Unit 3: Cytogenetics 10/9 & 10/14 - Chromosome Abnormalities & Chromosomal Disorders
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key vocabulary terms and concepts related to cytogenetics, chromosome abnormalities, and their implications.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Cytogenetics
The study of chromosomes and their role in heredity and genetic disorders.
Autosomal chromosomes
Chromosomes that are not sex chromosomes; humans have 22 pairs of autosomes.
X-chromosome inactivation
The process by which one of the two X chromosomes present in female mammals is inactivated.
Gametogenesis
The process by which cells undergo meiosis to form gametes (sperm and eggs).
2 types of Numerical abnormalities and their subgroups
Chromosomal abnormalities where the number of chromosomes is altered (e.g., aneuploidy). Mistakes during segregation in meiosis
Polyploidy
A cell with more than two haploid sets of chromosomes;
Triploidy; 69 chromosomes
Tetraploidy;
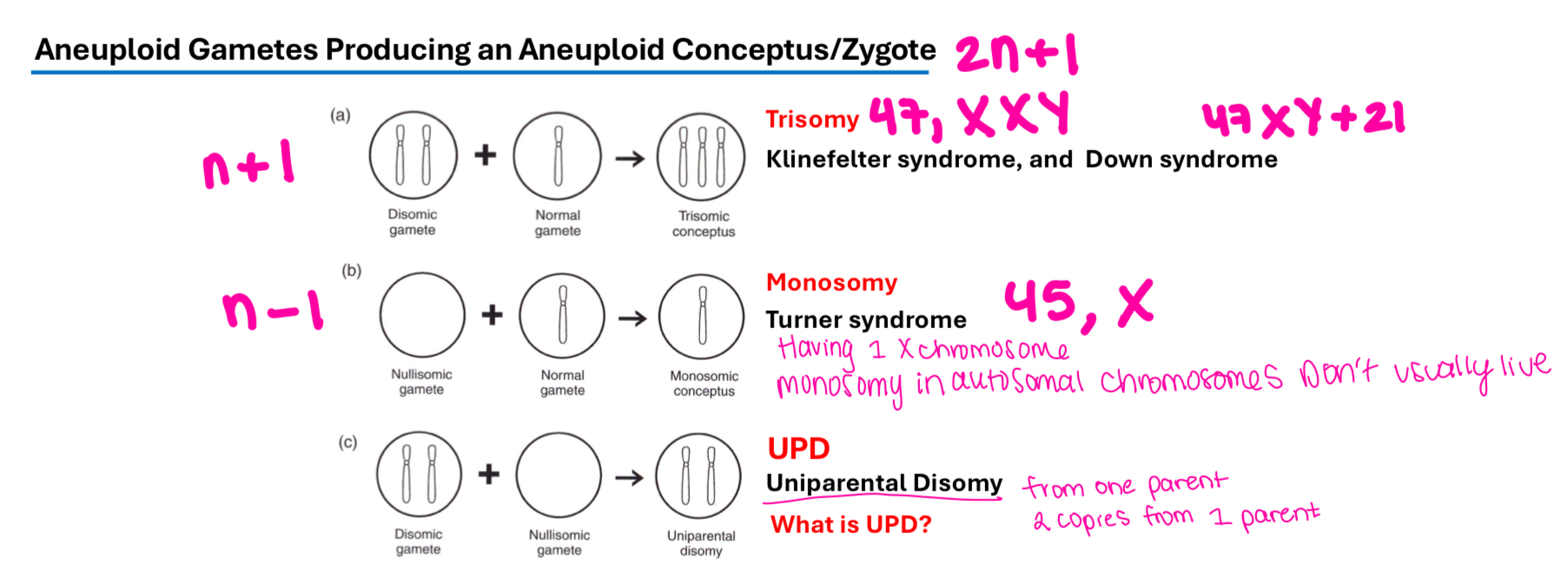
Aneuploidy
Cells with a chromosome number that is not an exact multiple of the haploid sets;
Monosomy (2n-1)
Trisomy (2n+1)
Uniparental Disomy
Structural abnormalities
Chromosomal abnormalities involving changes in the structure of chromosomes (e.g., deletions, duplications).
Polyploidy
A condition in which a cell has more than two complete sets of chromosomes. (anything other than the normal 46 chromosomes)
Triploidy (3n, 69 chromosomes) 69, XXX
Tetraploidy (4n, 92 chromosomes) 92, XXXY
Aneuploidy
A condition in which the number of chromosomes is not an exact multiple of the haploid set.
