Photosynthesis exam 3
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
what is the opposite of photo synthesis?
Give formulas for both
Cell respiration: C6H12O6 + 6O2+6CO2+ 6H20 + (~29)ATP
6CO2+6H2O (light ) —>C6H12O6
Site that all parts of photosynthesis in plants occur and other photosynthetic eukaryotes. And what is the significant structure of this
Chloroplasts, 3 membranes - innermost membrane
what does Chloroplasts form (flattened structures) and whats the fucntion. whats the stack of these called.
Thylakoids, high surface area and it houses important enzymes. Granum is tack of thylakoids.
In chloroplasts, what is the space caled that is between thylakoid membrane and the middle “inner membrane”
Stroma
Part of thylakoid membrane that absorb certain wavelengths of light? What happen to the other wavelength?
Pigments, wavelength. Reflected or transmitted
Why are plants green?
What colors are absorbed in photosynthesis?
Because that is the color tnot used in photosynthesis
mostly violet and blue and red light absorbed
What are two main forms of photosynthetic pigments? And what do they differ?
Chlorophylls: absorb purple and blue and red light. Appear green. Action spectrum closely follows so it is most directly involved in photosynthesis.
Carotenoids: absorb blue, green, and it appear yellow or orange: Carotenes and xanthophylls. Ex) carrots, fall leaves, orange yolks and red birds.
They dIffer in structure, absorption spectrum and main function.
__is not as directly involved in photosynthesis but still vital.
Carotenoids
Functions of carotenoid?
• Some herbicides stop carotenoid synthesis → lose chlorophyll →
turn white/die.
• Protect plant from free radicals
• (higher energy UV light can knock electrons out of atoms)
• creates chain reactions if not stopped
• antioxidants (stop free
radical damage cycle)
• Antioxidant-rich foods?
• it absorb wavelengths
chlorophylls can’t; pass
energy to chlorophylls
Photosynthesis has two stages
1st stage (light-capturing
reactions): light energy harnessed
to produce chemical energy
• In process: H2O → O2
• 2nd stage (Calvin cycle): takes that
chemical energy and produces
2nd form of chemical energy
• (now in bonds of a carb.)
• carbons come from CO2
• In process: regenerates energy
carriers for 1st stage
• Like the ETC and first three
stages of cell respiration,
regeneration of carriers is key –
everything stops without this
How does chlorophyll absorb energy?
A excited election has high potential energy. Photons of light excited electron when absorbed by chlorophyll. It is only absrobed in certain ranges.
Why chlorophyll doesnt absorb green well?
UV rejects it. Infarared too little
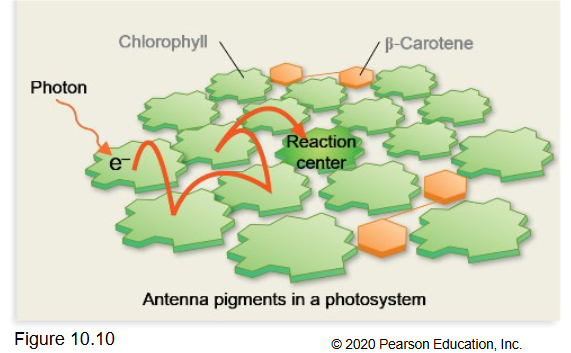
In the thylakoid membrane, chlorophyll molecules are not isolated.
They are arranged in groups called____.Each photosystem has_____
Most form light gathering ___.
and then reaction center
photosystems, 200–300+ pigment molecule, antenna
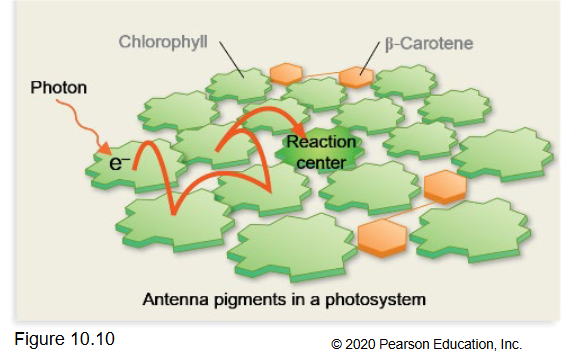
Reaction Center.
