BIO - photosynthesis
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
outline the stages of photosynthesis
oxidation vs reduction
oxidation - gains O2 loses H+
reduction - gains O2 loses H+
what is a co enzyme
co enzymes will assist specific enzymes by catalysing, or transferring chemical groups.
which coenzyme is used in photosynthesis
NADP - transfers H+ form one molecule to another so oxidises.
what is the grana
stack of thykaloids
site of light dependent reactions =
FINISH FC BEFORE
the eq for photosynthesis
6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2
what is NADPH
reduced NADP
what are the two photosystems
PSI - light at wavelength 700 nm
PSII - light at wavelength 680 nm
what is a photosystem
A photosystem is a complex of proteins and pigments within the thylakoid membrane of chloroplasts that captures light energy and converts it into chemical energy during photosynthesis.
what are the products of the light dependant reaction
02
NADPH
ATP
What is photoionisation
The process by which light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll, causing electrons to become excited and be released, initiating the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis.
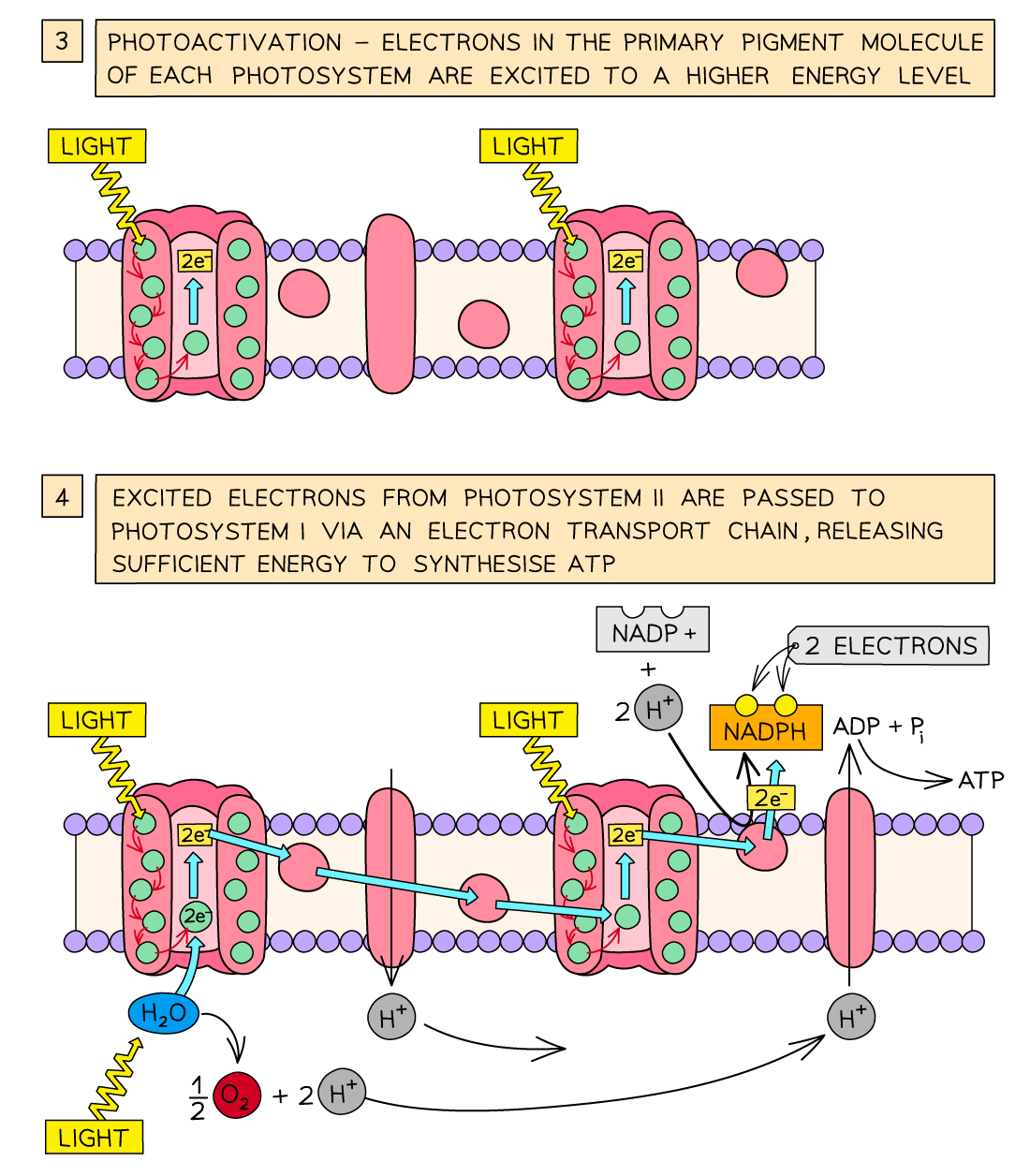
what is photoionisation used for
to make ATP from ADP - photophosphorylation
form reduced NADP from NADP
splitting water into protons (H+), electrons and oxygen - photolysis
process 1 of LDR
photoionisation
light energy is absorbed by 2 (PSII) in the thylakoid membrane. this excites the electrons.