Aneuploidy arises from faulty segregation of the chromosomes in meiosis or mitosis, nondisjunction.
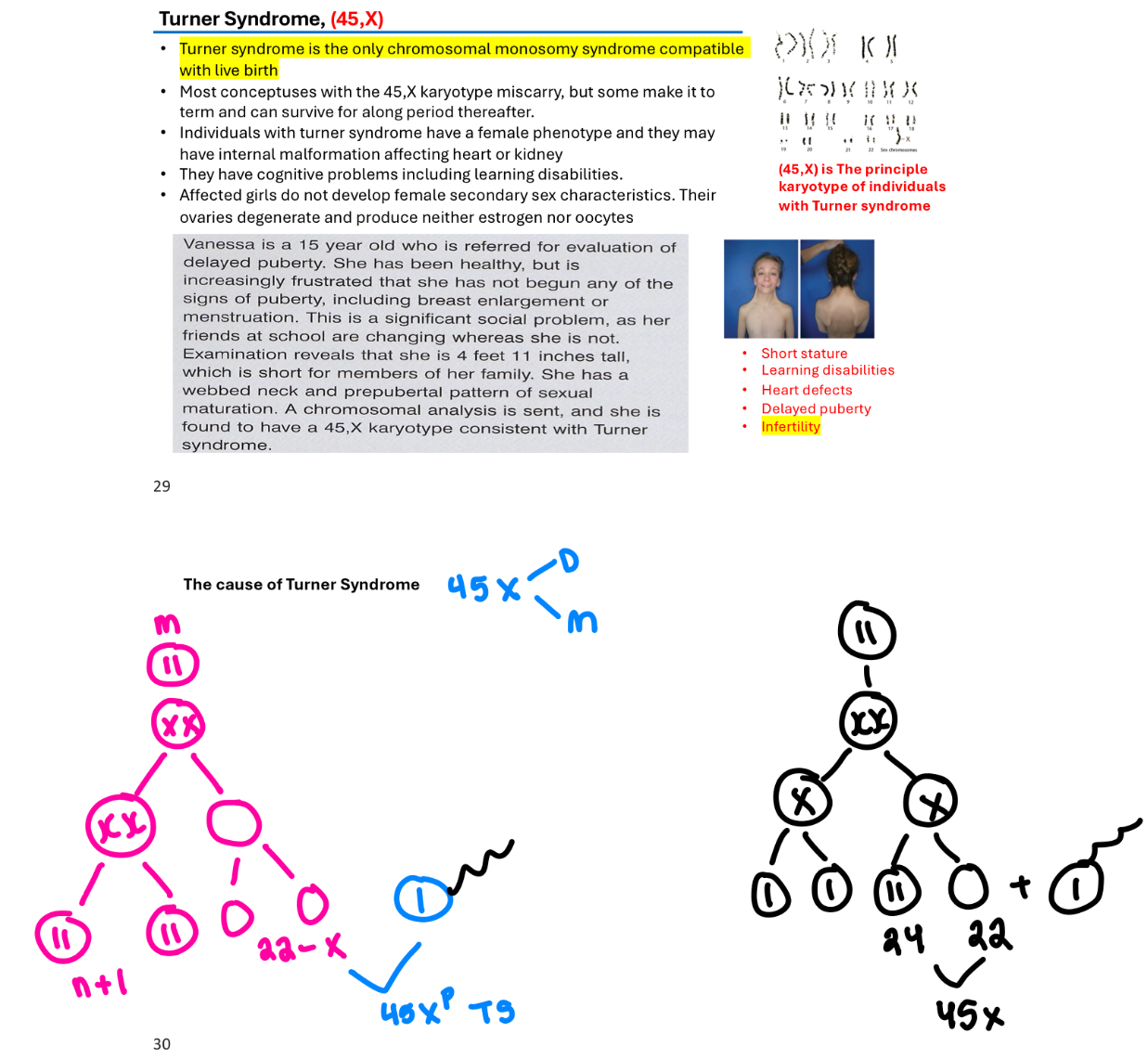
Can have autosomal aneuploidy, like Edward syndrome (47,XY,+18) or sex chromosome aneuploidy like Turner Syndrome 45,X (2n-1)
(Turner syndrome is the only chromosomal monosomy syndrome compatible with live birth)
Monosomy: 2n-1
Trisomy: 2n+1
Nondisjunction
The failure of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate properly during cell division.
