Physical Landscapes in the UK: River
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
1
New cards
How does a river erode?
Hydraulic action - vertical erosion in the upper course (makes valley deeper), horizontal erosion in the lower course (spreads out sides)
Abrasion - small boulders and stones scratch and scrape the rivers beds as they are transported
Solution - dissolving of rocks; rivers travelling over these rocks will dissolve them chemically
Attrition - a river’s load knock and collide with each other, making them smoother and more rounded
Abrasion - small boulders and stones scratch and scrape the rivers beds as they are transported
Solution - dissolving of rocks; rivers travelling over these rocks will dissolve them chemically
Attrition - a river’s load knock and collide with each other, making them smoother and more rounded
2
New cards
How does a river transport its load?
Solution - minerals are dissolved in the water, chemically changing them
Suspension - fine, light material is held up and carried within the river’s flow
Saltation - smell pebbles and stones are bounced along the river bed
Traction - large boulders and rocks rolled along the river bed
Suspension - fine, light material is held up and carried within the river’s flow
Saltation - smell pebbles and stones are bounced along the river bed
Traction - large boulders and rocks rolled along the river bed
3
New cards
Why do rivers deposit sediment
When velocity falls large boulders deposited first
Finest particles deposited last
Will deposit more of its load whenever it enters a sea or lake or whenever there is a drought
Finest particles deposited last
Will deposit more of its load whenever it enters a sea or lake or whenever there is a drought
4
New cards
Long profile or a river
Shows the gradient of a river as it journeys from source to mouth
Gradient is initially very high, then becomes concave and almost flat
Gradient is initially very high, then becomes concave and almost flat
5
New cards
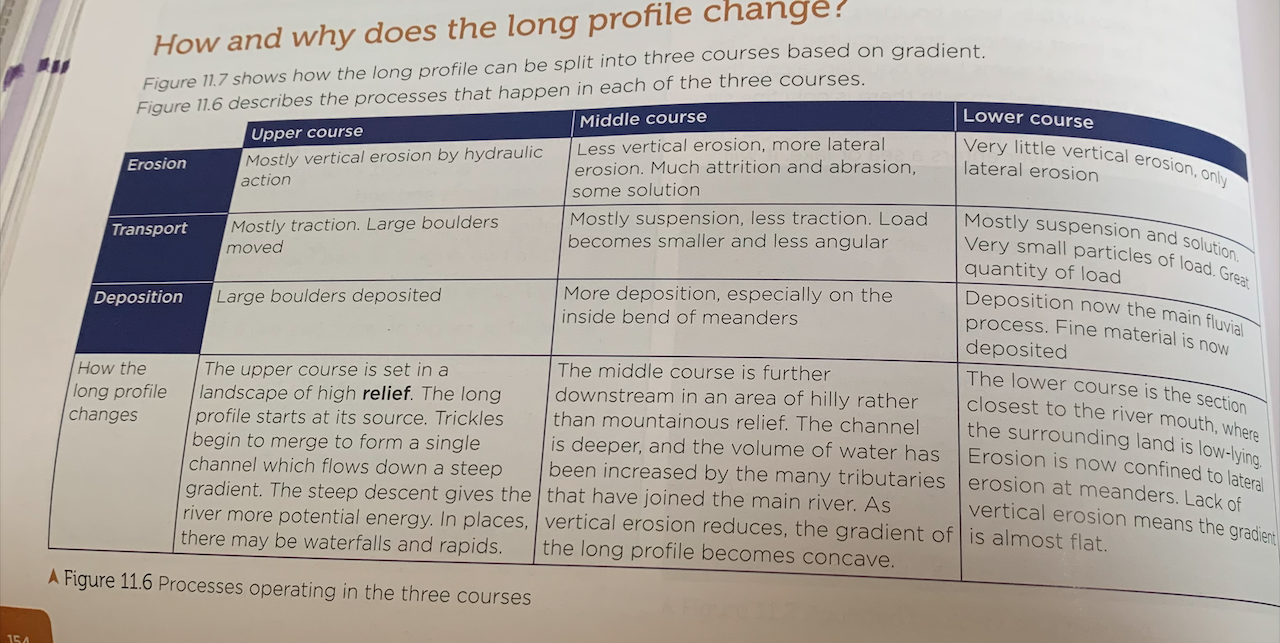
Why and how does long profile change?
6
New cards
Why do discharge and velocity increase downstream?