(electrons are lost from the chlorophyll meaning chlorophyll is ionised)
step two of LDR
electrons are transferred along a electron transport chain to PSI. - at each stage e is lost.
some of the e lost is used to fuel the pump moving H+ ions into the thylakoid
what are the steps in the process of photolysis of water
2H2 O → 4H+ + 4e- + O2
4H - reduces NADP + increases the conc. grad between thykaloid and stroma
4e- - replaces those lost by the chlorophyll
02 - by product, diffuses out of leaf or used in respiration
step three of LDR
as H+ is moved into the thykaloid from the stroma the H conc. in the thylakoid increases
so the protons move back into the stroma down the conc. grad via the enzyme ATP Synthase - found in thylakoid
e from this process allows ADP and inorganic phosphate to combine and form ATP. - into the stroma
this ATP feeds into the LIR
Step 4 of LDR
light energy absorbed by PSI excites the electrons to a higher level
they are passed down the electron transfer chain
eventually, electrons are transfered to NADP as well as H+ from the stroma to form NADP
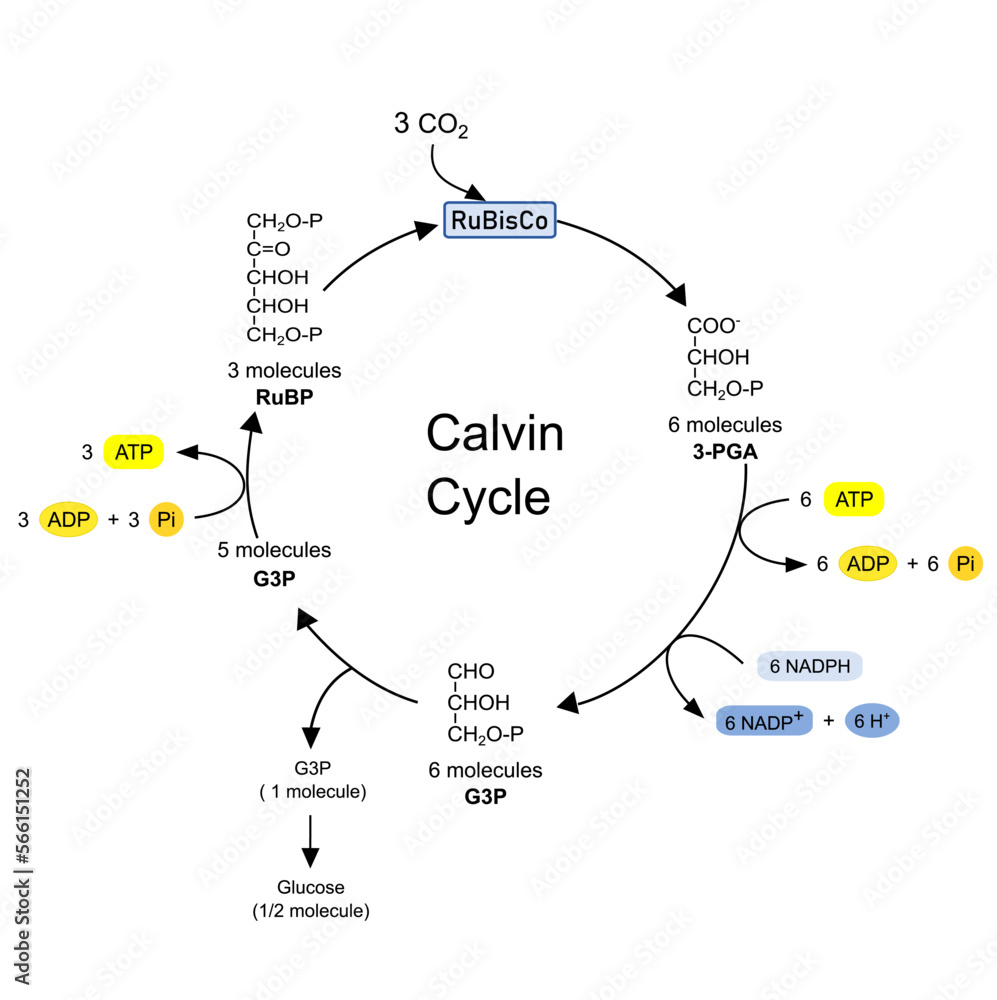
what is the first stage of the LIR
CARBON FIXATION
ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) is a five-carbon sugar
this undergoes carbon fixation by the enzyme RuBisCo
to form 3-phosphoglycerate (3-PGA).
what is the second stage of the LIR
REDUCTION
where 3-phosphoglycerate (3-PGA) is converted into
triose phosphate (TP)
using ATP and NADPH produced in the LDR.
what is the three stage of the LIR
REGENERATION
where TP is used to regenerate RuBP, allowing the cycle to continue.
what is the Calvin cycle
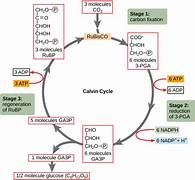
calvin cycle steps over view
CO2 diffuses into the leaf through the stomata and dissolves in the water around the mesophyll cells
then diffuses through the plasma membrane, chloroplast membrane, and into the stroma
carbon fixation; reduction - CO2 binds to the 5 carbon compound glycerate-3-phosphate - reaction is catalysed by rubisco to form 2 GP
