8. STP
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
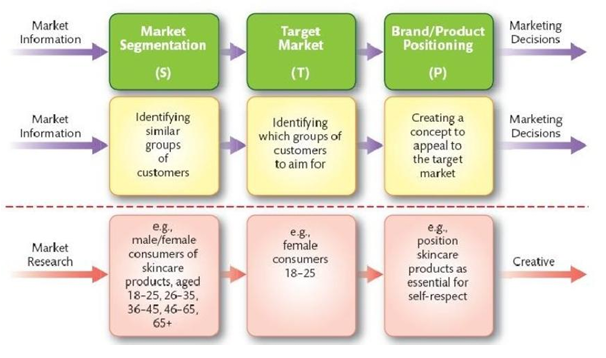
STP
Segmentation (identify homogeneous groups)
Targeting (aim for a certain group)
Positioning (brand image perception)
Benefits of STP
Enhances a company’s competitive position
Examines and identifies market growth opportunities
Effective and efficient matching of company resources to targeted market segments
Market segmentation
The division of a market into different groups of customers with similar needs and requirements
→ Company can focus specifically on certain customer needs
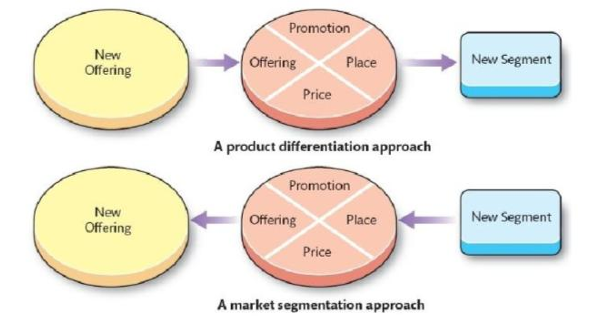
Market segmentation and product differentiation
Build-up method: start with the offerings, then identify markets with needs that fit it
Breakdown method: start from the segment and their needs, tailor offerings to them
Heterogeneous vs homogenous market
Heterogeneous market → different traits, needs and preferences
