Embryology 1 | Gametogenesis and Fertilization
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
What is spermatogenesis?
The process by which sperm are formed in males.
Where does spermatogenesis take place?
In the seminiferous tubules of the testes.
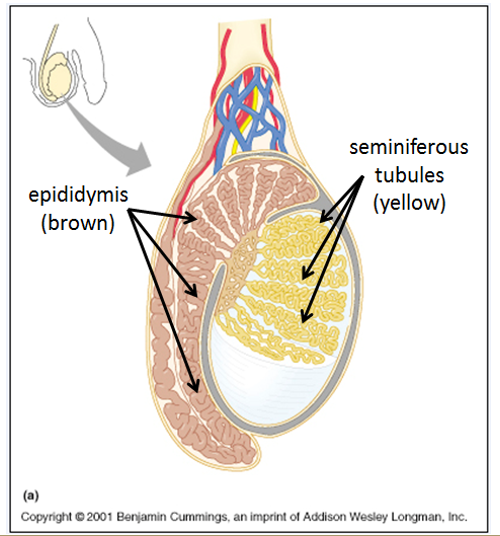
What type of cells help support the sperm-forming environment?
Sertoli (or sustentacular) cells form the walls of seminiferous tubules and support the development of sperm.
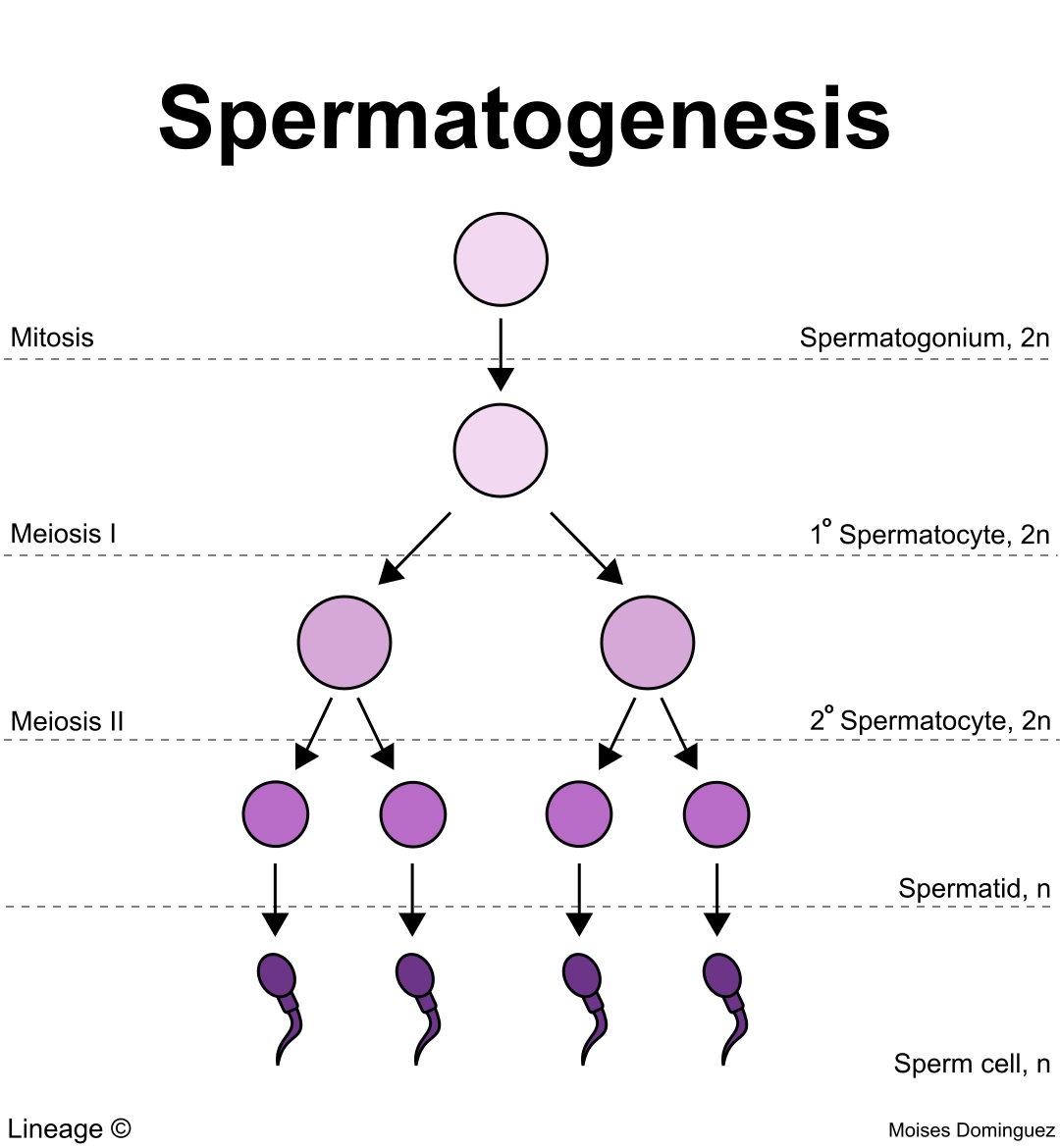
What are the three major stages of spermatogenesis?
Mitosis: creates stem cells (spermatogonia), some of which become primary spermatocytes.
Meiosis: produces haploid cells (spermatids) through two divisions.
Spermiogenesis: transforms spermatids into mature sperm (spermatozoa).
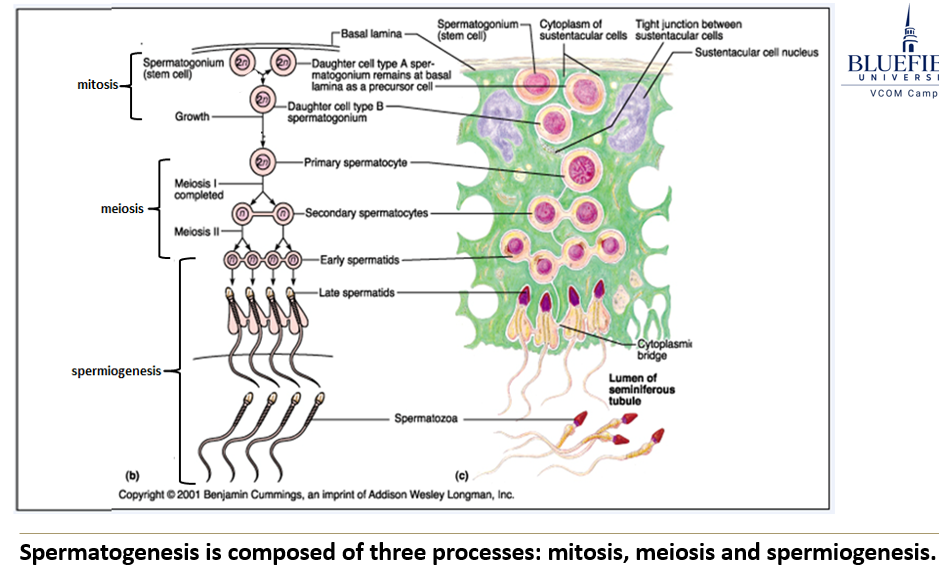
What happens during the mitosis phase of spermatogenesis?
Stem cells called spermatogonia divide to keep supplying new cells. Some of these become primary spermatocytes.