Discharge - VOLUME OF WATER PASSING THROUGH A GIVEN POINT ON THE RIVER
Increases downstream as tributary streams join main river
Velocity increases because more water is coming into contact with the channel’s banks and bed
Increases downstream as tributary streams join main river
Velocity increases because more water is coming into contact with the channel’s banks and bed
7
New cards
What is a river cross-profile and why does it change
A section taken sideways across a river channel and/or valley
Changes because the channel becomes wider downstream due to lateral erosion rather than vertical erosion
Changes because the channel becomes wider downstream due to lateral erosion rather than vertical erosion
8
New cards
Why does the valley cross profile change
In the upper course a slope is created so that weathered material from the valley can fall down → on reaching the river, this material is removed
In the middle course the river is flowing through lower country. the gradient is less steep, so lateral erosion occurs → as more energy is used on lateral erosion, it is not able to remove all of the weathered material, so this builds up on the valley floor to give a more gentle profile
In the lower course deposition from floods builds up the flood plain, widening the valley
In the middle course the river is flowing through lower country. the gradient is less steep, so lateral erosion occurs → as more energy is used on lateral erosion, it is not able to remove all of the weathered material, so this builds up on the valley floor to give a more gentle profile
In the lower course deposition from floods builds up the flood plain, widening the valley
9
New cards
What are interlocking spurs - characteristics
projections of high land that alternate from either side of a valley and project into the valley floor, formed by fluvial erosion
characteristics:
* steep gradient
* convex sides
* project from alternate sides of valley
* may have SCREE SLOPES
characteristics:
* steep gradient
* convex sides
* project from alternate sides of valley
* may have SCREE SLOPES
10
New cards
What are rapids?
Fast-flowing, turbulent sections of a river there the river bed has a relatively steep gradient, usually in the upper course
Bands of hard rock erode less easily so they protrude up on the river bed → soft rock eroded more easily so river bed is lowered
differential erosion occurs and makes the river bed uneven → the river’s flow becomes turbulent, result in white water sections typical of rapids.
Bands of hard rock erode less easily so they protrude up on the river bed → soft rock eroded more easily so river bed is lowered
differential erosion occurs and makes the river bed uneven → the river’s flow becomes turbulent, result in white water sections typical of rapids.
11
New cards
How is a waterfall formed
A slab of hard rock lies over a bed of soft rock
Differential erosion means the soft rock is eroded at a faster rate and the water falls vertically from the hard rock to the soft rock below
* Splash back causes hydraulic action to weaken the rocks behind the fall of water
* Pieces of soft rock break off and an indentation is formed at the base
* continued undercutting means that the hard rock capping loses support and overhangs the drop
* the unsupported cap breaks off
* the fallen rock breaks off and becomes trapped, causing the abrasion of the bed and creating a plunge pool
* the waterfall retreats upstream
Differential erosion means the soft rock is eroded at a faster rate and the water falls vertically from the hard rock to the soft rock below
* Splash back causes hydraulic action to weaken the rocks behind the fall of water
* Pieces of soft rock break off and an indentation is formed at the base
* continued undercutting means that the hard rock capping loses support and overhangs the drop
* the unsupported cap breaks off
* the fallen rock breaks off and becomes trapped, causing the abrasion of the bed and creating a plunge pool
* the waterfall retreats upstream
12
New cards
what is a gorge - characteristics
a narrow, steep-sided valley, with bare, rocky walls
gorge of recession is found immediately downstream of a waterfall
* very narrow valley
* very steep
* located immediately below a waterfall
* river channel takes up most of the valley floor
* turbulent, fast flowing water
gorge of recession is found immediately downstream of a waterfall
* very narrow valley
* very steep
* located immediately below a waterfall
* river channel takes up most of the valley floor
* turbulent, fast flowing water
13
New cards
Meander - characteristics
a meander is a bend in a river
* fast-flowing water on the outside bank causes lateral erosion through abrasion and hydraulic action → undercuts the bank and forms a river cliff
* some of the flow hits the outside bank and erodes it, then HELICOIDAL FLOW means this now goes to next inside bend, where it deposits the load as friction slows
* fast flow causes vertical erosion on the outside bend → results in asymmetrical cross-profile
* sand and pebbles are deposited on inside bank, forming a gentle slip-off slope
* fast-flowing water on the outside bank causes lateral erosion through abrasion and hydraulic action → undercuts the bank and forms a river cliff
* some of the flow hits the outside bank and erodes it, then HELICOIDAL FLOW means this now goes to next inside bend, where it deposits the load as friction slows
* fast flow causes vertical erosion on the outside bend → results in asymmetrical cross-profile
* sand and pebbles are deposited on inside bank, forming a gentle slip-off slope
14
New cards
An oxbow lake - how formed?
