Horticulture Exam 2
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
Photosynthetically active radiation (PAR)
Light spectrum plants can see
Sun loving plants
Evolved to grow in areas of high light —> might survive in shade but will likely display light seeking behavior
Etiolation
Classic light seeking behavior —> leggy plants that look tall and stretched (internodal stretching) and pale
Heliotropism
Light seeking behavior where plants stretch and turn towards light
Phytochrome
Photoreceptor that detects changes in R:Fr
R:Fr
Red light : Far red light
Pfr
Active form of phytochrome —> inhibits internodal stretching, causes leaf and chloroplast development
Pr
Inactive form of phytochrome
Shade loving plants
Evolved in areas with more continuous shade —> thin and broad leaves to maximize photosynthesis, less sensitive to R:Fr
Abscisic acid (ABA)
Plant hormone responsible for water conservation —> when root tips detect soil dryness they produce more ABA, signals stomata to close
Temporary wilt (aka “Sun wilt”)
Caused by a plant losing water by rapid transpiration on a hot, dry day (not soil dryness) —> will recover overnight when stomata close
Permanent wilt
Caused by low levels of water in the soil
Drought
Prolonged period of low rainfall leading to a shortage of water —> may occur randomly, seasonally, or semi-permanently depending on location
Drought avoidance
Mechanism that some plants have evolved to withstand drought conditions by avoiding them
4 major types of drought avoidance
1) Germination inhibition —> seeds are coated with water soluble germination inhibitor hormone, water must wash away coating
2) Geophytes —> go dormant and lose all above ground foliage after blooming, avoid losing water via transpiration during drought
3) Succulents —> store water in stems and leaves, shallow roots
