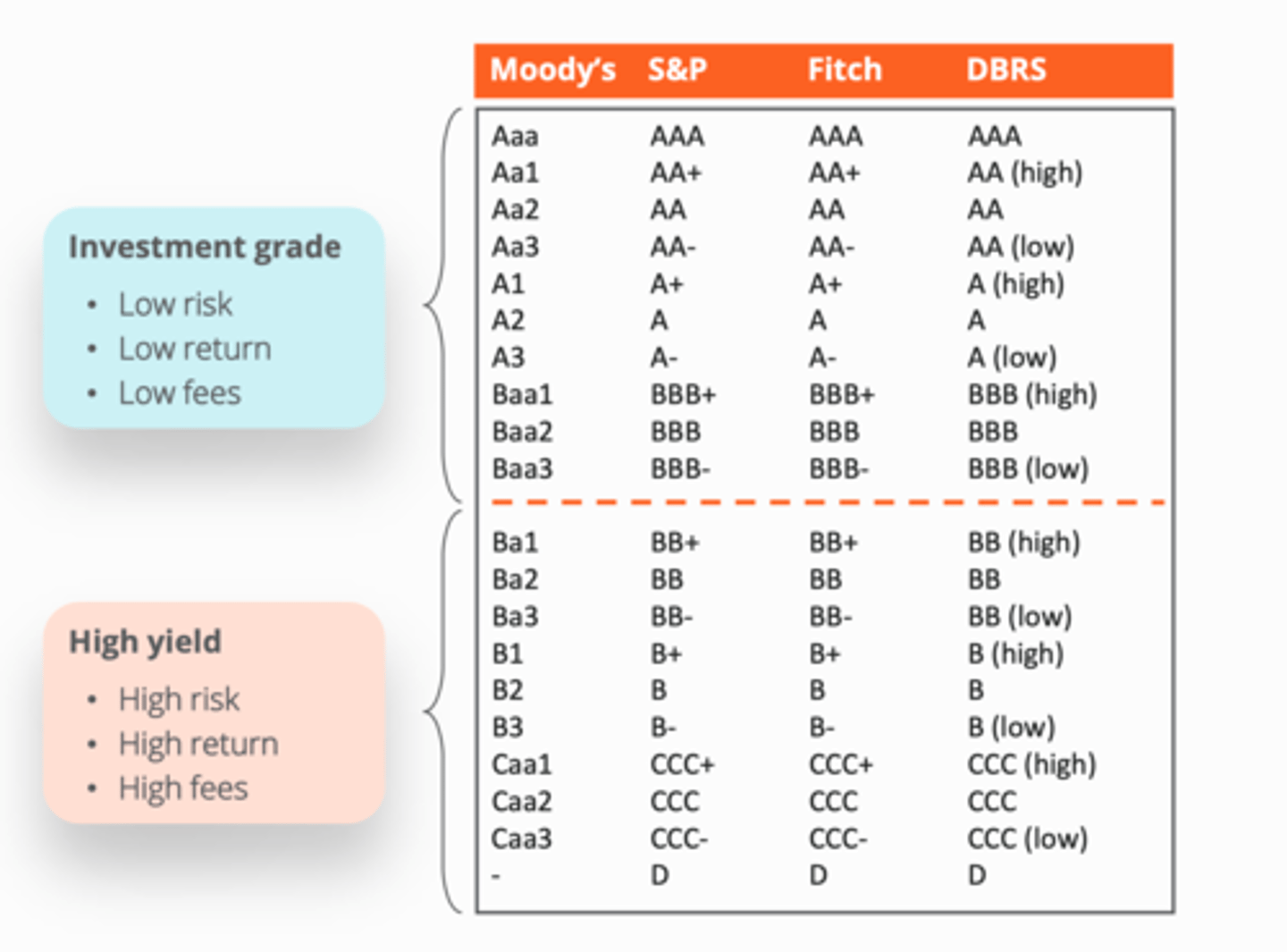
Mezzanine debt characteristics
Non-traded
Subordinated to senior debt
Repaid as a bullet (not amortized)
Combination of cash and accrued interest built into return
Can have equity warrants attached
Debt with warrants, convertible loan stock,
convertible preferred shares
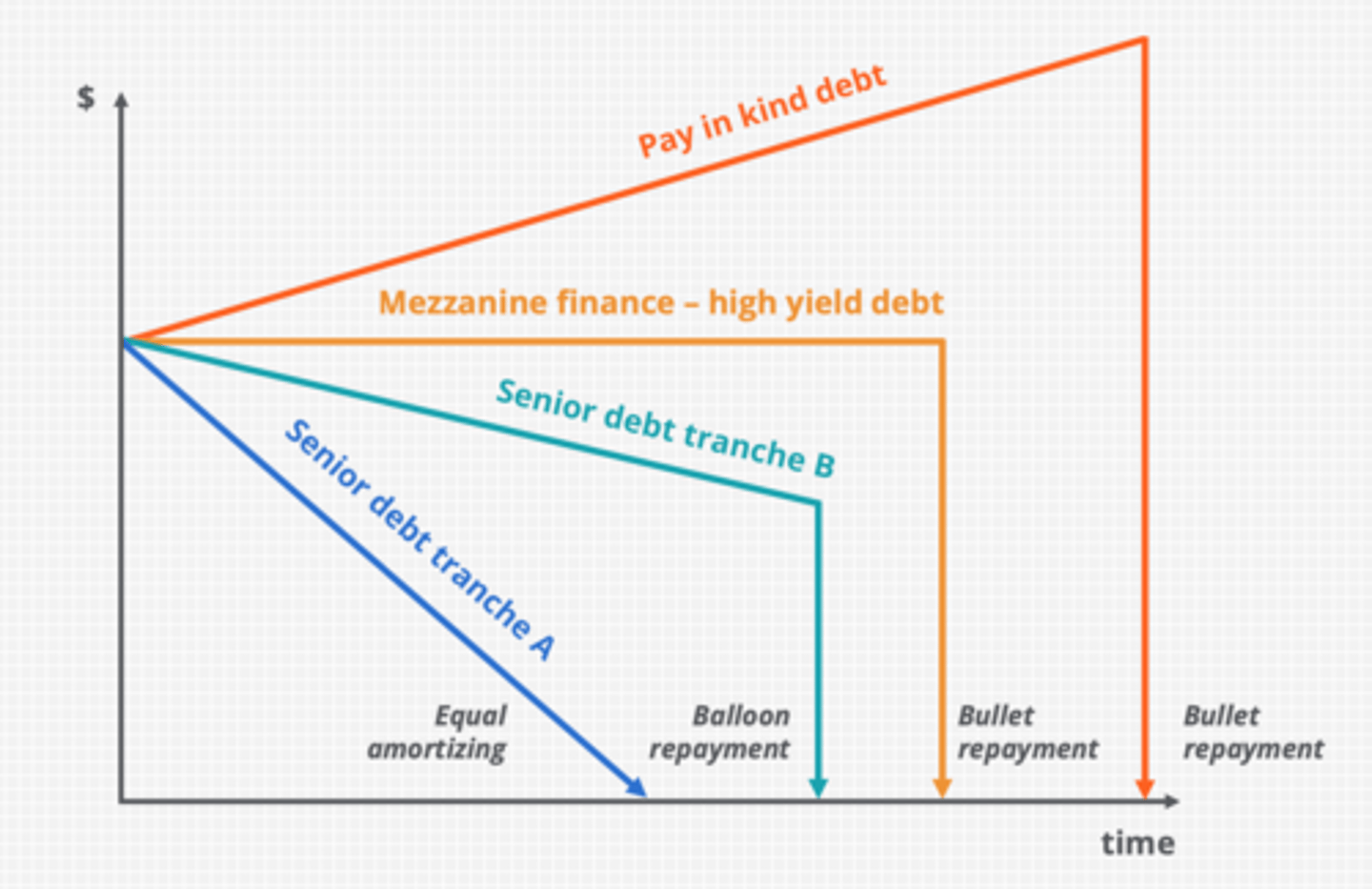
Debt repayment profiles
1. senior debt tranche A
2. senior debt tranche B
3. mezzanine finance - high yield debt