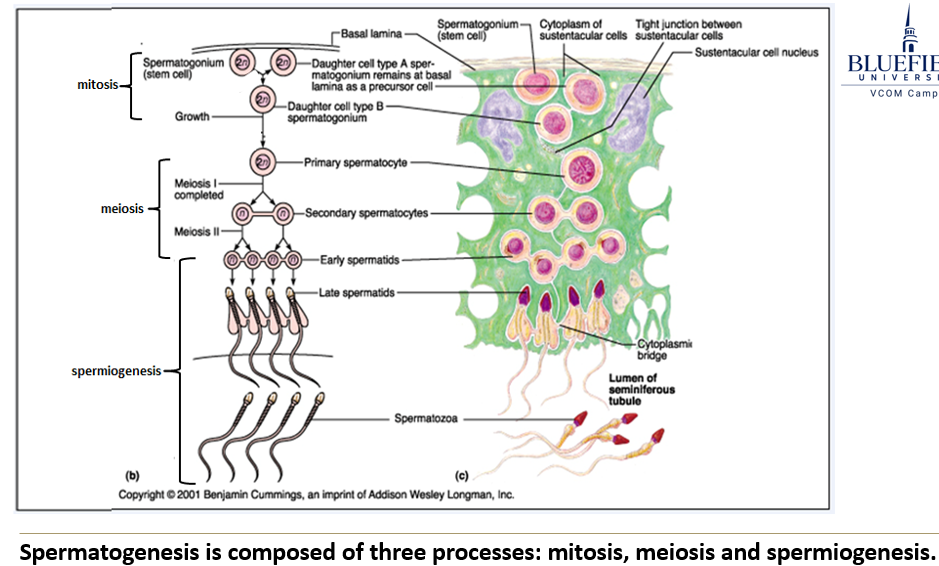
What happens during the meiosis phase?
A primary spermatocyte undergoes meiosis I to become a secondary spermatocyte, then undergoes meiosis II to become an early spermatid.
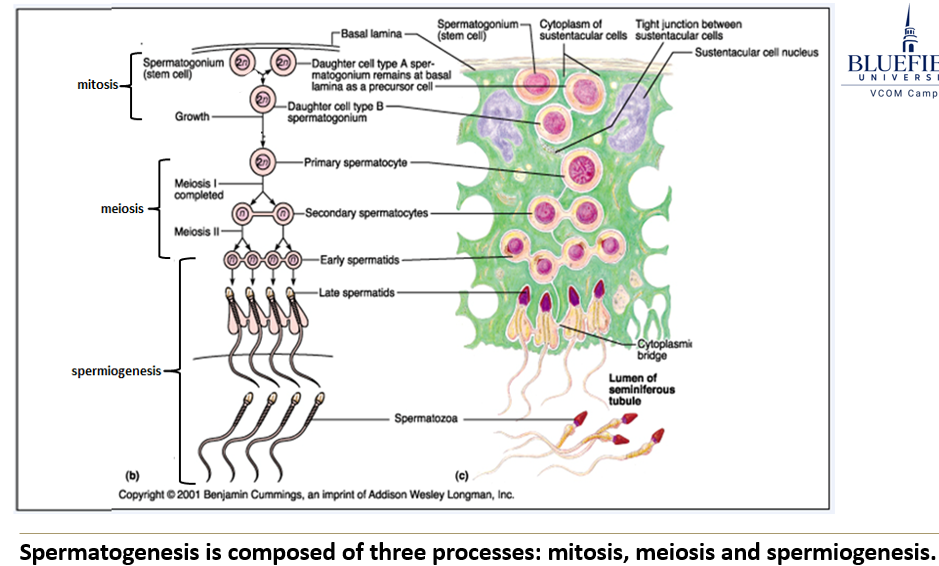
What is spermiogenesis?
It's the final stage where spermatids change shape and structure to become mature sperm cells (spermatozoa). It depends on proper temperature.
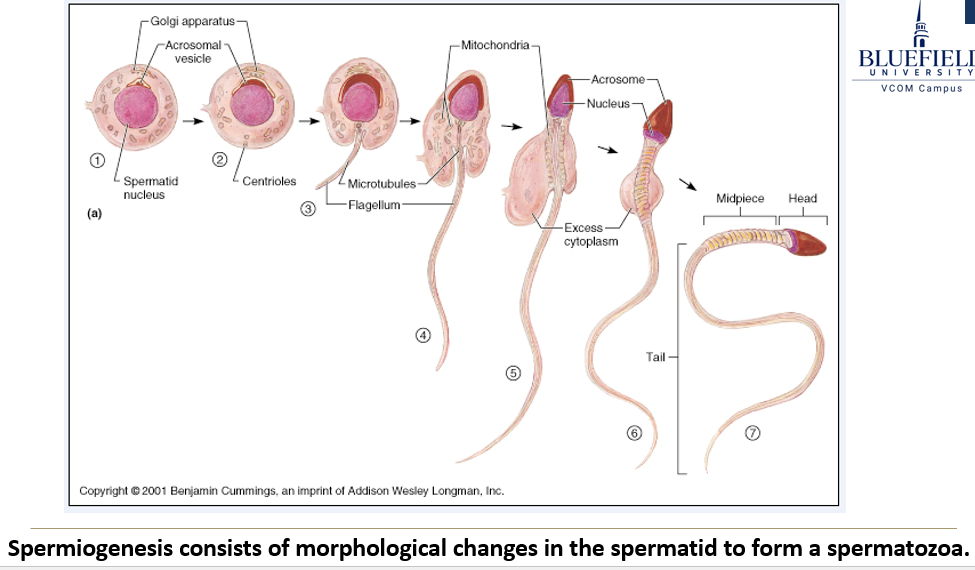
What key changes happen during spermiogenesis?
The nucleus condenses to form the sperm head.
The Golgi apparatus forms the acrosome, which caps the head.
Microtubules assemble to build the flagella.
Mitochondria multiply and move to the base of the tail to supply energy.
The cell loses most of its cytoplasm.
