EMT HOSA TERMS
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/167
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
168 Terms
1
New cards
contraindication
reasons not use the medicine
2
New cards
aspirin
prevents the platelets in the blood from the clotting
3
New cards
boots and back braces
accessories that the EMT use while lifting the patient
4
New cards
actions in controlling airway
opening and securing
5
New cards
hypoperfusion
inadequate supply of oxygen, glucose and other nutrients
6
New cards
examples of PPE
glowes, mask(pocket mask, respirator),isolation gown, goggles or face shield
7
New cards
basic skills for EMT (IAVB)
Infection control, airway control, ventilation, bleeding control
8
New cards
parenteral (pe-teran-tral)
inhalation and injection of medicine
9
New cards
6 emergency way to carry a patient
rescuer assist,pack strap, cradle carry, the firefighter carry, seat carry, chair carry
10
New cards
rescuer assist -
rescuer is carrying the patient, helping the patient walk

11
New cards
pocket strap
used to carry patient who is consious or unconsious for meetable distance

12
New cards
cradle carry
used especially for childrens

13
New cards
the firefighter carry

14
New cards
seat carry
15
New cards
chair carry
16
New cards
oropharyngeal
it is plastic molded device used to keep the tongue off the mouth
17
New cards
blood pressure readings
diastolic and systolic
18
New cards
**systolic**
it is **highest** level of pressure in the arteries when the heart pumps and pumps blood out of the body, it is an indicator that the heart is exerting pressure to pump blood throughout the circulatory system.
it is the sign that the heart is working harder and can be the sign of hypertension
pressure in the arteries during the contraction phase
it is the sign that the heart is working harder and can be the sign of hypertension
pressure in the arteries during the contraction phase
19
New cards
diastolic
It is the lowest level of pressure in the arteries when the heart is at rest between beats. it indicates that the resistance of blood flow through out of the circulatory system
a high diastolic blood pressure indicates that blood vessels are stiffened or narrowed, it increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, or other health problems
a high diastolic blood pressure indicates that blood vessels are stiffened or narrowed, it increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, or other health problems
20
New cards
a normal blood pressure reading is 120/80mmHg
120- systolic
80 -diastolic
80 -diastolic
21
New cards
highest diastolic pressure that the arteries can reach is
110mm Hg
22
New cards
on-line medical control
the doctor is with the patient in the EMT spot
23
New cards
neurogenic **s**hock- it is ==trauma==
vessels dilated losing pressure and ability to pump against gravity. spinal cord injury causes neurogenic shock. nerves in the spinal cord are damaged and could be able send messages to the nerves that control other functions of the body
shock -
s- spinal cord
shock -
s- spinal cord
24
New cards
extrinsic diseases
the diseases that are contagious and able to spread
25
New cards
bronchodilators
increasing airflow by increasing bronchioles diameter
26
New cards
bronchiolitis -
is the common lung infection that is often seen in the children, infants. irritation, swelling, mucus developing in the small airways. these small airways are called as bronchioles. it is starts with a common symptom common cold and it is caused by a virus
27
New cards
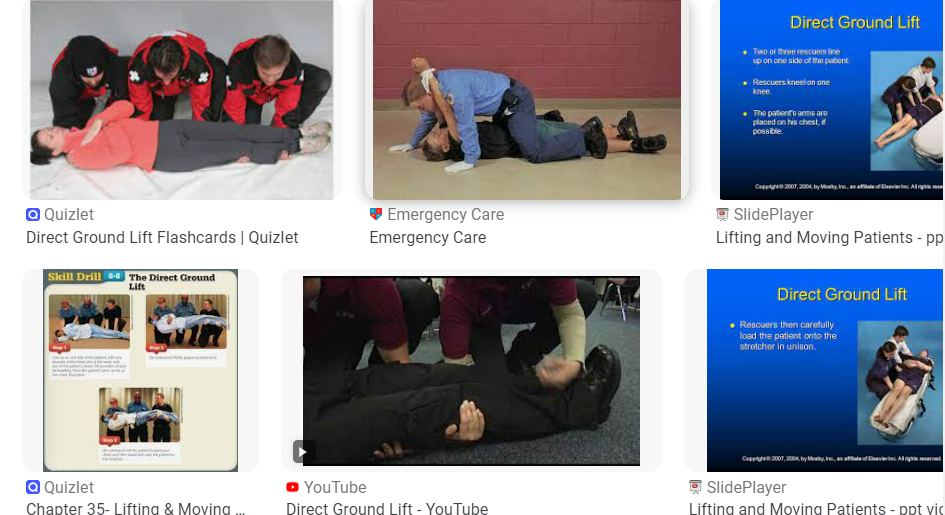
direct lift
from floor to the bed
\
\
\
\
28
New cards
discs
shock absorbers in the back that are painful
29
New cards
\
what do you administer if there is respiratory difficulty or patient suspected to be in shock, had stroke or seizure