4) Deep roots —> allow plants to harvest deep ground water reservoirs
Drought tolerance
Mechanism that some plants have evolved to withstand drought conditions —> can endure more water stress in their cells than other plants
6 drought tolerance adaptations
1) Sunken stomata
2) Reflective leaves
3) Small leaves
4) Leaf hairs (trichomes)
5) Ability to shed leaves during times of drought
6) C4 and CAM photosynthesis
C4 and CAM photosynthesis
Adapted by drought tolerant plants that cannot rely on their stomata being open during the day because of the risks of transpirational water loss —> use other means of harvesting CO2 for photosynthesis
PEP carboxylase
Important enzyme that catalyzes carbon fixation in C4 and CAM photosynthesis
C4 photosynthesis
Open and close stomata throughout the day depending on rate of water loss (common in monocot crops) —> CO2 captured by PEP carboxylase in mesophyll and fixed into 4 carbon chain
CAM (Crassulacean Acid Metabolism) photosynthesis
Stomata closed during the day and open at night (common in succulents), think waxy cuticle helps withstand high temperatures (no transpiration to cool during day) —> CO2 collected at night, fixed by PEP carboxylase into malic acid and accumulated in vacuoles, malic acid is broken down to create CO2 during the day
Halophytes
Plants that have adapted to tolerate salt water —> some have specialized glands on their roots filter salt out of water, others store excess salt in vacuoles or secrete it from specialized glands on leaves
Aerenchyma
Specialized tissue made up of long interconnected gas-filled spaces that span from shoot to root —> plants with roots in aqueous/low oxygen soil harvest atmospheric gas via stomata and shuttle oxygen to their roots through aerenchyma
Aquatic plants