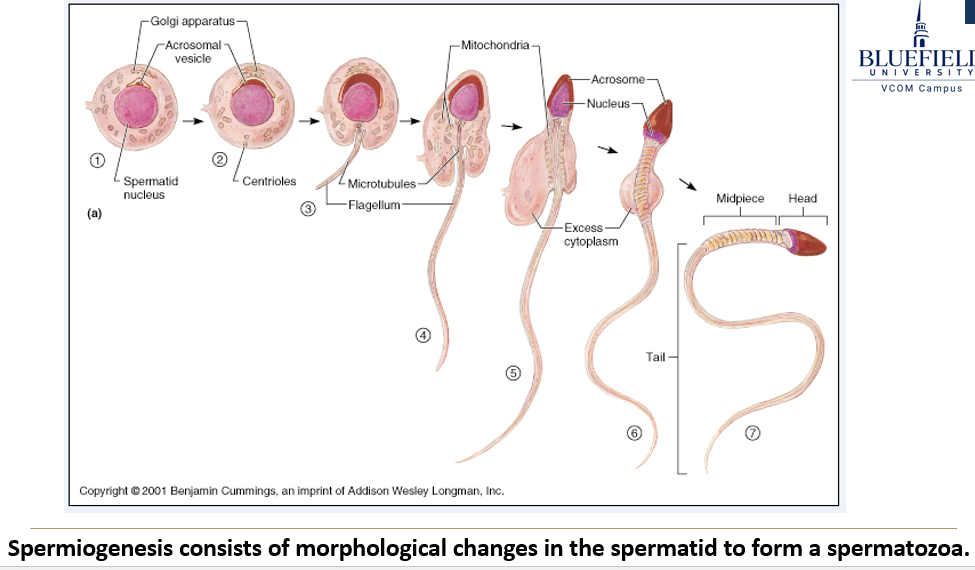
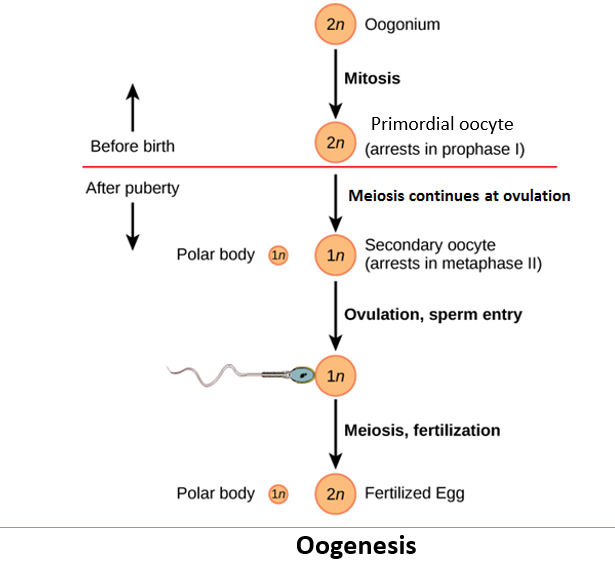
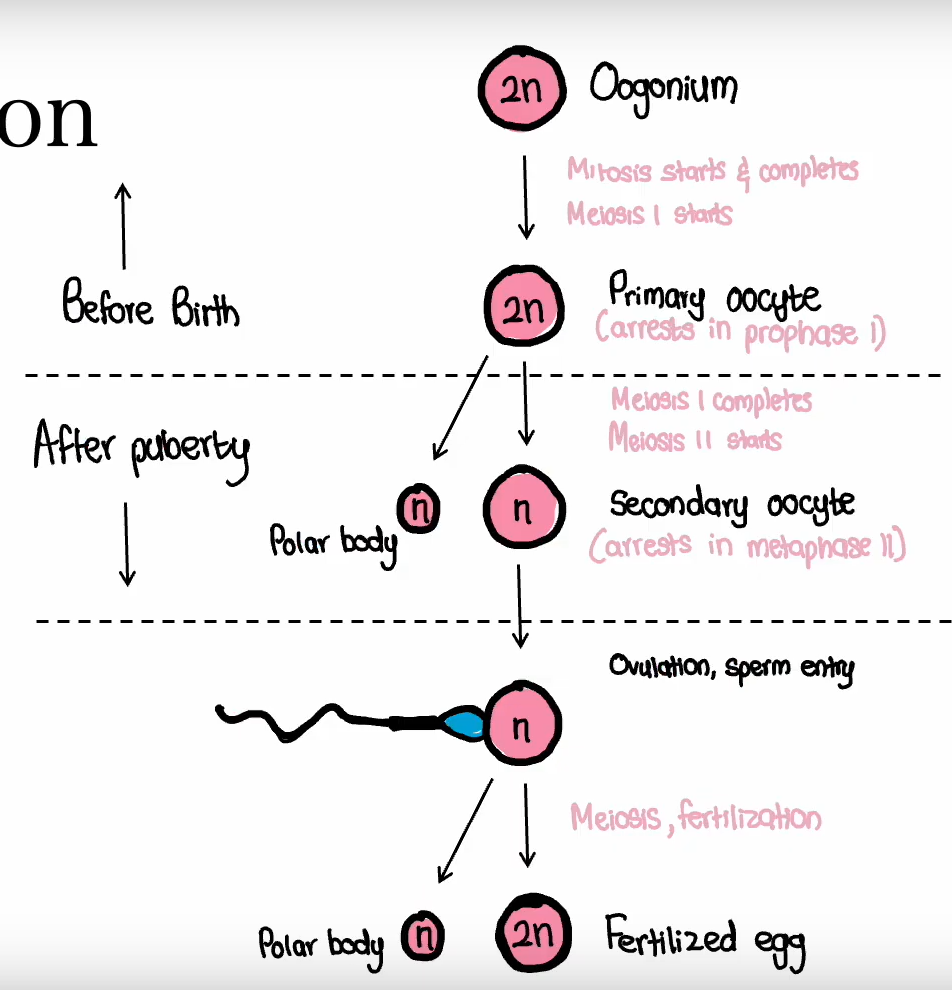
What is oogenesis?
It is the process of egg formation in females.
Where does oogenesis occur?
Occurs in the cortex of the ovaries.
What are oogonia?
Stem cells that undergo mitosis to produce about one million oogonia during fetal development.
What is the next step for oogonia after they are formed during fetal development?
All oogonia enter meiosis I and get arrested in the diplotene stage of prophase I.
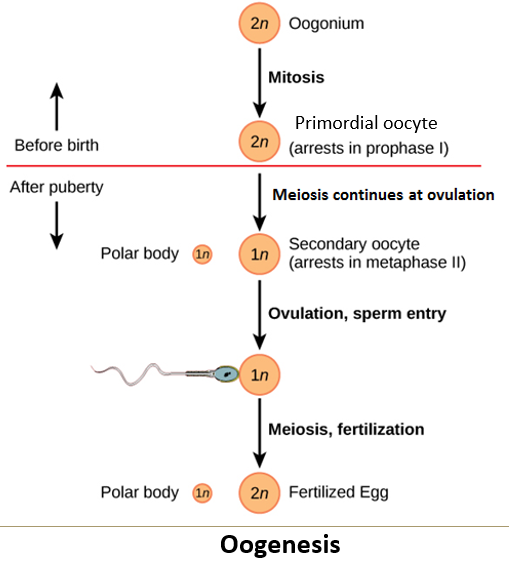
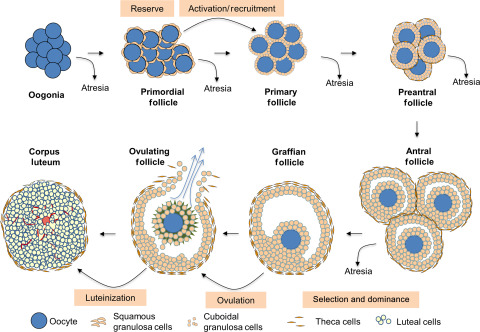
What is a primordial follicle?
The "starter pack" of a future egg. It contains an immature egg (oocyte) and the supportive cells needed for development.
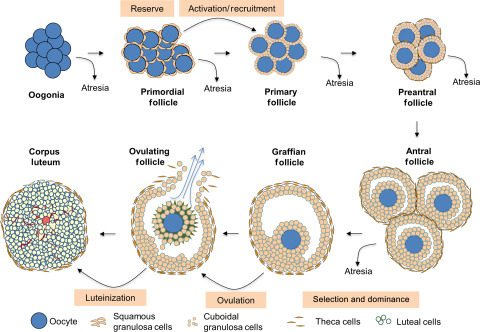
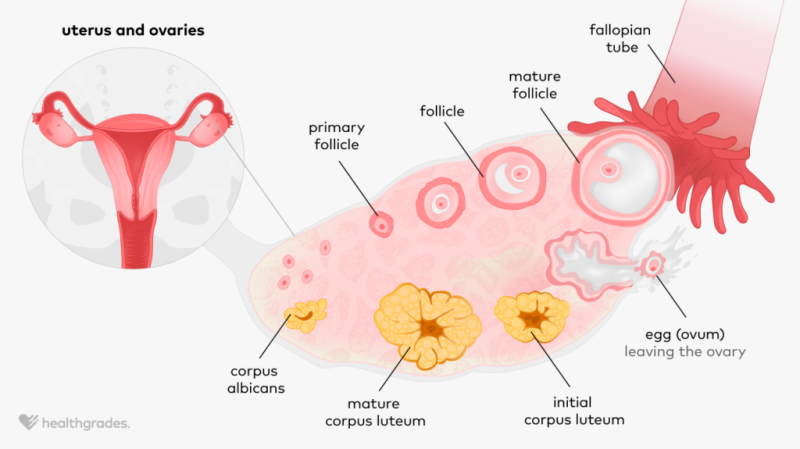
What happens after puberty during oogenesis?
Follicular cells change shape and increase in number.
