Plant Anatomy and Angiosperm Lab Overview
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
Allium cepa
Onion; dicot
Zea mays
Corn; monocot
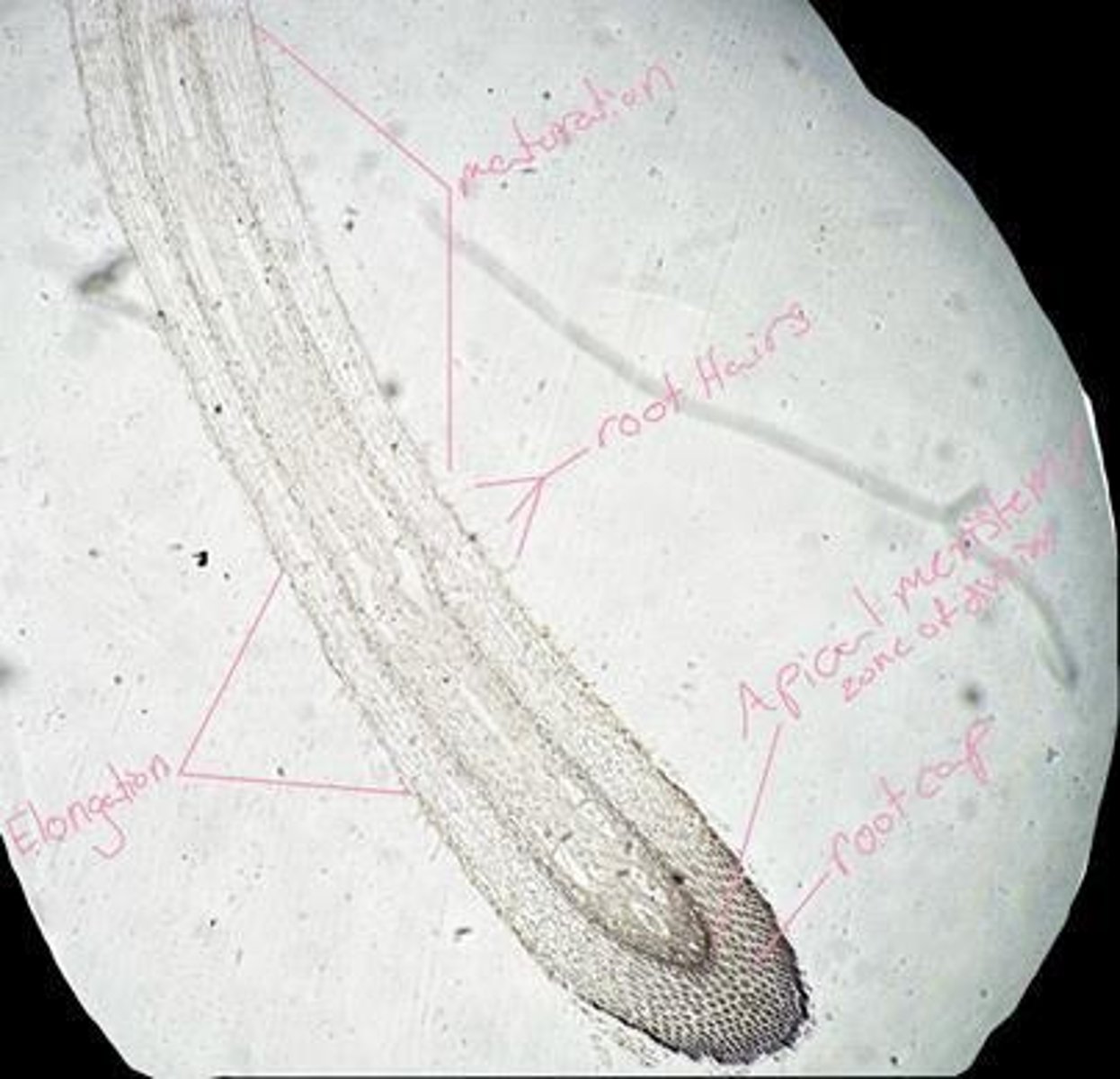
Maturation
The process of development and growth in plants.