Trisomy
A chromosomal condition where an individual has three copies of a chromosome instead of two.
Klinefelter syndrome: 47, XXY (2n+1)
Down syndrome: 47, XY, +21
Edward syndrome : 47, XY, +18
Patau syndrome: 47, XY, +13

Monosomy
A chromosomal condition where an individual has only one copy of a chromosome instead of two.
Autosomal monosomy is lethal and nearly always is incompatible with survival to term
Sex chromosome aneupoloidy
Turner syndrome 45, X (2n-1)

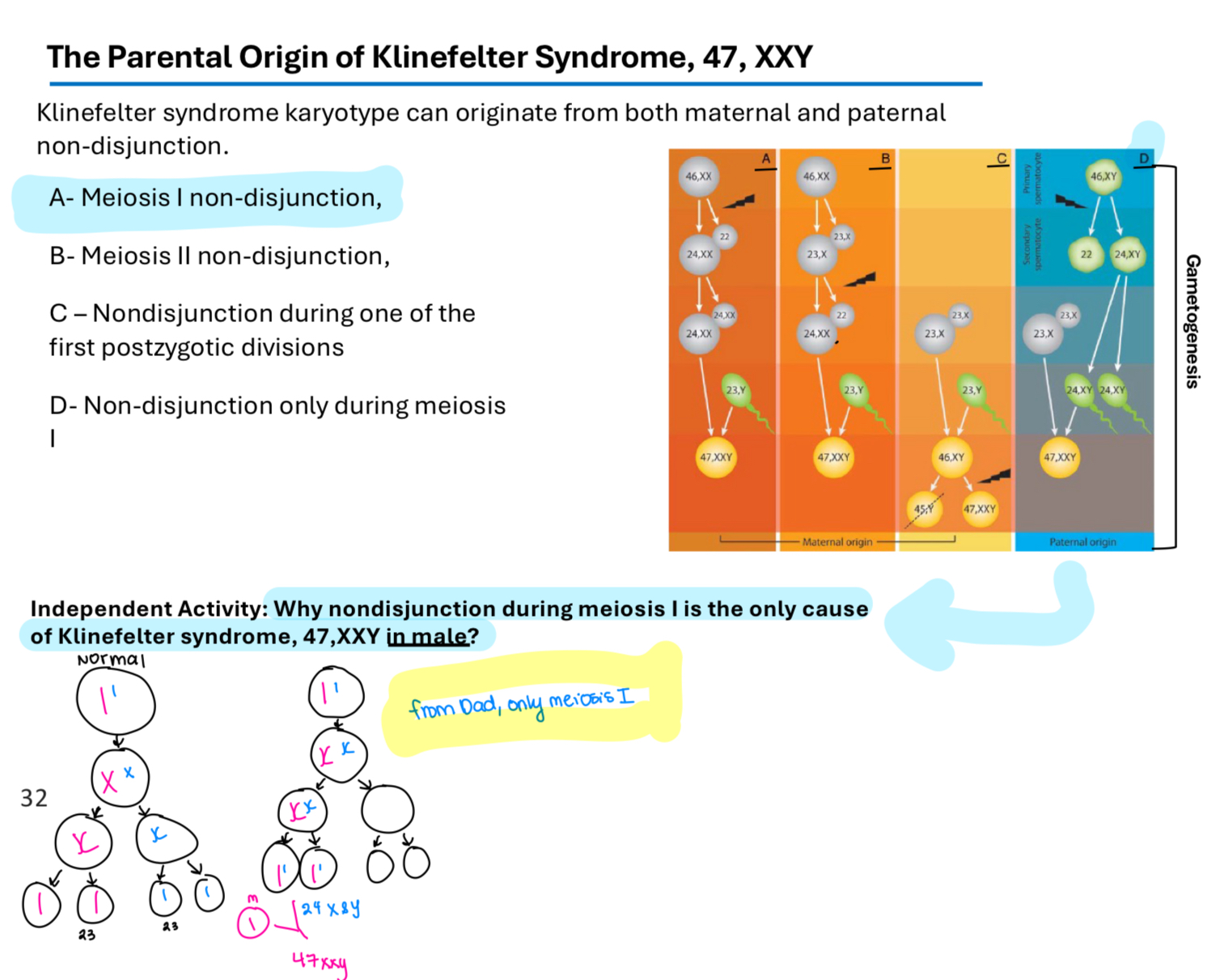
Klinefelter syndrome
A genetic condition in males caused by an extra X chromosome (trisomy) (47,XXY) leading to physical and cognitive developmental issues.