A fluid-filled cavity called the antrum forms in the follicle.
Ovulation occurs when the oocyte is released from the ovary.
How do emergency contraception pills work to inhibit ovulation?
By disrupting the estrogen/progesterone balance to inhibit ovulation.
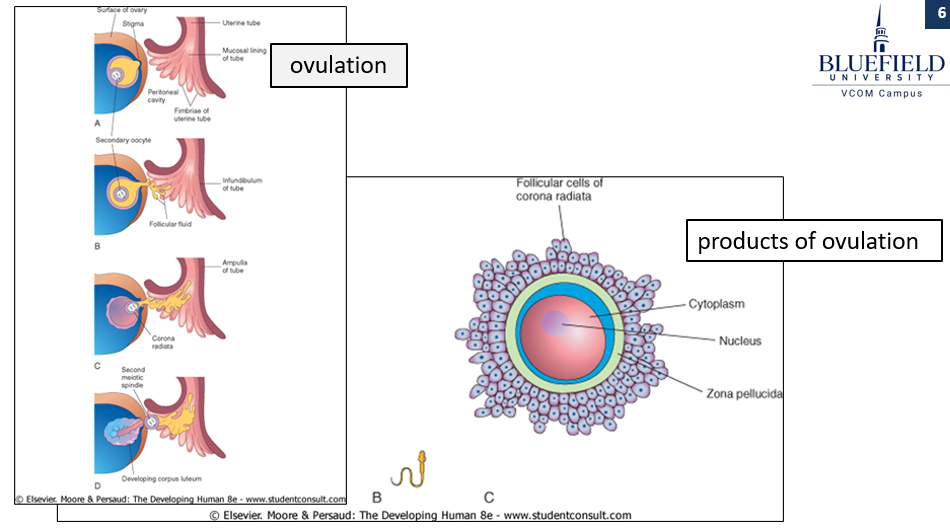
What key events and structures are involved in the maturation and release of the oocyte during and after ovulation?
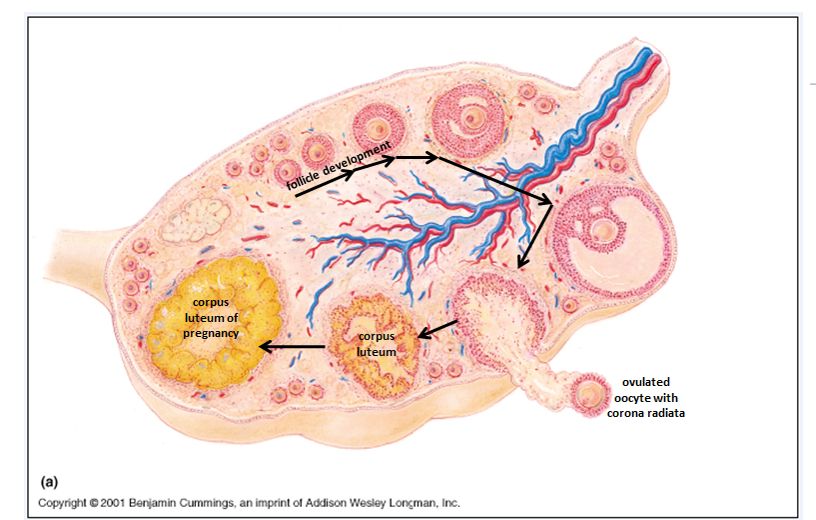
Remaining follicular cells become the corpus luteum, which secretes progesterone to maintain the uterine lining.
The corona radiata surrounds the oocyte.
The zona pellucida, a glycoprotein layer, encases the oocyte.
The ovum completes meiosis I, resulting in one haploid nucleus and a polar body due to uneven cytoplasm division.
The ovum then becomes arrested in metaphase II.
The oocyte does not complete meiosis until fertilization.
What happens to the follicle and its cells after ovulation?
The remaining follicular cells in the ovary transform into the corpus luteum, which secretes progesterone, essential for maintaining the uterine lining in preparation for possible implantation of a fertilized egg.
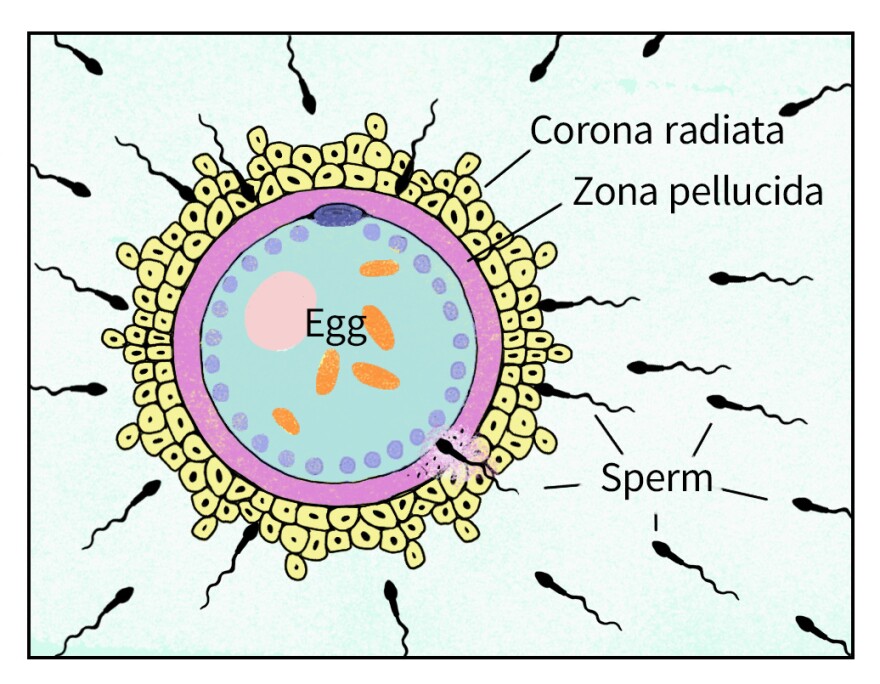
What structures surround and protect the oocyte during ovulation?
The corona radiata, a layer of granulosa cells, surrounds the oocyte and provides it with support and nutrients.
The zona pellucida, a glycoprotein layer, encases the oocyte and plays a critical role in sperm recognition and protection.
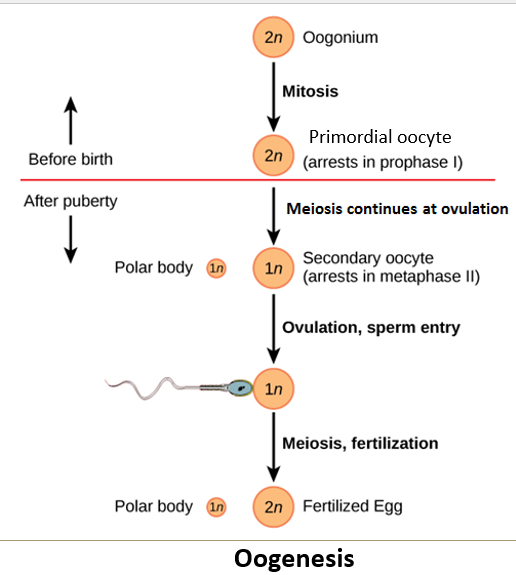
What stages of meiosis does the oocyte undergo, and when are they completed?
Before ovulation, the oocyte completes meiosis I, producing a haploid nucleus and a polar body through unequal cytoplasmic division.
After meiosis I, the oocyte becomes arrested in metaphase II, where it remains until fertilization.
The oocyte only completes meiosis II if fertilization occurs.
What is semen composed of?
Semen is a mixture of sperm and glandular secretions from the seminal vesicles (60%), prostate (30%), Cowper’s gland (5%), and sperm (5%).