Plants that have evolved several strategies for growing in aqueous environments —> most have stomata on top surface of leaves (not undersides), some have gas filled sacs that allow them to float on water’s surface, some have long petioles that stretch so leaves float atop water, some have no stomata (submerged, harvest gas using specialized glands)
Pest
any organism that is undesirable in a gardener’s environment —> subjective
Pesticide
Catch-all term for chemical used to eradicate a pest
Herbicide
Chemical treatment to kill weeds
Insecticide
Chemical treatment to kill insects
Acaricide
Chemical treatment to kill spiders and spider mites
Fungicide
Chemical treatment to kill fungal pathogens
Ovicide
Chemical treatment to kill the eggs of insects and mites
Pathogen
Fungal, bacterial, or viral disease
Pest insect
Cause plant damage by feeding on the sap, leaves, stems, roots, flowers, or pollen
4 invasive characteristics of pest insects
1) Rapid reproduction
2) Complex lifecycle makes it hard to eradicate at all life stages at once
3) Most are small, fast, experts at hiding
4) Some create nests in the cracks and crevices where they cannot be seen until populations explode
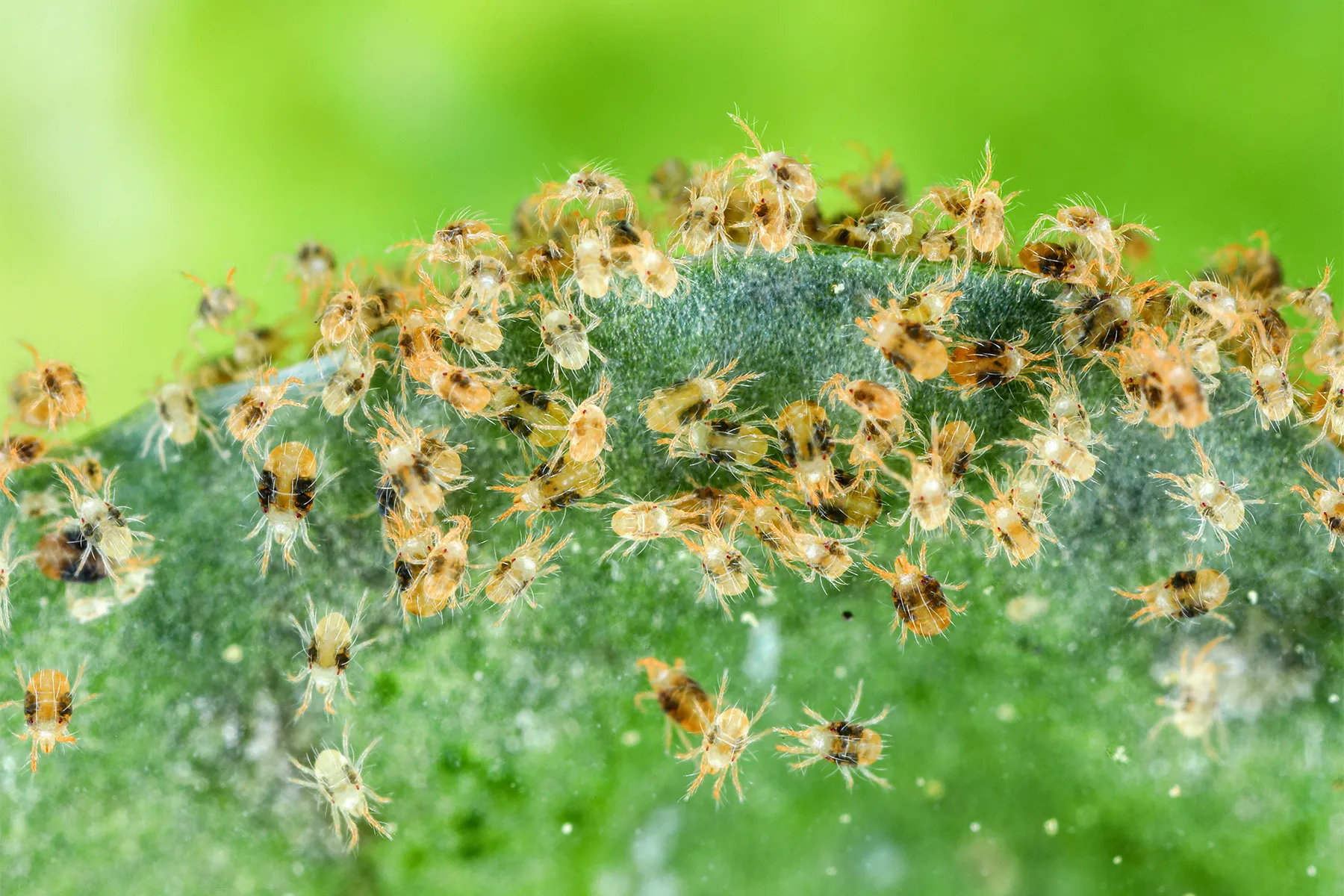

Mites
Suck sap from foliage with stippling mouthpart —> create stippling marks
Pale and mottled leaves
Severe infestation —> webbing at shoot tips
Thrive in hot, dry environments —> hate light and getting wet
Beneficial = predatory mites
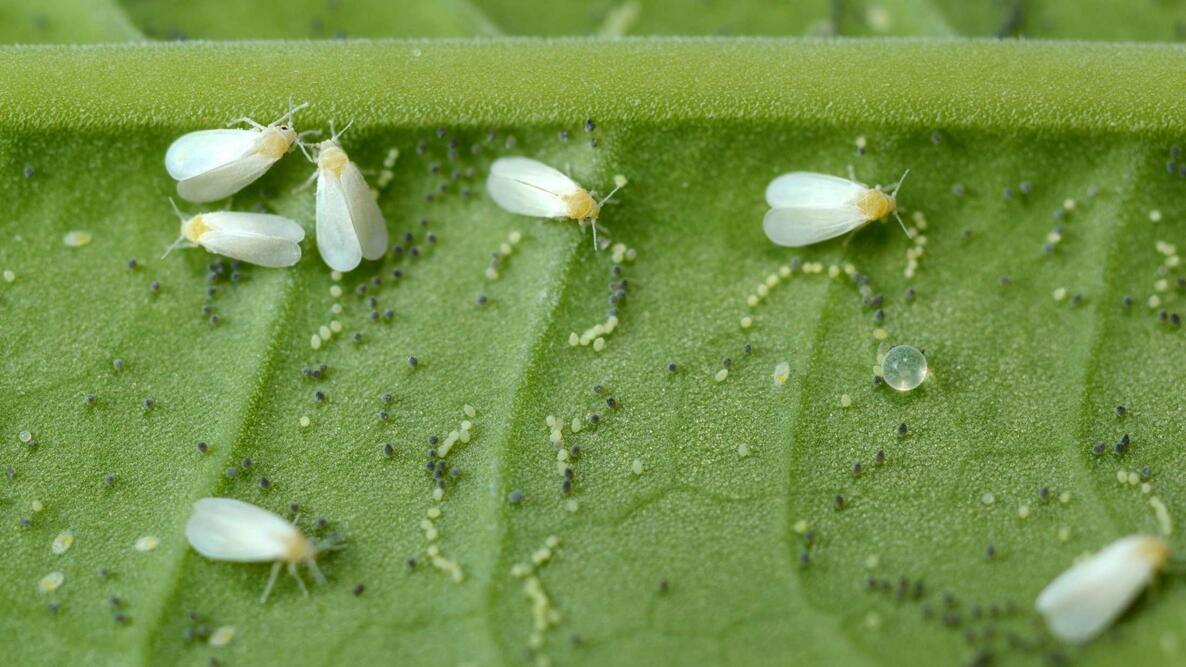

Whitefly
Feed on plant sap
Notorious for spreading damaging plant viruses
Live and lay eggs on underside of leaves
Beneficial = parasitic wasps (larvae hatch and eat whitefly eggs)
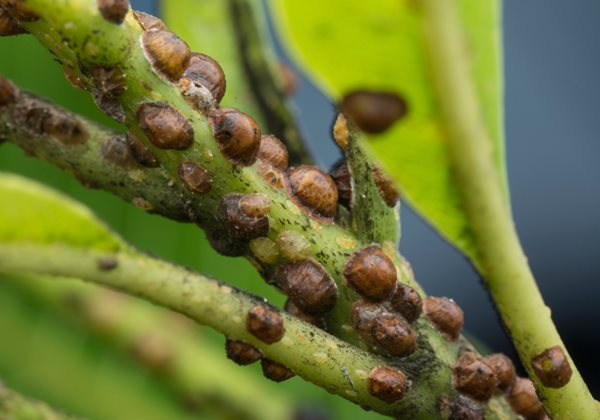

Scale
Adults are non-motile
Hard shell —> can extend into plant tissue
Adults lay eggs underneath their shell —> make small opening for juvenile crawling scale
