Cell Structure and Regulation of Phenotype
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Describe the plasma membrane
It is surrounded by a lipid bi-layer and proteins regulate what enters and exits the cell
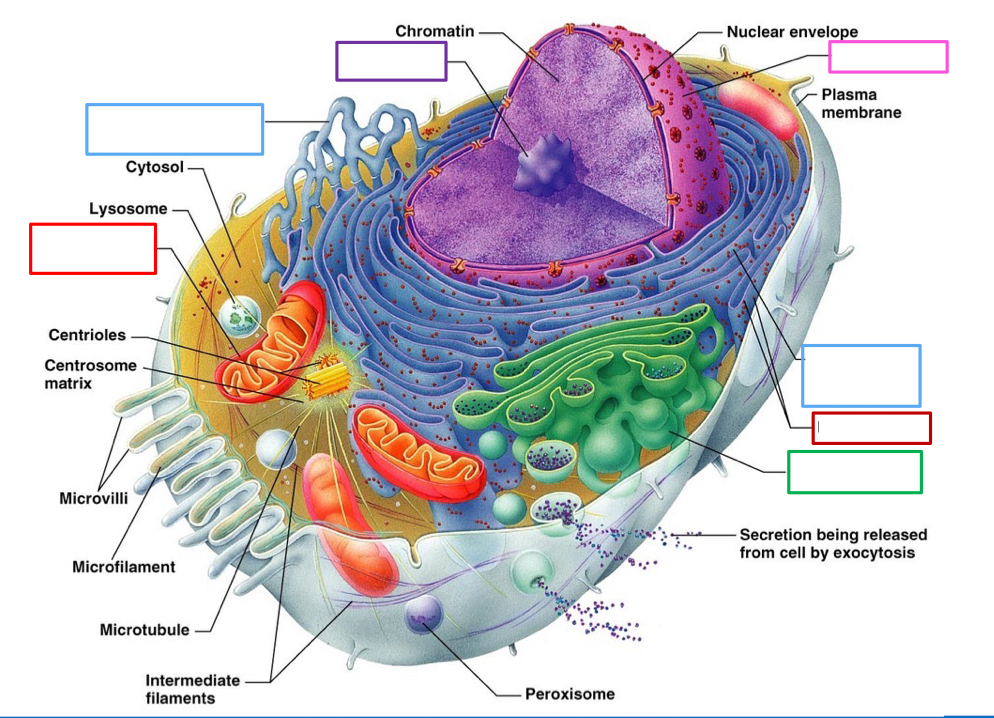
What is the pink box pointing to describe its function
Nucleus- carry 99% of genetic DNA