How much semen is typically deposited during intercourse?
Around 2–6 ml of semen is deposited in the vagina near the cervix.
What defines a normal sperm count, and what count leads to infertility?
A normal sperm concentration is about 100 million/ml, while counts below 10 million/ml indicate infertility.
Why is sperm motility important, and what is considered normal?
Motility affects the sperm’s ability to reach the egg.
Normal motility is at least 40% active movement after 2 hours, with some still motile after 24 hours.
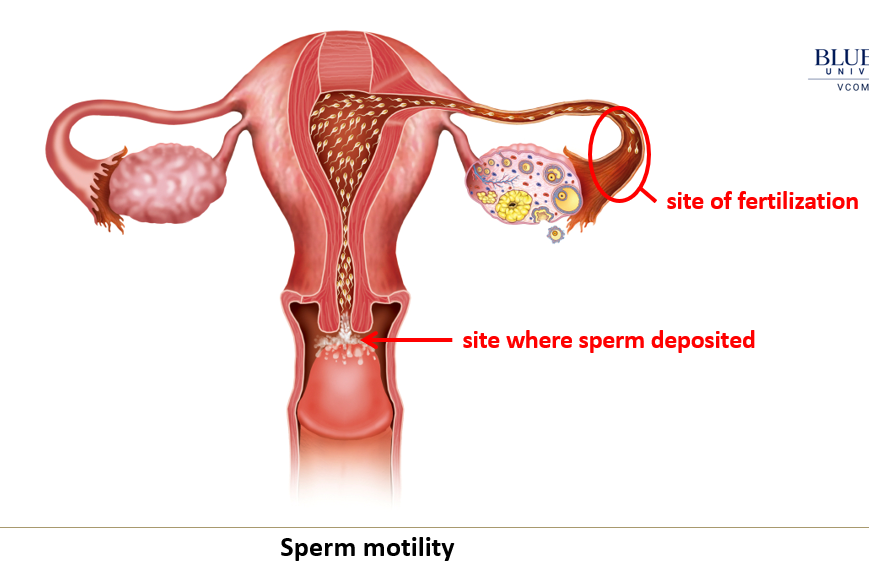
Where does fertilization usually occur?
Sperm must migrate through the uterus to the ampulla of the oviduct, where fertilization typically occurs.
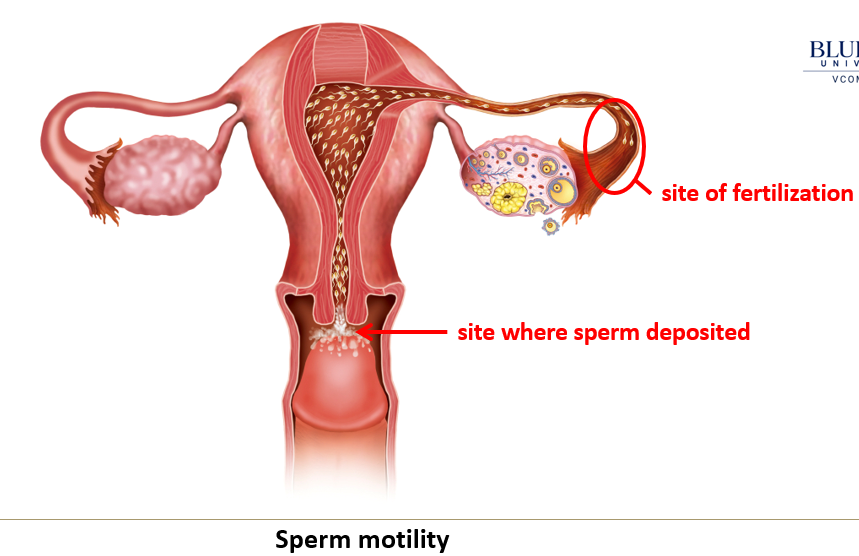
What is the viability of sperm and egg in the female tract?
Sperm survive up to 48 hours, while eggs must be fertilized within 12 hours of ovulation.
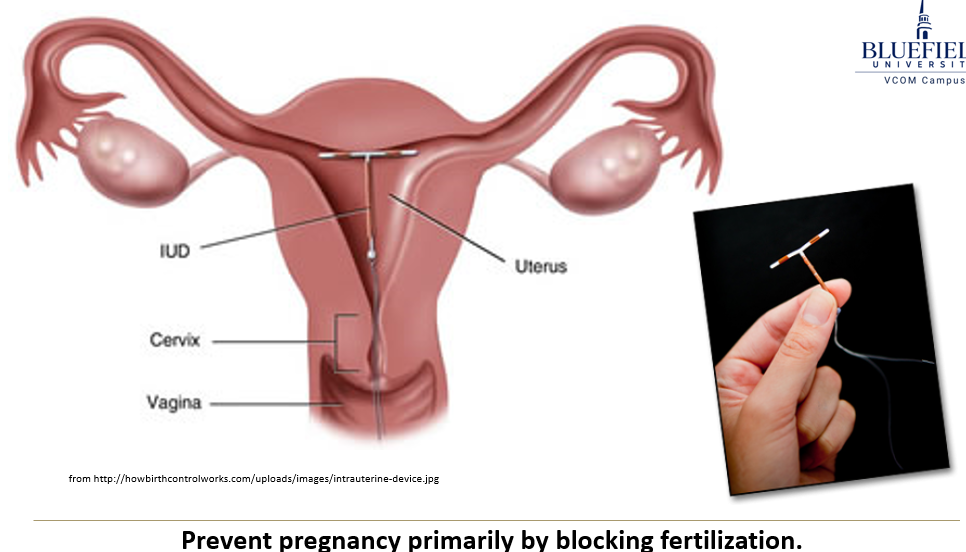
What are intrauterine devices and how do they work?
IUDs come in types like inert, copper, hormonal, or combination. They can shorten sperm lifespan, decrease sperm motility, and some forms may help prevent implantation.
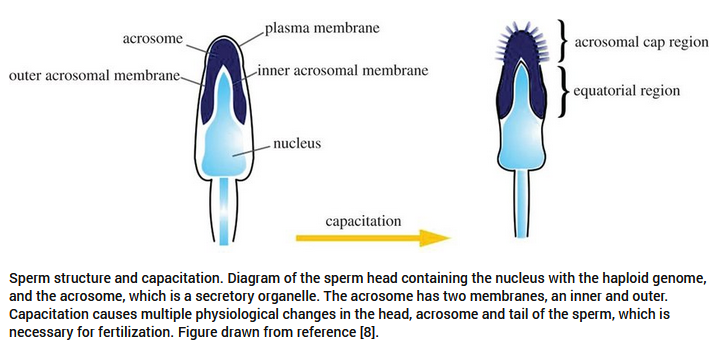
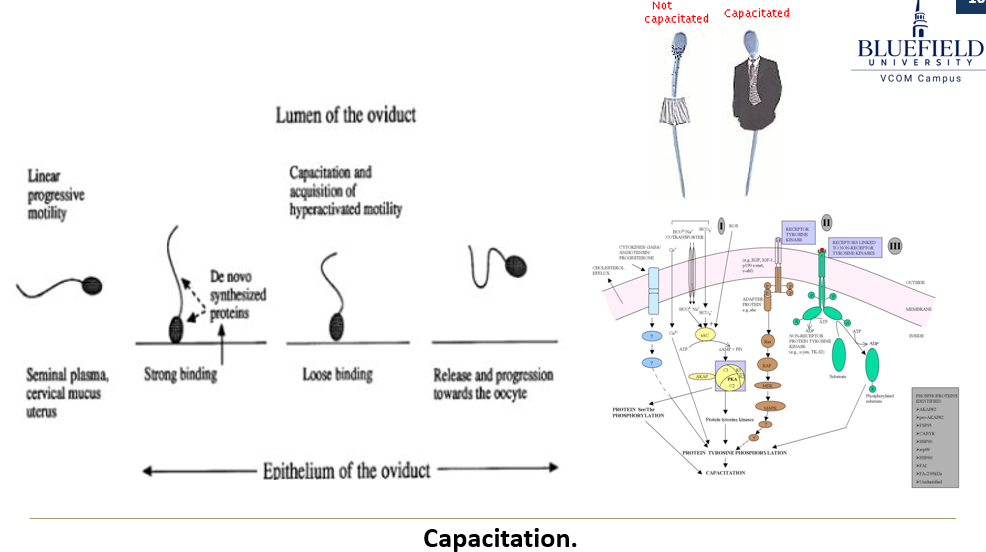
What is capacitation in sperm?