It is the first human sex chromosome abnormality to be reported the incidence is estimated to be between 1 in 500 and 1 in 1000 male neonates
Males with Klinefelter syndrome do not produce enough of the male hormone testosterone resulting in a lack of normal male sexual characteristics
Infertility
Klinefelter syndrome karyotype can originate from both maternal and paternal non-disjunction
Turner syndrome
A chromosomal disorder in females caused by the absence of one X chromosome (monosomy) (45,X), leading to various developmental issues.
Turner syndrome is the only chromosomal monosomy suyndrome compatible with live birth
Most conceptuses with 45,X karytoype miscarry
Uniparental Disomy (UPD), causes and the 2 types, 2 examples
Numerical abnormality, aneuploidy
A genetic condition where both copies of a chromosome pair come from one parent (a disomic gamete) , and no copies from the other parent (a nullisomic gamete).
UPD may occur with no apparent impact on the health and development of an individual. UPD can cause health concerns because of the effect of dosage imbalance.
Causes:
meitoic nondisjunction (failed separation of chromosomes during the formation of eggs or sperm, leading to gamete with an extra chromosome)
Mitotoic nondisjunction (similar error after fertilization, during cell division of the embryo)
Maternal UPD: both copies of chromosomes from mother
Paternal UPD: both copies of chromosomes from father
UPD can be
Isodisomy UPD: Inheritance of two identical copies of one parent’s chromosome
Heterodisomy UPD: inheritance of two different copies of the same chromosome from one parent
Examples of UPD
Angelman Syndrome (Paternal UPD, maternal chromosome 15 is missing/inactive)
Prader-Willi Syndrome (maternal UPD, paternal chromosome 15 is missing/inactive)

Mosaicism
A condition in which a single individual has two or more genetically different cell lines derived from a single zygote.
This type of mosaic is arises after fertilization and during the early cleavage stage of development.
Usually due to mitotic nondisjunction, post-zygotic nondisjunction

Triploidy and 2 types
(3n, 69)
accounts for roughly 20% of all chromosome abnormalities identified in spontaneous miscarriages. Survival rates is very small.
There are 2 types of Triploidy
Digynic Triploidy - occurs when an egg is a diploid egg (instead of a haploid like its supposed to be)
Diandric Triploidy - the most common cause of diandric triploidy is polyspermy, 2 sperms to 1 egg. Another case of occurrence is caused by a diploid sperm to a normal haploid egg.
Dosage effect and chromosome abnormalities
normal dosage = 2 copies
One copy deletion dosage = haplo-insufficiency
Three copies/duplication dosage - excess
Disomic Gametes
Gametes that contain two copies of a particular chromosome instead of one, leading to abnormal chromosomal distribution. (Normal is n=23)
N=24 chromosomes
Nullisomic Gametes
Gametes that lack both copies of a particular chromosome, resulting in a total absence of that chromosome in the resulting zygote. (Normal is n=23)
N=22 chromosomes
Risk of Nondisjunction
autosomal nondisjunction in oogenesis occurs at meiosis i and meiosis II, and it occurs far more frequently than in spermatogenesis.
Roughly 90% of nondisjunction are of maternal origin
Nondisjunction in Female: Maternal age risk
Duration of meiosis in female. Eggs that are produced at the age of 40 have been in meiosis I for more than 40 years. During this time the cell may be damaged and so Aneuploidy results when meiosis resumes at ovulation.
It could be the interaction between the embryo and the uterine environment.
Maternal selection: normally, the embryo-uterine interaction results in the spontaneous abortion of a chromosomally abnormal embryo. With age, maternal selection may become less effective, allowing more chromosomally abnormal embryos to implant and develop.
Down Syndrome
A chromosomal disorder caused by the presence of an extra copy of chromosome 21, leading to developmental delays, characteristic facial features, and a higher risk of congenital heart defects.
47, XY, +21 or 47,XX,+21
Nondisjunction Down syndrome- nondisjunction resulting in uniformed presence of an extra chromosome 21
Mosaicism Down syndrome- mosaicism seen in 2-4% of trisomy 21. The individuals have some normal somatic cells and some cells with trisomy 21. It is usually associated with milder clinical expression of the phenotype
Chromosomal abnormalities
Numerical abnormalities
Structural abnormalities