what do you administer if there is respiratory difficulty or patient suspected to be in shock, had stroke or seizure
oxygen
30
New cards
vector
an living organism that transmit disease from the infected animal to human or animal
31
New cards
crowing
sound that occur when the muscles around the ***larynx spasm***
32
New cards
auscultation
the act of listening
33
New cards
vital signs
the signs that should be repeated every 10-15 minutes
34
New cards
snoring
tongue block the airway
35
New cards
septic shock
caused by a infection that results in dilated blood vessels
36
New cards
EMT’s should be able to lift at least
125 lbs- 56kg
37
New cards
signs of shock
tachycardia, tachypnea, thirst, nausea confusion, cool and pale skin
38
New cards
questions when handling medication
right medication?right patient?right route?right date? right dose?
39
New cards
tracheostomy and stoma
holes that are created surgically and used to create airways
40
New cards
normal breathing rate (adult)
12-20bpm
41
New cards
normal breathing rate (child)
15-30bpm
42
New cards
normal breathing rate(infant)
25-50bpm
43
New cards
sequence for basic airway control
open, asses, suction, secure
44
New cards
OPQRST
O- Onset- what were you doing when this happen
P- provokes? triggers?
Q- quality of discomfort ? how you feeling nausea, vomiting, headache
R- radiation - does it spread to other place ; where did the pain start
S- signs and symptoms
T- time - when did it start
P- provokes? triggers?
Q- quality of discomfort ? how you feeling nausea, vomiting, headache
R- radiation - does it spread to other place ; where did the pain start
S- signs and symptoms
T- time - when did it start
45
New cards
SAMPLE
signs and symptoms
allergies
medications
past medical history
last oral intake
event leading to the illness
allergies
medications
past medical history
last oral intake
event leading to the illness
46
New cards
cardiogenic shock
due to the inadequate pumping of the heart
47
New cards
neurological, brain and eye alters
pupil dilation
48
New cards
***pro***phylaxis
pro- advanced
pro- advanced
action taken to prevent exposure to the disease
49
New cards
treatment of shock
reduce heat loss, control bleeding, oxygenation
50
New cards
reassesment
procedure for detecting changes in the patient’s condition
51
New cards
steps for reassessment
1. primary assessment
2. reassess
3. record vital signs
4. **repeat pertinent part of the history and physical exam**
5. check interventions
52
New cards
interventions
A procedure taken to prevent disease, treat disease and improve health in other ways
53
New cards
enteral
ingestion(absorption) of medication
54
New cards
nitroglycerin - vasodilatory drug
dilates blood vessel and reduce blood pressure, help for anginal chest pain, can be used during heart attack
55
New cards
anaphylaxis
exposure to the severe allergic reactions
in medical terms an means away
in medical terms an means away
56
New cards
epinephrine
constricts blood vessels, dilated airway, stimulate fight or flight reaction, used to treat extreme allergies
57
New cards
pulse rate is also known as heart rate (adults)
60-100bpm
58
New cards
normal pulse rate for new born baby (0-1 month)
70-190 beats per minute
59
New cards
infants normal pulse rate
80-160 bpm
60
New cards
children 3-4 years
80- 120 bpm
61
New cards
children 5-6
75-115bpm
62
New cards
children 7-9
70-110bpm
63
New cards
four emergency ways to carry a patient **CBAF**
clothing
blanket
arm
firefighters
blanket
arm
firefighters
64
New cards
cricoid pressure
should not use during cardiac arrest, used in endo intubation tracheal to reduce the risk of regurgitation in simple words
65
New cards
what can determine an obstruction of the airway
abnormal sounds
66
New cards
compression rate
