Electron Transport Chain & NADH Shuttle Systems
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Glycerol-3-phosphate Shuttle
skeletal muscle
enzymes:
cytoplasmic Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
mitochondrial Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
Mechanism for Glycerol-3-phosphate Shuttle
NADH+H+ is oxidized to NAD+ while DHAP is reduced to Glycerol-3-phosphate by Cytoplasmic Glycerol-3-phosphate dehyrogenase
Glycerol-3-phosphate is oxidized to DHA while FAD is reduced to FADH2 by Mitochondrial Glycerol-3-phosphate dehyrogenase
FADH2 transfers its electrons to coenzyme Q (ubiquinone) → QH2
QH2 (ubiquinol) enters ETC
Malate-Aspartate Shuttle
heart and liver cells
enzymes:
cytoplasmic malate dehydrogenase
mitochondrial malate dehydrogenase
cytoplasmic aspartate aminotransferase
mitochondrial aspartate aminotransferase
malate-a-ketoglutarate antiporter (membrane bound)
glutamate-aspartate antiporter (membrane bound)
Malate-Aspartate Shuttle Mechanism
NADH+H+ is oxidized to NAD+ while oxaloacetate is reduced to malate by cytoplasmic malate dehydrogenase
malate traverses mitochondrial membrane via malate-a-ketoglutarate antiporter and a-ketoglutarate goes out
malate is oxidized back to oxaloacetate as NAD+ is reduced to NADH+H+ by mitochondrial malate dehydrogenase
a-ketoglutarate must be present in matrix and oxaloacetate must be present in cytoplasm to make the shuttle function
How to keep Malate-Aspartate Shuttle working?
mitochondrial aspartate aminotransferase transfers an amine group from glutamate to oxaloacetate to produce aspartate and a-ketoglutarate
aspartate is shuttled to cytoplasm via glutamate-aspartate antiporter (glutamate goes in)
cytoplasmic aspartate aminotransferase transfers an amine group from aspartate and a-ketoglutarate to produce glutamate and oxaloacetate
Negative Reduction Potential
oxidized form of a substance has a lower affinity for electrons than H2 (ex. NADH is more likely to donate electrons)
Positive Reduction Potential
oxidized form of a substance has a higher affinity for electrons H2 (ex, O2 is more likely to accept electrons)
What is the driving force of electron-transfer potential?
electrons always flow to components with more positive reduction potentials
Ubiquinone
Q
fully oxidized form
Semiquinone, Radical
Q*-
addition of one electron
Semiquinone
QH*
addition of one electron and one proton
Ubiquinol
QH2
fully reduced form
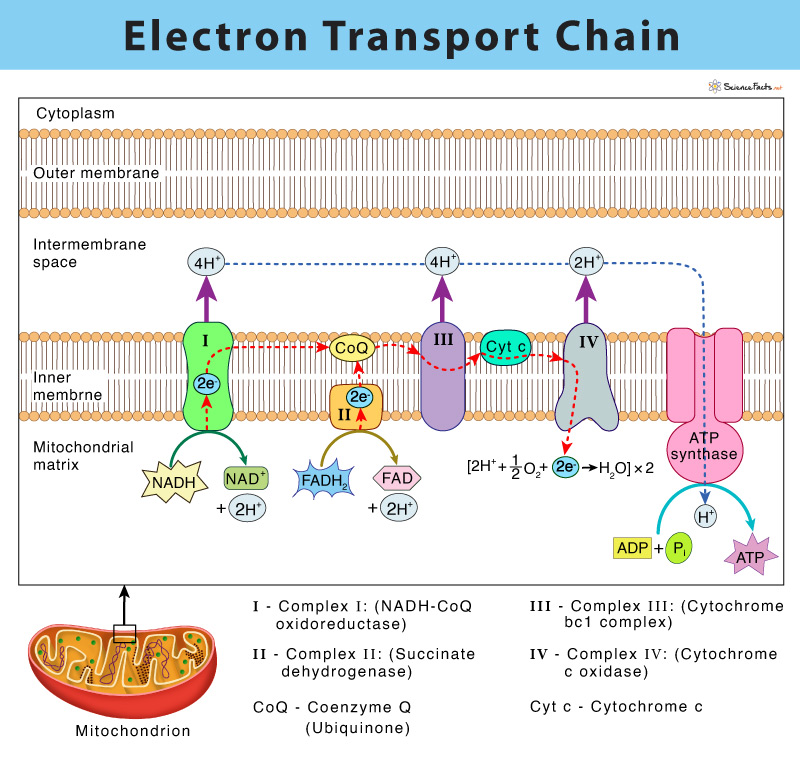
Complex I (NADH Dehydrogenase)
NADH reduces FMN to produced FMNH2
FMNH2 donates ep to iron-sulfur cluster proteins (one at a time)
Iron-sulfur proteins donate e- to Q (one at a time)
QH2 leaves the complex (travels to complex III)
flow of 2 e- from NADH to Q pumps out 4 protons
Complex II (Succinate Dehyrogenase)
Succinate reduces FAD to FADH2
FADH2 donates e- to iron-sulfur cluster proteins (one at a time)
Iron-sulfur proteins donate e- to Q (one at a time)
QH2 leaves the complex (travels to complex III)
flow of 2 e- from FADH2 does not pump out any protons
Complex III (Cytochrome c reductase)
QH2 is oxidized and donates 2 e- to complex
one e- goes to iron-sulfur cluster. e- is transported to Cyt c1 and then Cyt c which pumps out 2 protons
one e- is sent to Cyt bH which is transported to Cyt bL and then back to Q to generate Q*-
remaining Q becomes a part of “Q pool”
a second QH2 enters and repeats 1-3, except e- sent to Cyt bH is transported to Q*- and is reduced back to QH2, 2 protons are pumped out
Complex IV (Cytochrome c oxidase)
two Cyt c each donate an e- each to 1 CuA peptide
1 CuA reduces 2 Cyt a
2 Cyt a reduces 2 Cyt a3
1 Cyt a3 reatains e-
1 Cyt a3 donates its e- to CuB peptide
Cyt a3 and CuB bind and reduce O2 to form peroxide bridge
repeat 1-4, except peroxide bridge gets cleaved to form ion-oxygen adjuncts from uptake of 2 protons
uptake of 2 more protons converts the ion-oxygen adjuncts to 2 H2O
Overall ETC
Complex I: 4 protons
Complex II: 0 protons
Complex III: 4 protons
Complex IV: 2 protons