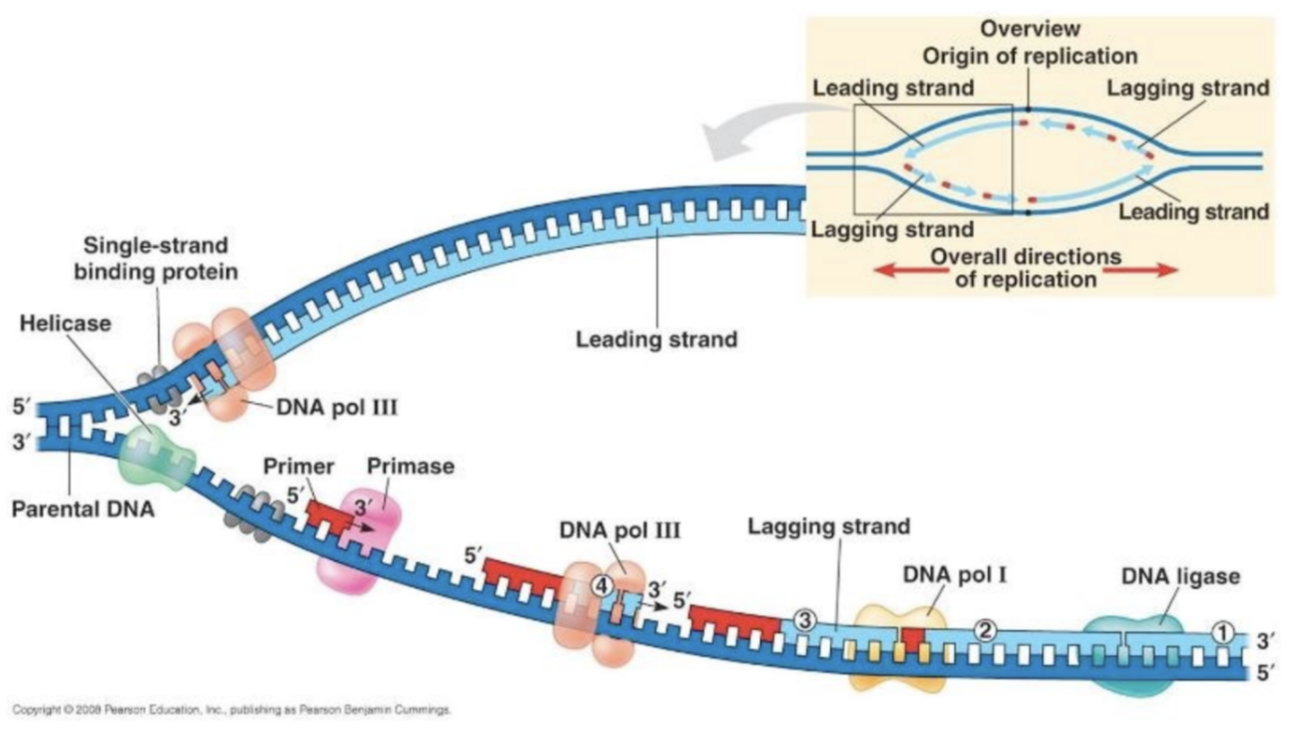
DNA Replication
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
When and where does DNA replication occur?
In the nucleus during interphase before nuclear division
Function of helicase
Unwinds the double helix formation
Function of DNA polymerase
Replicates molecules and builds them with the help of the RNA primer
Function of primase
Makes the RNA primer to instruct DNA polymerase
Function of ligase
Glues Okazaki fragments
What happens at the origin of replication?