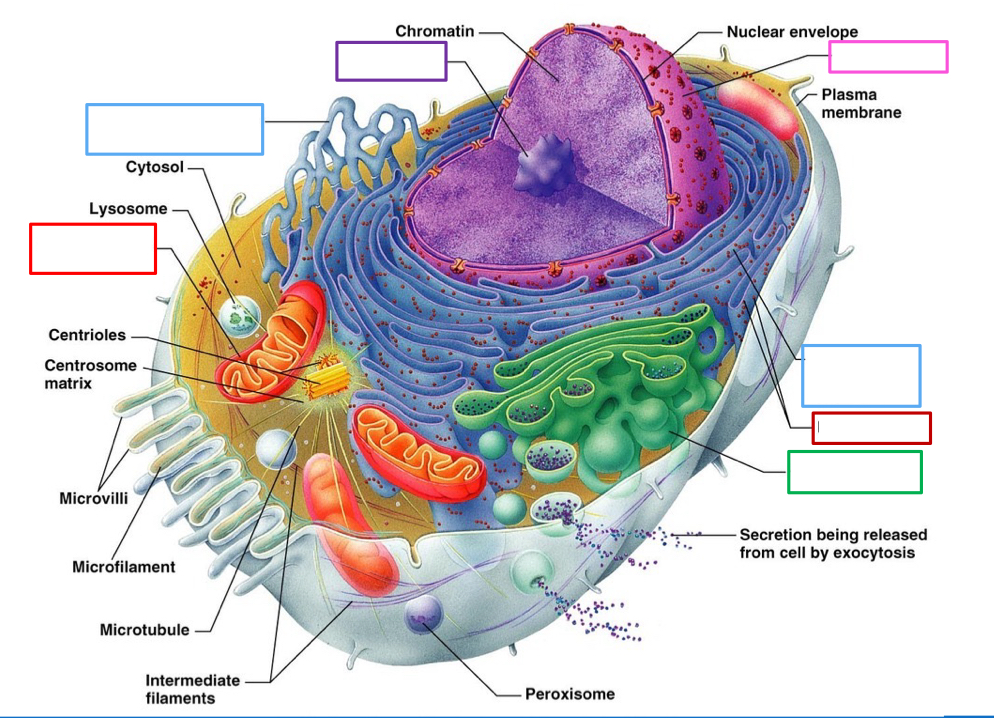
What organelle is the blue box on the right point to and what’s its function
Rough Endoplasmic reticulum- protein synthesis
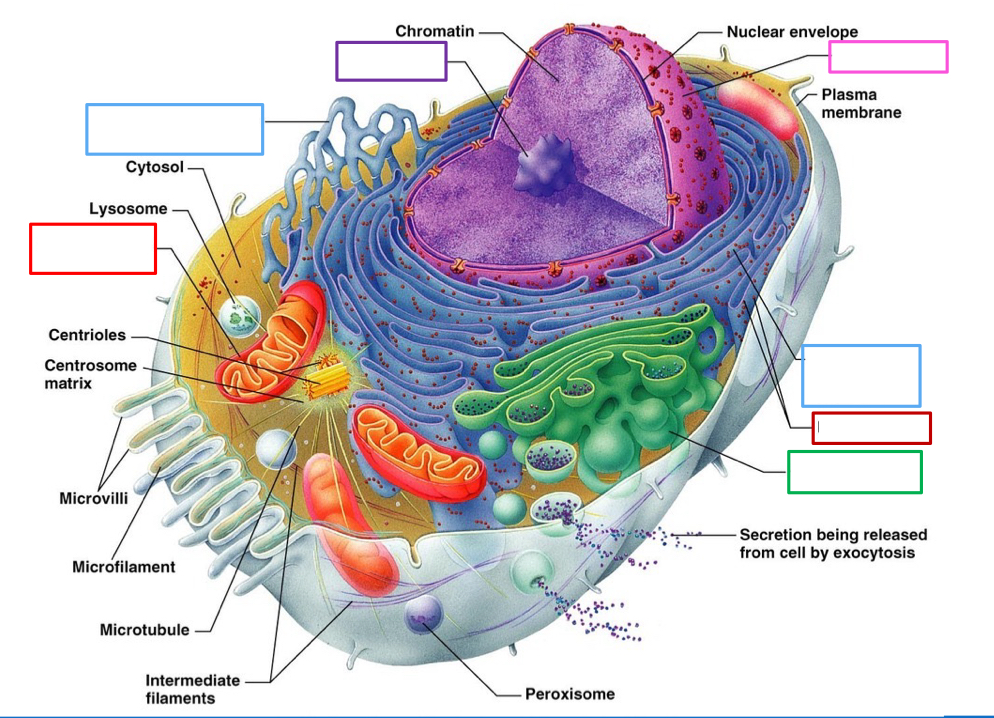
What organelle is the red box on the right point to and what’s its function
Ribosome- synthesize protein via making amino acids into peptide chains
