IB Business - Operations Management
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Define Operations Management
provision of goods and services in the right quantities and quality in a cost effective and timely manner
- turn inputs into outputs
what are the five m's
- useful for making marketing and production plans
- materials
- money
- manpower
- machines
- management
how does production affect marketing
- production methods affect the quality of the product
- high quality products can be marketed at high prices
how does production affect HR
- size of workforce
- training and development
- recruitment and selection of different skills
how does production affect finance
- capital investment
- investment appraisal
- contingency funds for emergencies
define efficiency
maximise output with min costs per unit of output
define productivity
the rate at which businesses transform inputs into outputs
- used to measure efficiency
define job production
individual product, tailor made, one-off items ex. wedding dresses
adv and dis of job production
a - high quality
- usp
- flexibility and customization
d - time consuming, labour intensive
- few eos
define batch production
producing a limited number of identical products
- each batch is fully completed before switching to a new batch
ex. bakeries, shoes in diff sizes
adv and dis of batch production
a - economies of scale
- specialization, increased productivity
- higher sales
- can still be tailored
d - inflexible
- storage costs
- repetitive work
- equipment costs
define mass production
- large amts of standardized product
- assembly of individual components
define flow production
like mass production but more continous using automated systems
adv and dis of mass/flow production
a - large scale output
- eos
- standardized quality
- low labour costs
d - low levels of motivation, boredome
- breakdowns cause major issues
- capital intensive
- lot of storage
3 factors to consider when selecting an appropriate method
- cost of capital and labour
- size of market
- corporate objectives
define labour intensive production
- greater proportion of labour
- personalized services
ex. healthcare, farming
define capital intensive production
high proportion of capital costs compared to labour costs
- no usp
define mass customization
large quantities are produced using batch, mass and flow but still can be tailored
ex. custom shoes
define location
refers to the geographical position of a business
name the 6 quantitative factors for location decisions
- cost and availability of land
- same w/ labour
- proximity to customers
- same w/ raw materials
- gov incentives
- e-commerce
name the 7 qualitative factors for location decisions
- management preferences (personal)
- local knowledge
- infrastructure (communication, transportation and support networks)
- political stability
ethical issues
- clustering (clos to other related businesses)
- gov restrictions
- economic freedom
define reorganizing production
- taking adv of the best thar locations nationally and internationally have to offer
define outsourcing
moving to another company
- production and services outsourcing
adv and dis of outsourcing and offshoring
a - better quality
- reduced production costs
- reduced labour costs
- flexibility
- develop struggling economies
d - can be worse quality
- quality management is difficult
- culture clashes
reason for insourcing
to improve quality in-house
reasons for reshoring
close supervision and quality of output
- bring jobs back to economies
- rising transportation costs
limits of relocating
- relocation costs
- low morale
- damage to corporate image
define break-even analysis
- firm does not make a profit or loss
formula for unit contribution
selling price - variable cost
formula for break even quantity
fixed cost / unit contribution
total revenue
Price x Quantity
total costs
fixed costs (variable costs x quantity)
break even point
tr = tc
profit or loss
tr - tc
margin of safety
level of demand - break even quantity
target profit quantity
(Fixed cost + target profit) / (Price - variable cost per unit)
define contribution
money left after costs have been taken away from revenue (paying for costs)
unit contribution vs total contribution
uc
- proportion price per unit of output going towards paying off total fixed costs
tc
- output needed to pay off
purpose of contribution analysis
- Determine pricing strategies
- Prioritise products in their portfolio
- Decide on whether to make or buy in products
- Perform break-even analysis
break even chart
A graphic presentation of the break-even analysis that shows when total revenue and total cost intersect to identify profit or loss
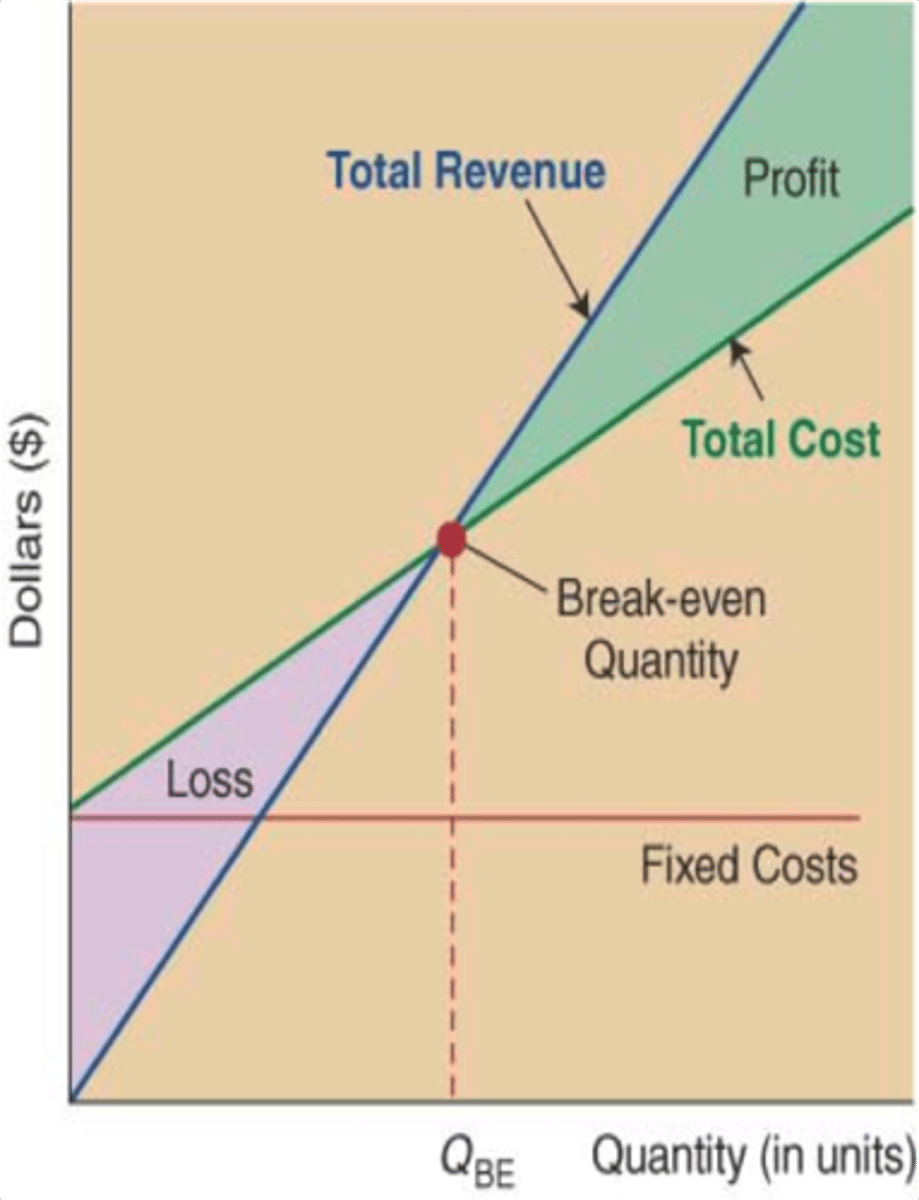
what is the margin of safety
measures the amt of demand for a product and how much it exceeds the BEP
causes of changes in break even
- external factors
- level of risk (more risk higher BEP)
- innovation
- trends
dis of BEP
- assumes revenue and costs are linear
- not useful for a dynamic business env
- useful for single product