The removal of the glycoprotein coat and seminal proteins from the acrosomal membrane, enabling fertilization. It requires contact with the oviduct epithelium and takes around 8 hours.
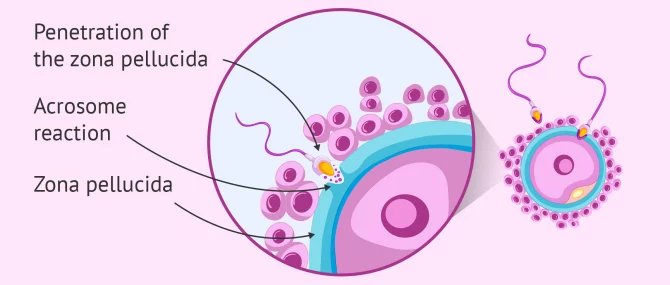
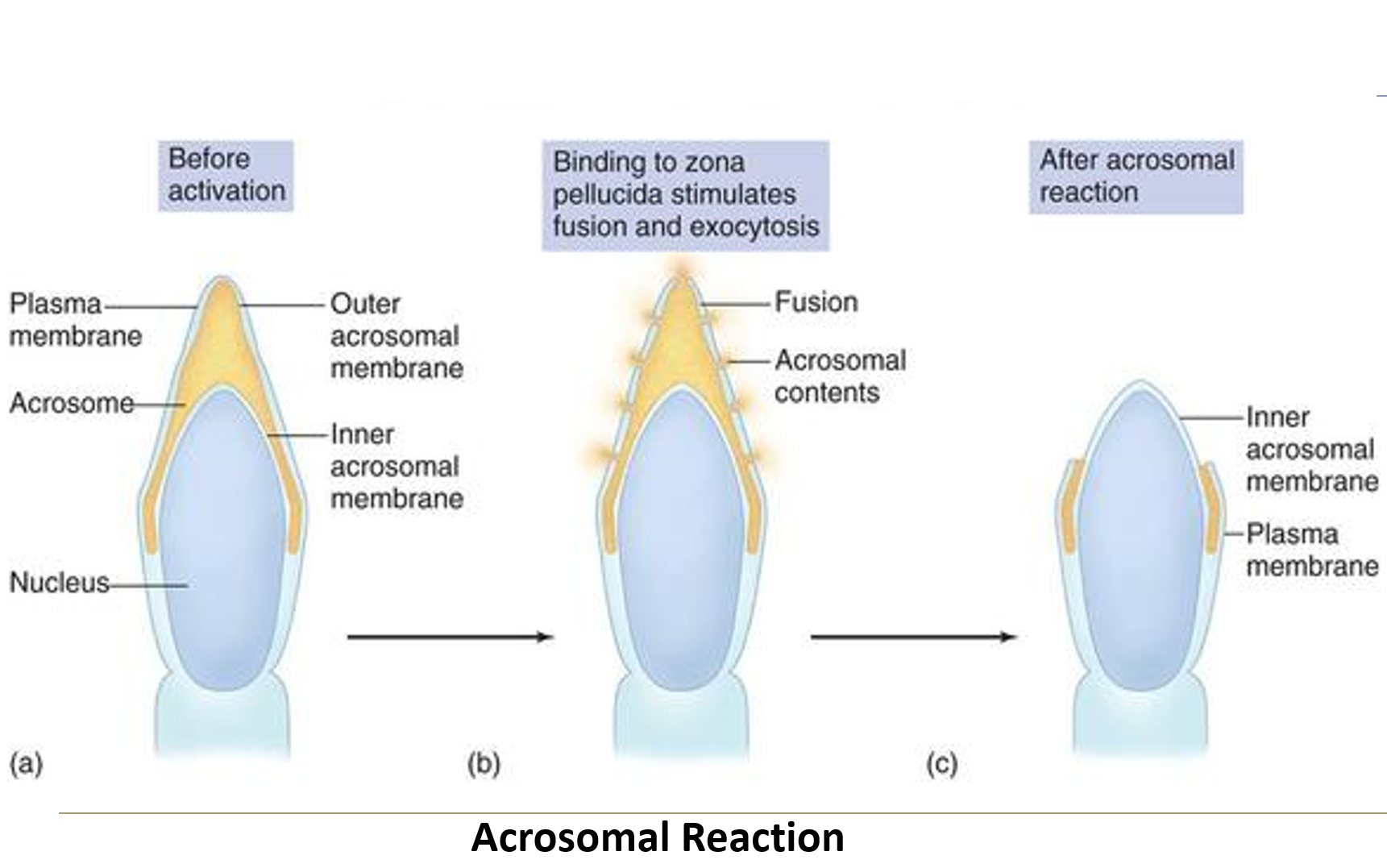
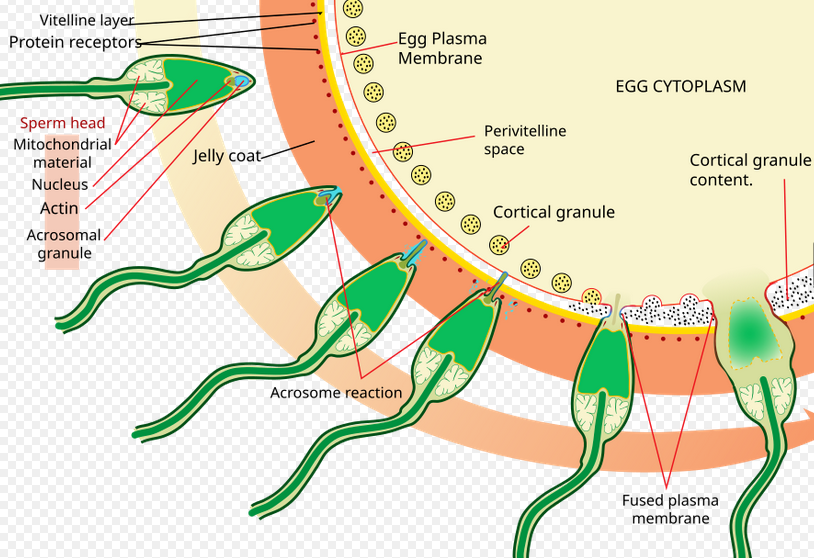
What is the acrosomal reaction?
The activation and release of enzymes from the sperm’s acrosome that are needed to penetrate the zona pellucida. This process is induced by proteins in the zona pellucida.
What is fertilization?
The process by which male and female gametes fuse to form a diploid zygote.
How many sperm are deposited and how many reach the site of fertilization?
About 500 million sperm are deposited, but only around 300 reach the ampulla, the site of fertilization.
What is required for sperm to penetrate the corona radiata?
Capacitation is required
Is a single sperm enough to penetrate the corona radiata?
No, it requires collective action from many sperm; a single sperm is not capable of penetrating alone.