Homogenous market → share traits or need (homogenous markets are different from each other, only similar WITHIN the market)
Market Segmentation in Consumer Markets (Consumer criteria
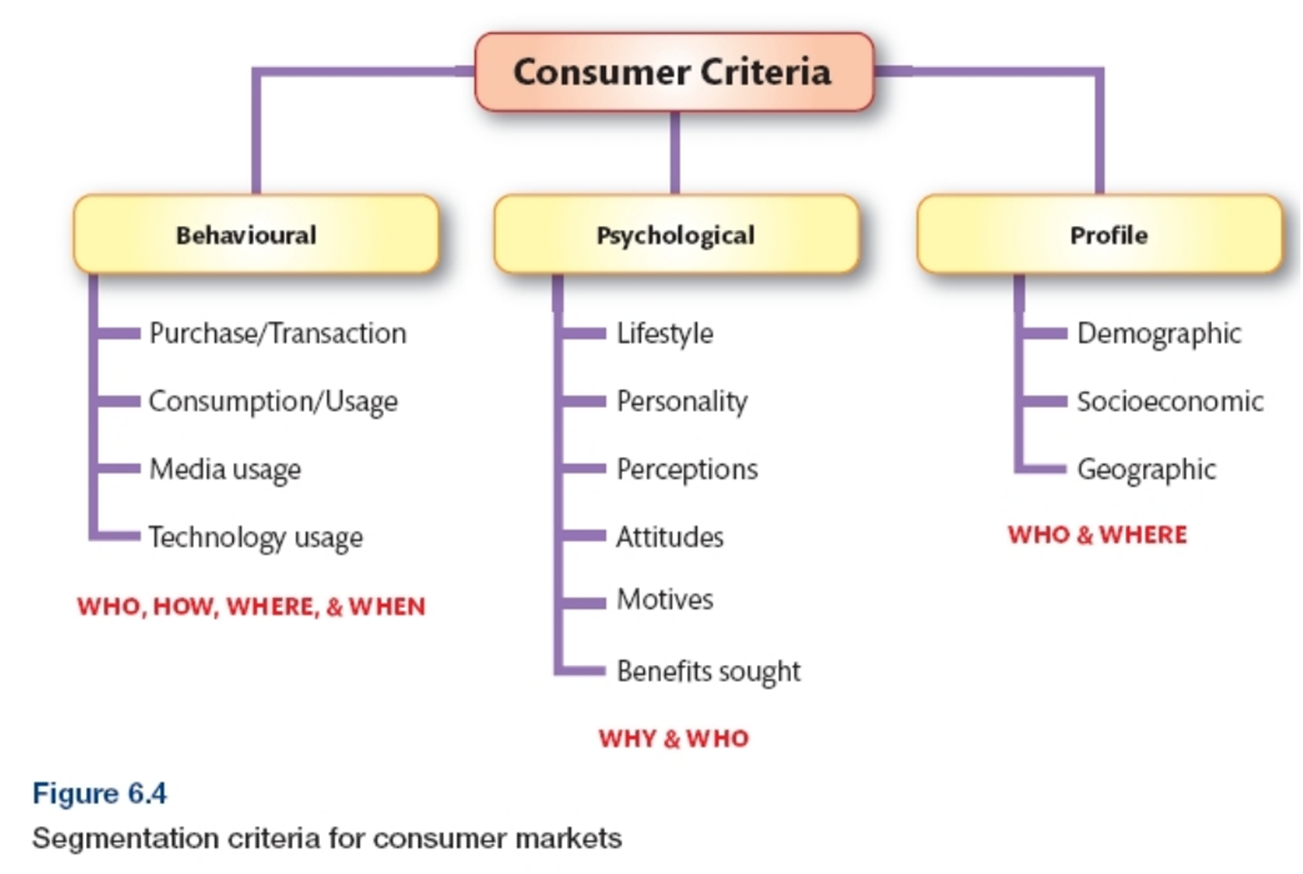
Profile segmentation (Consumer criteria)
Demographic (age, gender, family)
Socio-economic (social class, income)
Geographic (continent, region, density)
Geo-demographic segmentation
Affluent achievers = High-income earners
Rising prosperity= Upwards economic trajectory
Comfortable communities= middle-income earners, stable
Financially stretched= difficulty to make ends meet
Urban adversity= financially very challenged
→ Make sure to fit your offering to the segment of your choosing

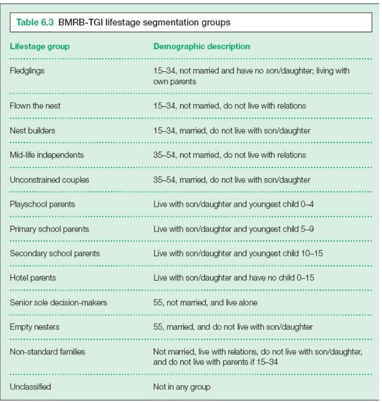
BMRB-TGI life-stage analysis
We can use different life stages to target people (age, marriage status, eldest/youngest child etc)
Psychographic segmentation
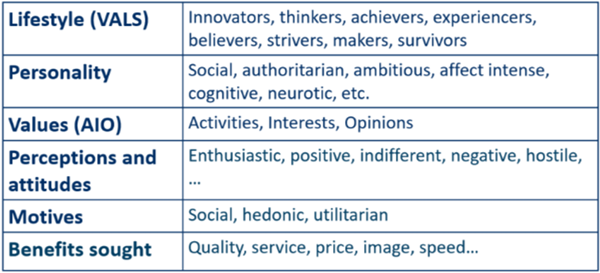
Behavioral segmentation

Usage
Why do people use a certain product?