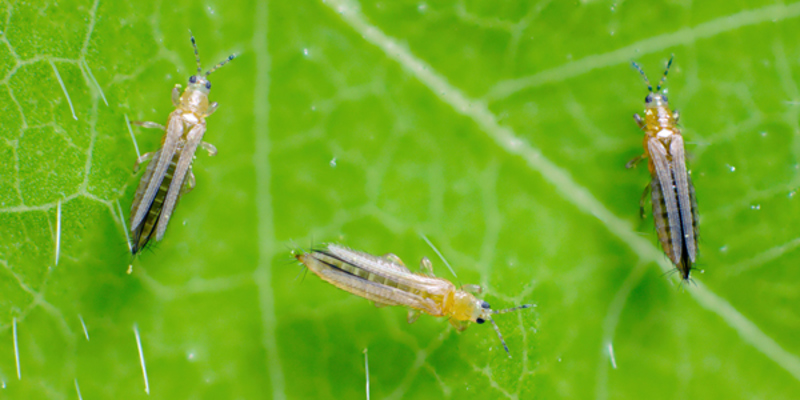

Thrips
Eat plant tissue, sap, and pollen with their rasping mouthpart
White patches and streaks on leaves
Undersides usually contain black specks (thrip waste)
Pupate in soil —> makes infestation hard to eradicate
Adults are fast but weak fliers
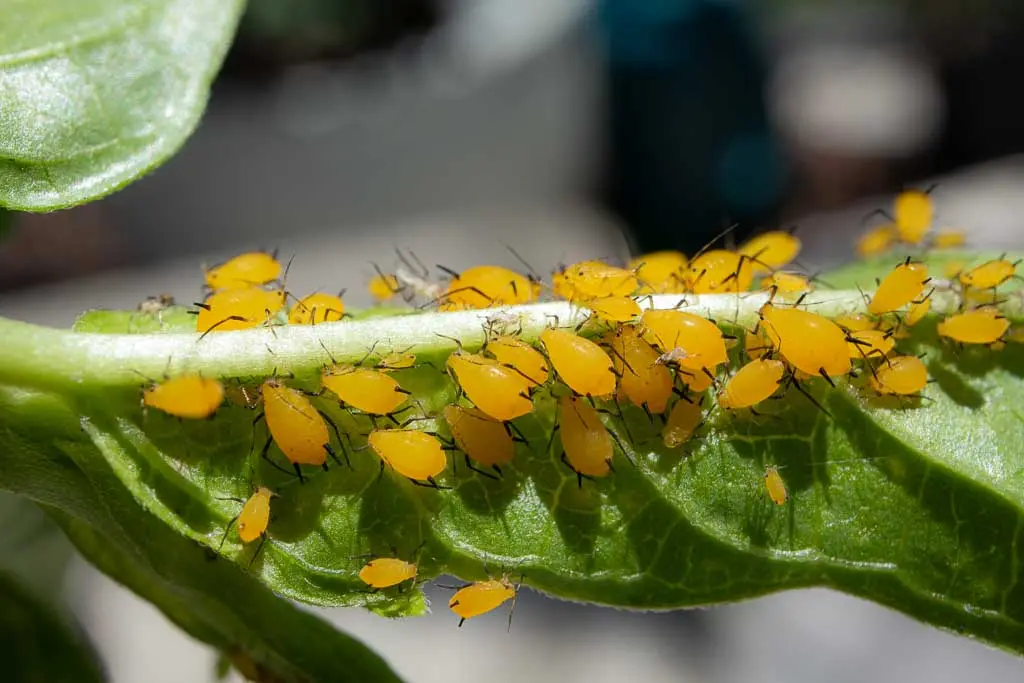

Aphids
Suck sap —> produce sticky “honeydew” waste that attracts other pests and pathogens
Soft-bodied and slow
Give live birth and born pregnant —> populations boom overnight
Easily washed away
Often concentrated around new growth
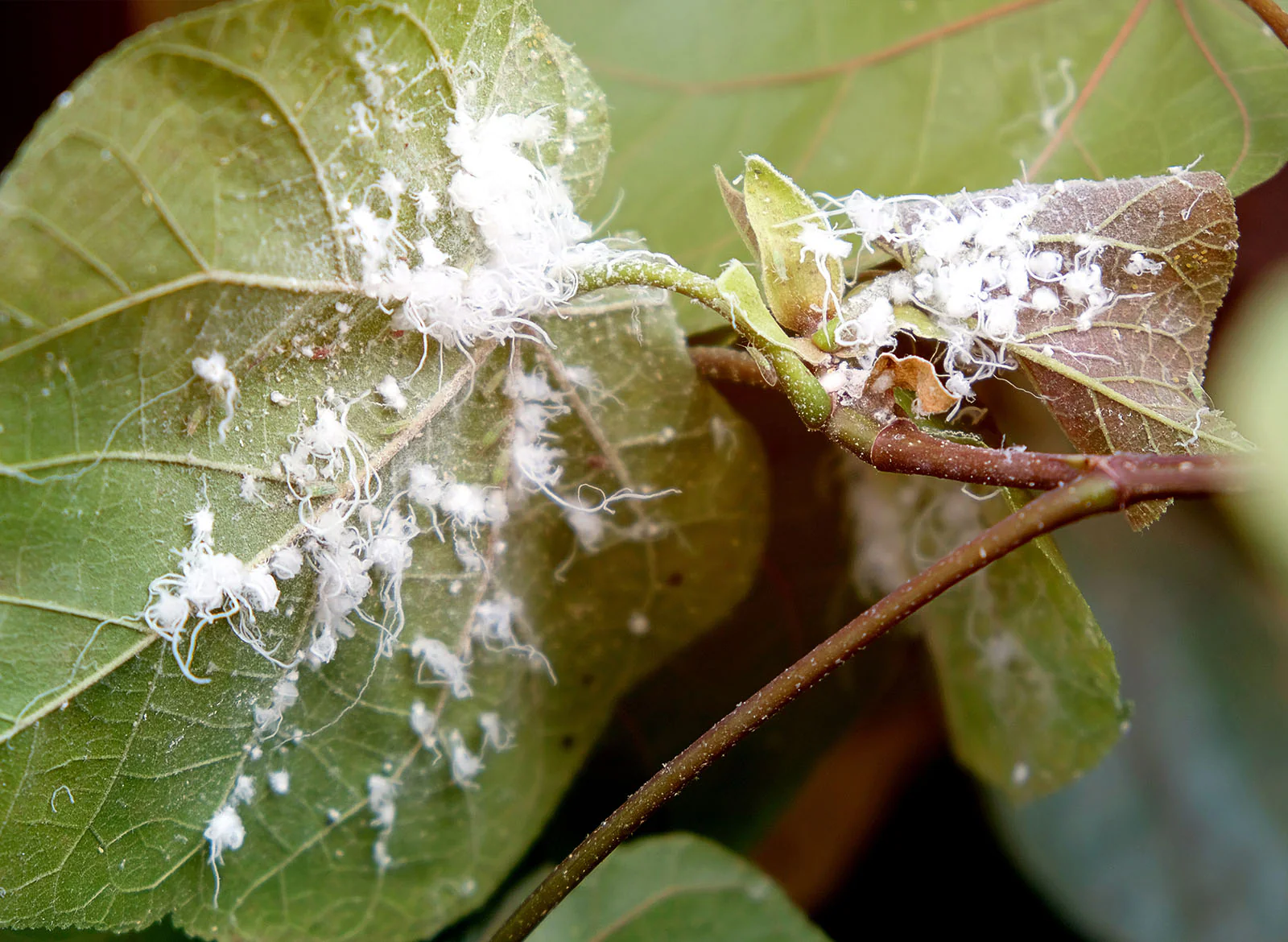

Mealybugs
Soft-bodied and slow
Squeeze into tiny cracks and crevices
Build cottony protective nests
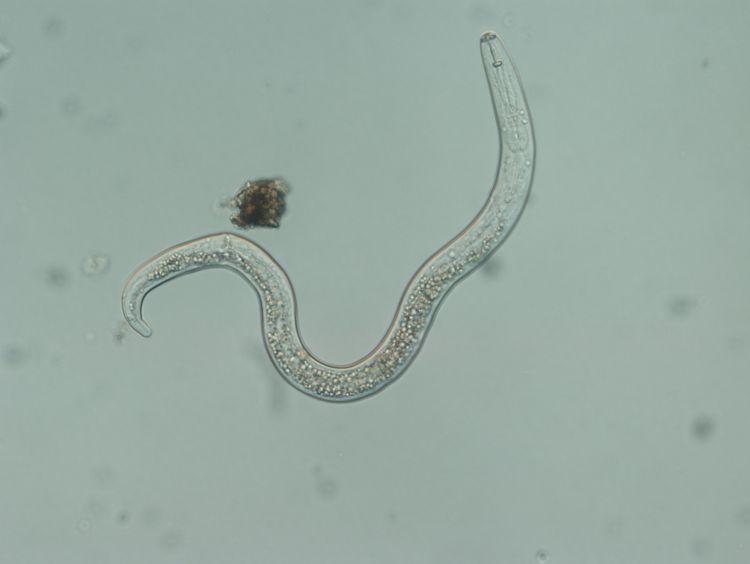
Nematodes
Microscopic roundworms
Live in soil or within plant
Have a small mouthpart that allows them to suck sap from plant cells
Vector
Organism that spreads disease
Beneficial insect
Helps reduce pest insect populations by eating or parasitizing them

Minute pirate bug (beneficial)
Equal opportunity omnivore —> eats many types of soft-bodied insects and pollen
Can eat 45 thrips in a day
Loves ornamental pepper flowers

Green lacewing larvae (beneficial)
Big, fast, very hungry
Will eat any soft-bodied organism (even each other)
Can eat 60 aphids in a day
Beneficial nematodes
Can eat pests living in the soil —> mixed with water and drenched into potting media
Disease triangle
3 points must be present for a pest or pathogen outbreak to occur…
1) Plant host
2) Pest or pathogen
3) Ideal environmental conditions for host and pathogen to survive
Fungal pathogen
Grow between or through plant cells secreting enzymes, toxins, or hormones that cause disease symptoms —> harvest nutrients released as plant cells die —> reproduce sexually or asexually via spores that are created in the fruiting body of fungus