Elongation
The process by which plant cells increase in length.
Root hair
Extensions of root epidermal cells that increase surface area for water and nutrient absorption.
Apical meristem
The region of actively dividing cells at the tip of a plant root or shoot.
Root cap
A protective structure at the tip of a plant root that helps it penetrate the soil.
Casparian strip
A band of cell wall material in the endodermis that forces liquids to cross the plasma membrane of endodermal cells.
Ranunculus
Buttercup; dicot
Epidermis
The outer layer of cells covering a plant.
Cortex
The tissue in a plant root or stem that lies between the epidermis and the vascular tissue.
Parenchyma
A type of plant tissue composed of living cells that function in storage, photosynthesis, and tissue repair.
Endodermis
The innermost layer of the cortex in plant roots, surrounding the vascular tissue.
Pericycle
A layer of cells just inside the endodermis that can give rise to lateral roots.
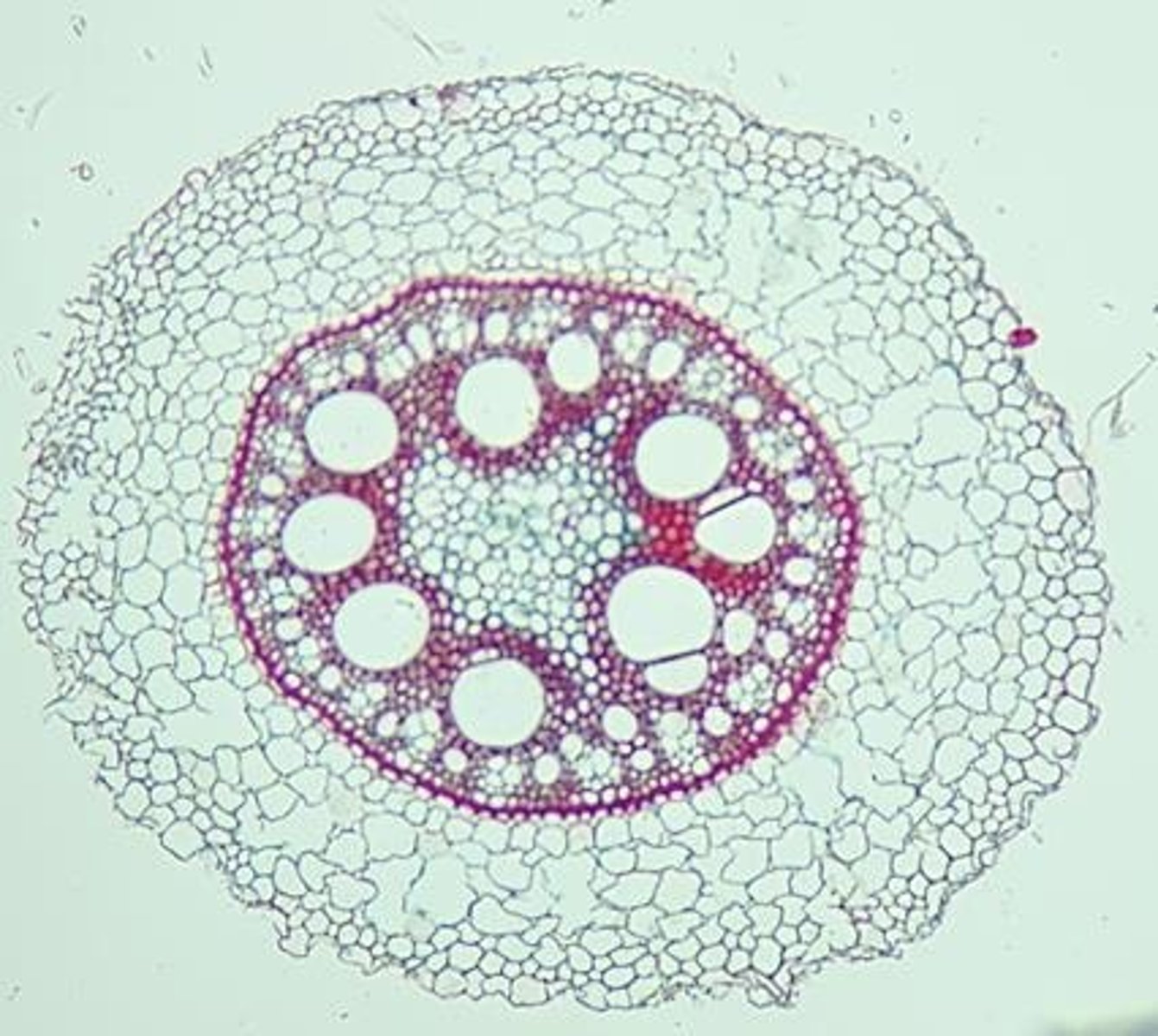
Phloem
The vascular tissue responsible for the transport of nutrients and carbohydrates produced by photosynthesis.