4. pay in kind debt
1. equal amortizing
2. balloon repayment
3. bullet repayment
4. bullet repayment
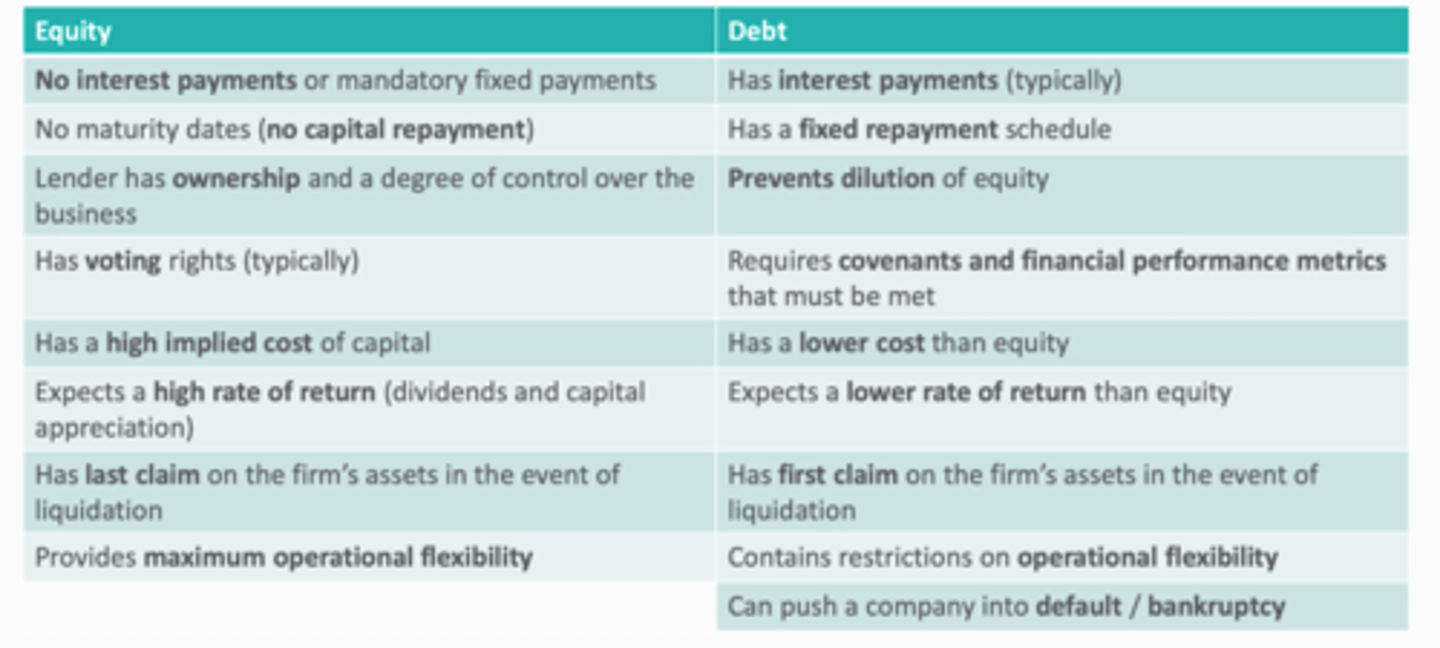
Tradeoffs between debt and equity (8)
Underwriting - the process where a bank...A...for a...B..., or...C...from investors in the form of...D... or...E...
A) raises capital
B) corporation
C) institution
D) equity
E) debt securities.
Types of Underwriting Commitments
1) ... - the underwriter agrees to buy the...A...and assume full...B...for any...C...
2) ... - underwriter commits to...A...at the agreed-on offering price, but can...B...to the...C...without...D...
1) firm commitment - A) entire issue B) financial responsibility C) unsold shares
2) best efforts

Underwriting advisory services: (3)
1. planning
2. issue structure
3. timing and demand

Underwriting - the book building process
1. ...range
2. ...A...investor commitment at...B...