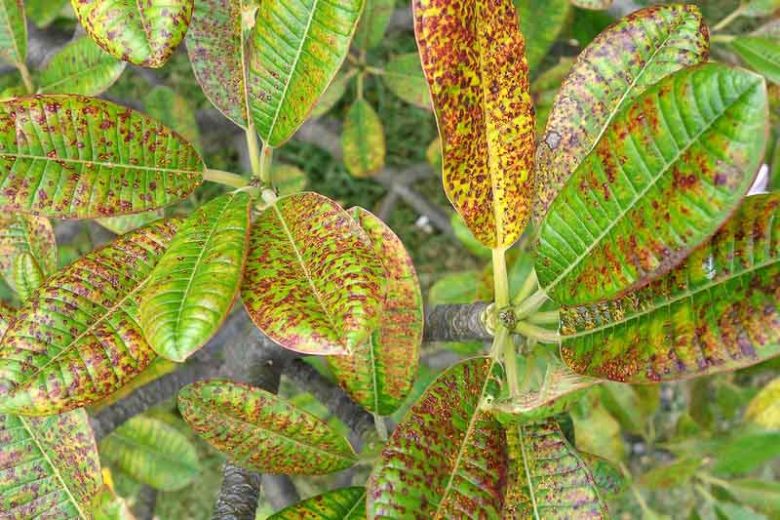

Rust (fungal pathogen)
Appears on leaves
Characteristic rusty color
Looks raised, grainy texture
Control
Reduce leaf wetness
Biofungisides
Prune affected foliage
Mildew
Characteristic silver/gray blotches look raised and fuzzy
May contain black dots above or below leaf (fungal fruiting body)
Spreads quickly via splashing water
Sooty mildew —> indicative of sap-sucking insects
Control
Reduce leaf wetness
Prune affected foliage
Biofungisides
Hyphae
Tiny tube-like structures that fungal pathogens use to invade plant cells/intercellular space
Fruiting body
Spore producing structure created by fungus —> used to diagnose specific fungal pathogens (rest of body can be difficult to ID)
Viral pathogen
Cannot move, must be introduced to a plant via a vector —> extract nutrients from living cells without killing them, use plant cells to reproduce
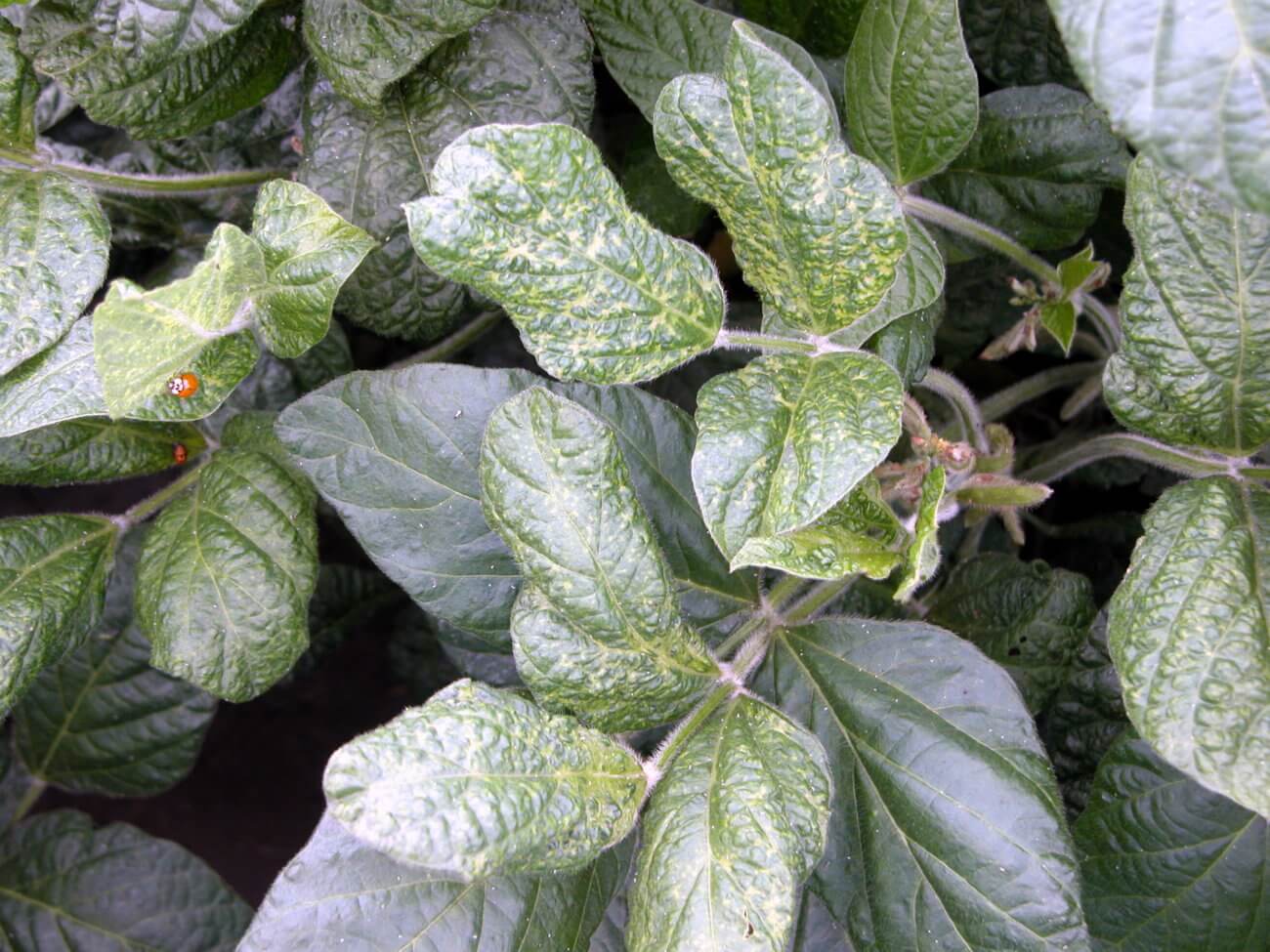

Mosaic virus
Blotchy, mottled, stunted foliage
Spread via vector
Control
Sterilize plants, tools, and soil before greenhouse introduction
Reduce pest populations to control vectors
Destroy heavily affected plants
Bacterial pathogen
Grow in or between plant cells in slimy single-cell masses, secreting enzymes and toxins to kill plant tissue and harvest nutrients the cells release as they die —> favor warm, wet conditions, often spread by water (or via a vector)
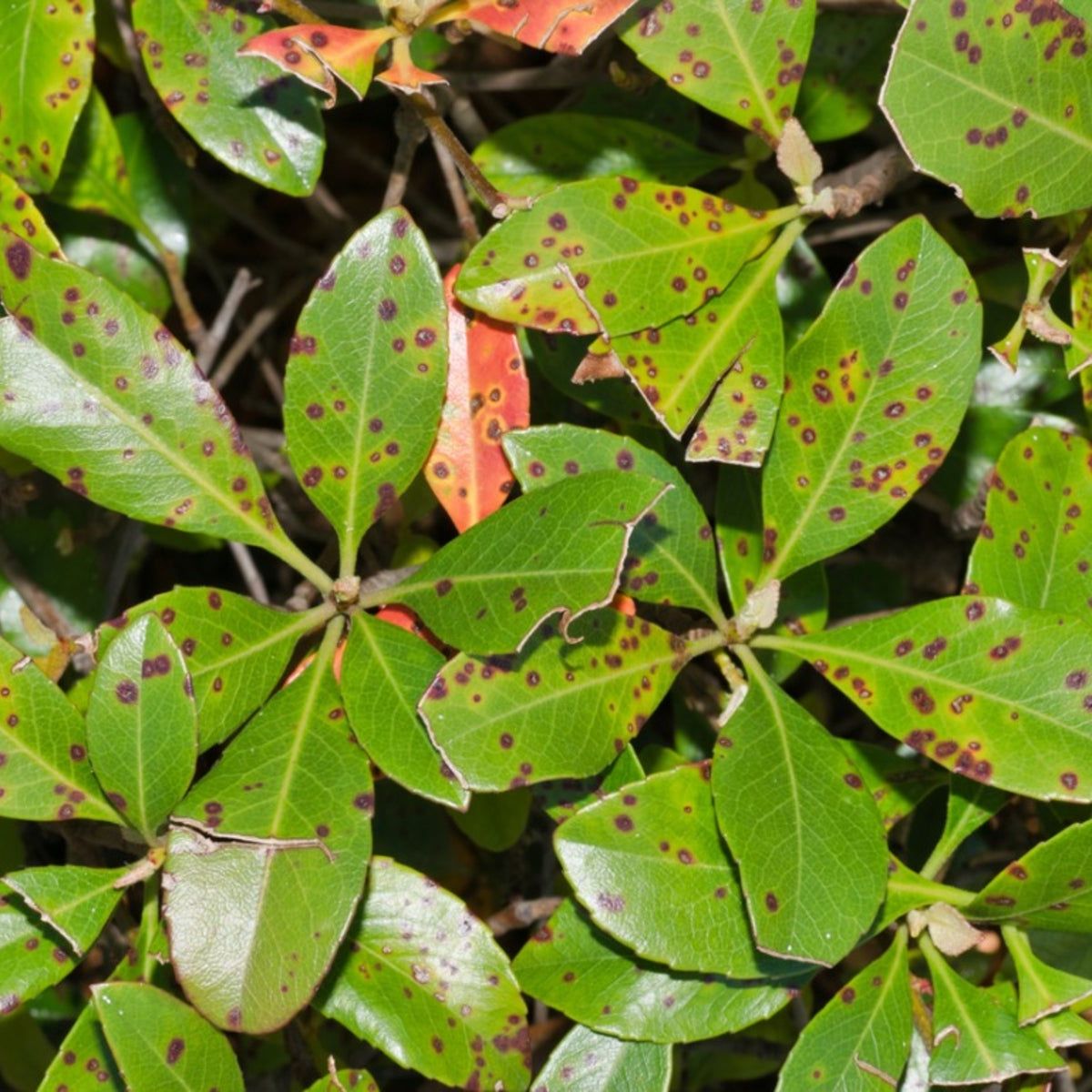

Bacterial leaf spot
Foliar infection with a characteristic yellow halo
Spreads via splashing water
Control
Reduce leaf wetness
Space for increased air flow
Prune affected foliage

Bacterial fruit blotch
Water soaked spots —> lesions expand rapidly

Bacterial, stem, and crown rot
Soil borne infection affecting the vascular tissues