an oxbow lake is a small, horseshoe-shaped lake that is seen in the middle and lower courses of a river
* meander neck becomes very narrow
* river floods, so water flows straight across the neck
* this path begins to become more and more prominent with every flood
* it becomes so established by lateral and vertical erosion that it becomes the main channel
* the loop of the old river channel is increasingly detatched
* the subsequent flooding causes silt to be deposited on the new river banks - aids detachment of loop
* marsh plants colonise the area, further detaching the loop
* meander neck becomes very narrow
* river floods, so water flows straight across the neck
* this path begins to become more and more prominent with every flood
* it becomes so established by lateral and vertical erosion that it becomes the main channel
* the loop of the old river channel is increasingly detatched
* the subsequent flooding causes silt to be deposited on the new river banks - aids detachment of loop
* marsh plants colonise the area, further detaching the loop
15
New cards
How are leveés formed
when a river bursts its banks, friction with the land reduces velocity, causing deposition
heavy sediment is deposited closest to the river
the size off sediment then becomes progressively smaller with increased distance from the river
\
heavy sediment is deposited closest to the river
the size off sediment then becomes progressively smaller with increased distance from the river
\
16
New cards
What is a floodplain and how is it formed
a large area of flat land either side of a river that is prone to flooding
formed due to meander migration where the outside bends erode into the edges of the valley, vutting a wider valley. the floods have receded, the floodplain is slightly higher due to the deposits created
formed due to meander migration where the outside bends erode into the edges of the valley, vutting a wider valley. the floods have receded, the floodplain is slightly higher due to the deposits created
17
New cards
what is an estuary - characteristics and formation
the tidal part of a river where the channel broadens out as it reaches the sea
* high tidal range
* very wide
* has mudflats
* TIDAL BORES
\
* after the ice age, letting ice caused a rise in sea level
* this cause low-lying valley sides either side of the river to become flooded
* the original channel of the river is now on the estuary flow
* high tidal range
* very wide
* has mudflats
* TIDAL BORES
\
* after the ice age, letting ice caused a rise in sea level
* this cause low-lying valley sides either side of the river to become flooded
* the original channel of the river is now on the estuary flow
18
New cards
how are estuary mudflats formed?
form in sheltered areas where tidal water flows slowly. as a river transports ALLUVIUM down to the sea, the incoming ride transports sand and silt up the estuary
the waters meet and velocity is reduced, causing deposition
this builds up layers of mud called mudflats which can only be seen at low tide
the waters meet and velocity is reduced, causing deposition
this builds up layers of mud called mudflats which can only be seen at low tide
19
New cards
Physical causes of flooding
continuous heavy rain
sudden bursts of heavy rain
prolonged light rainfall
sudden snow melt
sudden bursts of heavy rain
prolonged light rainfall
sudden snow melt
20
New cards
Key terms for flooding
precipitation - any source of moisture reaching the ground
interception - water being prevented from reaching the surface
surface storage - water held on the ground’s surface
infiltration - water sinking into soil/rock
soil moisture - water held within the soil layer
percolation - water seeping below the surface
groundwater - water being stored in the rock
transportation - water lost through pores in vegetation
evaporation - water lost from surface
surface runoff - water flowing on top of the ground
throughflow - water flowing through the soil slayer
groundwater flow - water flowing through the rock layer
water table - the current upper level of saturated rock/soil where no more water can be absorbed
interception - water being prevented from reaching the surface
surface storage - water held on the ground’s surface
infiltration - water sinking into soil/rock
soil moisture - water held within the soil layer
percolation - water seeping below the surface
groundwater - water being stored in the rock
transportation - water lost through pores in vegetation
evaporation - water lost from surface
surface runoff - water flowing on top of the ground
throughflow - water flowing through the soil slayer
groundwater flow - water flowing through the rock layer
water table - the current upper level of saturated rock/soil where no more water can be absorbed
21
New cards
how can geology increase risk?
* impermeable rock, found in upper areas
* low-lying areas also contain impermeable areas
* relief - high relief means high levels of surface runoff
* low-lying flood plains have high flood risk - not enough gradient to remove the water
* low-lying areas also contain impermeable areas
* relief - high relief means high levels of surface runoff
* low-lying flood plains have high flood risk - not enough gradient to remove the water
22
New cards
human causes of flooding
new infrastructure, new houses, deforestation, farming (more crop farming than cattle farming) disappearing fields and gardens
23
New cards