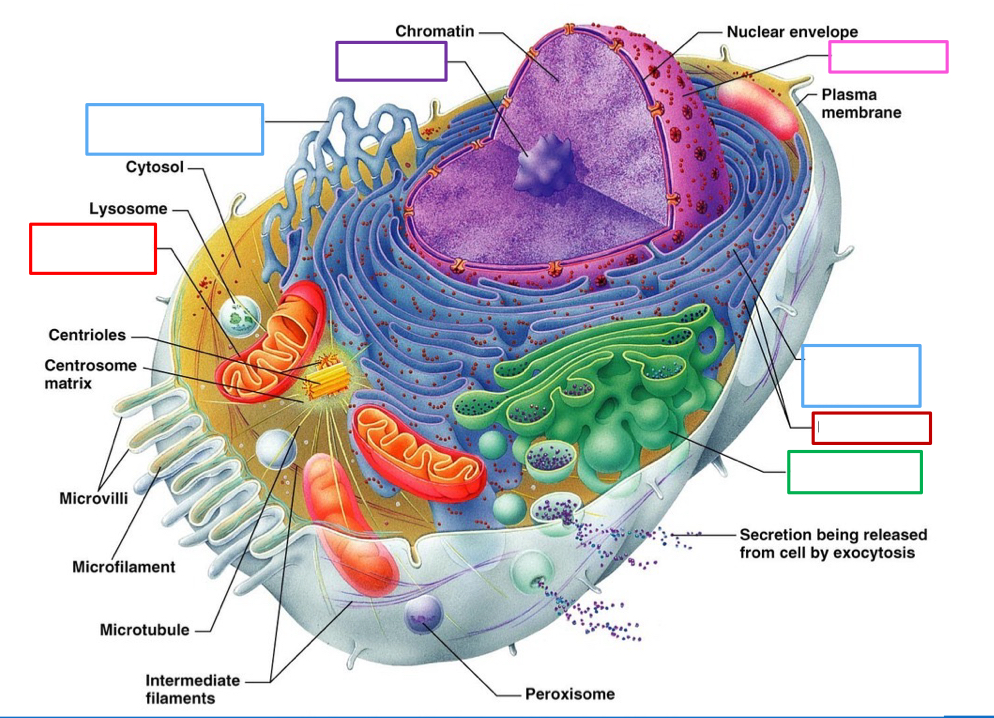
What organelle is the green box pointing to and what’s its function?
Golgi Apparatus
further folds proteins from the neoplasm in recticulum and send it out
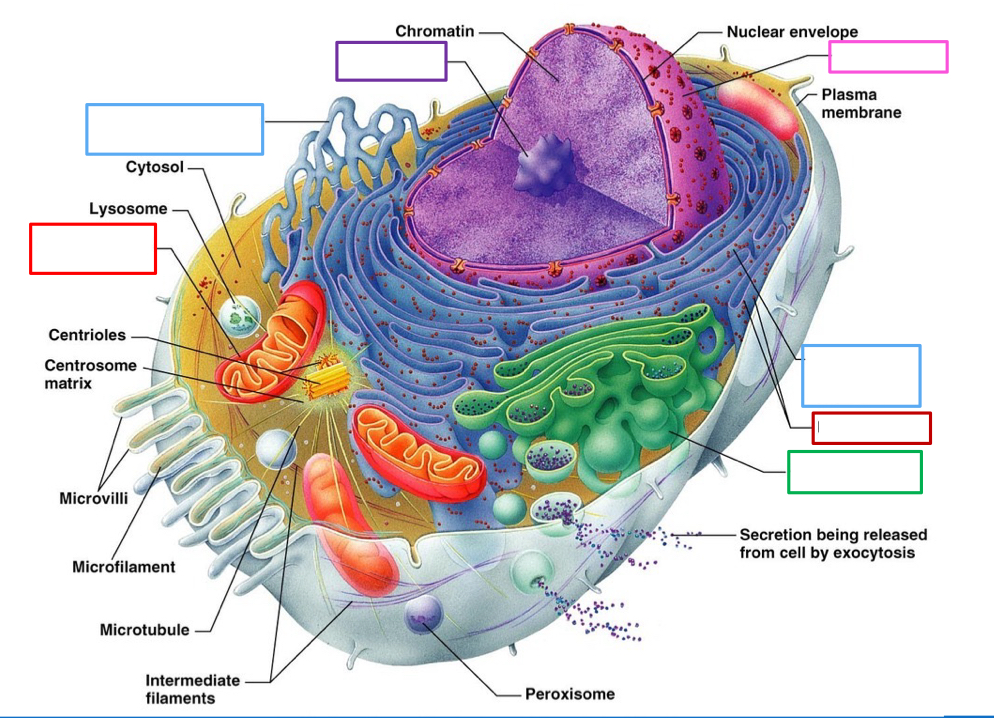
What is the purple box pointing to and what’s its function?