Water-soaked lesions giev rise to open cankers
Crown rot will collapse small or rosette plants
Wilt diseases —> entire plant wilts and dies despite adequate water
Weeds
Pest plants that have evolved to quickly overtake and out-compete surrounding plants
7 weed strategies
1) Produce massive quantities of seeds
2) Rapid germination
3) Reproduction via runners
4) Tolerance to temperature and precipitation extremes
5) Vining and choking behaviors
6) Thorns or other irritants that make them hard to remove
7) Extensive root systems
Cultural control methods
“Best practices” of growing, inhibit and prevent pest/pathogen infestation
8 cultural control strategies
1) Plant selection for pest/pathogen resistance
2) Soil management
3) Crop rotation
4) Spacing for air flow
5) Pruning
6) Manipulation of environmental controls
7) Hygiene
9) Quarantine
Physical control methods
Physical removal of a pest or physical barriers to prevent pest infestation
Examples
Picking caterpillars off by hand
Installing weed cloth
Applying horticultural oils and soaps
Horticultural soaps and oils
Clog insect pores and cause them to suffocate —> plants vary in tolerance to their application
Biological control methods
Using natural predators to reduce pest populations (beneficial insects)
Selective pesticide
Targets a specific pest
Broad spectrum pesticide
Kills most or all pests (including beneficial organisms)
Contact pesticide
Kills pest on contact —> either immediately or over a series of days
Systemic insecticide
Chemical is taken up by the plant and distributed via the phloem to all plant parts —> renders plant toxic to herbivores
Targeted spraying
Spraying of specific plants that are being affected by a pest or pathogen
Broadcast spraying
Spraying of entire crop, regardless of pest or pathogen presence on individual organisms