GP is reduced and activated to form TP - ATP and reduced NADP from the LDR provide the e for this step
the ADP and Pi and NADP return to the thylakoid membrane for recycling
most of the TP continues to regenerate the RuBP and complete the cycle. requires ATP. NADP is reformed and goes back into t6he LDR.
clavin cycle
what are the limiting factors of photosynthesis
light intensity
temperature
CO2 conc.
what is the limiting factor
the factor in shortest supply
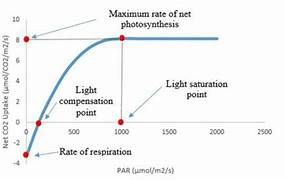
what is the compensation point
the light intensity at which the rate of photosynthesis equals the rate of respiration in a plant.
in what conditions will plants reach the compensation point
Plants will reach the compensation point in low light conditions where light intensity is insufficient for photosynthesis to exceed respiration rates.
how to calculate the compensation point
measure the O2 production and consumption (photosynthesis and respiration) and where they are equal is the CP
how would you represent the compensation point on a graph
why is temperature a limiting factor to photosynthesis
rubisco and ATP synthase will denature above 45 and be inactive below 10
and stomata will close to conserve water - high temp
why is water a limiting factor to photosynthesis
too little - supply stops
too much - soil becomes waterlogged ( has less O2 so less ATP and less minerals)
who investigated photosynthesis in the lollipop experiment
Melvin Calvin
outline the procedure of the lollipop experiment
placing aquatic plants, such as chlorella, in a lollipop-shaped glass apparatus filled with a solution containing radioactive carbon dioxide.
The plant was illuminated, allowing it to photosynthesize, and then samples were taken at various time intervals to track the incorporation of carbon into organic compounds.
outline the findings of the lollipop experiment
The experiment demonstrated that carbon dioxide is incorporated into carbohydrate molecules during photosynthesis.