Nucleolus assembles ribosomes
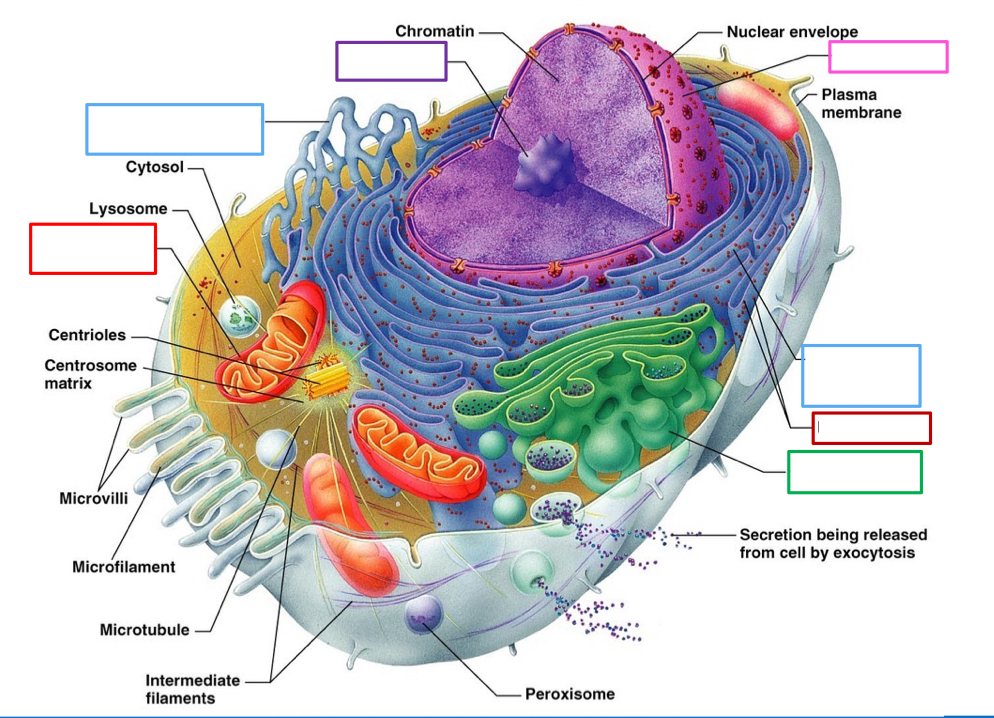
What organelle is the blue box on the left point to and what’s its function
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum- lipid synthesis
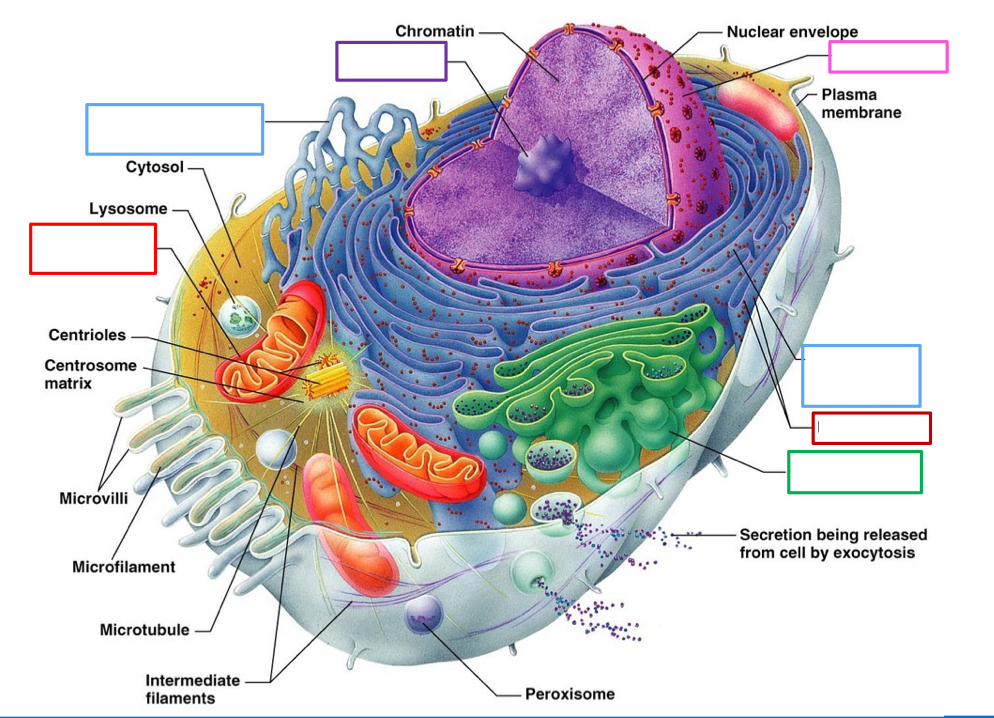
What organelle is the red box on the left point to and what’s its function
Mitochondria- produces ATP and encodes 13 protein, 1% of genetic DNA
T/F organelles are static and don’t move
False they are dynamic and “dance”
What is the function of a lysosome?