Pesticide resistant organism
Strain of pest/pathogen that is not affected by pesticide —> result of consistent pesticide over use
Integrated pest management (IPM)
Series of strategies for growing plants without relying on chemical pesticides (in response to pesticide overuse in 1980s)
1) Set action threshold
2) Monitor and identify pests (physical control)
3) Prevention (cultural control)
4) Control —> evaluate proper control methods for both effectiveness and risk (pesticides are last resort)
Re-entry interval (REI)
Amount of time after spraying a pesticide that it is safe for a person not wearing PPE to enter the greenhouse
Mode of action (MOA)
How a pesticide kills a pest, on a physiological level —> rotating chemicals with different MOAs when spraying is key to avoid pesticide resistance
USDA APHIS (Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service)
Prevent the movement of the most harmful plant pests and pathogens —> inspection stations at major airports and seaports to oversee all plant product import/export
Size
In horticulture refers to height and width of plant
Form
Refers to lateral growth and overall shape
Gibberellins
Group of plant hormones responsible for stem elongation and branching
Auxins
Group of plant hormones responsible for rooting and cell elongation
Cytokinins
Group of plant hormones responsible for cell division
Phototropins
Type of photoreceptor that moves auxins out of tissue that is in direct sun
Dwarf variety
Plants bred to be miniatures of wild type of same species —> lower concentration of gibberellins
Apical dominance
Phenomenon whereby main/central stem of plant grows more strongly than side/lateral branches —> controlled by auxin (produced in terminal bud and flows down to roots), inhibits development of lateral buds as it moves downward
Plant growth regulators (PGRs)