Symbolic value
To experience something
Practocality
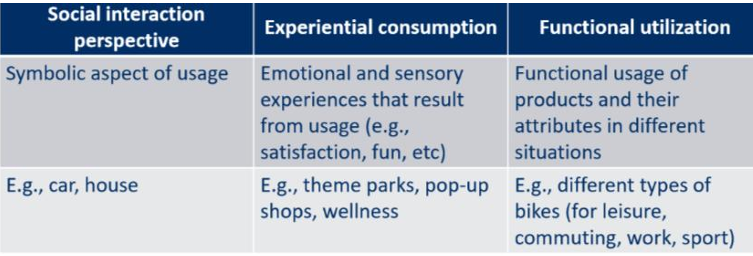
Behavioural segmentation: RFM metrics
Recency= How recently has the customer interacted with the company
Frequency= How often does the customer interact with the company
Monetary= How much/often does the customer give money to the company
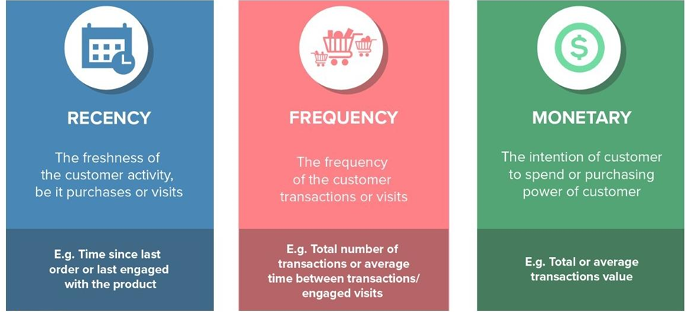
Segmenting consumer markets
Businesses make decisions based on this graph
vertical = Acquisition cost
horizontal = Predictability
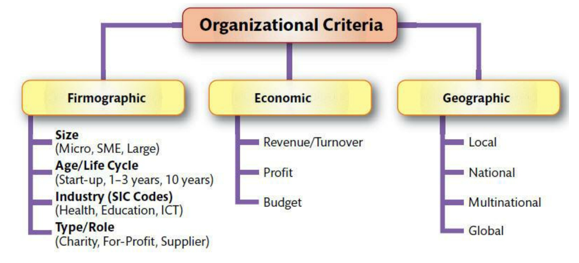
Segmentation in business markets: Organizational criteria
Very big!!
Firmographic (info about the firm)
Economic (How they’re doing economically)
Geographic (Where they operate)
SIC = Standard Industrial Classification Code = Identify and categorize industries and businesses
Segmentation of business markets: Customer characteristics
= Characteristics of the company you’re targeting
Decision-making unit
Choice criteria
Purchase situation

Why targeting markets?
To better tailor the marketing mix to a specific market segment
Four criteria for effective targeting
DAMP
Distinct (Clear difference between each segment?)
Accessible (Are we able to reach the buyers?)
Measurable (Is the segment easy to identify?)
Profitable (Sufficient people to make production profitable)
Segment attractiveness factors
What makes a segment more attractive?
Mission fit
How does a segment fit with the mission, resources, capabilities of an organization?
Superior value?
Impact on organization image?
Resources vs required investment?
Targeting approaches
Broad focus ←→ Narrow focus
Undifferentiated (mass) marketing: Reaching each market with the same marketing mix
Differentiated marketing: Target multiple segments, WITH changes to the marketing mix for each segment
Concentrated (niche) marketing: Focus on 1 segment, make sure that the marketing mix is well-tailored to it
Customized marketing (= One-to-one marketing): Target specific individual customers & personalize products to each specific customer

Undifferentiated marketing
= Mass marketing
Look at the market as 1 big group of people, 1 segment
Focus on needs that are common → Basic products
Advantages: Cost-effective
Risk: Being outperformed by others (they can tailor it better)
Ex. MNM’s

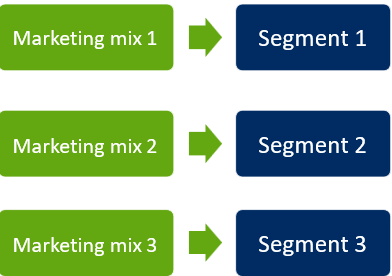
Differentiated marketing
Change marketing mix for each targeted segment
Advantage: Better tailored products & services (people will likely choose you)
Disadvantage: Expensive!!