Helicase unwinds the double helix by breaking the hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs in the parental strands
Each parental strand is the template for the synthesis of new DNA
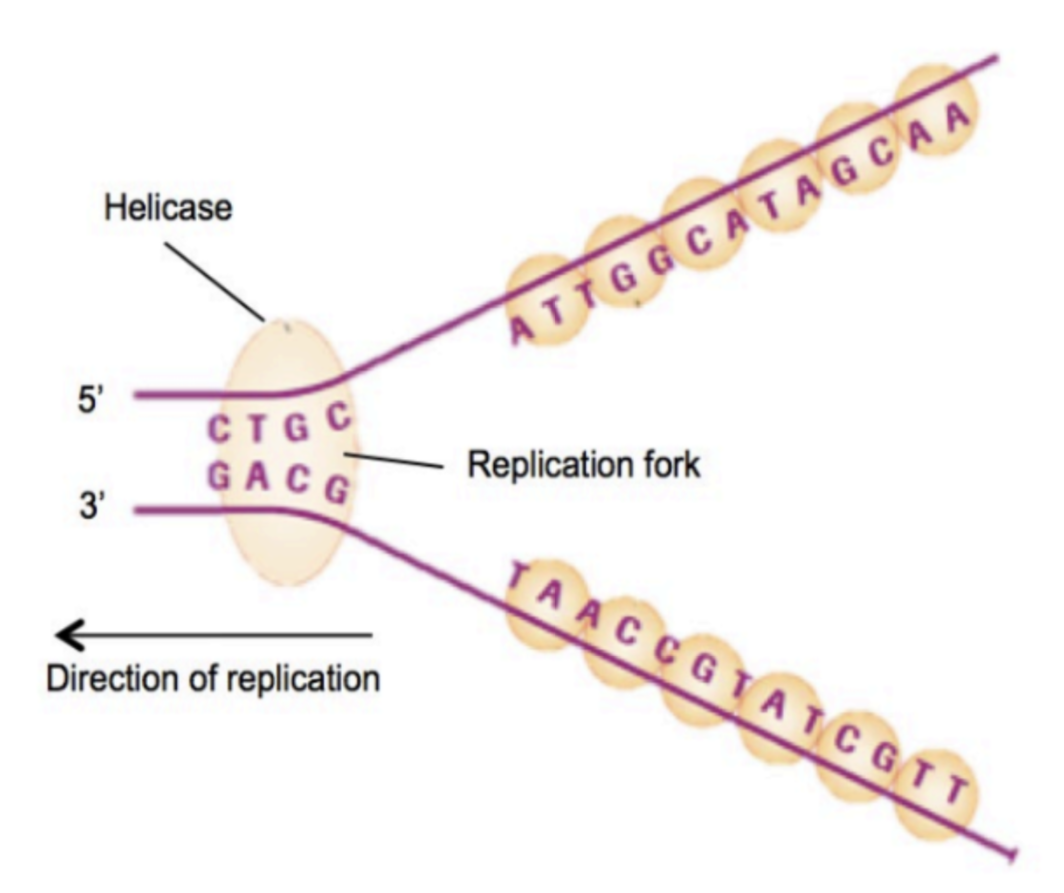
How and why is RNA primer synthesized after DNA is unwound?
Primase attaches to the unwound chain and catalyses the synthesis of RNA primer
Provides free 3’ OH ends for DNA Polymerase III
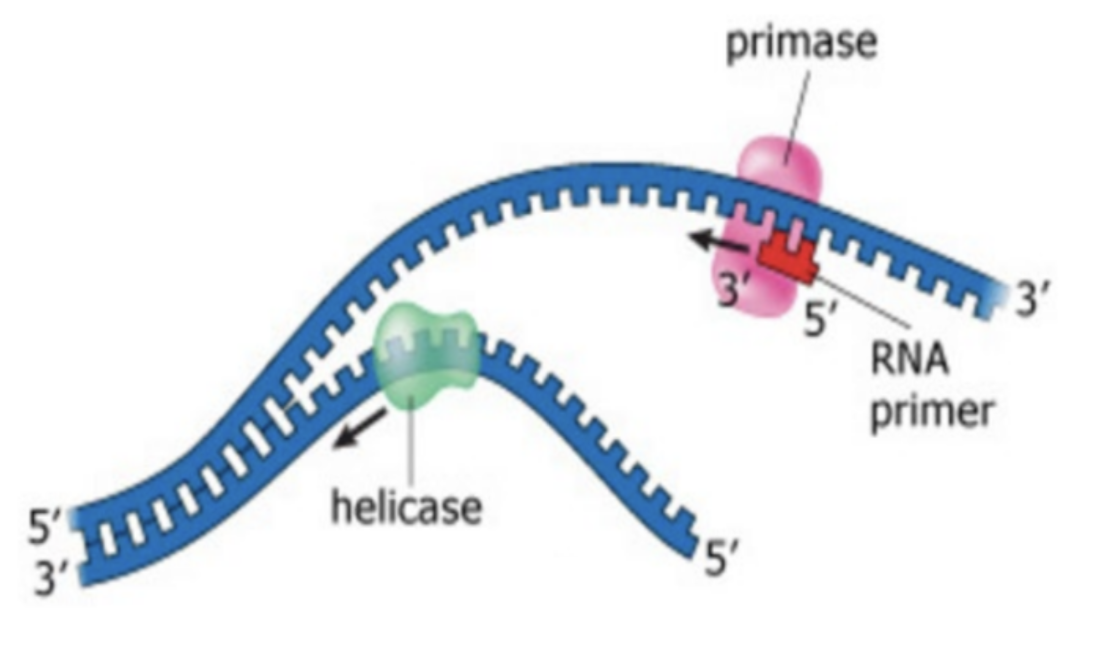
What does primase and DNA polymerase do during the synthesis of new daughter strands?