3. ...built
4. ...A...is set to ensure...B...
5.
1. indicative price
2. A) institutional B) fair price
3. book of demand
4. A) price B) clearing
5. allocation

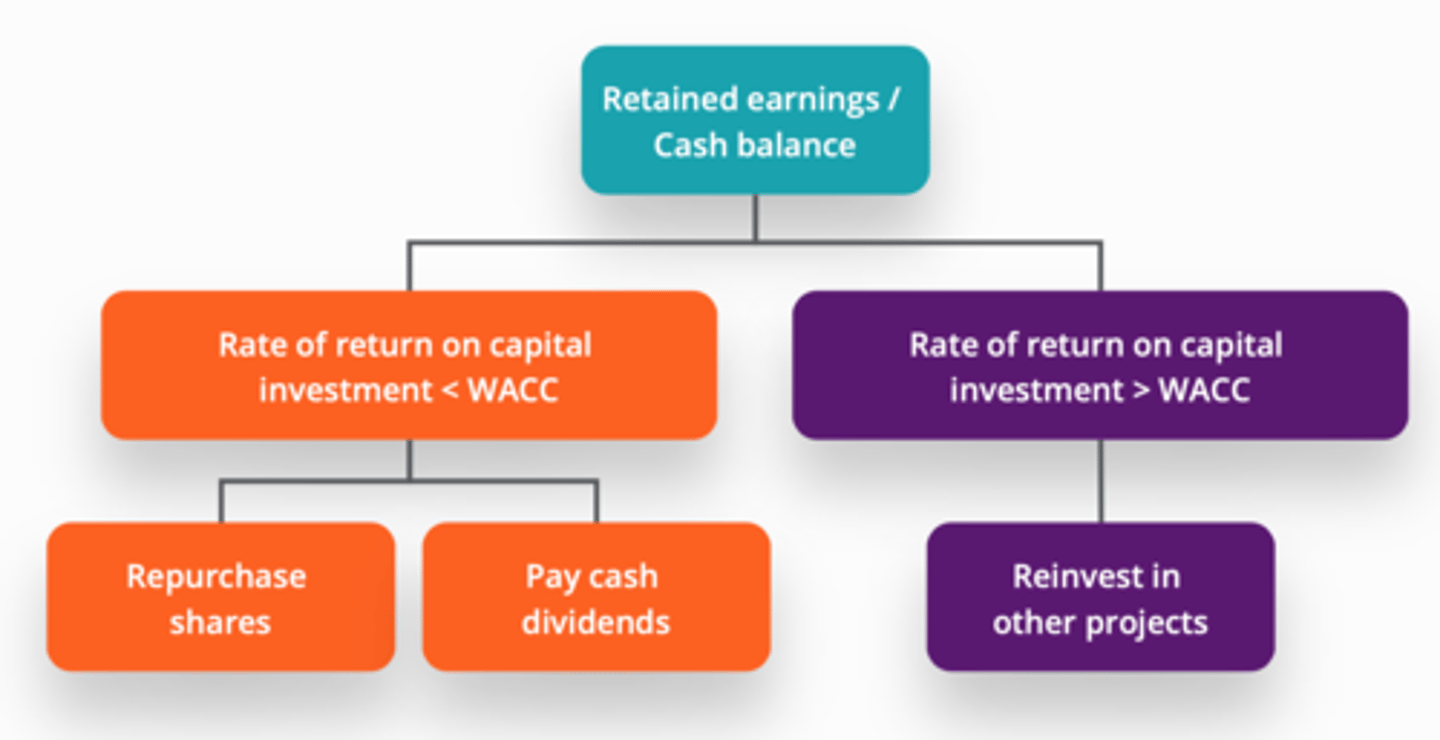
decision to return capital to investor is based on
IRR vs WACC
Retained earnings / excess cash decision flowchart:
1) ROIC < WACC : (2)
2) ROIC > WACC: : (1)
1)
a. repurchase shares
b. pay dividends
2) reinvest in other projects