Ex. Ariel = Dreft = Dash (All with different segments, like affordable, gentle on skin…)
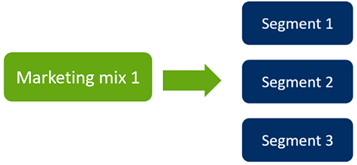
Concentrated marketing
= Niche marketing
Only target one segment with a specialized marketing mix
Go deeper, personalized products
More expensive
Ex. Vegan products
Customized marketing
Customized per customer
Advantage: Better tailor your products to the customer needs
Disadvantage: Extremely expensive and complex logistics/processes
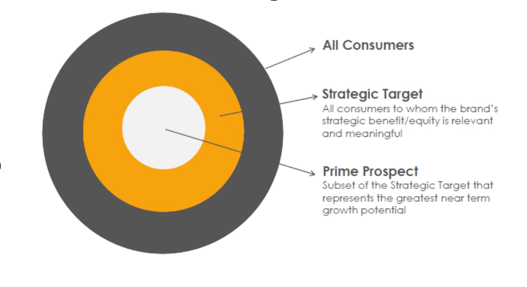
Target groups
Search for prime prospects that are likely to buy your product in the future
Strategic target: consumers that are relevant and meaningful
All consumers
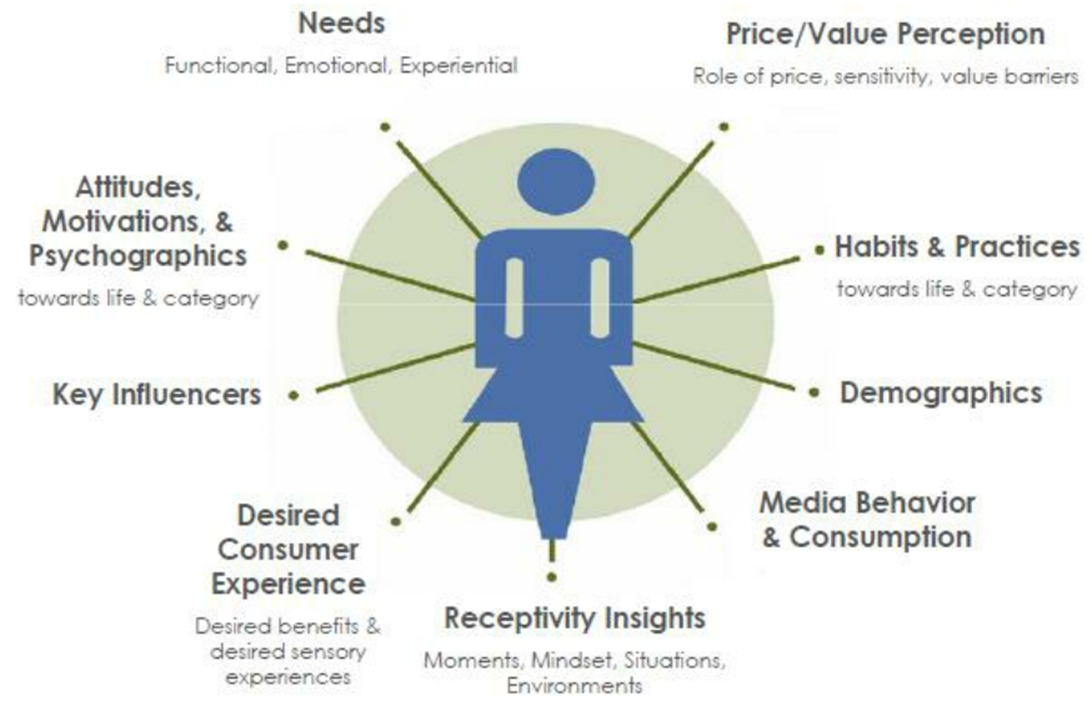
Holistic consumer profile
→ Make full customer profiles (360° view)
Persona
= A fictional character created to represent a user type that might use a site, brand or product in a similar way
→ Representative for specific segments
Used to help guide decisions
Customer journey
From being aware of the brand to post-purchase
All touch points (interactions with the brand)
→ Important to map the consumer journey and make them satisfied during each step of it
Positioning
= The act of designing a company’s offering and image, so that they occupy a meaningful and distinct competitive position in the target customers’ minds
= The place you take in the mind of the customer
→ Perceptual mapping (how customers see our brand)
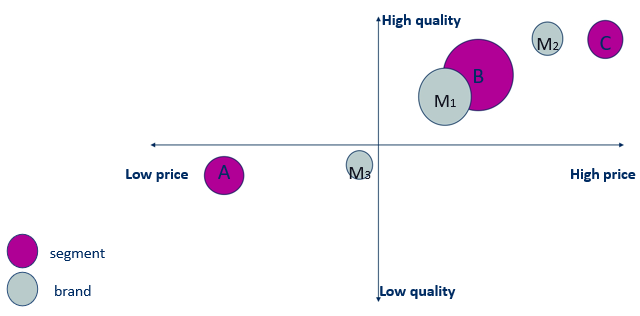
Perceptual mapping
How consumers see our brand
Identify competing brands
Identify important attributes when choosing between brands
Compare your positioning to other brands
In this example: A is not targeted yet!! Gap in the market
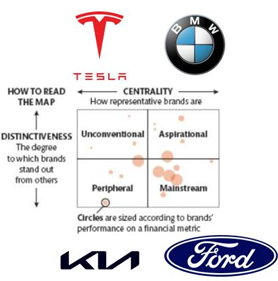
C-D Map
= The Centrality and Distinctiveness Map
Used to know what consumers’ perceptions are about different brands
1.Aspirational: Representative for category and distinct
2.Unconventional: Not representative, but very distinct
3.Mainstream: Very representative, but not that distinct or unique
4.Peripheral: Don’t really stand out or aren’t that representative
Value proposition (!!!)