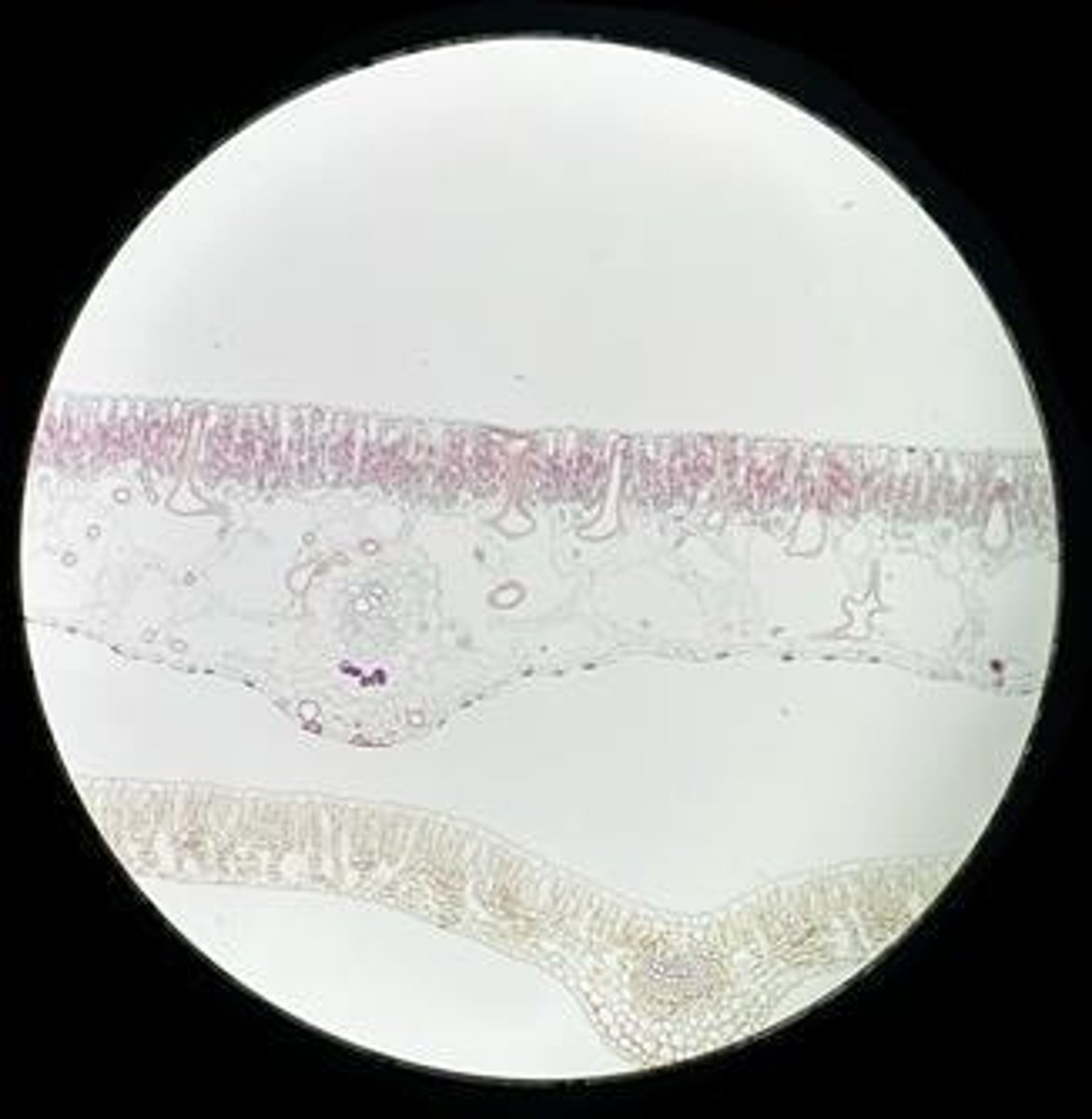
Xylem
The vascular tissue responsible for the transport of water and minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant.

Coleus
A type of dicot plant.
Tillia
A genus of trees commonly known as linden or lime trees.
Secondary growth
Growth that results in an increase in the thickness of stems and roots.
Periderm
The protective outer layer of a plant stem that replaces the epidermis in woody plants.
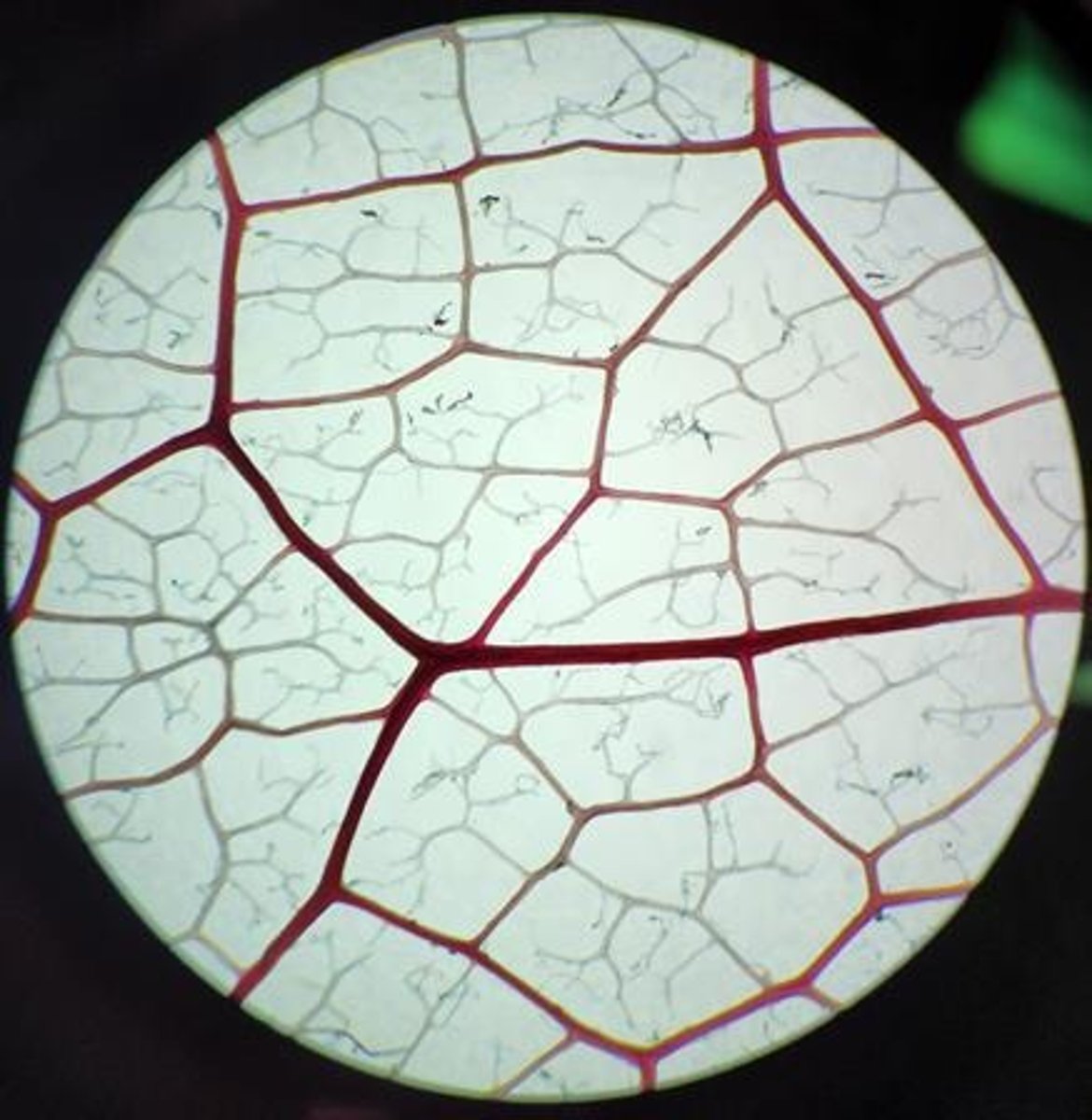
Quaternary veins
The smallest veins in a leaf that branch from tertiary veins.
Tertiary veins
The veins in a leaf that branch from secondary veins.
Secondary veins
The veins in a leaf that branch from primary veins.
Primary veins
The main veins in a leaf that provide structural support.
Xeromorphic leaves
Leaves adapted to dry habitats.
Mesomorphic leaves
Leaves adapted to moderate habitats.
Hydromorphic leaves
Leaves adapted to wet habitats.