Once energy reaches reaction center, absorbed by
pair of chlorophylls that transfer e - to electron carrier
• Key transformation: now light energy—→ ____
chemical energy
Does ATP leave the chloroplast? Why?
No, • Inner/middle membrane of chloroplast are
impermeable to ATP and
NADPH
Calvin cycle take ___
from CO2 and ____ from
ATP/NADPH to produce __
Carbons, Energy, G3P (glyceraldehyde-3-
phosphate)
What macromolecules can G3P be used to create?
-Sucrose when photosynthesis is slow (Sucrose is how sugar is transported between plant cells (similar to glucose transport in blood)
-Starch when rapid (temporary storage in
chloroplast
Where are all three phases of Calvin Cycle?
CO2 is fixed to —- immediately spkits into —-
Where does energy come from, and what do they form also where do they end up?
Stroma
• Fixation of Carbon dioxide- CO2 “fixed” to 5-carbon sugar(RuBp), immediately splits into 2 3-carbon sugars(3PGA). (one carbon is addedfrom 2CO2)
• Reduction of 3PGA to G3P- Energy comes in via 6 ATP and 6NADPH to form 1G3P, some leaves cycle
• Regeneration of RuBP and G3P Most G3P continues cycle to reform 5-carbon sugar (RuBp) 3 ATP used
What is the initial enzyme that catalyze fixation of CO2 to the 5- carbon sugar is called?
Rubisco
Most common enzyme on Earth
Rubisco
Whats the problem with Rubisco’s active site?
O2 and CO2 can both bind to rubisco’s active sites
What happens if O2 binds to Rubisco instead of CO2
Photorespiration occurs instead of photosynthesis and it is inefficient because it uses energy and releases CO2 and no sugar produced.
Why the most problematic situation for plants in hot/dry environments?
Hot/ Dry environments makes plants close their stomata (pores that allow CO2 and O2 in and out). , So inside the leaf the O2 increase while CO2 decrease since O2 from photosynthesis and CO2 cant enter into leaf because it usually gets them from air. So Rubisco start binding to increased O2 instead of CO2 and the PHOTORESPIRATION occurs
How does some plants get around with dry and hot situation that ends up with high photorespiration?
1) Carbon fixation from Calvin cycle.
2) attach CO2 to a 3 carbon compound to store, then release CO2 as needed.
3) C4 plants (corn) - spatially separated from Calvin cycle
CAM plants (cacti)- temporally separated. opening stomata at night and during the dat its closed it stil do photosynthesis during the day, just stockpiling CO2 at night.
where does light capturing reaction happen
thylakoid membrane
where does calvin cycle happen
stroma
which one occur first photosystem 1 or 2
2
what happens in Photosystem 2 and 1
Photosystem 2- 4 photons go through reaction center, electron transfered to an ETC with pheophytinPQ. ATP produced using ETC.
photosystem 1- 4 photons through reaction center, electron tansfer to form NADPH with Ferredoxin. does not use H+ gradient, no ATP produced, it produce NADPH.
where is proton gradient in light capturing reactions?
thylak
where does photosynthesis happen
chloroplast
what is photophosphorylation?
production of ATP in Thylakoid membrane (light capturing reaction.)
what happens to eectron that is missing from the ractioncenter? in light capturing reaction in thylakoid membrane.
Replaced by electron from water.
Splitting of water forms ___ and add ___
O2and H+ gradient
what happens to and exra electron at the end of ETC in light capturing reaction?
transferred to photosystem 1
Zschemee- difference in energy difference compared to mitochondiral ETC
Mito- final e acceptor O2 has lower energy than NADH.
Chloro- final acceptor NADPH e donor is higher in energy in water
They can pass on this energy to other nearby pigment molecules by exciting an
electron of that adjacent molecule
• They do not pass the electrons to the next pigment, however. The excited
electron merely goes back to its ground state when the energy has been
passed on
true
In photosystems, this energy is passed via ____ from pigment molecule to
pigment molecule until it reaches the reaction cente
resonance
inputs and Outputs of Calvin Cycle
Inputs: 3 CO₂, 9 ATP, 6 NADPH
Outputs: 1G3P, 9 ADP, 6 NADP⁺