Eats cells and recycles the material to form new cells
What drives cell movement
The cytoskeleton
What is the cytoskeleton?
A network of filaments and tubules in a cell
What are the 3 major components of a cytoskeleton?
Intermediate filament, microtubule, actin filament
What are the 6 chemical composition of a cell and what’s its are examples of each
Nucleotides- DNA, RNA, ATP
protein- enzymes, cytoskeleton
Lipids- tricylcerides, phospholipids, cholesterol
Water
Inorganish- calcium, magnesium sodium, etc.
What is a central dogma
It describes the flow of genetic information
Describe the central dogma of molecular biology
Start with the genome (DNA), which is transcipted into the transcriptome (RNA), then translated into a proteome (protein) then lastly becomes a metabolome( metabolite ex: amino acids, sugars, lipids) all of which gives us a phenotype
Describe chromatin
It packages DNA to fit in the nucleus and controls replication and gene expression
Describe what a chromosome is and what it is composed of
What are the 3 different gene sequence variations
Single-nucleotide polymorphism
Copy number variations
Quantitative trait loci
What is a single nucleotide polymorphism?
It is a gene sequence variant where only nucleotide in a gene is either silent or expressed associated with developmental disease
What is a copy number variations in gene sequence variants?
Additional or loss of longer segments of genomic DNA via chromosomal rearrangement Associated with developmental disease
Describe what a quantitative trait loci is in gene sequence variants
Genetic variation linked to a quantitative trait ex milk or meat production
give an example of a single nucleotide polymorphism and how it affects an animal
polysaccharide storage myopathy (PSSM) - a muscle disease in quarter horses, it is an overactivation of an enzyme via GYS1 gene this causes too much glycogen storage and thus not enough glucose to support muscle movement via ATP.
what is an epigenetic modification?
It is a modification of the DNA from environmental factors. it does NOT change the DNa seq. but instead is a modification to the DNA or histones before transcription and IS reversaible
What are the 4 types of phenotype regulation?
Transcriptional
Post-Transcriptional
Translational
Post-Translational
describe the the role of Transcription as it relates to phenotype control
Regulates which genes are transcribed or the rate at which transcription occurs
Describe the the role of Post-Transcription as it relates to phenotype control
Pre-mRNA undergoes RNA processing which then becomes mRNA. and the mRNA undergoes changes in nucleus before translation occurs. intron are removed and exons are spliced together.
Describe the the role of Translation as it relates to phenotype control
after the mRNA is in the cytoplasm translation determines how fast mRNA is translated into proteins. it also determines the length of time for mRNA activation and speed of degradation
Describe the the role of Post-Translation as it relates to phenotype control
it is the further processing to make the polypeptide function via cleavage and/or modification. their are also other control mechanism that determine how long it takes for a protein to become active and how long it stays active for.
Give an example of a non-coding RNA
microRNA (miRNA) it is about 22 nucleotides long and is important for repressing gene expression. This can be achieved through blocking translation, as well as destabilizing and clevaning mRNA.
what is the maternal role in expressing phenotypes when it comes to the callipyge sheep?
maternal expression of gene regulates the paternal expression via silencing.
what does the amino acid sequence determine?
1) the shape and 3D structure
2) function
3) how the protein will assemble with other proteins
why is protein degradation helpful?
it removes damaged proteins, controls how active other proteins are, and recycles amino acids to form other proteins or as energy.
what does epigenetics modify?
Histone proteins and DNA