DNA Polymerase III elongates the new daughter strand in the 5’ to 3’ direction by catalyzing phosphodiester bond formation between the incoming deoxyribonucleotides and the free 3’ OH ends of the daughter strand
Free deoxyribonucleotides are incorporated by DNA Polymerase III to the parental DNA strand in complementary base pairing
RNA primers are removed on the parental strands and replaced by deoxyribonucleotides by DNA Polymerase I
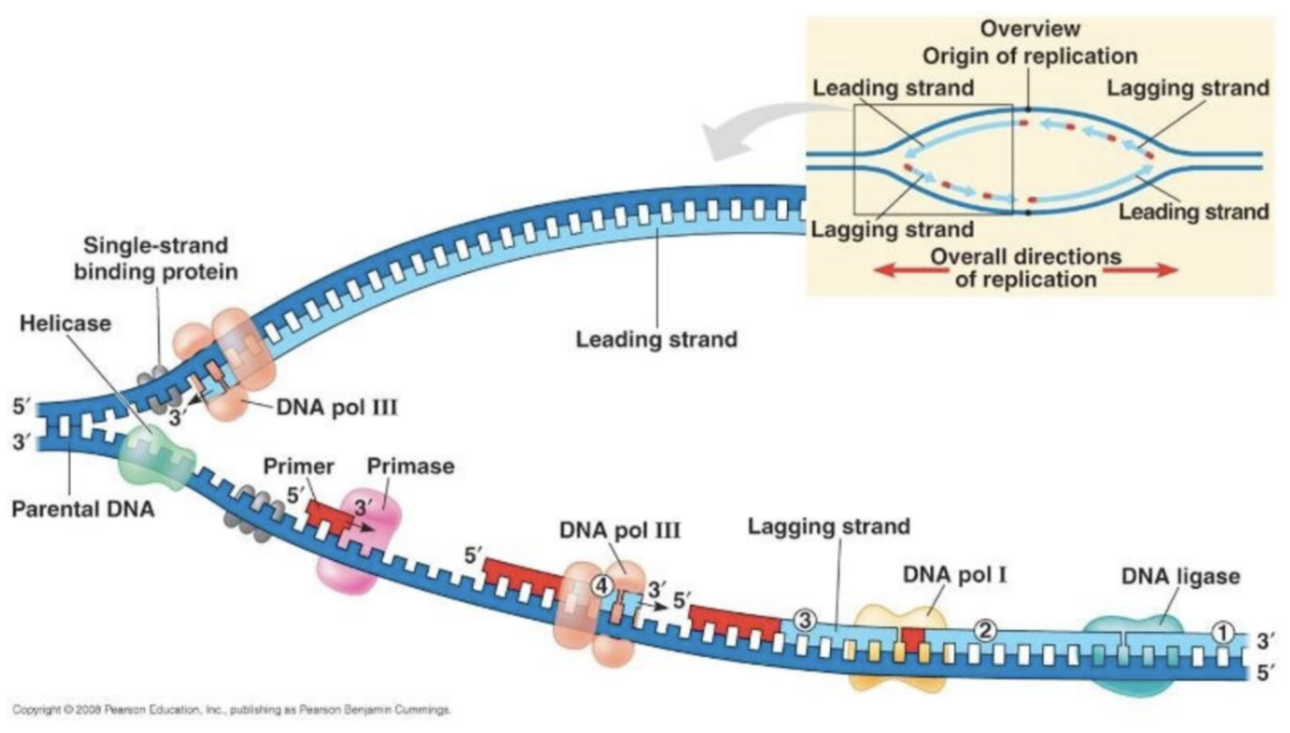
What are the lagging and leading strands in a replication fork?
The leading strand is synthesised continuously
The lagging strand is synthesised discontinuously to form Okazaki fragments
Nicks between Okazaki fragments are filled in by DNA ligase by forming phosphodiester bonds