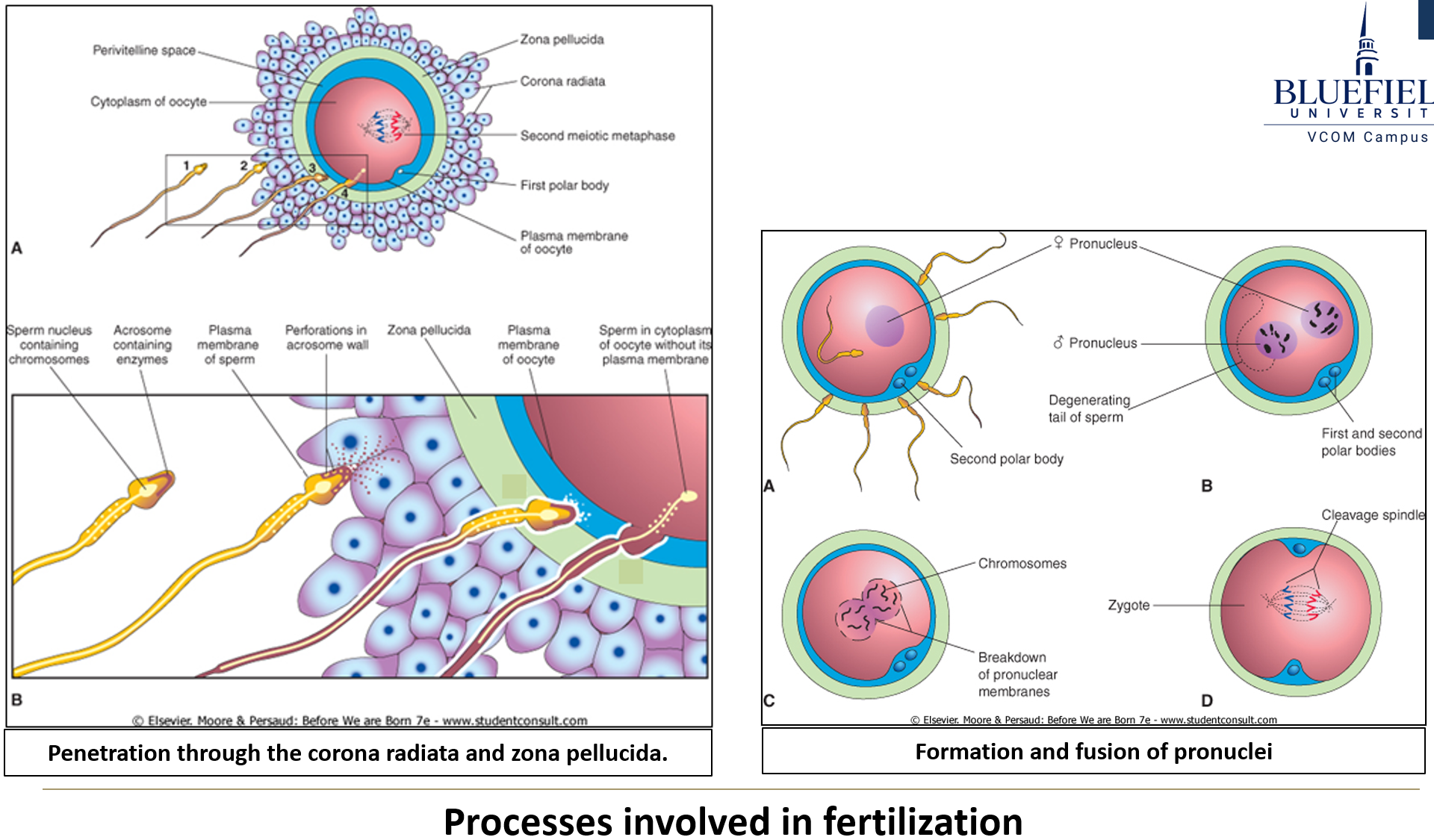
What enzyme helps sperm penetrate the corona radiata?
Hyaluronidase allows penetration through the corona radiata
What initiates penetration of the zona pellucida?
Zona pellucida glycoproteins act as ligands, triggering the acrosomal reaction when they dock with sperm membrane receptors.
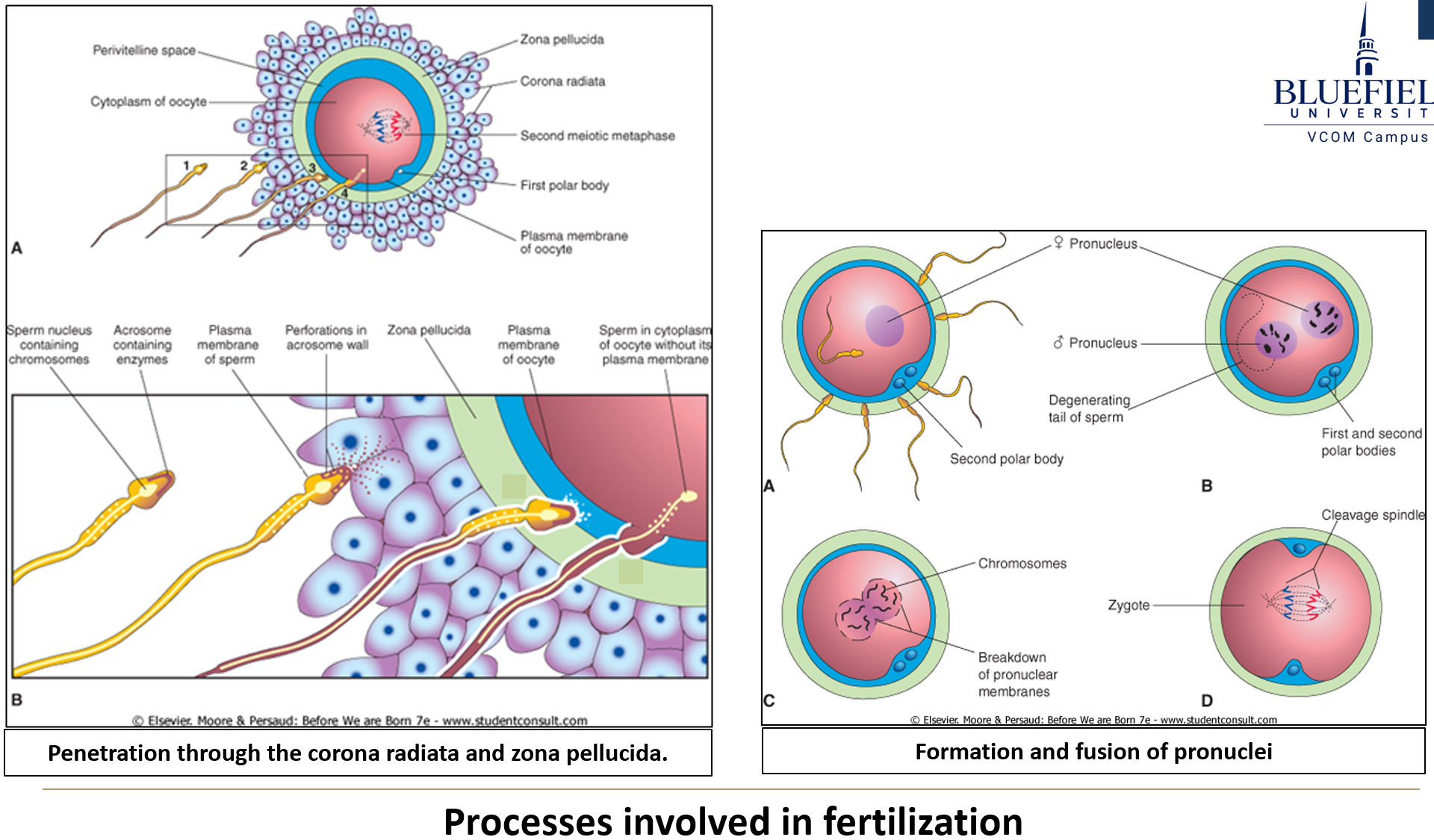
What enzyme is responsible for penetration through the zona pellucida?