Unique benefits and values of an offering
Differentiate from competitors
Attract the right customers
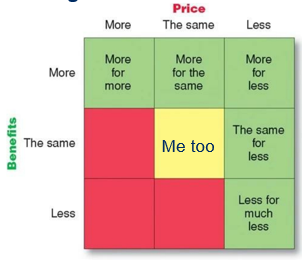
Red = Not interesting
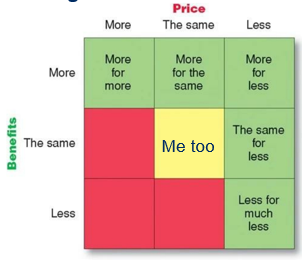
More for more
Offer specific benefits: status and identity
Higher prices: quality = questionable
Ex. Rolex
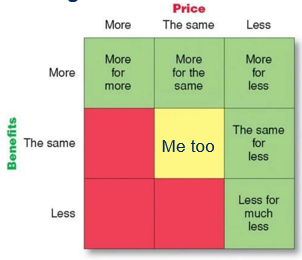
More for the same
More benefits for the same price
Ex. Toyota
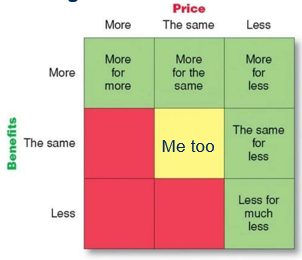
More for less
More benefits for a lower price
Longer usage & Lower acquisition cost
Ex. Dreft, Xiaomi (Basically cheaper alternatives)
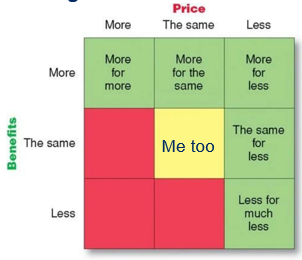
The same for less
Ex. Aldi or discounters
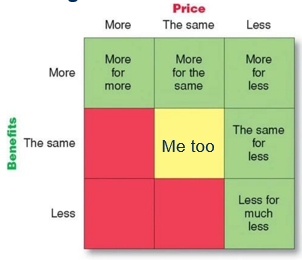
Less for much less
Ex. Everyday, Ryanair…
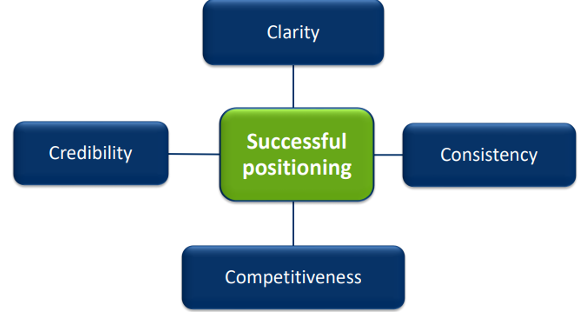
Key to successful positioning (!!!)
Clarity= what we stand for needs to be clear
Consistency= be consistent with how we communicate with our consumers
Competitiveness= Which distinct advantages the product has
Credibility= create and maintain trust
Unique Selling Proposition (USP)
Pick one attribute & aim to be the number 1 in it
Ex. Colruyt: focus on being the one with the most affordable prices
Multiple differences (Positioning)
Appeal to multiple segments
Risk: People may not believe you & Brand dilution (people get confused on what the brand exactly stands for)
Proposition positioning strategies
Functional (Features, price-quality, use)
Expressive (User, benefit, heritage)
Benefits (How it makes you feel: beauty, status…)
Values (Customize to the beliefs of customer (sustainability, animal welfare…))
Heritage (Traditions, knowledge (“established since 1803”))