Chemicals applied as foliar spray that alter form of plant —> less labor intense than pruning and will not affect bloom time
Growth retardant PGR
Chemicals that inhibit action of gibberellins to create shorter, less leggy plants (effects wear off with time)
Growth enhancement PGR
Synthetic gibberellins applied to increase stem length and encourage branching
Root:shoot
Ratio of root biomass to shoot biomass —> plant maintains fairly constant root:shoot ratio, pruning one without the other will not reduce plant size
Notching
Cutting off a small wedge of tissue directly above lateral bud to encourage its development —> reduces flow of auxins from terminal bud
Nicking
Cutitng off a small wedge of tissue directly below a lateral bud to discourage its development —> damaging vascular tissue reduces flow of water and nutrients
Dwarf rootstock
Many dwarfs are created by grafting a desirable scion onto a dwarf rootstock —> dwarf rootstock won’t grow very large, limits growth of aboveground biomass
Cordon
Technique common in fruit trees, reduced to a single stem and grown on an angle —> eliminating branches makes the trees easy to spray and allows fruit to get light from all sides (encourages larger fruit)

Espalier
Ornamental technique in which several horizontal branches on each side of the trunk are allowed to develop (sometimes in a pattern) along a wall/fence
Coppice
Tree is cu down to a foot or less above ground level —> encourages fast growth of many new canes emerging from coppiced trunk
Pollard
All upper branches of tree are cut off —> keeps flowers on ornamental trees at eye level (Crepe myrtles)
Topiary
Form of garden art where bushes are pruned to a decorative shape
Bonsai
Centuries old art form where trees are intentionally dwarfed and pruned in such a way as to resemble a large, old tree