Acrosin allows penetration through the zona pellucida
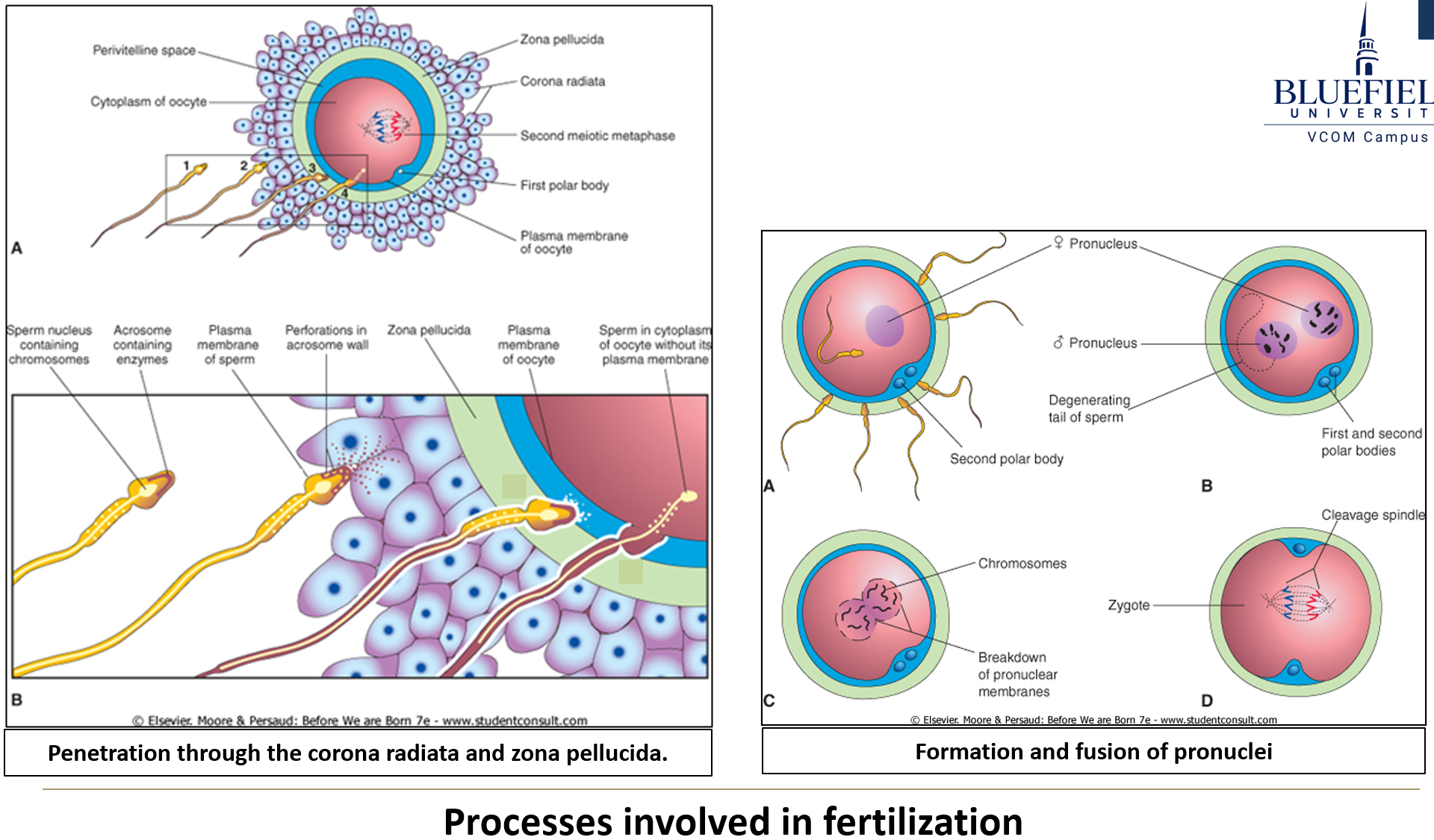
What happens to the egg when the zona pellucida is penetrated?
The egg completes meiosis II, forming a second polar body.
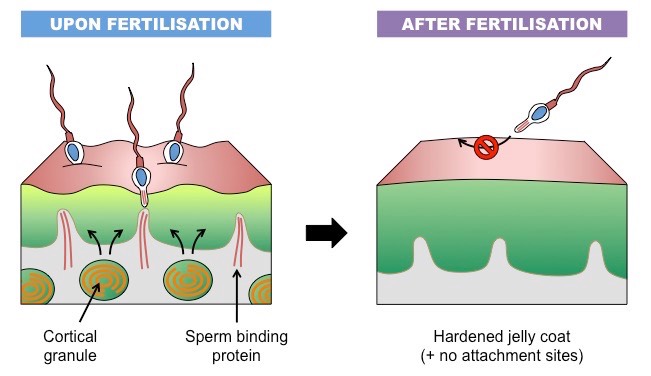
What is the zona reaction?
After the first sperm penetrates, the zona pellucida becomes impermeable to other sperm.
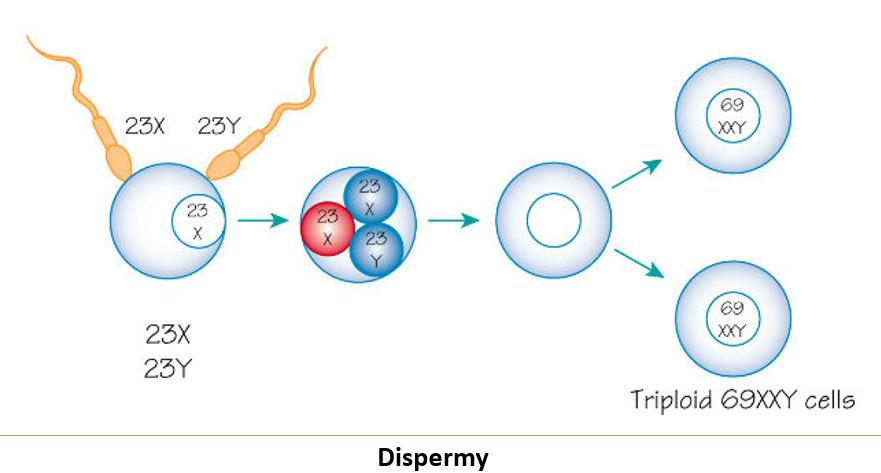
What is dispermy and what are its consequences?
Dispermy is when two sperm enter the zona pellucida simultaneously, causing a triploid fetus, which usually results in spontaneous abortion.
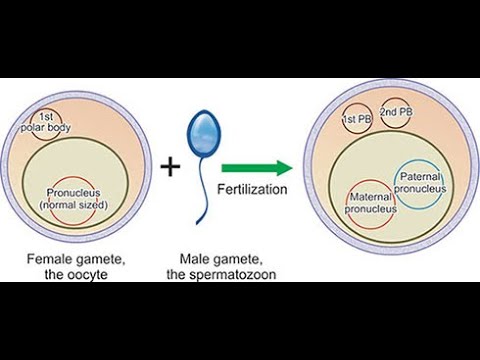
What happens when the oocyte and sperm membranes fuse?
The sperm nucleus enters the egg cytoplasm and joins the haploid egg nucleus.
What forms after fusion of the gamete nuclei?
The pronuclei form and replicate DNA, then fuse to create a zygote.
What are the stages of development after fertilization?
Pre-embryonic stage: fertilization through implantation.
Embryonic stage: implantation to 8 weeks.
Fetal stage: from 9 weeks to birth.