Sun leaves
Leaves that are adapted to high light intensity, often with two layers of palisade cells.
Shade leaves
Leaves that are adapted to low light intensity, often with one layer of palisade cells.
Stomata
Small openings on the surface of leaves that allow for gas exchange.
Leaf modifications
Alterations in leaf structure that enhance survival in specific environments.
Spines
Modified leaves that protect from herbivores and help in water conservation.
Trichomes
Hair-like structures on leaves that provide protection against herbivores and environmental stress.
Tendrils
Leaf or leaflet modifications that provide support to climbing plants.
Node
The area of the stem where leaves begin to grow.
Internode
The space between two nodes on a plant stem.
Bud
An undeveloped or embryonic shoot on a plant.
Axil
The angle between the upper side of a leaf or stem and the supporting stem or branch.
SA:V ratio
Reduces to minimize water loss in hot, humid climates.
Sunflower: disk
Complete, perfect flower with 1 bract, 2 pappus, dicot, actinomorphic, head, inferior, epigynous.
Sunflower: ray
Incomplete, imperfect flower with 1 united stigma & anther, dicot, zygomorphic, head, inferior, epigynous.
Peruvian lily
Complete, perfect flower with 3 petals, 3 sepals, monocot, zygomorphic, simple umbel, inferior, epigynous.
Azalea
Complete, perfect flower with 5 petals, 5 sepals, dicot, zygomorphic, N/A, superior, hypogynous.
Japanese Andromeda
Complete, perfect flower with 5 fused petals, 5 sepals, dicot, actinomorphic, pendulus, superior, hypogynous.
Hydrangea
Incomplete, imperfect flower with 4 petals, dicot, actinomorphic, panicle, half-inferior, perigynous.
Spiderwort
Complete, perfect flower with 3 petals, 3 sepals, mono, actinomorphic, N/A, inferior, epigynous.
Kalanchoe
Complete, perfect flower with 4 petals, 4 sepals, dicot, actinomorphic, cyme, superior, hypogynous.