100 compressions per min
67
New cards
HOW TO DO CPR
1. first give 30 compressions(5 cycles of 30 compressions)
2. give breaths by tin lift and place your mouth over the persons mouth
3. two breaths or for 2 minutes
68
New cards
braxton hicks contractions
irregular pre-labor contractions of the uterus
69
New cards
placenta previa
the placenta is formed in the abnormal location which will not allow for normal delivery of the fetus. causes excessive amount of bleeding during pre-birth
70
New cards
placenta
the organ that is formed in the uterus during pregnancy
71
New cards
==***pre***==eclampsia
a complication of pregnancy where the women retains large amounts of fluids and hypertension. sometimes experience coma or seizure which is every risk for the infant
72
New cards
premature infant
any newborn weighing 5’1/2 pounds and born before 37th week of pregnancy
73
New cards
amount of blood in adult
1\.2 -1.5 gallons and 5 liters of blood
74
New cards
***amount of blood in children who weighs* ==*80 pounds*==**
**2650** ml, approximately **2** litters of blood**; 0.5** gallons
75
New cards
amount of blood in baby who weighs 8 pounds
0\.7 gallons, 270ml, 0.264 liters, 0.3 liters
76
New cards
amount of blood in newborn
0\.075 liters, 75 ml
77
New cards
AVPU
alert, voice, pain, unresponsiveness
78
New cards
hypoxia
inadequate supply of oxygen to the body tissues to maintain homeostasis
symptoms include:
confusion
blueish skin
restlessness
difficulty breathing
symptoms include:
confusion
blueish skin
restlessness
difficulty breathing
79
New cards
diaphoretic
induced perspiration or in simples words more sweating
80
New cards
avulsion
force-fully tearing of the skin or other parts of the body
81
New cards
**hematoma**
pool of clotted blood in an organ or tissue. it caused by broken blood vessels by surgery or injury. can occur anywhere in the body including the brain
82
New cards
vasculitis
Inflamation of the blood vessel
83
New cards
phl*e*bo
v***e***in
84
New cards
cephalo
relating to head or skull
\
\
85
New cards
entero
intestines
86
New cards
PCR
patient care report
87
New cards
dilated pupil
may indicate blood loss, drugs, prescription, eye-drop
88
New cards
constricted pupils
miosis refers to small or constricted pupils, the muscles of the iris will tighten around the pupil
89
New cards
pupil -
the black colored middle part of the eye, inside iris
90
New cards
iris
colored part of the eye
91
New cards
unequal pupil
anisocoria, stroke, head injury, artificial eye, prescription eyedrops
92
New cards
lack of reactivity in the pupils
injury or compression of the third cranial nerve and upper brain stem, due to lack of brain supply to the brain
93
New cards
the area where the patient indicated was hurting
where do you palpate last
94
New cards
palpate
the doctor is touching the patient for medical purposes
95
New cards
jaundice
yellowish tinge of the skin, breakdown in the red blood cells
96
New cards
renal failure
occurs when the kidneys lose their ability to filter the blood and remove toxins in excess fluid from the body
97
New cards
dialysis
the process which the blood is filtered and removed toxins by the a machine. treatment for renal/kidney failure
98
New cards
shunt
the passage that allows the blood or other bodily fluids to move from the one part of the body to the other
drainage that runs from the brain to the abdomen to relieve excess CSF cerebrospinal fluid
drainage that runs from the brain to the abdomen to relieve excess CSF cerebrospinal fluid
99
New cards
perfusion
supply of oxygen to and removal of waste from the body cells and tissues as a result of blood flowing through the capillaries
100
New cards
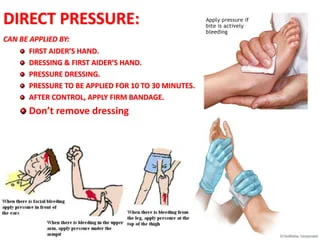
most common and effective way to control bleeding
direct pressure