Dandelion
Complete, perfect flower with 5 petals, 5 sepals, dicot, actinomorphic, umble, superior, hypogynous.
Wild Carrot Flower
Complete, perfect flower with unspecified petals and sepals, dicot, actinomorphic, compound umble, superior, hypogynous.
Peanut
Dry fruit, dehiscent, legume.
Grape
Fleshy fruit, berry.
Raspberry
Fleshy fruit, aggregate drupe.
Strawberry
Fleshy fruit, aggregate achene.
Olive
Fleshy fruit, drupe.
Cucumber
Fleshy fruit, berry.
Jalapeno
Fleshy fruit, berry.
Nectarine
Fleshy fruit, drupe.
Pomegranate
Fleshy fruit, berry.
Locoweed
Dry fruit, dehiscent, legume.
Jimson Weed
Dry fruit, dehiscent, capsule with spikes for protection.
Lemon
Fleshy fruit, hesperidium.
Pear
Fleshy fruit, pome.
Avocado
Fleshy fruit, drupe.
Corn / maize
Dry fruit, indehiscent, caryopsis.
Corn on the cob
Fleshy fruit, multiple caryopsis.
Magnolia
Dry fruit, dehiscent, capsule.
Sunflower
Dry fruit, indehiscent, nut.
Maple
Dry fruit, indehiscent, winged samara.
Banana
Fleshy fruit, berry.
Dragon fruit
Fleshy fruit, berry.
Papaya
Fleshy fruit, pepo.
Acorn / oak
Dry fruit, indehiscent, nut.
Pigment Experiments
Leaf of Coleus shows original colors of burgundy, pink, green, yellow, white; color changes after hot water and ethanol bath.
Retention factor
Ratio of actual distance pigment traveled vs.
Japanese Camellia
Camellia japonica, Family: Theaceae, Non-Native
American holly
Ilex opaca, Family: aquifoliaceae, Native, Uses: Skincare (flowers & seeds)
Southern live oak
Quercus virginiana, Family: Fagaceae, Native, Uses: Wound healing (tannins from bark)
Eastern redbud
Cercis canadensis, Family: fagaceae, Native, Uses: Fevers
dogwood
Cornus florida, Family: cornaceae, Native, Uses: fever
American Sweetgum
Liquidambar styracfula, Family: Altingiaceae, Native, Uses: Antiseptic
Crepe myrtle
Lagerstroemia indica, Family: lythraceae, Native, Uses: cold treatment
American sycamore
Platanus occidentalis, Family: Platanaceae, Native, Uses: Antidiarrhea
Chinese elm
Ulmus parvifolia, Family: ulmaceae, Non-native, Uses: Furniture
Red maple
Acer rubrum, Family: Sapindaceae, Native, Uses: Eye conditions
Spanish oak/Pin Oak
Quercus palustris, Family: fagaceae, Native, Uses: Colds
Japanese maple
Acer palmatum, Family: Aceraceae, Non-native, Uses: Eye complaints
Trident Maple
Acer buergerianum, Family: sapindaceae, Non-native, Uses: Ornamental trees & bonsai
Dawn Redwood
Metasequoia glyptostroboides, Family: Cupressaceae, Non-native, Uses: antioxidant & anti-inflammatory
Winged Elm
Ulmus alata, Family: Ulmaceae, Native, Uses: Diuretic, treatment for skin abrasions
Common Fig
Ficus carica, Family: Moraceae, Non-native, Uses: Food source; sap treats calluses or warts
Dwarf Post Oak
Quercus margaretta, Family: Fagaceae, Native, Uses: Anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory uses
Japanese privet
Ligustrum japonicum, Family: Oleaceae, Non-native, Uses: Commercial insect wax, ornamental uses, wine coloring (berries)
American Elm
Ulmus americana, Family: Ulmaceae, Native, Uses: External uses such as a wash for wounds, or as a treatment for eye infections